Chapter 18 The Government and the Macroeconomy
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is the budget balence?
a type of givernment spending and revenue which refers to the difference between tax reveniues and givernment spendings
what is a budget surplus?
this is a tyype of government spending and revenenue where… tax revenue > spending
what is a budget deficit?
a type of government spending and revenue that refers to when… tax revenue < spending
givernment must borrow by sellling bonds
what s a balenced budget?
type of government spending and revenue where,
tax revenue = spendings
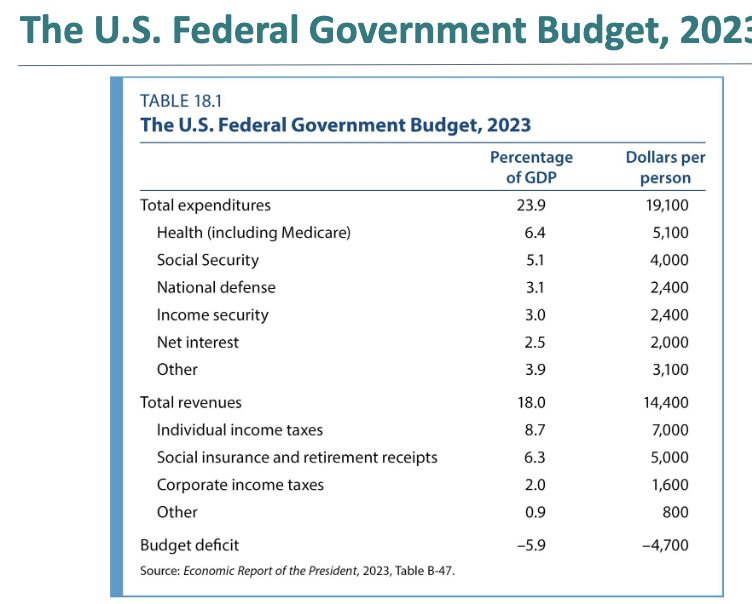
What is happening inside this balence sheet?
this is the US federal government budget which show that the US spends more than it collects in taxes, a deficit of about 6% of GDP in 2023, driven mainly by health, social security and the income support program
net interest is what you have to pay
most of the revenue is coming from income taxes
How did WW2 changed spendings and revenue over time?
when this event happened taxes and givernment spending oncreased sharply
how did the post war period affect spending and revenue over time?
in this case spendings and revenue stablized as a share of GDP
how has spending and revenue over time affected since the 1970s
since then, budget deficits beome more common, especially during recessions
what type of government spending is happening here?
here the government is runing a budget deficit

What are government debt?
This is the outstanding stock of bonds that have been issed in the past
How hhas the US debt GDP ratio changed over time?
in 2005 debt GDP accounted for about 35% of GDP
in 2023 debt GDP accounted for close to 100% of GDP
about half of the US federal debt held by public is owed by foeing investors
What is the government budget constraint? and how can we remeber it?
The flow government budget constraint applies each period and is where: government purchase + transfer payment + interest on existing debt is equivalent to (=), taxes + new borrowing + new money issued
in short uses of fund (left) = sources of funds (right)
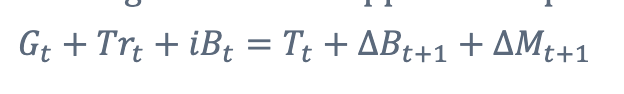

what are the variables and what do they represent in “uses of funds” and :sources of runds"
extra definitions…
change in Bt+1 is deficits brought into the new period?

What are the TWO assumption we use when dealing with government budget constraints
The change on the stock of money is zero
Transfer payment are zero
what is the government budget constraint?
i. whats the primary deficit in this
ii. whats the Total deficit in this
where Gt - Tt is the primary deficit (excludes spending on interest
where Gt + iBt - Tt is the total deficit
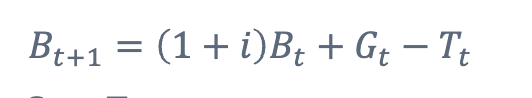
What are the intertemporal budget constraint?
Its an economic concept that represents the trade-off between spending and saving over multiple time periods
showing that the present discounted value of consumption cannot exceed the present discounted value of income
how do we write the government budget constraint for two periods?

