Week 3 - Body Systems II
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Lymphatic system
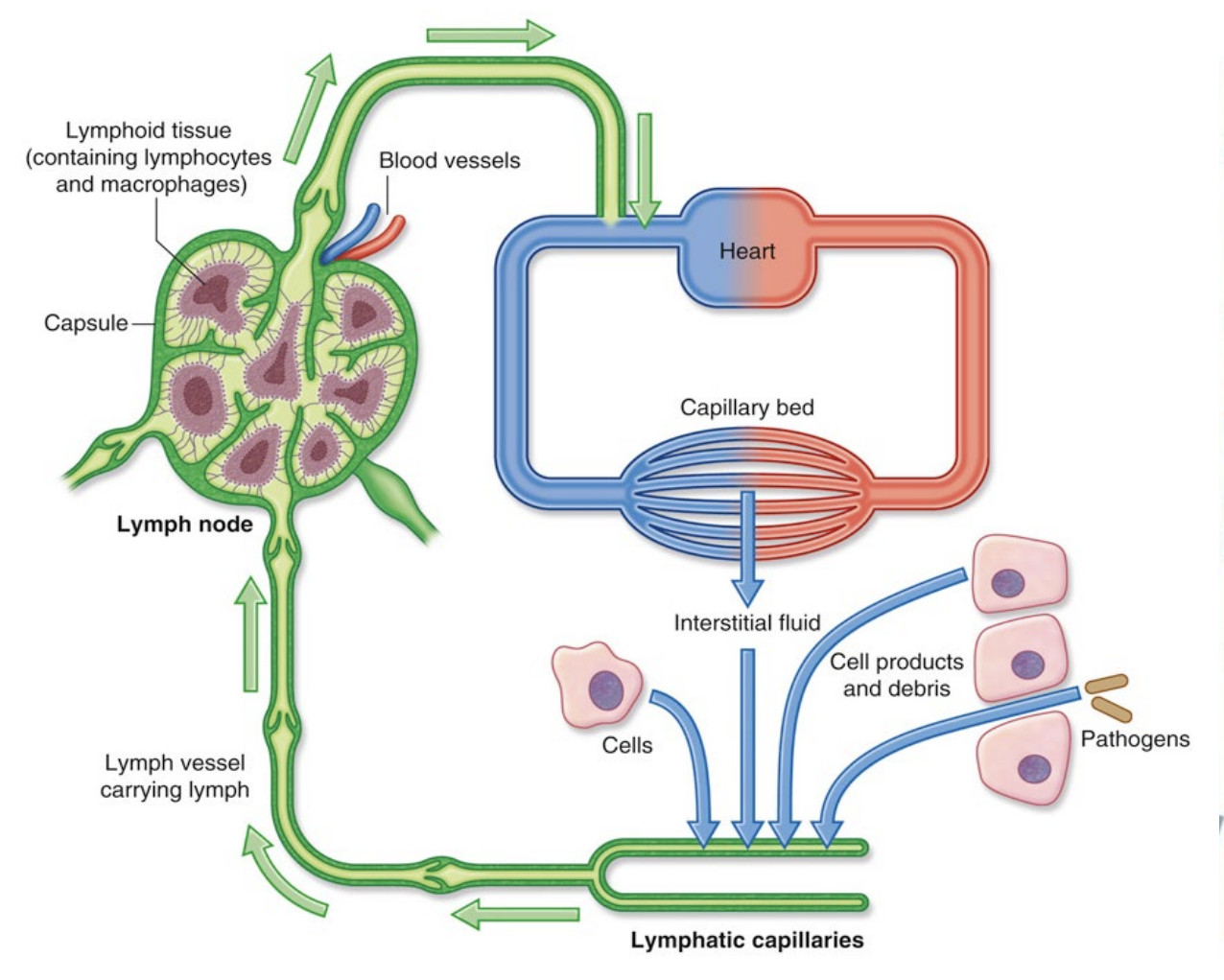
Approx 3L of fluids are returned by the lymphatic system daily.
Without this drainage, blood pressure would go dangerously low
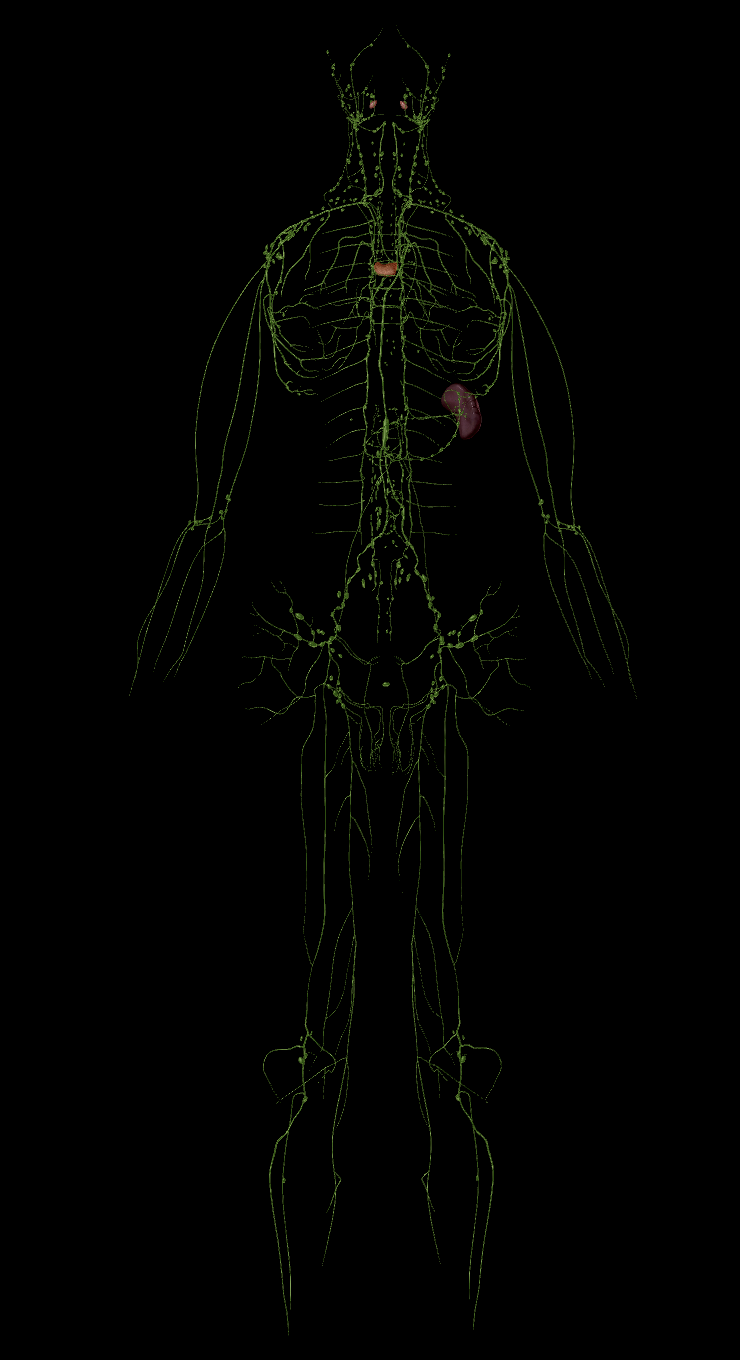
Lymphatic system
Lymph vessels
Lymph nodes
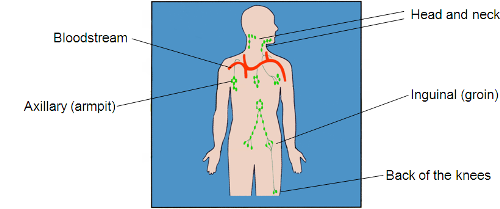
Identifiable lymph nodes
Cervical nodes
Axillary nodes
Inguinal nodes
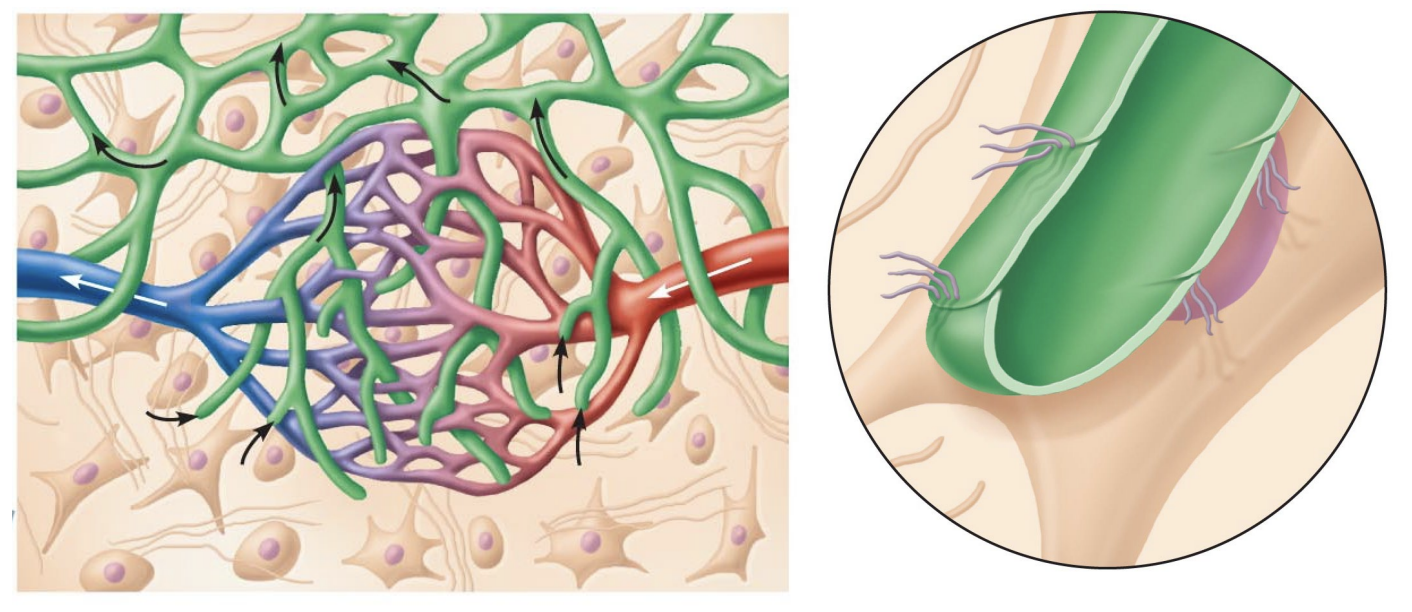
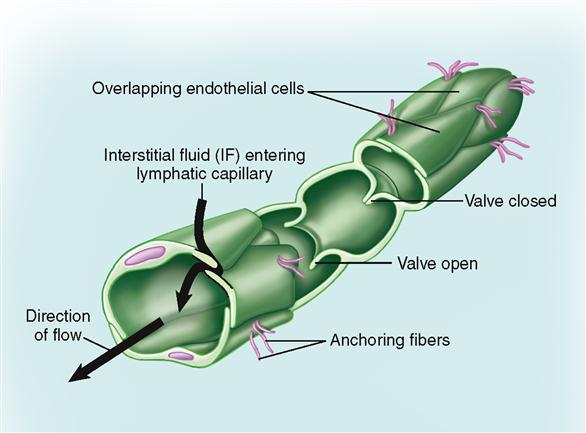
Found surrounding and nearby cappilaries
Pressure regulated
When there is an excess of extracellular fluid, it pressure lymph valves to open, seeping into lymph vessels
Fluid in lymph vessels (called lymph) travels up back towards the heart to re-enter the bloodstream.
