urinary system
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What sits higher? The left or right kidney? Why?
- The left kidney sits higher
- The liver, located on the right side, pushes the right kidney lower.
What are the four organs of the excretory system?
1. Kidneys – Remove waste from the blood.
2. Ureters – Carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
3. Bladder – Holds urine until it’s ready to be released.
4. Urethra – Carries urine out of the body.
What are the four major structures of the urinary system?
- Kidneys – Filter waste from the blood.
- Ureters – Transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder – Stores urine.
- Urethra – Carries urine out of the body.
List AND describe the five functions of the urinary system
Excretion – Removes waste.
Blood Volume – Controls water balance.
Blood Pressure – Regulates pressure.
Blood pH – Maintains acid-base balance.
Electrolytes – Controls ions like sodium and potassium.
How does EPO regulates blood volume.
- EPO (erythropoietin) is a hormone made by the kidneys.
- It stimulates the production of red blood cells.
- More red blood cells increase blood volume and improve oxygen levels.
Summarize the pathway of how blood calcium levels are regulated by calcitriol. Make sure to focus on its effects on the intestine, bone, and kidney.
- In the intestine: Increases calcium absorption.
- In bones: Releases calcium into the blood.
- In kidneys: Reduces calcium loss, raising blood calcium levels.
Compare and contrast the locations AND functions of the renal capsule, adipose capsule, and renal fascia
Renal Capsule:
- Location: Directly around the kidney.
- Function: Protects and shapes the kidney.
Adipose Capsule:
- Location: Surrounds the renal capsule.
- Function: Cushions and holds the kidney in place.
Renal Fascia:
- Location: Outer layer around the adipose capsule.
- Function: Anchors the kidney to nearby structures.
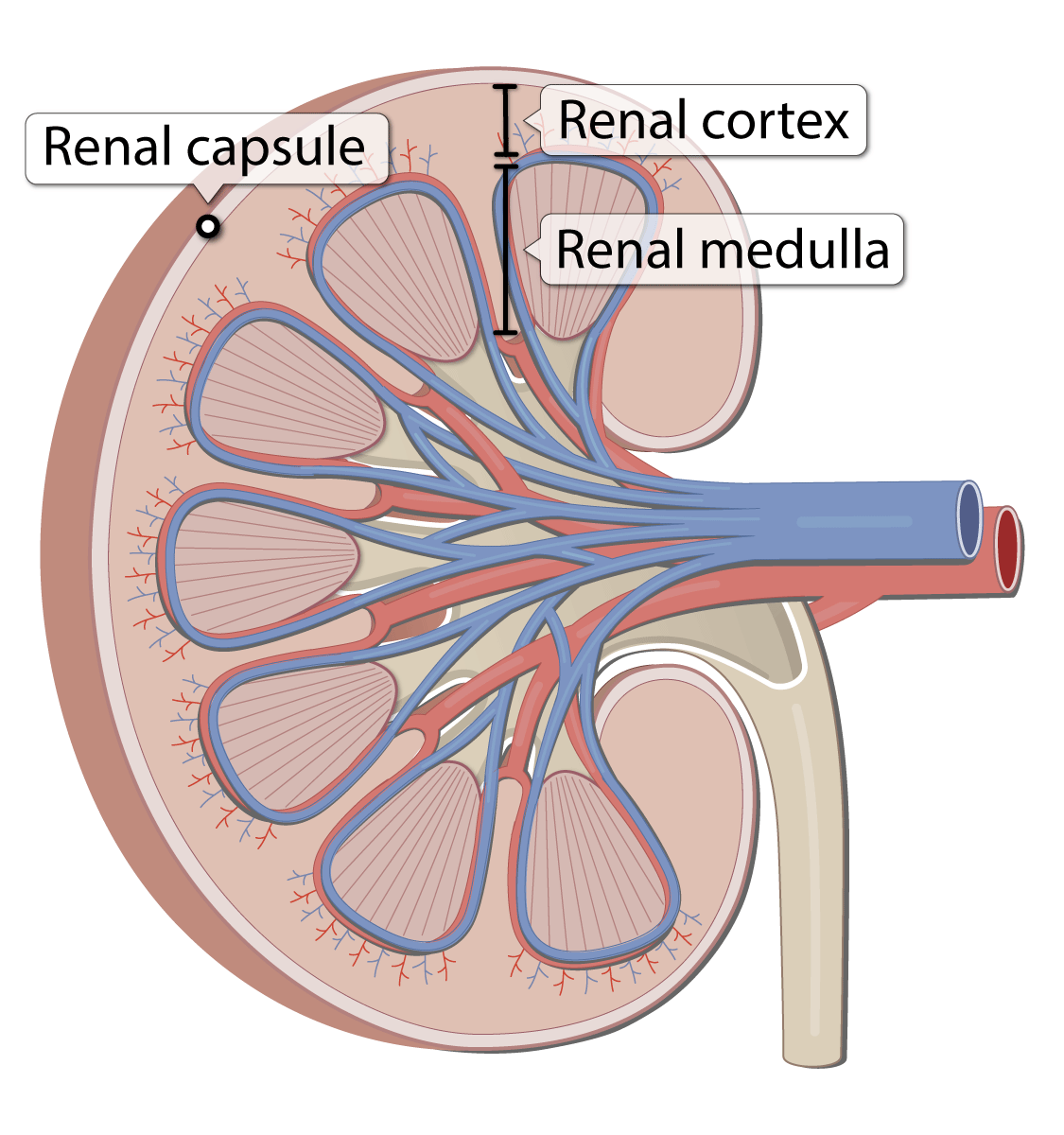
What is going on at the renal hilum?
where blood vessels, the ureter, nerves, and lymph vessels enter and exit the kidney.
a.Hilum
b.Renal sinus
c.Renal cortex
d.Renal pyramids
e.Renal lobe
f.Renal papilla
g.Major calyx
h.Minor calyx
i.Renal pelvis
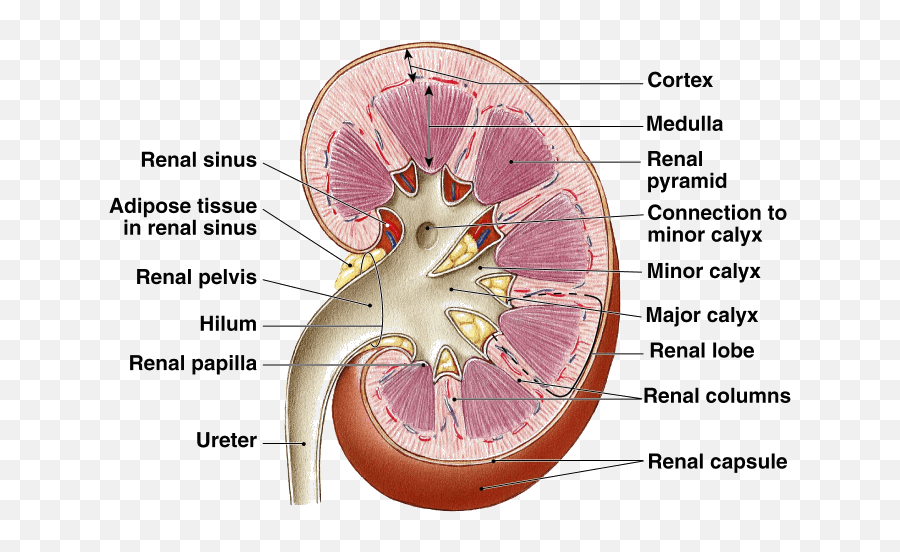
Make a flow chart illustrating the flow of blood through the kidneys
- Renal artery → Segmental arteries → Interlobar arteries → Arcuate arteries → Cortical radiate arteries → Afferent arterioles → Glomerulus → Efferent arterioles → Peritubular capillaries → Cortical radiate veins → Arcuate veins → Renal vein.
