Transcription Regulation in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Regulatory DNA sequences
In addition to the promoter, the vast majority of genes include regulatory DNA sequences that are used to switch the gene on or off, depending on the needs of the cell.
Transcription Regulators
Regulatory DNA sequences do not work by themselves. To have any effect, these sequences must be recognized by proteins called transcription regulators. It is the binding of a transcription regulator to a regulatory DNA sequence that acts as a switch to control transcription.
How are transcription regulators able to bind to regulatory DNA sequences/
Transcription regulators that recognize specific nucleotide sequence do so b/c the surface of the protein fits tightly against the surface features of the DNA double helix in that region. Because the surface features will vary on the nucleotide sequence, different DNA binding proteins will recognize different nucleotide sequences.
Transcription Switches
Allow cells to respond to changes in their environment
How do bacteria regulate the expression of their genes?
Bacteria regulate the expression of many of their genes according to the food sources that are available in the environment.
When the tryptophan amino acid is scarce in bacteria
Five genes code for enzymes that manufacture tryptophan when this amino acid is scarce.
Operons
A cluster of genes in bacteria that are arranged together on the chromosome and transcribed from a single promoter into one long mRNA molecule, allowing the genes to be coordinately regulated and expressed together.
When tryptophan concentrations are low the trp operon is
transcribed and the resulting mRNA is translated to produce a full set of biosynthetic enzymes which work in tandem to synthesize the amino acid from simple precursor molecules.
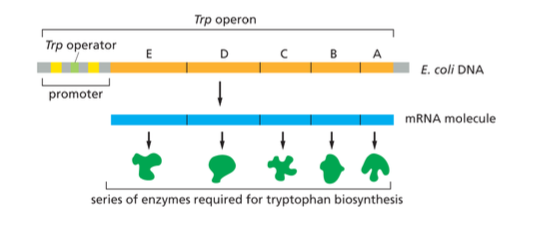
When tryptophan is abundant such as when the animal in which bacteria resides just ate a protein rich meal
the amino acid is imported into the cell and shuts down the production of biosynthetic enzymes that are no longer needed
Operator
-short DNA sequence within the operon’s promoter
-recognized by a transcription regulator
-when the transcription regulator binds to the operator it blocks RNAP from transcribing the operon and ultimately stops the production of the tryptophan synthesizing enzymes.
Tryptophan Repressor
-Transcription Regulator that binds to operator (DNA sequence in promoter) when tryptophan is too high in abundance
-Can only bind to operator if bound to tryptophan → Making it an allosteric protein since the binding of tryptophan causes a subtle change in its three dimensional structure that allows it to bind tightly to operator sequence
Tryptophan Repressor
The tryptophan repressor protein is always protein is always present in the cell and the gene that encodes it continuously is transcribed at a low level so that a small amount of the repressor protein is always made.
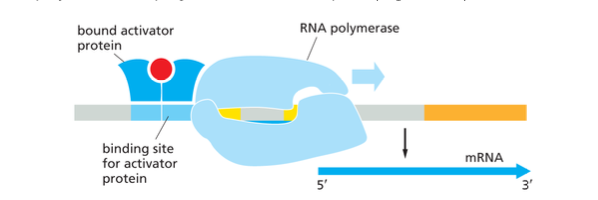
Transcriptional Activator Proteins
Work on promoters that on contrast to the promoter for tryptophan, are only marginally stable and position RNA polymerase on their own.
These inefficient promoters can be made full functional by activator proteins that bind to a nearby regulatory sequence and make contact with the polymerase, helping initiate transcription
What are the conditions necessary for a lac operon to operate?
Glucose absent
Lactose Present
What is the Lac operon used for in E.Coli and what is it controlled by?
The Lac Operon is controlled by the Lac repressor and CAP activator. The Lac Operon in E.Coli encodes proteins required to import and digest the disaccharide lactose.
In the absence of glucose the bacterium make cAMP which activates CAP to switch on genes that allow the cell to utilize alternative sources of carbon including lactose.
Why must lactose be present in the lac operon?