Lymphatic system
Lymph vessels
Lymph nodes
Identifiable lymph nodes
Cervical nodes
Axillary nodes
Inguinal nodes
Situated between lymph capillaries & the heart.
Filters out foreign bodies within the lymph
Within these nodes are lymphocytes - macrophages and other white blood cells
Lymphatic system
Lymph vessels
Lymph nodes
Identifiable lymph nodes
Cervical nodes
Axillary nodes
Inguinal nodes
Can be used to track/document progress of disease.
When lymph nodes filter lymph from infected tissue, the nodes can swell and become hard or tender
Lymphatic system
Lymph vessels
Lymph nodes
Identifiable lymph nodes
Cervical nodes
Axillary nodes
Inguinal nodes
Filters lymph from the head and neck.
Noticeable ailments:
Glandular fever
Flu
Tonsilitis
etc.
Lymphatic system
Lymph vessels
Lymph nodes
Identifiable lymph nodes
Cervical nodes
Axillary nodes
Inguinal nodes
Filters lymph from the chest, upper limbs, abdomen & back.
Noticeable ailments:
Infection in drained areas
Swelling can indicate breast cancer
Lymphatic system
Lymph vessels
Lymph nodes
Identifiable lymph nodes
Cervical nodes
Axillary nodes
Inguinal nodes
Filters lymph from the navel, lower limbs & genitalia.
Noticeable ailments:
STDs
Genital cancer
Lower limb skin infections
Respiratory system
Enables breathing to occur with gas exchange.
External respiration - At capillaries & alveoli
Internal respiration - At capillaries & muscles
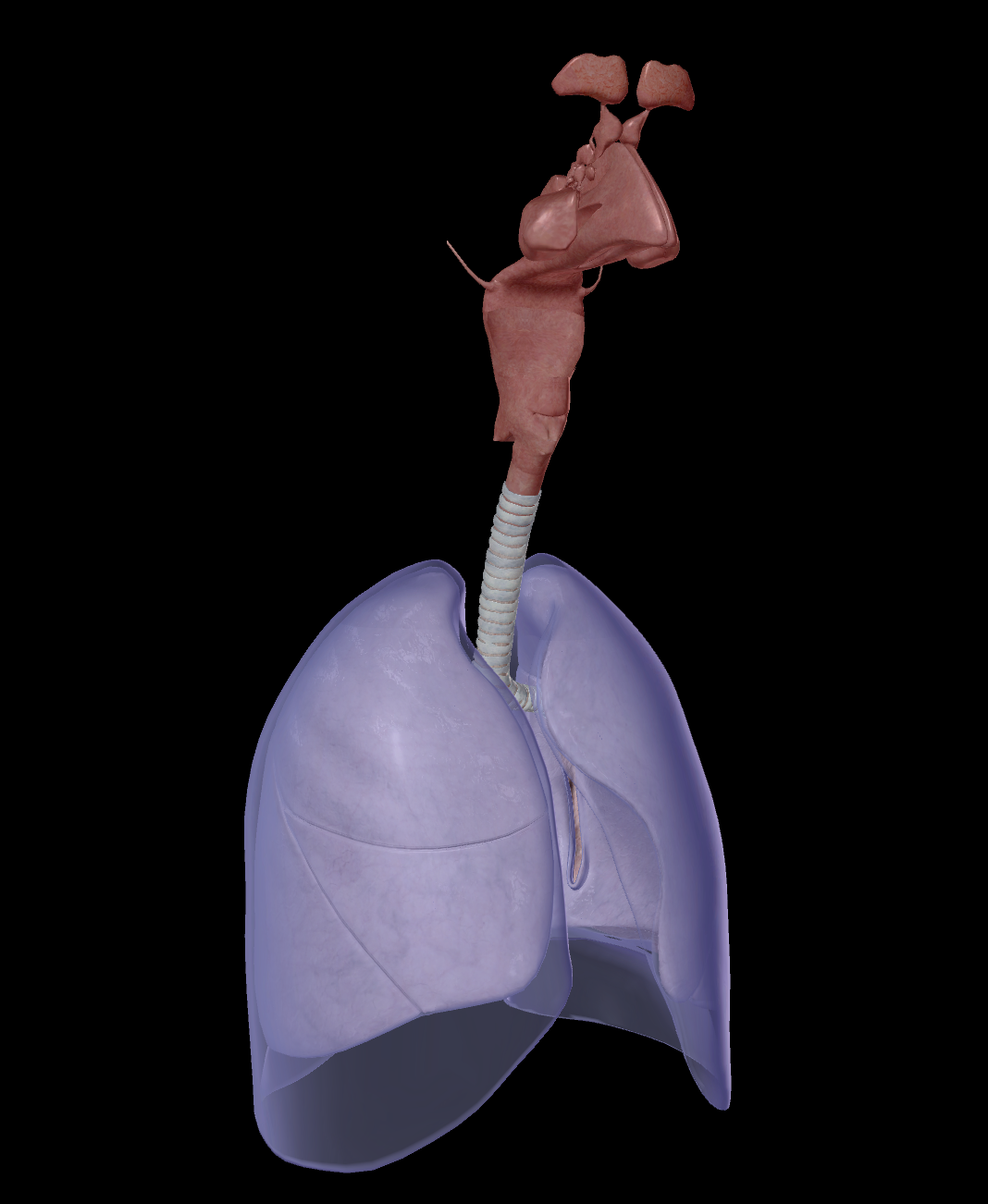
Organs are there to aid the flow of air - Ventilation
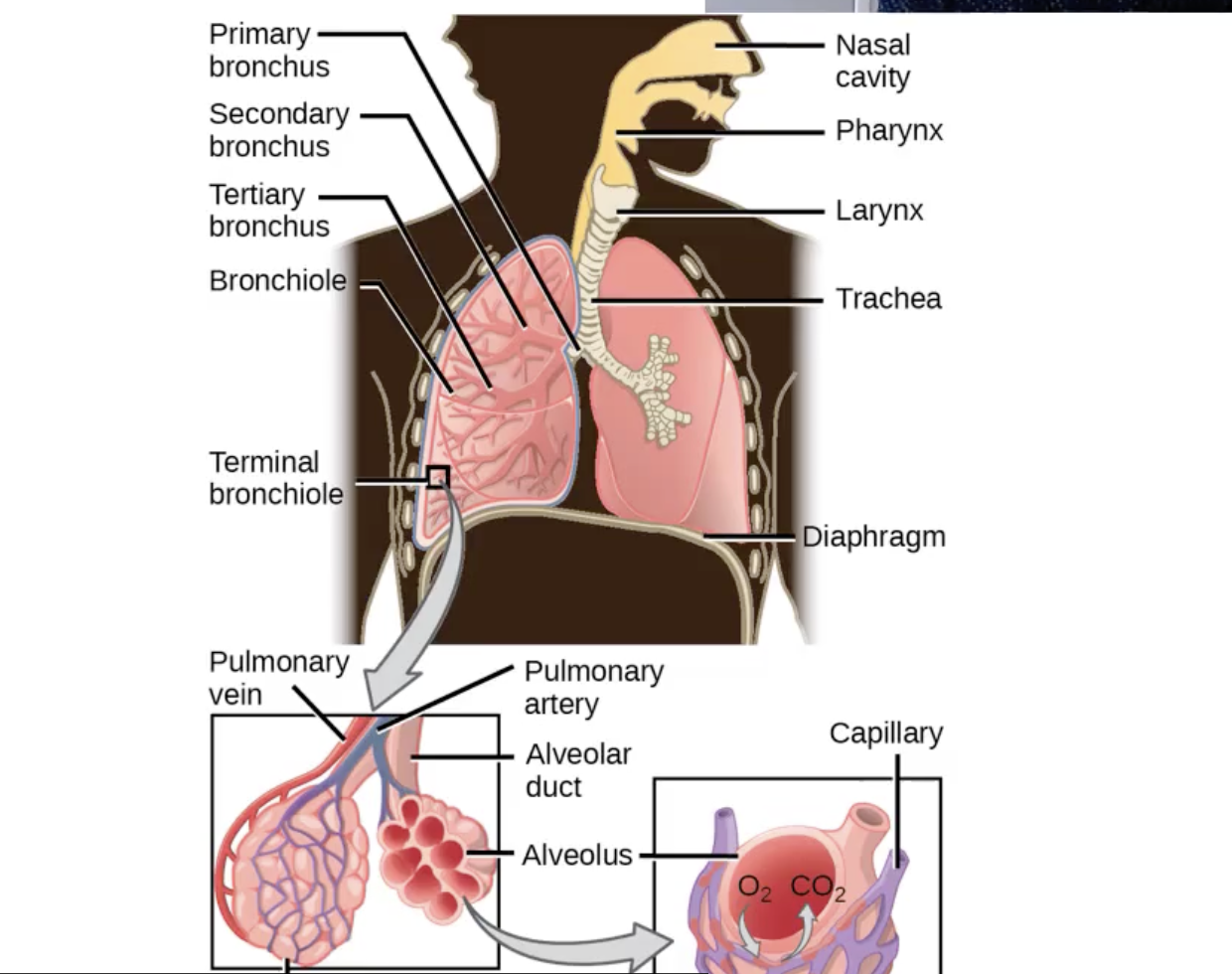
Respiratory system
Nose & nasal cavity
Pharynx & oral cavity
Larynx
Trachea
Primary bronchi
Lungs
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Mouth and Throat.