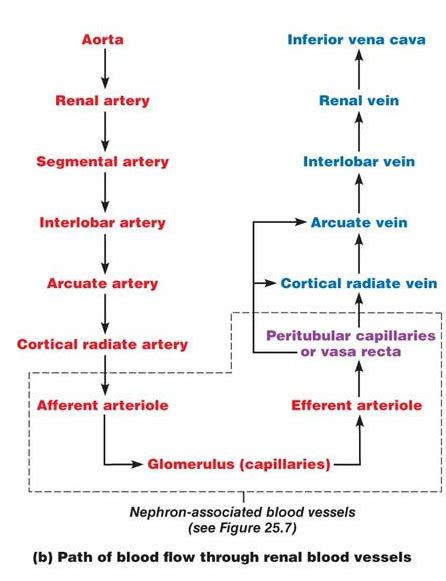
What are the two major structures that make up a nephron
The two major structures of a nephron are:
- Renal corpuscle: Filters blood.
- Renal tubule: Processes the filtered blood.
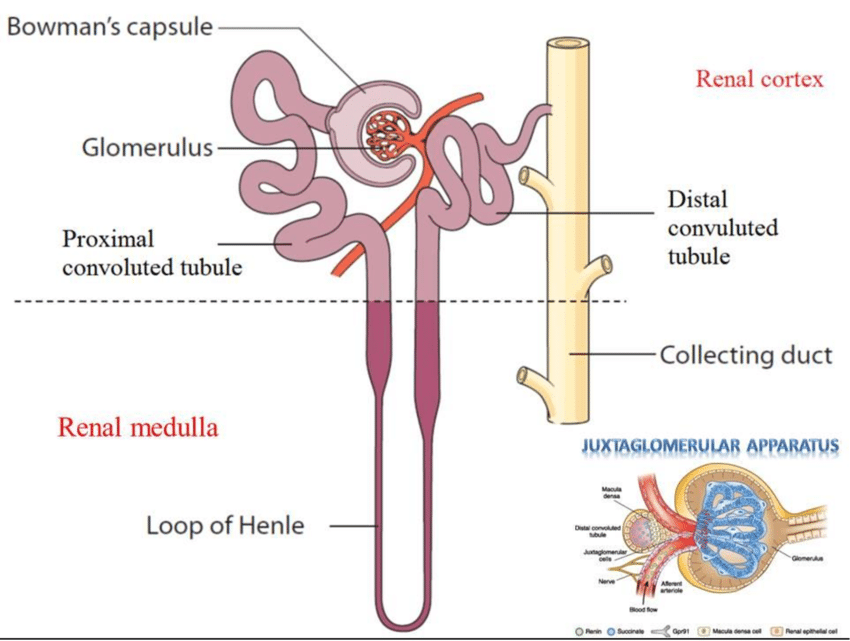
What two structures make up the renal corpuscle?
The two structures of the renal corpuscle are:
- Glomerulus: Filters blood.
- Bowman's capsule: Collects filtered fluid.
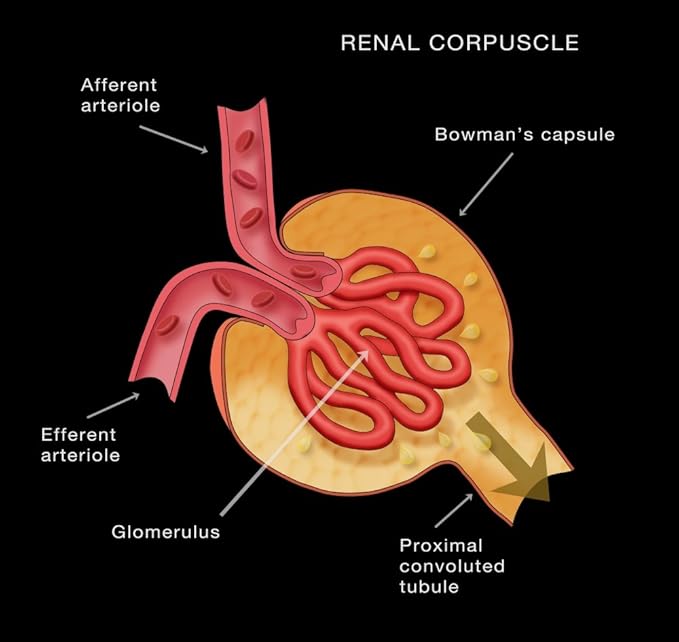
What is another name for the capsular space?