It would be wasteful for CAP to induce the expression of the lac operon if lactose itself were not present. Thus, the lac repressor shuts off the operon in the absence of lactose. This arrangement enables the control region of the Lac operon to integrate two different signals, so that the operon is highly expressed only when two conditions are met; glucose must be absent and lactose must be present.

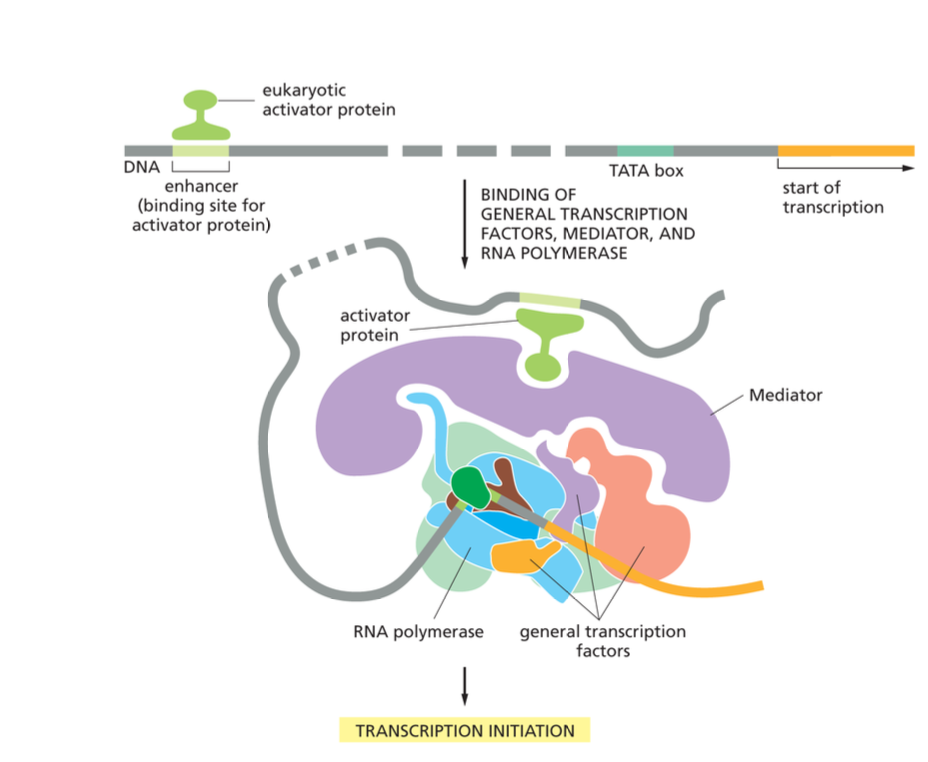
Enhancers
LOCATED IN EUKARYOTES. DNA sites to which eukaryotic gene activators bind. Their presence dramatically enhances the rate of transcription.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic activator proteins?
Unlike their bacterial counterparts, eukaryotic activator proteins can enhance transcription even when they are bound thousands of nucleotide pairs upstream- o even downstream of the gene’s promoter.
How do enhancers communicate with the genes promoter even when they are so far?
The DNA between the enhancer and the promoter loops out brining the activator protein bound to the enhancer- even one that is thousands of nucleotide pairs away- to interact with the proteins in the vicinity of the promoter
The DNA thus acts as a tether allowing a protein that is bound to an enhancer- even one that is thousands of nucleotide pairs away- to interact with the proteins in the vicinity of the promoter.
What does the mediator do?
Proteins close the loop DNA makes to make sure the enhancer interacts with the promoter.
In eukaryotic cells, activator and repressor proteins can exploit the mechanisms used to
package DNA to turn genes on and off.
Histone Acetyltransferase
A gene activator that promotes the attachment of acetyl groups to selected lysines in the tail of histone proteins that promote transcription, including some general transcription factors. These acetyl groups themselves attract proteins that promote transcription including some GTF.