Air moves anteriorly in through the larynx and enters the trachea.
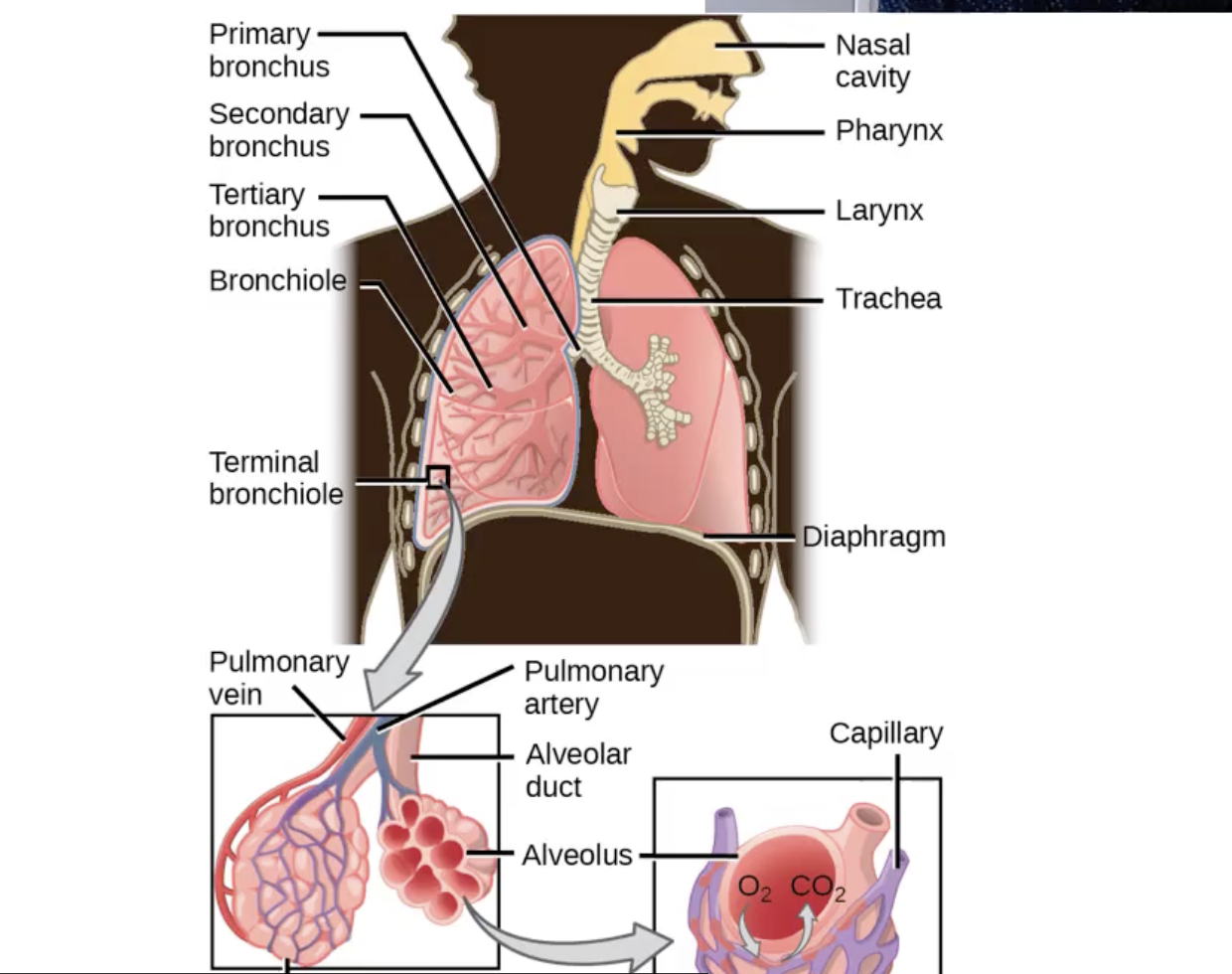
Respiratory system
Nose & nasal cavity
Pharynx & oral cavity
Larynx
Trachea
Primary bronchi
Lungs
Bronchioles
Alveoli
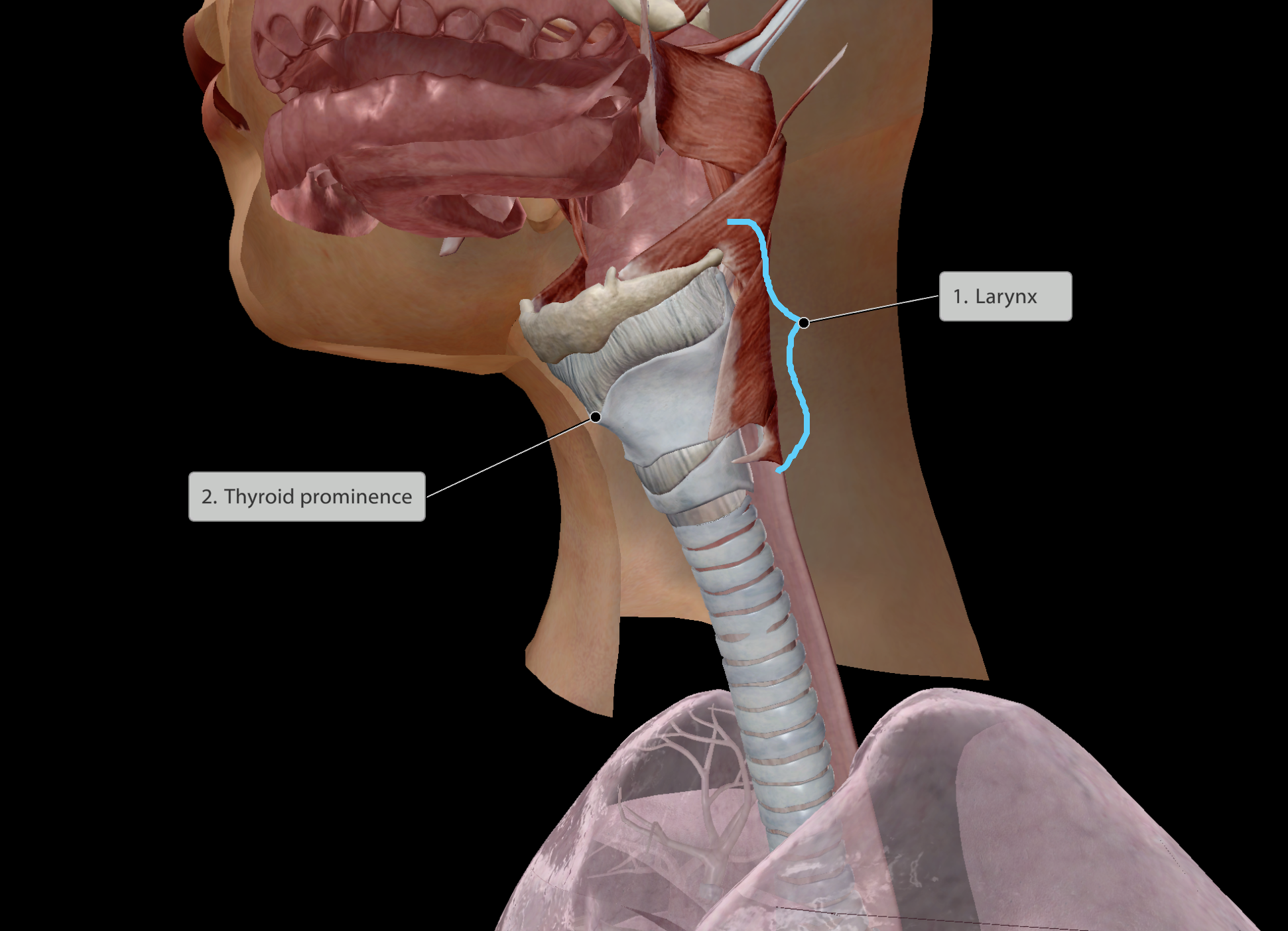
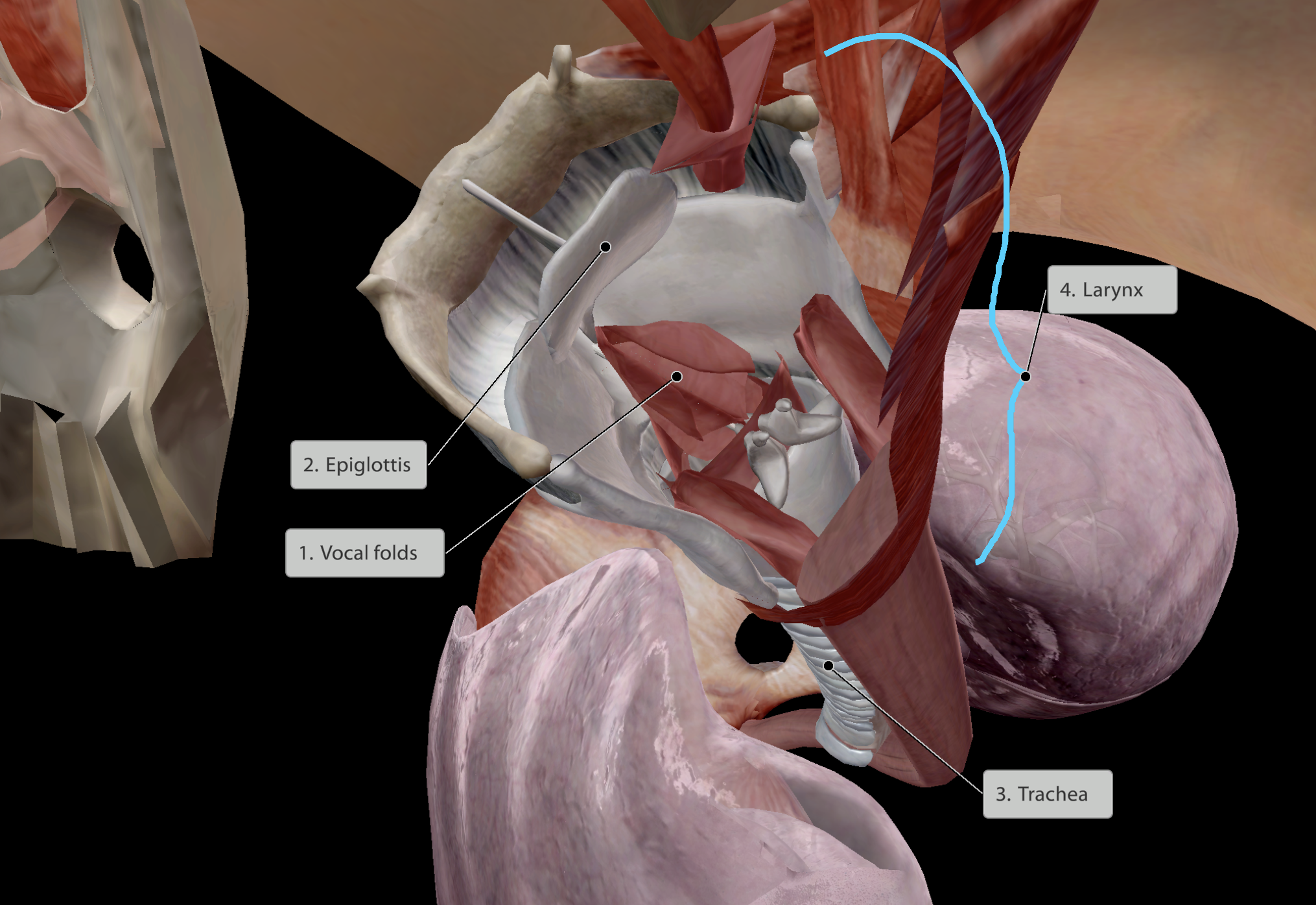
Voicebox
Voice created by vibrating as air passes the vocal folds
Made of cartilage
Landmark - Thyroid prominence, aka Adam’s Apple
Respiratory system
Nose & nasal cavity