Bowmans capsule
Describe the blood flow into and out of the glomerulus, making sure to explain the significance of the differing diameters of the afferent and efferent arteriole.
- Blood enters the glomerulus through the afferent arteriole (larger diameter).
- Blood exits the glomerulus through the efferent arteriole (smaller diameter).
Why the difference matters:
- The larger afferent arteriole allows more blood in.
- The smaller efferent arteriole creates higher pressure in the glomerulus, helping filter the blood.
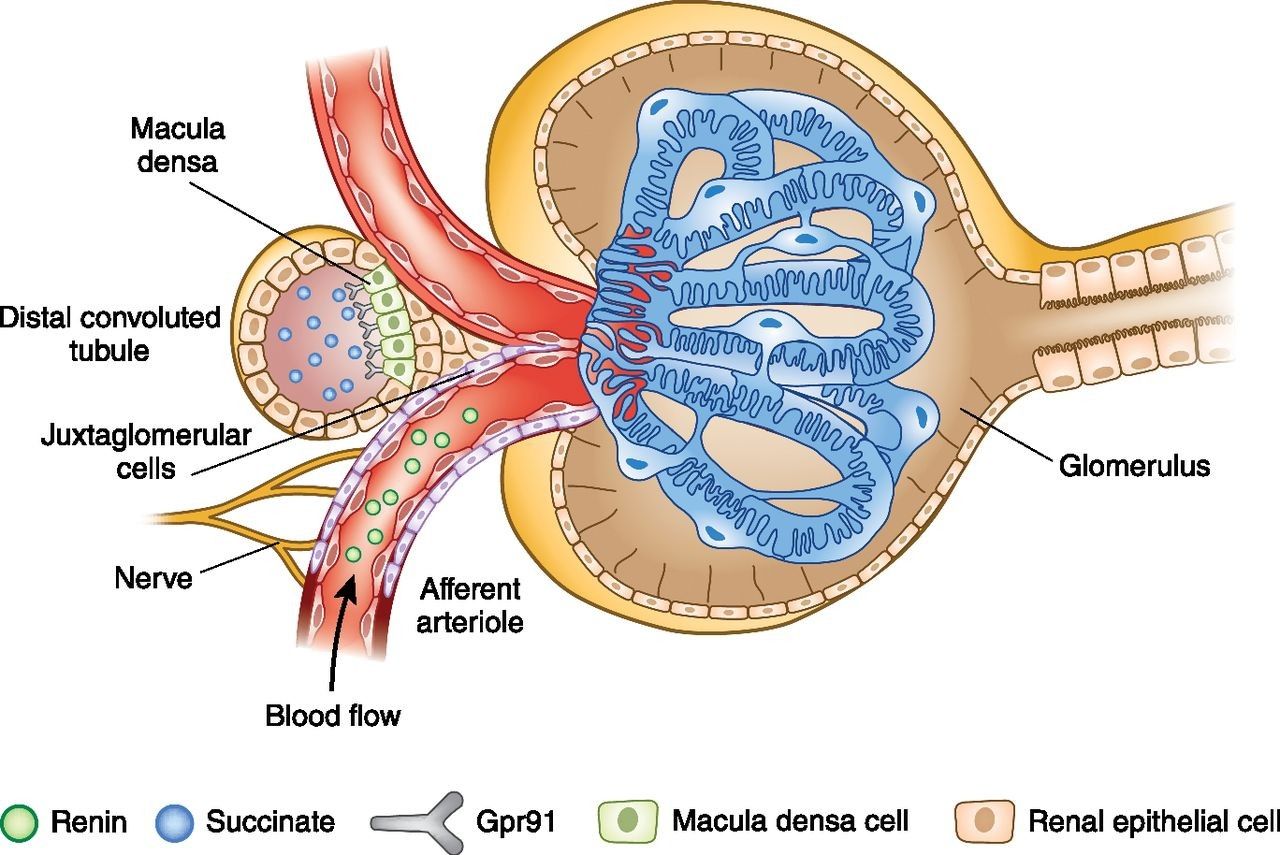
What are the main structures and functions of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
Main Structures:
- Juxtaglomerular cells: Secrete renin.