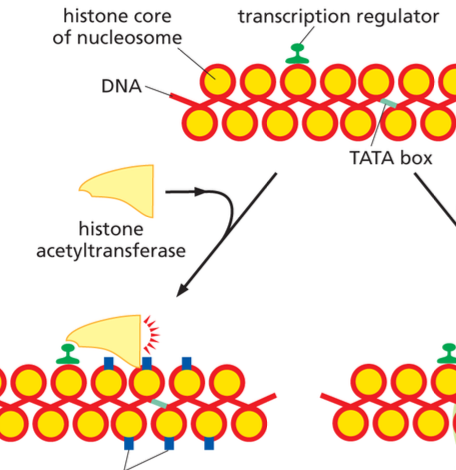
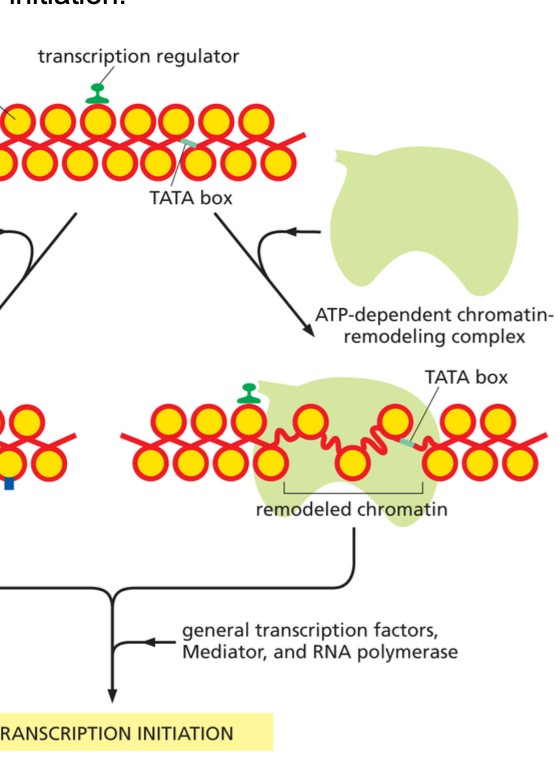
ATP dependent chromatin remodeling complex
Render the DNA packaged in nucleosomes more accessible to other proteins in the cell, including those required for transcription initiation; for example the increased exposure of the TATA Box.
Eukaryotic repressor proteins
Histone deacetylases-enzymes that remove the acetyl groups from histone tails which thereby reverses the positive effects that acetylation has on transcription initiation.
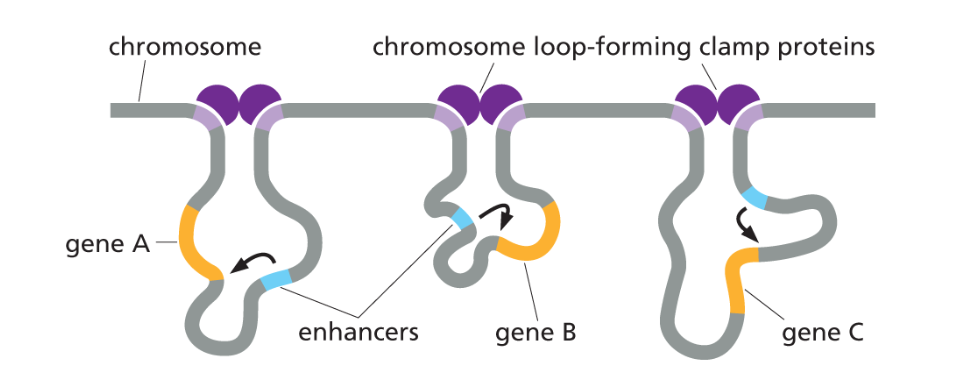
What prevents a transcription regulator bound to the enhancer of one gene from looping in the wrong direction and inappropriately influencing the transcription of a neighboring gene?
Chromosome loop forming clamp proteins arrange a series of loops (topological associated domains) that hold individual genes and their regulatory regions in rough proximity. This localization restricts the the action of enhancers, preventing them from straying towards the wrong genes.