Pharynx & oral cavity
Larynx
Trachea
Primary bronchi
Lungs
Bronchioles
Alveoli
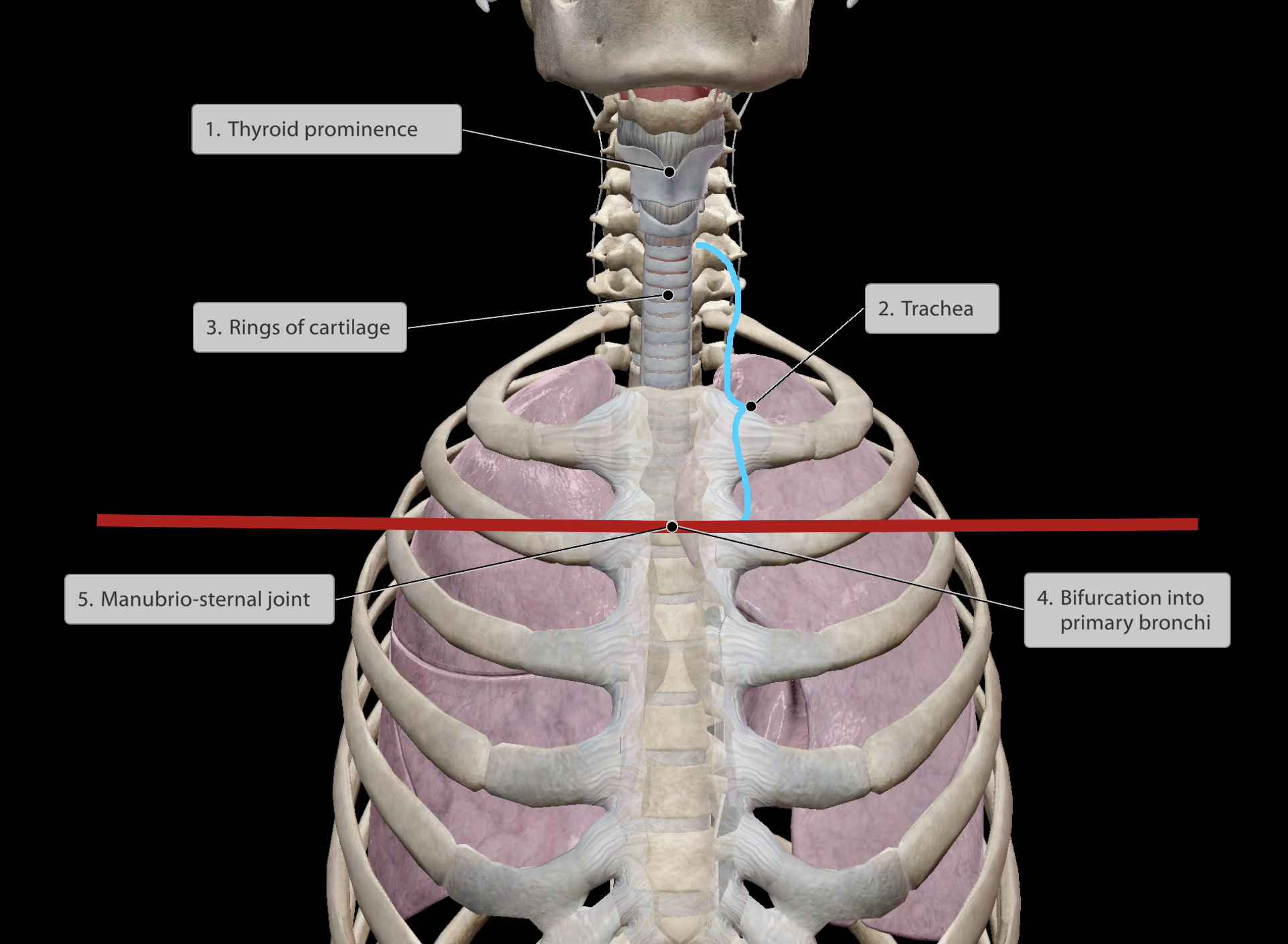
Airway that is ringed with cartilage.
Pathway continues inferiorly until is bifurcates into primary bronchi.
Splits at manubrio-sternal joint
Respiratory system
Nose & nasal cavity
Pharynx & oral cavity
Larynx
Trachea
Primary bronchi
Lungs
Bronchioles
Alveoli
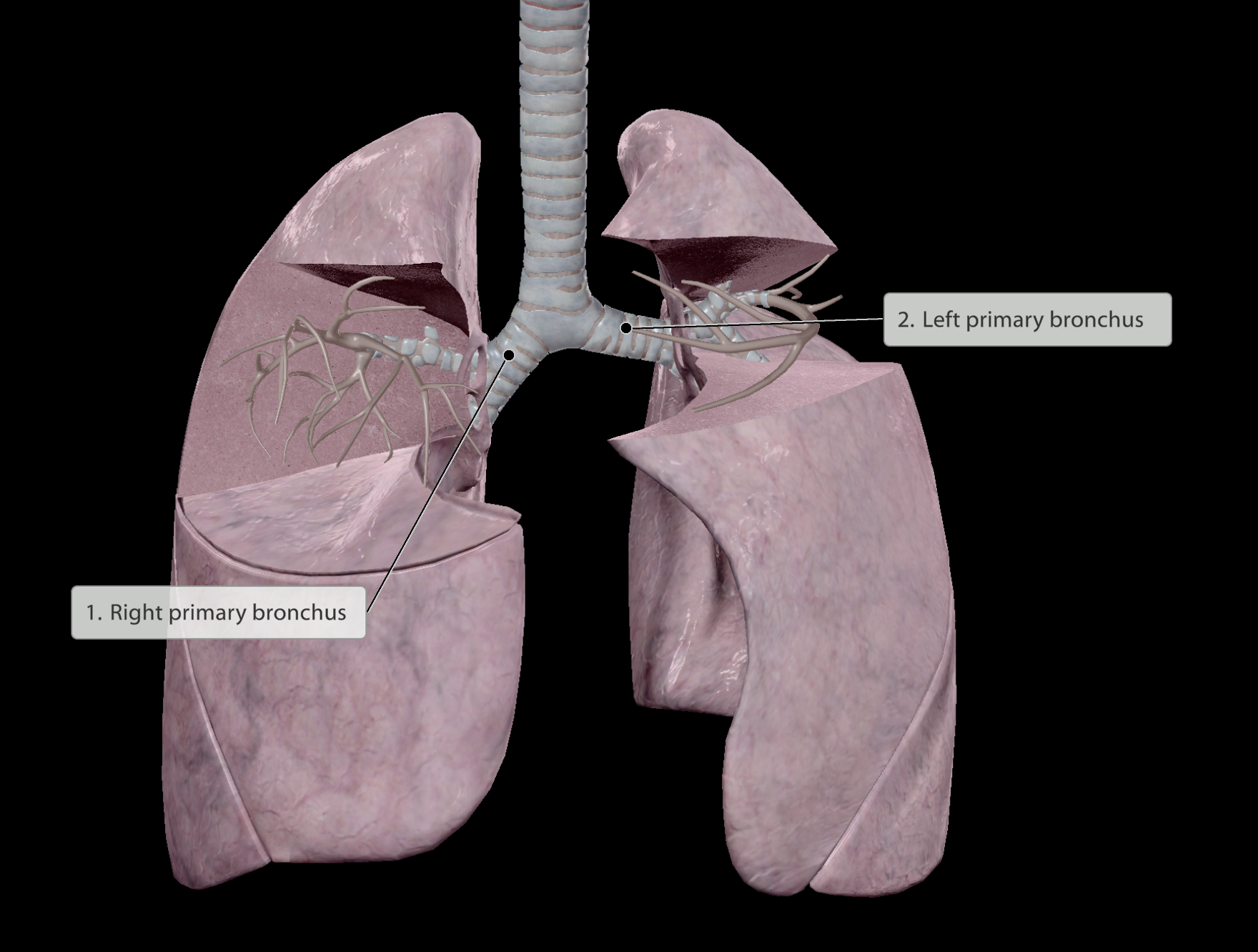
Left primary bronchus runs more horizontal and is narrower compared to right.