- Macula densa: Detects sodium levels.
Functions:
- Regulate blood pressure by releasing renin.
- Control filtration rate of the kidneys.
Which “force” drives glomerular filtration? What exactly is filtrate
- Glomerular blood pressure drives glomerular filtration.
- Filtrate is the fluid filtered from blood, containing water, salts, glucose, and waste, but no large proteins or blood cells.
Change | Effect on GFR
Afferent dilation | ↑ Increases GFR
Afferent constriction | ↓ Decreases GFR
Efferent dilation | ↓ Decreases GFR
Efferent constriction | ↑ Increases GFR
Once the blood is filtered by the glomerulus, what are the possible fates of the filtrate?
The filtrate can either:
- Re-enter the blood: Most substances are reabsorbed.
- Become urine: Waste and excess substances are excreted.
Which regions of the renal tubule are in the cortex of the kidney and which are in the medulla of the kidney?
- Cortex: Proximal and distal convoluted tubules.
- Medulla: Loop of Henle and collecting ducts.
Compare and contrast cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons.
- Cortical Nephrons:
In the cortex,
short Loop of Henle
mainly for filtration.
- Juxtamedullary Nephrons:
At the cortex-medulla border
long Loop of Henle
for water conservation.
Draw out the microscopic anatomy of the glomerulus making sure to include the relationships of the following structures:
1. Fenestrated Capillaries: Small blood vessels with pores.
2. Podocytes: Cells with foot-like extensions around the capillaries.
