SCSC UNIT 3
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 3 and 14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
youngest soils
Soils with no B horizon (Only A&C) with a potentially weakly developed B horizon
Fairly young Soils
Soils found in arid climates with Bk, By, Bz horizons (id), volcanic, frozen, or organic soils.
Moderately developed
Grassland/prarie soils, shrink/swell soils, savannah soils, or coniferous forest soils.
Well-developed soils
forest soils with Bt horizon (moderately high to low base status) or tropical soils with Bo horizons (low base status oxisols)
Soil formation reactions
Transformations, translocations, additions, losses
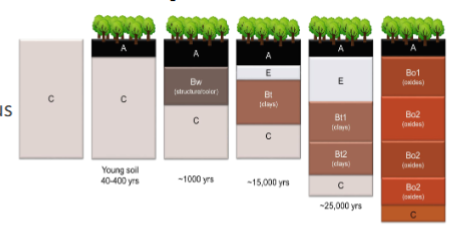
Humid climate transformation
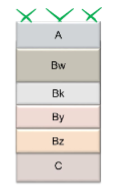
Arid to semi-arid transformation
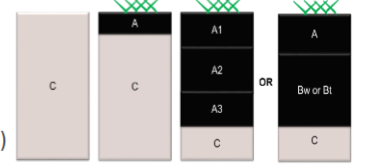
Semi-arid to subhumid climate transformation
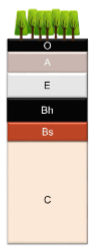
Humid Sandy, acidic parent materials
Elluviation
Process of removing minerals from the soil in the zone of elluviation (E horizon)
Illuviation
the accumulation of minerals in the zone of illuviation (B horizon)
Subordinate distinctions
Distinctive features of each horizon designated by lowercase letters
Oi
slightly decomposed (fibric)
Oe
moderately decomposed (hemic)
Oa
well decomposed (sapric)
Ap
Plowing disturbance
Bw
no acumulation, weakly weathered
Bt
acumulation of clay
Bo
acumulation of iron and aluminium oxides
Bhs
accumulation of humus, iron and Al oxides
Btn
accumulation of clay and sodium
Bk
Accumulation of carbonates
By
accumulation of gypsum
Bss
Accumulation of slickenslides
Epipedon
diagnostic surface horizon (O, A)
Endopedon
diagnostic subsurface horizon (E, B)
Diagnostic horizon
horizons with specific properties that help with classification
moisture regime
classify the soils ability to supply plants with water
temperature regime
classify soils mean annual temperature
map unit
a collection of areas that have the same soil components
area of interest (AOI)
region that you identify to evaluate soil properties
Mollic
An epipedon in the A horizon with dark, thick and soft soil. has HIGH bases
Umbric
An epipedon in the A horizon with dark, thick, soft soil. has LOW bases
Ochric
An epipedon in the A horizon that is light and shallow
Histic
An epipedon in the O horizon that is dark, thick and completely organic
Albic
An endopedon in the E horizon that is white in color
Cambic
An endopedon in the new B horizon with no illuviation (Bw)
Argillic
An endopedon with high bases (Bt)
Kandic
An endopedon with low bases (bt)
Oxic
An endopedon with oxides (Bo)
Spodic
An endopedon with humus and oxides leached below an E horizon (Bhs)
Calcic
An endopedon with carbonates (Bk)
Petrocalcic
An endopedon with carbonates and is massive (Bkm)
Gypsic
An endopedon with gypsum (By)
Petrogypsic
An endopedon with gypsum and is massive (Bym)
Salic
an endopedon with salts (Bz)
Natric
An endopedon with clay and sodium (Btn)
Duripan
An endopedon cemented by Silicon (Hardpan)
Fragipan
brittle hard pan
Entisol
Ent order that is a baby soil
Surface - Ochric
Inceptisols
Ept - beginning of soil profile development
surface - ochric
subsurface - cambic (Bw)
Mollisol
Oll - prarie soil rich in bases found in the midwest
surface - mollic
sub - NOT oxic/spodic
Alfisol
Alf - more strongly weathered, well developed, found in the savanna
surface - mostly ochric
sub - argillic
Ultisol
ult - #2 most weathered, low productivity, red due to iron
surface - ochric or umbric
sub - kandic
Oxisol
ox - most weathered and leached, low fertility, tropical regions
surface - ochric, sometimes umbric
sub - oxic
Vertisol
ert - due to shrink/swell clays
surface - mollic or ochric
sub - various
Aridisol
id - very dry arid climate
surface ochric
sub - various
spodosol
od - dark horizon under E
surface - histic, ochric, or umbric
sub - spodic with albic E endopedon
Histosol
ist - organic soil
surface - histic
Andisol
and - Must have PM from volcanic ash or cinders
Gelisol
el - contains permanent permafrost layer
Alfisol
What is the order for the Fine, smectitic, thermic Udertic Paleustalfs?
Ustalf
what is the suborder for Fine, smectitic, thermic Udertic Paleustalfs?
Paleustalf
what is the Great Group for Fine, smectitic, thermic Udertic Paleustalfs?
Fine, smectitic, thermic udertic Paleustalf
what is the family for Fine, smectitic, thermic Udertic Paleustalfs?
Consociation
series + texture + specific slope
complex
series +series complex => soils mixed on the landscape
Associations
series + series association => cannot separate soils
Undifferentiated gorups
series-series-series, or XXX soils => groups due to interpretations (least specific)
Land Use capability class I
best class for cultivation
land use capability class 8
worst land capability class for cultivation
erosion
subclass e for land use capability
wet/drainage
subclass w for land use capapbility
shallow
subclass s for land use capability
climate
subclass c for land use capability
Detachment, transportation, and deposition
steps of erosion
splash erosion
Erosion of soil through rainfall
Sheet erosion
a sheet of water covers the ground causing erosion
rill erosion
a shallow, narrow, ridge formed through water erosion
gully
a deep, big ridge formed through water erosion
Cover crops, tillage, contoru cultivation, strip cropping, etc…
water erosion control
Suspension
A type of wind erosion where the wind picks up the smallest of soil particles and suspends them in the air
Saltation
A type of wind erosion that picks up medium-sized particles and brings them in the air briefly, moving the particles along the ground.
soil creep
A type of wind erosion where the biggest of particles are only moved across the ground. No air-borne movement is apparant.
Soil moisture, wind barriers, cover crops
Types of wind erosion control
USLE equation
A = RKLSCP
A
Annual soil loss in USLE equation
R
rainfall in USLE equation
K
erodibility in USLE equation
L
slope length in USLE equation
S
Slope steepness in USLE equation
C
crop cover in USLE equation
P
practices to prevent erosion in USLE equation