Due to the left lung only supplying air to 2 lobes.
The heart sits on the left side of the thoracic cavity, thus left lung is smaller and left bronchus must run above unobstructed
In the event of foriegn matter falling down the trachea, it is more likely to fall down into the slope of the right primary bronchus, than the left horizontal bronchus.
Respiratory system
Nose & nasal cavity
Pharynx & oral cavity
Larynx
Trachea
Primary bronchi
Lungs
Bronchioles
Alveoli
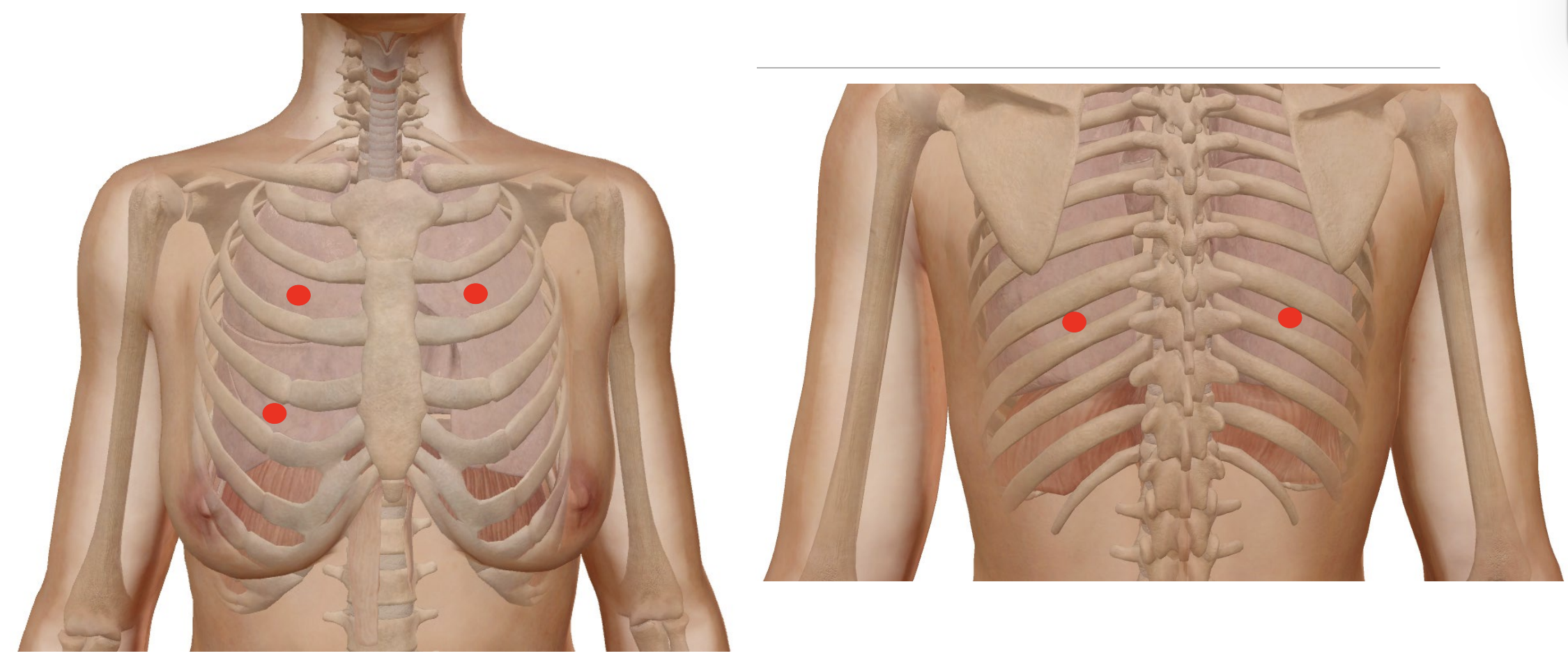
Left lung is smaller to compensate space for the heart.
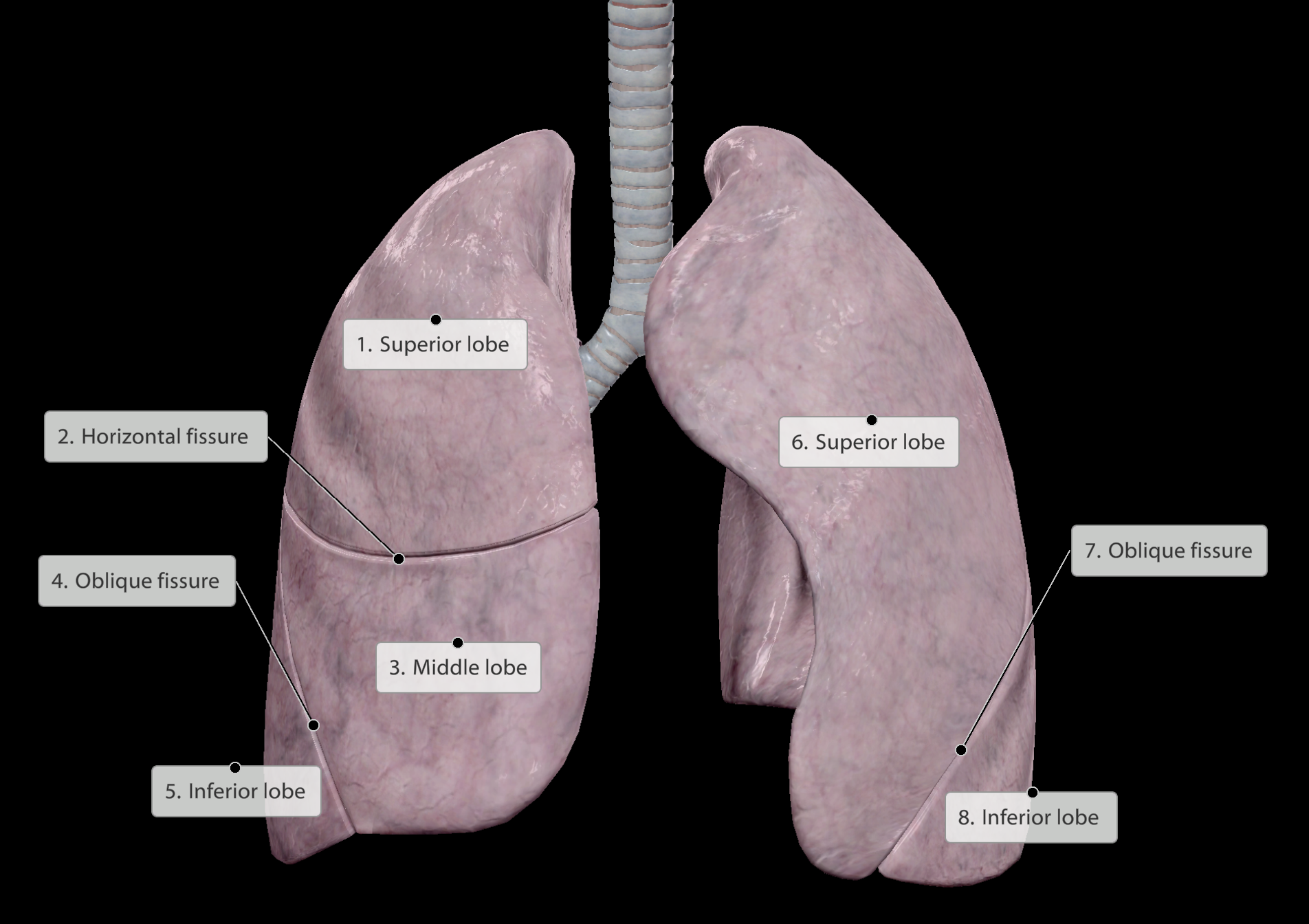
Lungs are subdivided into smaller lobes to limit the spread of infection.