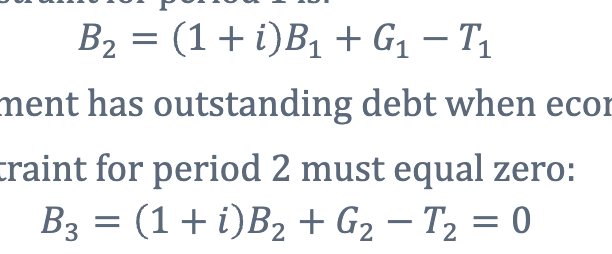
explain this? (hint intertemporal budget constraint)
this is this a hypothetical budget constraint where in period one the government has outstanding debt when the economy start and where in period two no one is willing to lend the government in the final period because loans can never be repaid
What is the government’s 2-period budget constraint?

What does (T₁ – G₁) represent?
Period 1 budget balance (surplus or deficit).
What does (T₂ – G₂)/(1 + i) represent?
Present value of the period 2 budget balance.
What does (1 + i)B₁ represent?
Initial debt plus interest that must be repaid.
Does the government need to balance the budget every year?
No. It can run deficits as long as future surpluses cover them (in present value).
Does the government budget nust balence?
yes it does
What must the government do to pay off today’s deficits?
They MUST Run future budget surpluses (in present value).
otherwise debt would grow witgout bound
what must the government consider when deciding to borrow or not? (4)
The government when considering economic conseqience’s of deficits, they must consider first…
economic growth
the possibility of high inflation or default
intergenerational equity: (which is the principle that present generations have a moral obligation to ensure that future generations have the same opportunities and resources as they do.)
the extent to which deficits crowd out investment
Suppose the government owes $100 at the start of period 1 and pays an interest of $10 for that period. How much does the government owe at the start of period 2 if the primary deficit is equal to $25?
a. $110 b. $125 c. $135 d. $145
note…
G2-T2 is primary deficit

How much can the government borrow/ what is it limited by?
the amount the government can borrow is limited by…
the amount it can credibly be expected to pay back
partly on how large the economy GDP is
The stock of debt can grow time if GDP is growing even faster
the debt GDP ratio will fall if this happens
Is it possible to grow out of debt?
Yes, it is possible to "grow out of debt," particularly for governments where a growing economy makes a large debt burden relatively smaller over time (debt-to-GDP ratio). However, this is a complex process that is not automatic and requires active management
What happens if debt GDP ratio becomes too high? (2)
lenders worry about the ability of the government to repay
investors demand higher interest rates
what if the lenders stop lending to the government?
the government prints more money to satisfy the budget which generates inflation
What is the core risk of a very high debt-to-GDP ratio?
Losing market access → forced money printing → inflation default.
Memory trick for high debt risk?
Too much debt → no lenders → print money → inflation.
what does it mean to (sovereign) default?
this is when the government declares it will not repay certain debts OR it will repay them at less than face value
What does (sovereign) default typically lead to?
it usually leads to bad ECONOMIC outcomes
examples are inflation/hyperinflation, currency devaluation, banking crisis, exclusion from international capital markets
What is generational accounting?
The idea that when the government borrows, the people who benefit may not be the same people who repay the debt.
Why is government borrowing a generational issue?
Because today’s spending can create taxes for future generations.
Why do we discount?
we discount based on the idea that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future
what do we use to convert a future payment into today value?
PDV or present discounted value

Whats the national income identity?
Its an identity where investments equal total savings
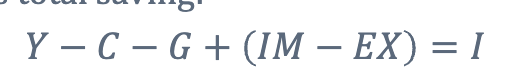

What happened here?
This is the same national income identity but we just added and subtract tax revenue (T-G).
i think tax revenue is profit from tax minus government spendings
What are ways investments can be finaced?
savings from the private sectors
government savings (a surplus)
foreign savings ( capital inflows)
What is crowding out
a concept where the government runs a large deficit, it uses up part of the available savings
whats cool is that it can reduce private investment
what does Ricardian Equivalence suggest about PDV?
if the present discounted value of government spending stays the same, the timing of taxs does not affect total consumption
budget deficits do not necessarily crowd out investments
( economists debate how strong crowding out effects are
How does slide 20 and 21 relate to one another when looking at debt and borrowing? (YT this)
G2-T2 is primary deficit
What is Ricardian equivalence?
an economic theory stating that consumers will save any extra income from a government's tax cut to pay for the anticipated future taxes needed to repay the debt incurred to finance that cut