3. Pedicels: Finger-like extensions of podocytes, creating filtration slits.
4. Filtration Slits: Gaps between pedicels that allow filtration.
5. Lamina Densa: Barrier between capillaries and podocytes.
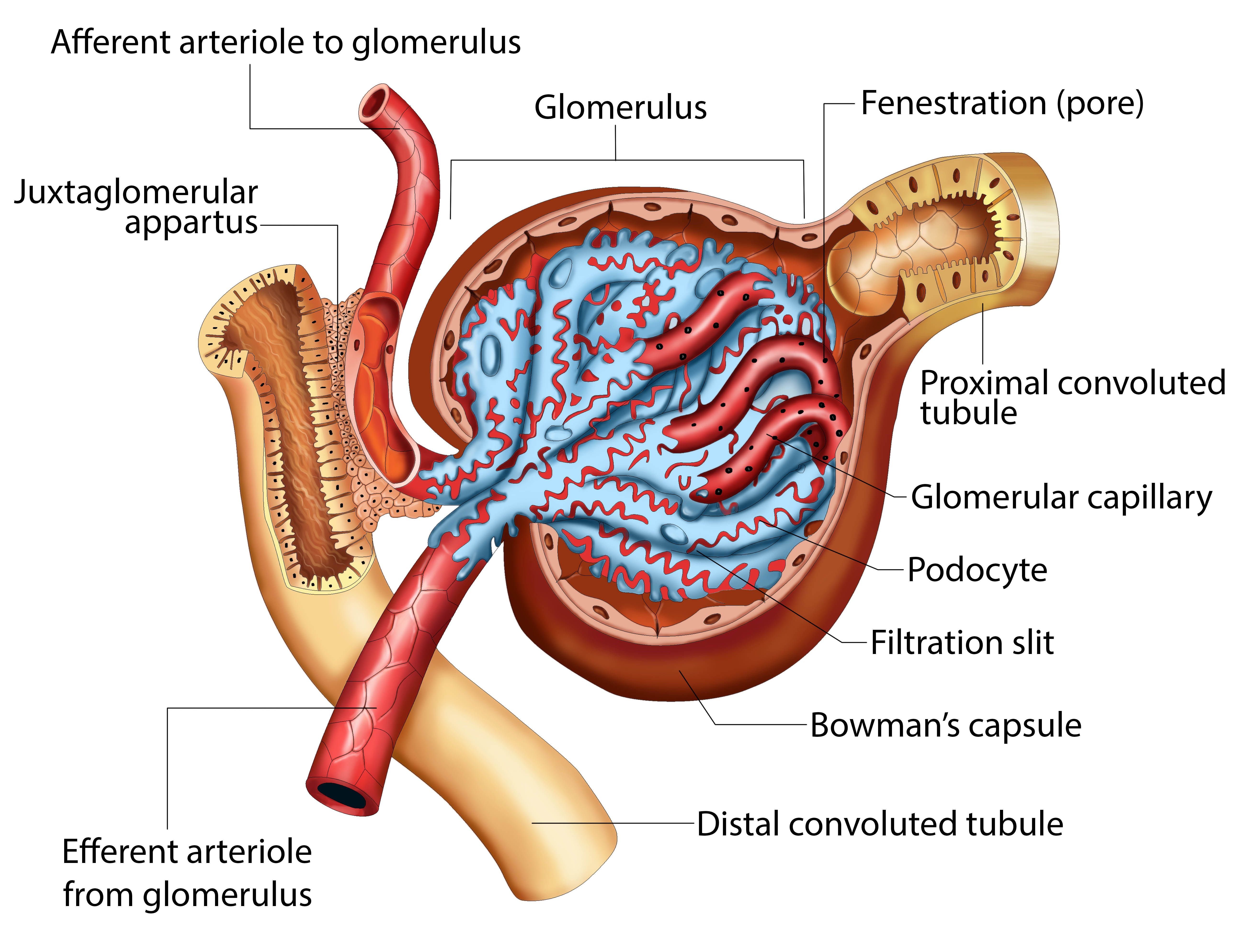
Explain which substances are normally filtered by the renal corpuscle based on their sizes.
- Small molecules (water, glucose, ions) pass through easily.
- Medium molecules (urea, creatinine) are filtered.
- Large molecules (proteins, blood cells) are not filtered.
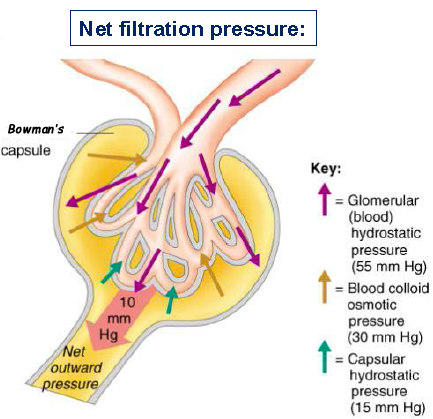
How does the normal architecture of the renal corpuscle become compromised with glomerulonephritis? What would happen to the capsular hydrostatic pressure? How about the amount of filtrate formed?
In glomerulonephritis:
- The renal corpuscle is damaged, blocking normal filtration.
- Capsular hydrostatic pressure increases.
- Filtrate formation decreases, leading to less urine.
Define osmolarity and explain osmotic pressure.
- Osmolarity: Solute concentration in a solution.
- Osmotic Pressure: Pressure needed to prevent water movement into a solution.
Compare and contrast hydrostatic pressure and colloid osmotic pressure.
- Hydrostatic Pressure: Pushes water out of capillaries.
- Colloid Osmotic Pressure: Pulls water into capillaries.
Draw out a simple diagram that illustrates glomerular filtration including
GHP: Forces water out of the capillaries into the capsule.
BCOP: Pulls water back into the glomerulus.