Clefts/cuts/division lines of lobes called fissures
Right lung:
3 lobes. Fissures conjoin on the lateral aspect of the right lung
Left lung:
2 lobes
Listening for individual lobes on a stethoscope:
Respiratory system
Nose & nasal cavity
Pharynx & oral cavity
Larynx
Trachea
Primary bronchi
Lungs - Surface anatomy
Bronchioles
Alveoli
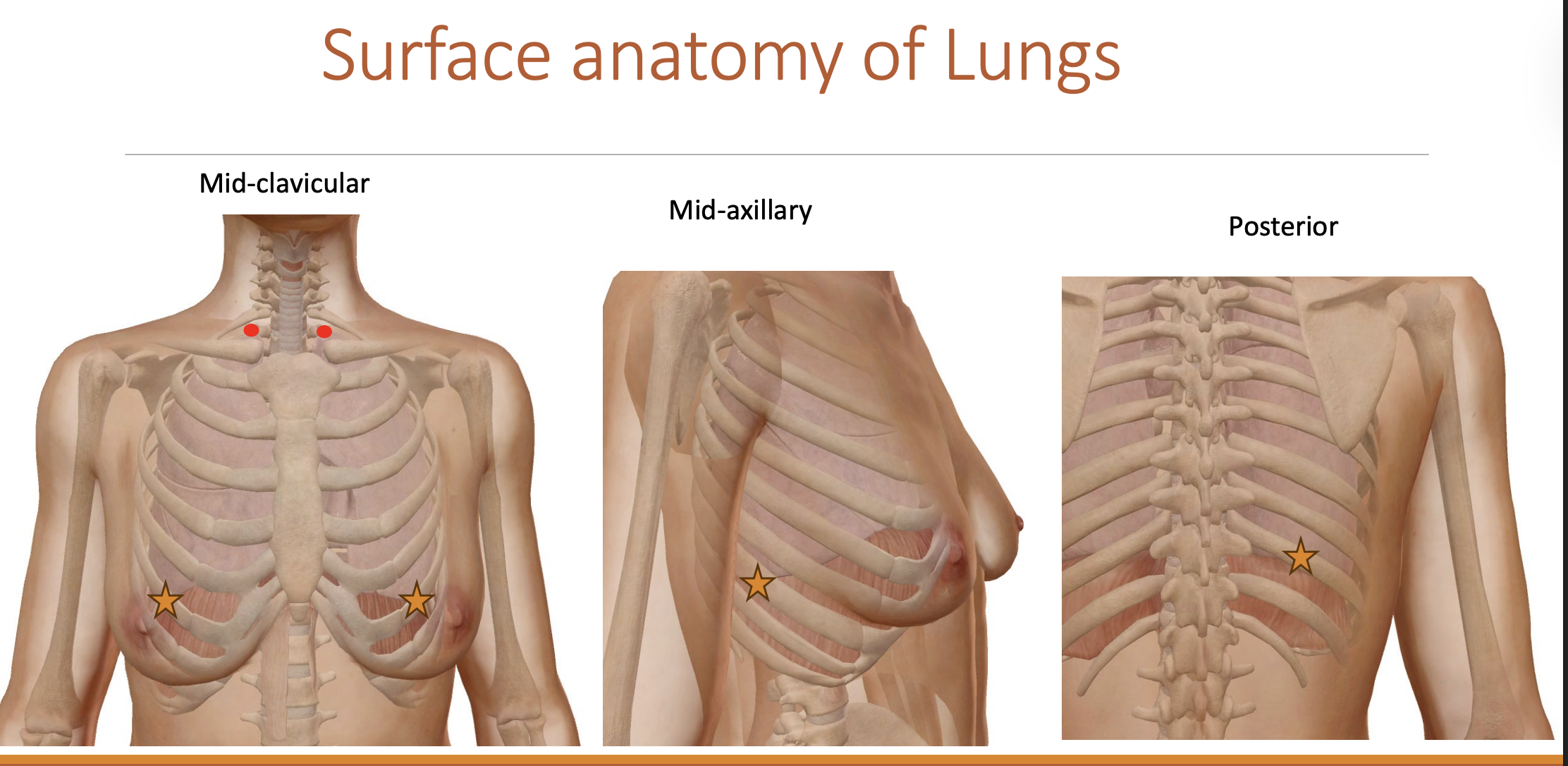
Apex of lungs:
Superior-ally to the medial third of the clavicle
injury can cause a pneumothorax
Base of lungs:
Found along the mid-clavicular line on the 6th rib
Found along the mid-axillary line on the 8th rib
front to side to back
6 to 8 to 10
Pseudo-respiratory system
Nose & nasal cavity
Pharynx & oral cavity
Larynx
Trachea
Primary bronchi
Lungs
Bronchioles
Alveoli
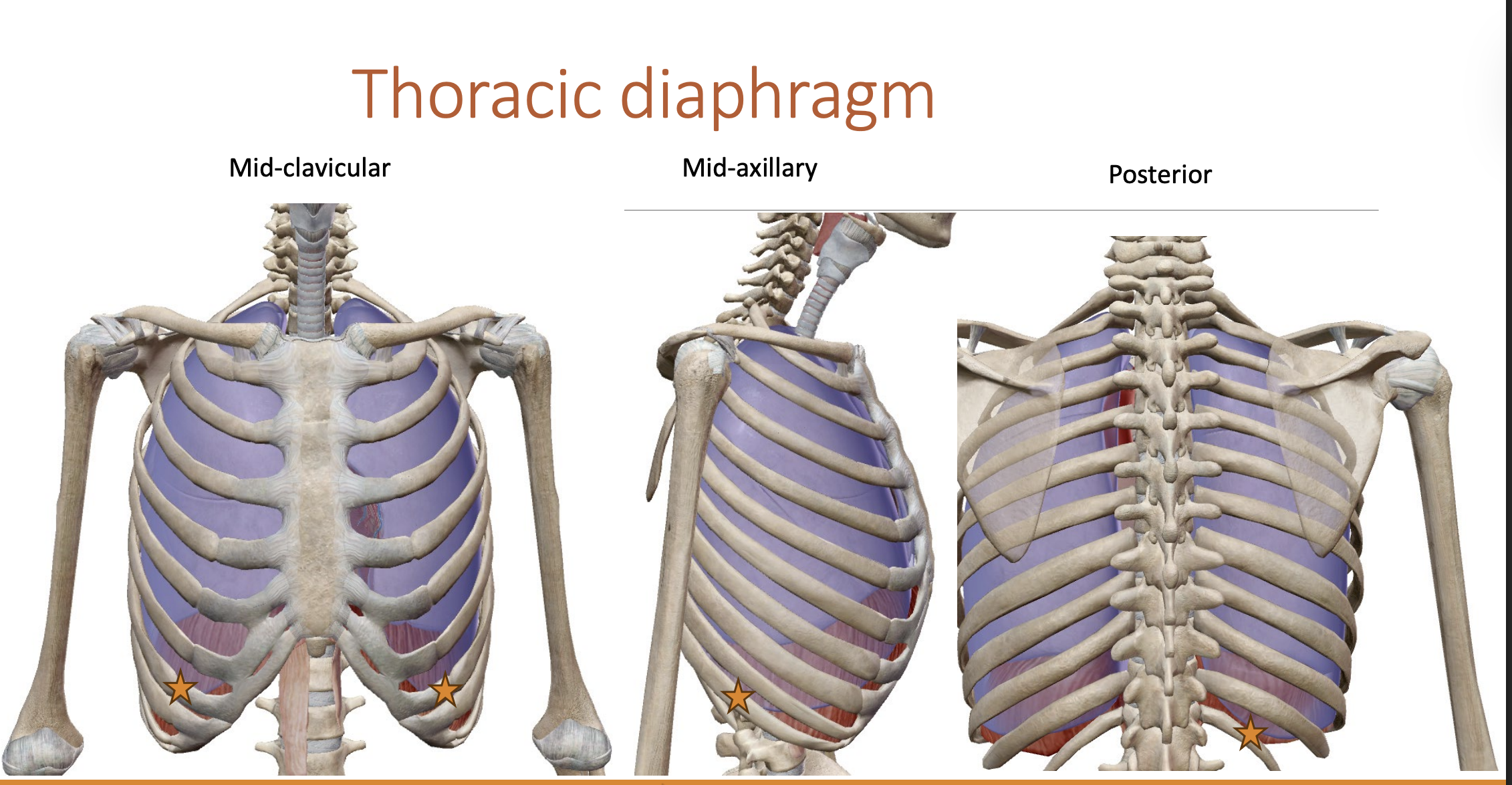
Diaphragm
Makes up the inferior border of the thoracic cavity.
Part of the muscular system (skeletal muscle)
There is space present between the bottom of the lungs and the diaphragm.
