Immunoprecipitation
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the purpose of Immunoprecipitation ?
Isolate and concentrate protein of interest
What are two methods of precipitation ?
centrifugation or magnetism
Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
Used to analyze protein-protein interactions
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
-can determine if proteins can bind to a particular region of DNA in the chromatin of living cells
RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP)
Study the physical association between individual proteins and RNA molecules in vivo
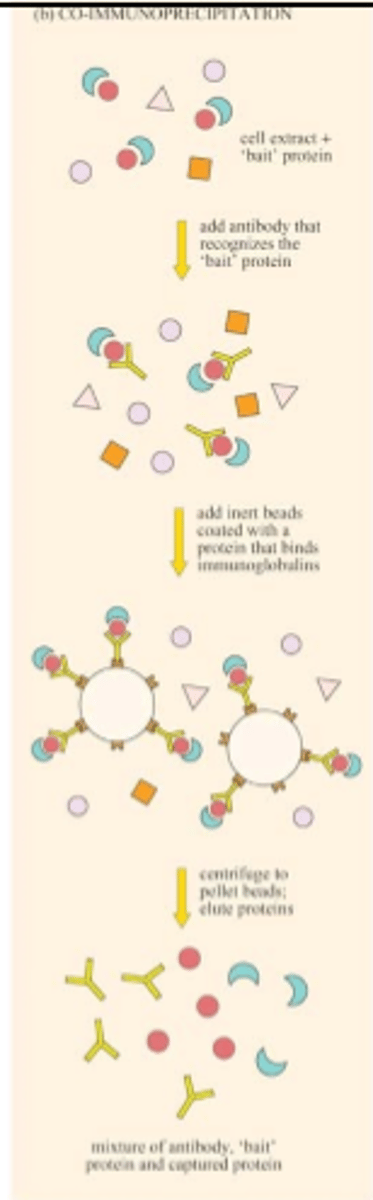
What are the steps of Co-IP ?
-Sample preparation
-Pre-clearing (just beads)
-antibody incubation
-Precipitation of protein/protein complexes
-Washing
-Elution and analysis of precipitate (low pH or high salt solution)
-SDS-PAGE, western blotting, Mass spec
What does eIF stand for ?
eukaryotic initiation factor
What is the function of the protein 4E-T ?
A eIF4E-transporter protein that promotes P-body formation
What happens when 4E-T interacts with eIF4E ?
represses translation - which is believed to focus on targeting MRNA to P bodies
What is decapping?
Enzymatic removal of 5' cap structures from MRNA in eukaryotic cells
What do 5' cap structures do ?
Enhances translation and stability
Examples of decapping factors ?
CNOT1, PATL1, LSM14, DDX6 (enriched in P bodies)
What are the steps of ChIP ?
-Cross link and harvest cells
-Cell lysis and chromatin fragmentation
-Immunoprecipitation
-Wash, elution and cross link reversal
-DNA cleanup and analysis of DNA
Controls for ChIP
Input DNA : A chromatin sample processed parallel to the other samples but lacks the IP step
No Ab control : A chromatin sample processed parallel to the other samples but immunoprecipitated without specific antibody
Isotype Ab control : A chromatin sample processed parallel to the other samples and immunoprecipitated with an isotype Ab control (IgG or IgM)
Histone H3 antibody : A chromatin sample processed parallel to the other samples and immunopreciptated with anti-H3 ab
Analysis of ChIP DNA
-PCR and real time PCR
-DNA microarray (ChIP-chip)
-sequencing (ChIP-seq)
What is Analysis of DNA- PCR and qPCR ?
-Identification of DNA regions associated with the protein/modification of interest
What is a limitation of PCR and qPCR for analysis of DNA ?
-Use of primers bias toward the sequences of interest
-Makes the identification of unknown, potentially interesting binding sites unlikely
What is the ChIP-chip Approach ? (Analysis method)
-Protein of interest is selectively ChIPed
-ChIP-enriched DNA amplified by PCR and fluorescently labelled
-An aliquot of purified input DNA is labelled with a another fluorophore
-Two samples are mixed and hybridised onto a microarray
-Binding of the precipitated protein to a target site is inferred when intensity of the ChIP DNA significantly exceeds that of the input DNA on the array
What is ChIP-Seq Approach ? (Analysis)
-Instead of hybridizing the ChIP DNA to a microarray - each sample is processed directly into a DNA library for sequencing and subsequent bioinformatics analysis
What are some ChIP applications ?
To discover...
-DNA sequences occupied by specific target proteins
-Binding sites and distribution of a particular protein, such as transcription factor throughout entire genome
-Gene transcription and RNA polymerase activity
-Complex DNA/protein interactions underlying disease phenotypes
-Modification to protein, such as histones, that many influence chromatin structure and gene expression
-Nucleosome architecture and regulation of chromosomal maintenance
What are the two main classes of RNA immunoprecipitation ?
-Native
-Crosslinked
What is Native RIP used for ?
-used to identify RNAs directly bound by the protein and their abundance in the sample
What is Cross-linked RIP used for ?
-used to precisely map the direct and indirect binding site of the RBP of interest to the RNA molecule
What is used for the crosslinking process (CH-IP)
-Formaldehyde to initiate reaction
-glycine to end reaction
What is the concept of crosslinking (CH-IP)
'lock' protein-DNA complexes
What happens from over fixation of chromatin (CH-IP)
-reduce fragmentation in next step which inhibits binding of antibodies to protein targets
What methods are used for chromatin fragmentation (CH-IP)
-sonication
-nuclease
-enzyme digestion
What is the ideal size of chromatin fragments (CH-IP)
-200-800 BP
Why is it that we need 'chromatin fragments' during CH-IP
-solubilised chromatin allows immunoprecipitation to occur
-increased resolution
What antibodies are used in CH-IP
-CH-IP validated antibodies
How does cross link reversal occur ?
-heat incubation
How can DNA be purified ?
-using phenol chloroform followed by ethanol precipitation or column based purification