CHP: Resists the flow of filtrate into the capsule.
COP: A minor pressure, pulling water back into the glomerulus.
Explain what exactly what GFR stands for and what it measures.
- GFR: Glomerular Filtration Rate
- Measures: How much blood is filtered by the kidneys per minute
- Indicates: Kidney function
- Lower GFR: May suggest kidney problems
How does the body regulate GFR when blood pressure changes, and what role does the juxtaglomerular apparatus play in adjusting blood flow through the afferent and efferent arterioles?
Autoregulation of GFR:
- JGA controls blood flow by adjusting afferent and efferent arterioles.
- High blood pressure: Afferent constricts, efferent dilates.
- Low blood pressure: Afferent dilates, efferent constricts, renin is released.
This helps maintain a steady GFR.
Summarize how GFR is regulated by the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic Nervous System:
- When blood pressure is low, it releases norepinephrine.
- This narrows the afferent arteriole, reducing GFR to conserve water.
Parasympathetic Nervous System:
- Has little effect on GFR.
In short, the sympathetic system helps lower GFR during stress to maintain blood pressure.
Where in the nephron does the majority of reabsorption occur? What is the significance of epithelial microvilli in this region?
- Majority of reabsorption occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
- Microvilli increase surface area, aiding in the absorption of water, glucose, and salts.
Draw the arrangement of the following and use this to explain the process of reabsorption in the PCT:
a.Tubular fluid
b.Peritubular fluid
c.Peritubular capillary
Reabsorption Process in the PCT:
1. Tubular Fluid: Filtrate inside the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
2. Peritubular Fluid: Fluid surrounding the PCT, between the tubule and capillaries.
3. Peritubular Capillary: Capillaries around the PCT that reabsorb substances.
Process:
- Substances in tubular fluid are reabsorbed into the peritubular fluid.
- Then, they move into the peritubular capillaries to return to the bloodstream
Draw out the major regions of the loop of Henle, indicating the permeability of water and ions. Use this to explain how the loop of Henle concentrates the urine via the countercurrent multiplier.
Loop of Henle and Countercurrent Multiplier:
1. Descending Limb: Water is reabsorbed, but not ions.
2. Ascending Limb: Ions (Na+, Cl-) are reabsorbed, but not water.
3. Countercurrent Multiplier: The opposite flow in the limbs creates a concentration gradient in the medulla, allowing water reabsorption and concentrating the urine.
This system helps conserve water and concentrate urine.
How would a longer loop of Henle be beneficial to a desert mammal?
- More Water Reabsorbed
- Better Water Conservation
- Concentrated Urine
- Helps Survive in Dry Areas
What is the significance of the epithelial cells of the DCT not having many microvilli?
- Ion and pH Regulation
- Less Surface Area Needed
- Specialized Function
List AND describe the four processes of the DCT
- Reabsorption: Absorbs ions (sodium, calcium) and water.
- Secretion: Releases waste like hydrogen and potassium.
- Acid-Base Balance: Regulates pH by reabsorbing bicarbonate and secreting hydrogen ions.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Controls sodium and water reabsorption via RAAS.
Illustrate how acid base balance of the blood is maintained by the DCT.
- Secreting Hydrogen Ions (H⁺): Reduces blood acidity.
- Reabsorbing Bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻): Increases blood alkalinity.
This keeps blood pH stable.
Illustrate the Na+/K+ pump in the DCT and how aldosterone affects its action.
- Na+/K+ pump: Moves sodium into the blood and potassium into urine.
- Aldosterone: Increases pump activity, boosting sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion.
What ion is “lost” in the urine due to the effects of aldosterone?
potassium (K⁺).
Explain how the macula densa of the juxtaglomerular apparatus would respond to a decreased concentration of NaCl in the lumen of the DCT.
- Macula densa detects low NaCl in the DCT.
- Signals renin release from juxtaglomerular cells.
- Activates RAAS, producing angiotensin II.
- Aldosterone is released, increasing sodium reabsorption.