Pleural cavity
Listened to with stethoscope to see if there is any fluid buildup
front to side to back
8 to 10 to 12
Digestive system
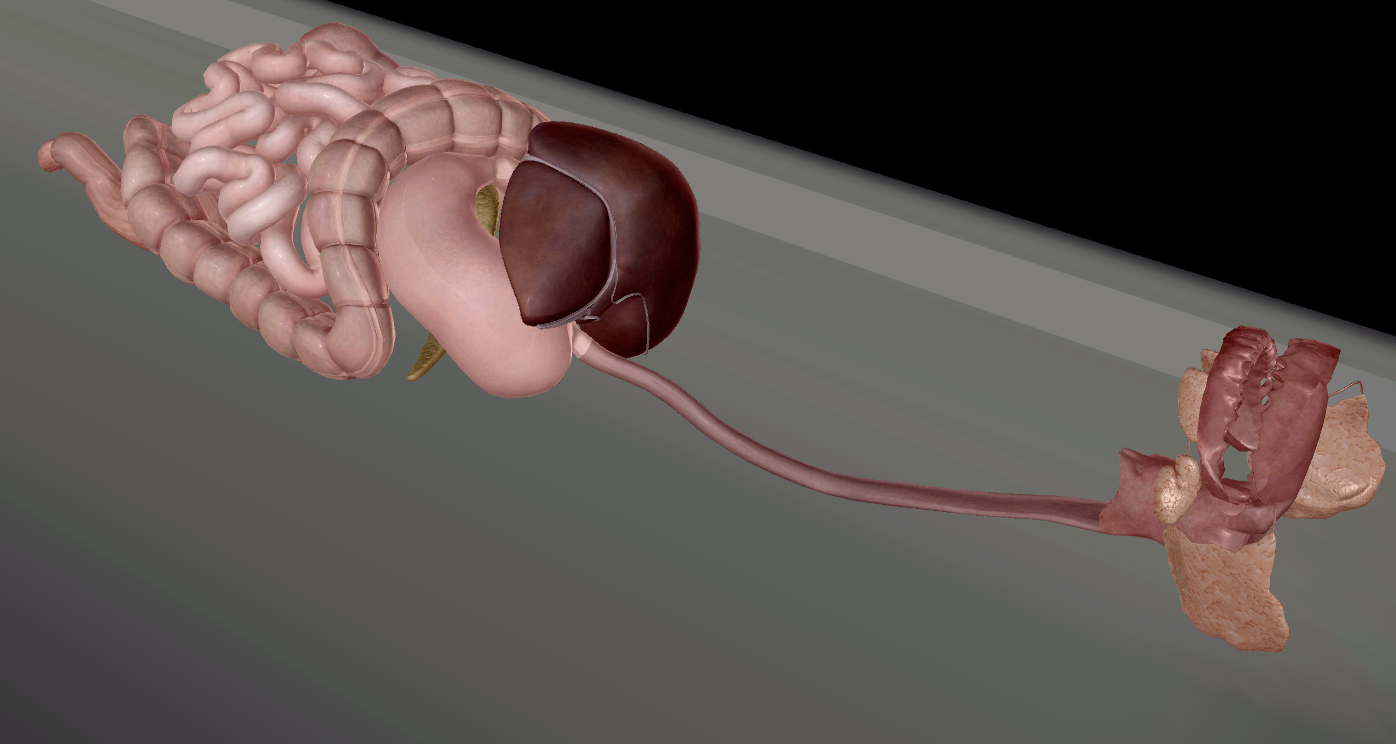
Digests food to provide energy
Digestive system
Alimentary Canal
Accessory organs
“Aliment” - Nourishment
Pathway of food from mouth to anus.
Mouth
Pharynx
Oesophagus
Stomach
Left upper quadrant
Small intestine
Large intestine
Rectum
Anus
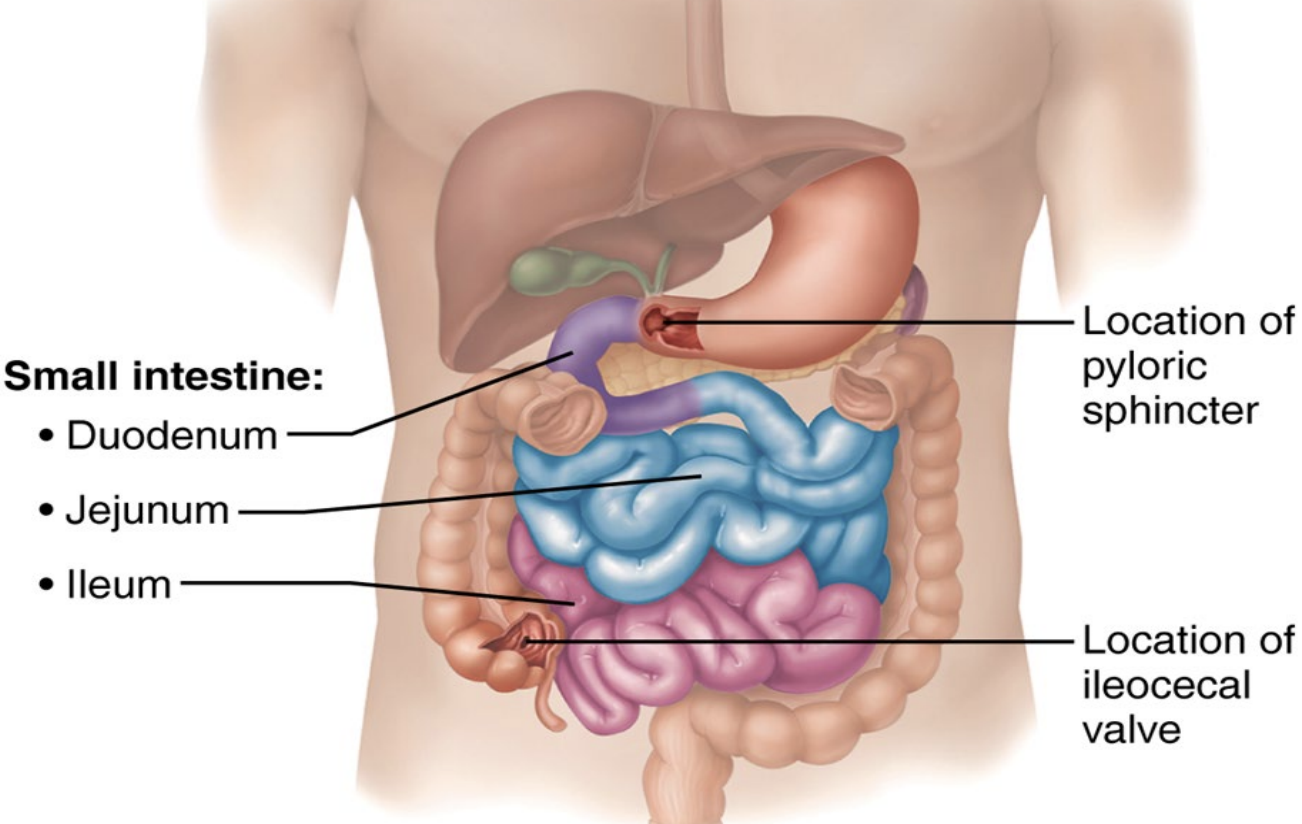
Digestive system
Alimentary Canal
Small intestine
Accessory organs
3 segments:
Duodenum
In contact with the pancreas, which releases ions that neutralise stomach acid
Right upper quadrant
Jejunum
Mobile structure, found in all quadrants
Ileum
Mobile structure, found in all quadrants
Ileocecal valve into the large intestine
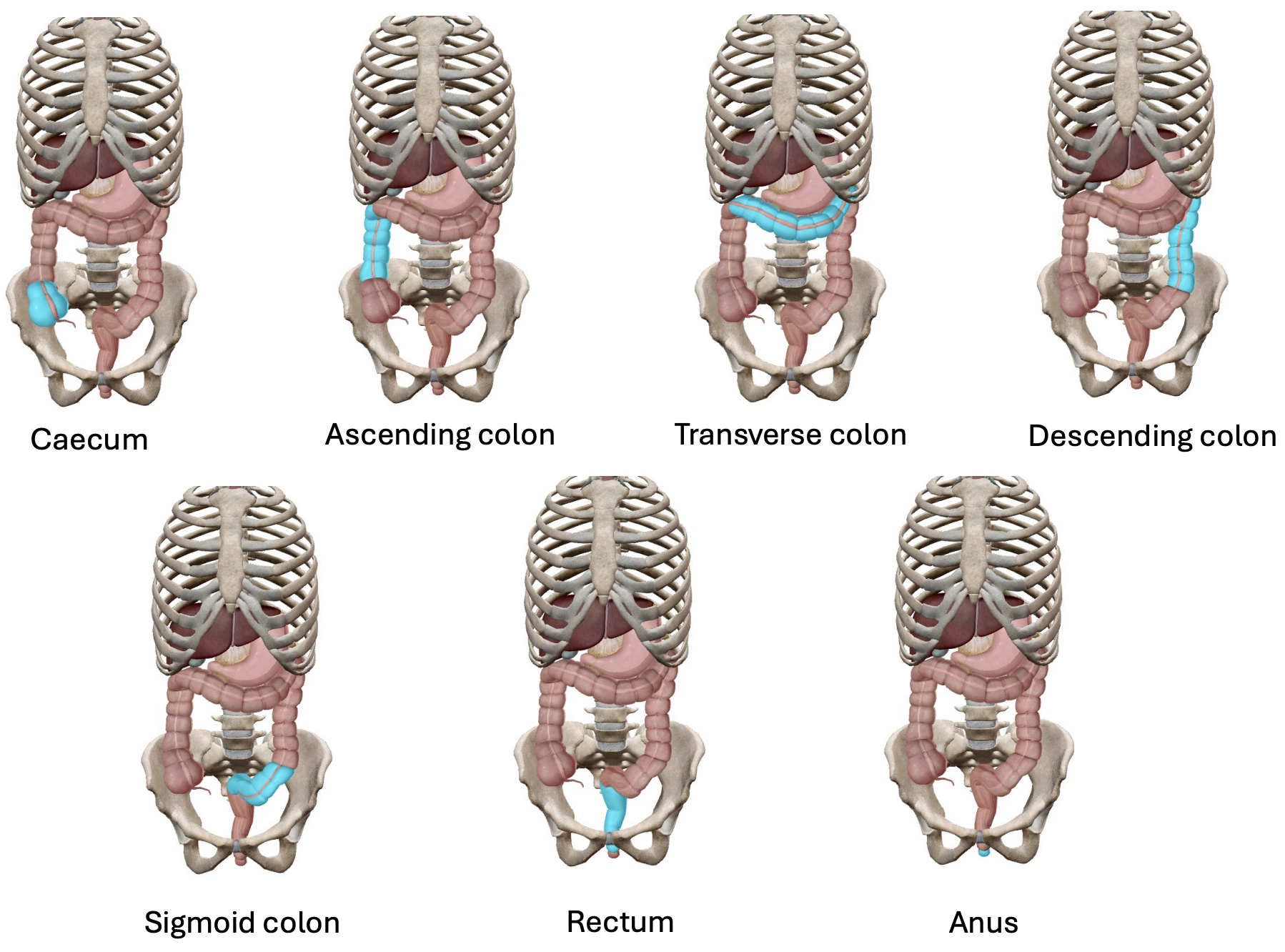
Digestive system
Alimentary Canal
Large intestine
Accessory organs
6 segments:
Caecum
Right lower quadrant
Linkage of appendix
Ascending colon
Right upper quadrant
Transverse colon
Travels from right to left upper quadrants
Descending colon
Left upper and lower quadrants
Sigmoid colon
Left lower quadrant
Rectum
Located at the midline of both quadrants
Anus
Located at the midline of both quadrants
Digestive system
Alimentary Canal
Accessory organs
Teeth
Breaks down food
Tongue
Manipulates position of food when swallowing
Salivary glands
Enzymes that break down food
Produces saliva to make food slippery so it can be swallowed easily
Liver
