15. Speciation Hybridization
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Speciation
The “formation” of a new species over geological time, when members of a population can no longer successfully interbreed
Requires: Reproductive isolation related to behavioral traits, habitat use, physiology, etc.
Allopatric Speciation
The evolution of a new species through the process of geographic isolation
Over time, populations become so different that, cannot interbreed, evolve into new speices
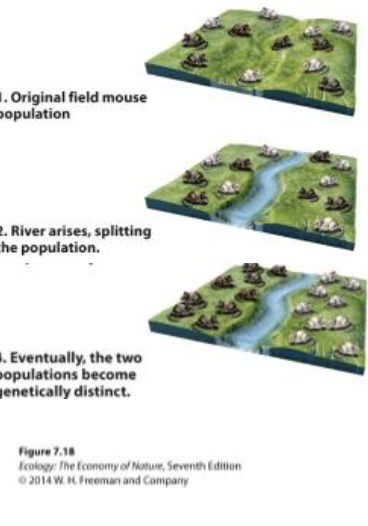
Process of Allopatric Speciation
Geographic seperation: creates two populations who are isolated from each other as a result, no genetic exchange can occur between them
Allopatric Speciation
occrus whena opulation is divded into geograhically isolated populations
Vicrance allopatric speciation
geographic subpopulations, river divding
Disperal allopatric Speceiation
indivudals colinaiize a remote area
Gene pool os isolated populations may diverge through
mutation, natural selection, and genetic drift
Allopatric Speciation etc.
reporduive isolation may arise as a by-porudct of genetic divergence
Allopatric speceation is the most comon form of specation
Divergence invovles
accumulation of indepedent genetic difference between groups (often after population shave become repordviley ioslated.
Evidence of allopatric speciation
isolated/highly subdivded regions usally have more species that those with fewere barriers
Ex: hawaiian islands have many uniqe plants and animals
Allopatric speciation examples
isolated populations of mosqutiofish have become repdorucitley isoaltes as a reuslt of slesection under differente levels or predation
predaiton selected for different body shapes
perenrefre for mating with individuals that have a similar body shape
Sympatric Specation
The evolution of a new species without geographic isolation
Ex: chchild fish in lake Tanganikya have veolved into 200 unique speices from a single common ancestor
Distint micrhabitats throughout the lake, distnics types of food resrources, speiclaizations, etc.
Porcess of sympatric speciation
populations live in the same geographic area
gene flow is reducced by factros such as
poluplodiy
sexual selection
habitat differentation
Drivers of Sympatric Speciation: Polyploidy
Polupiodiy: accidents during cell dividsio, the presence of extra sets of chromosomes
This process can form a new speices withing a single gnereation
can happen with (allopolopolidy) and withouth (autopoluplody) hubridzation
Many importnat agriculatral crops are polyploids
Examples of polploid speciation
at least five new plant speices have orginated by polypiod specation since 1850
ex: two allopolpios speices have evolved from three diploid parent speices in the genus trgopogon
Drivers of sympatric Speciation Seciaul Selection
Sympatric specation can be riven by seicual selection
Speciaton of chcilids Lake Victroia was likely driven by female mate choise based on male breeding coloration
Drivers of sympatris speication: Habitat Differentiation
Sympatric speciation can also result from the exloitation of new habitats or resources
Apple magoot flies evolved in North America after swithciing hosts from hawthorn to apple
How fase does speication happen?
rate of speceation
fossile record invldues manu eposies where new speices apperar suddenly, persit uncahged throuhgl several strate then dissaper
Puncutrated equilibira describes periods of apperant stasis (squilibrieum) follwer by sudden change
Rather than a puncatred pattern, other speices appear to have changed gradually over timeS
Speication in the lab
Reporudtive barriers develope between isolated laboratroy populations subjected to different envriomenttal condtions for only 40 generations
Fruti flies taken from a sinlge parent population but fed different dies over several generations perfer mates adapted to the same diet
Speciation can be rapid or slow
the puncturated pattern in the fossile recor, evidence form lab studies, and instatnaenous polyploid specation show that speication can be rapis
in a sudy of 84 groups of plants and animals, the interval between speication events ranged from 4,000 years (chichilids) to 40 million years (beetles)
The average time between speciation events was 6.5 million years
What happens when geogrhaically isoalted speices come back into contact
Hybris are the result of mating bwettne speices with icnomplte reprodutive barries
a hybruz zone is a region in whcih members of differente speices mate to produdce hybird offpsring
hybis zones are located where habitats of intrebreeding speices meets
often occurs as islates pathes scattered across the lansdacpe, rahter than a continous ban
Possible outocme ina hybriz zone: reinfornemcnet
hybrids are less fit than the parent speices, then there will be astrong selection for prezygotic barries sthat reudced hybrid production
refornces reoductive barries
ex: male pied flycahters closesly reseme male collared flycahters in allopatric but no sympatric populations
Possible outcomes in a hybriz zone stability
Extenseive gene flow from outside they hybrid zone can overwheml seletion for increased repordutive isoaltion inside the hybirz zone
ex: members of both parent speices of Bomiba todas rotuntley migrate into narrow hybriz zone, resulting in ongoing hybrization and production of fir hybirds
Possible ourcomes in ahybird zone: hybri speciation
Hybirs in a hybrz zone may becoome repodurive islaoted from both parental types (fusion)
Ex: sunflower, hellanthsu anomalues ws formed by hybrization bweent tow other sunflower speices follwed by rapid seceation