Describe the release and effects of ADH in a well hydrated vs. a dehydrated individual.
Well-hydrated: Low ADH, more dilute urine.
Dehydrated: High ADH, more water reabsorption, concentrated urine.
Summarize the goals of urine production, including the three organic waste products (and where they come from).
Urine production aims to remove waste, balance fluids/electrolytes, and regulate pH. The main organic wastes are:
- Urea: From protein metabolism.
- Creatinine: From muscle metabolism.
- Uric acid: From purine metabolism.
Explain the concept of the Transport maximum (Tm) and renal threshold of the kidney, and explain how Diabetes Mellitus is related to these two concepts
- Transport Maximum (Tm): Max amount a substance the kidneys can reabsorb before excretion.
- Renal Threshold: Blood concentration at which a substance appears in urine.
Diabetes Mellitus:
- High blood glucose exceeds renal threshold.
- Glucose is excreted in urine when Tm is surpassed.
The Renin – Angiotensin – Aldosterone System. Draw it out in detail including all organs, how it begins, what effects it has and other hormones it stimulates
1. Trigger: Low blood pressure or sodium detected by kidneys.
2. Renin Release: Kidneys release renin, converting angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
3. Angiotensin II: Converted in the lungs (by ACE), raises blood pressure.
4. Effects:
- Vasoconstriction (increases BP)
- Aldosterone (sodium/water retention)
- ADH (increased water reabsorption)
- Thirst (increases fluid intake)
5. Result: Increased blood pressure and volume.
How do ANP and BNP counter the effects of the RAA System?
ANP and BNP counter RAAS by:
- Lowering blood pressure (vasodilation)
- Increasing sodium excretion
- Inhibiting aldosterone and ADH
What three structures make up the urinary tract?
The three structures that make up the urinary tract are:
1. Kidneys
2. Ureters
3. Bladder
Relate the pain of a kidney stone to the anatomy and physiology of the ureter
- Kidney stone moves into the ureter.
- Causes blockage and muscle spasms in the ureter.
- Results in sharp, cramp-like pain in the flank, lower abdomen, or groin.
Summarize the causes, symptoms, and treatments for kidney stones
Causes:
- Dehydration, poor diet, genetics, and certain health conditions.
Symptoms:
- Severe flank pain, painful urination, blood in urine, nausea.
Treatments:
- Drink fluids, pain relievers, medications, shock wave therapy, or surgery if needed.
Describe the anatomy of the bladder wall, making sure to address the detrusor muscle
The bladder wall has:
1. Mucosa: Stretchable inner lining.
2. Submucosa: Supportive connective tissue.
3. Detrusor muscle: Contracts to expel urine.
4. Adventitia: Outer connective tissue.
The detrusor muscle helps push urine out during urination.
Compare and contrast the locations and control of the internal and external urethral sphincters
Internal Sphincter:
- Location: Bladder-urethra junction.
- Control: Involuntary.
External Sphincter:
- Location: Near pelvic floor.
- Control: Voluntary.
Comparison: Internal is involuntary and higher, external is voluntary and lower.
Relate urethral gender differences to the UTI’s.
Women: Shorter urethra and proximity to the anus increase UTI risk.
Men: Longer urethra reduces UTI risk.
Women are more prone to UTIs due to these differences.
What is cystitis?
- Cystitis: Bladder inflammation.
- Often caused by a UTI.
- Symptoms: Painful urination and frequent urination.
Draw out the micturition reflex, making sure to include the following:
a.Stretch receptors in the bladder.
b.Afferent fibers to the sacral spinal cord.
c.Efferent motor fibers from the sacral spinal cord.
d.The central pathway components to and from the thalamus of the brain
### Micturition Reflex:
1. Stretch receptors in the bladder detect filling.
2. Afferent fibers send signals to the sacral spinal cord.
3. Efferent motor fibers trigger bladder contraction and sphincter relaxation.
4. Signals travel to the brain (via the thalamus) for conscious control.
This process controls the urge to urinate.