Produces bile secreted into the small intestine that helps break down lipids
Majority in right upper quadrant, however part is found in the left upper quadrant
Gallbladder
Stores bile
Right upper quadrant
Pancreas
In contact with the small intestine (specifically duodenum)
Secretes enzymes to aid digestion
Secretes ions to balance the acidic pH of chyme exiting the stomach
Positioned posterior to the stomach and in the left upper quadrant. Head of the pancreas is found in the right upper quadrant/
Digestive system
Positioning
Abdomen quadrants:
Split at navel bellybutton
RUQ = Right Upper Quadrant
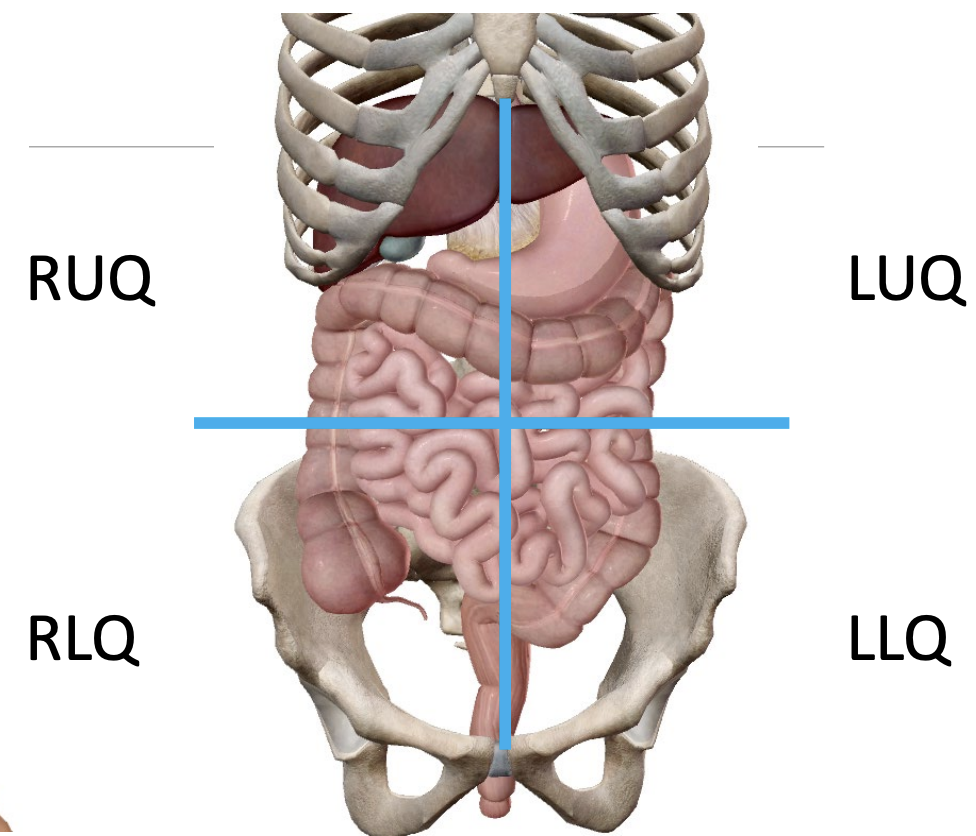
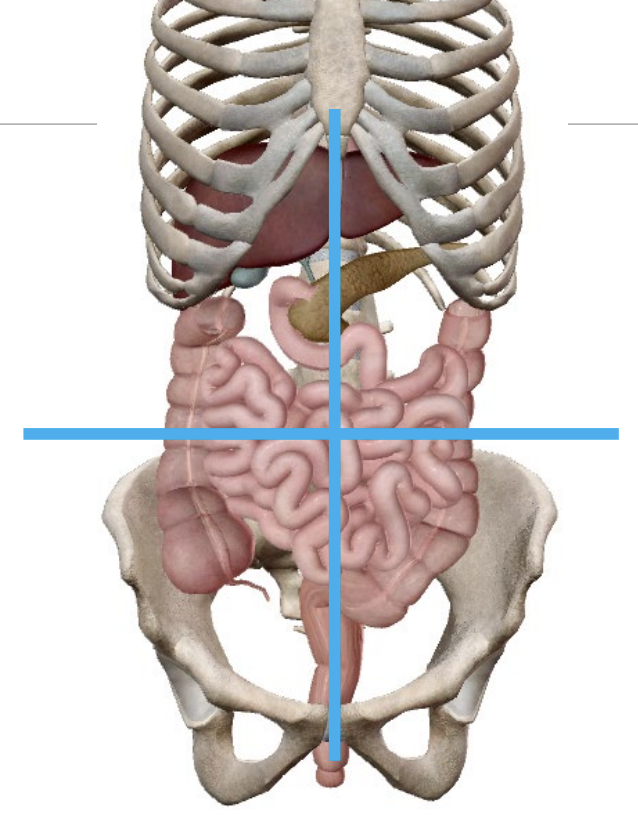
Urinary system
Function:
Filter blood and releases waste as urine
Pathway:
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
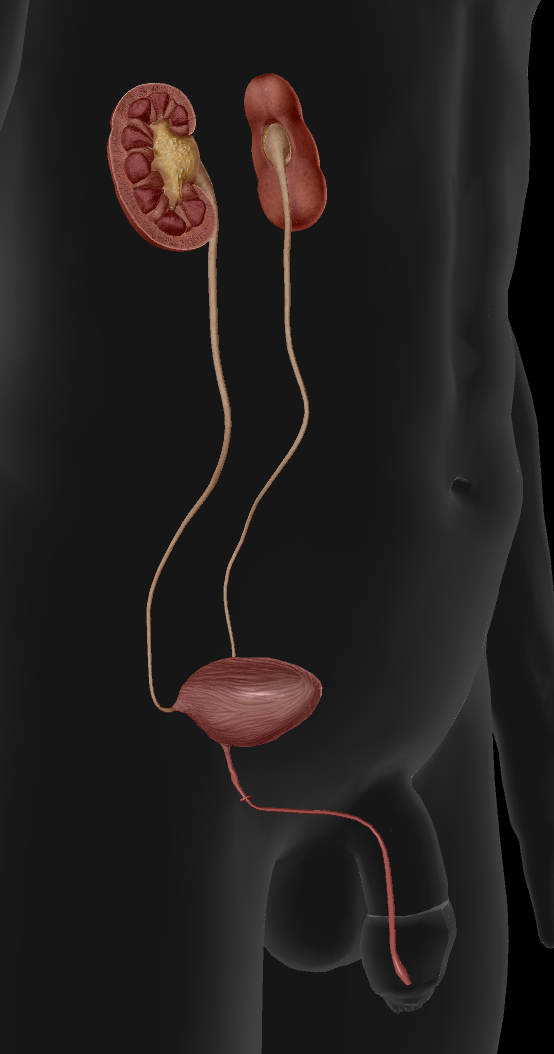
Male (above):
Female (below):
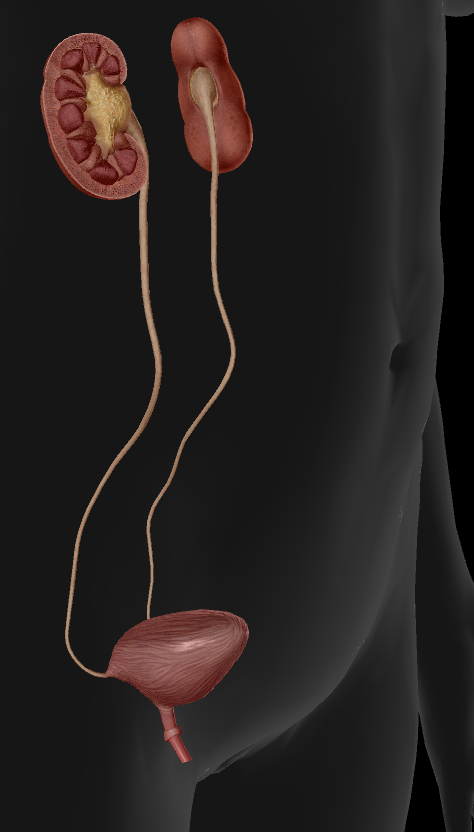
Difference: Male urethras are longer than female urethras.
Urinary system
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
Filters blood approx 60 times per day
~1.8L of urine is produced
Paired organ
Location:
Upper left and right quadrants
Located closer to the posterior aspect of the body & spine
Greater chance of collateral injury when back is injured
Partially protected by 11th & 12th ribs (floating ribs)
Right kidney positioned lower than the left kidney
Due to majority of the liver being found above the right kidney in the right upper quadrant
Spleen found in the left upper quadrant
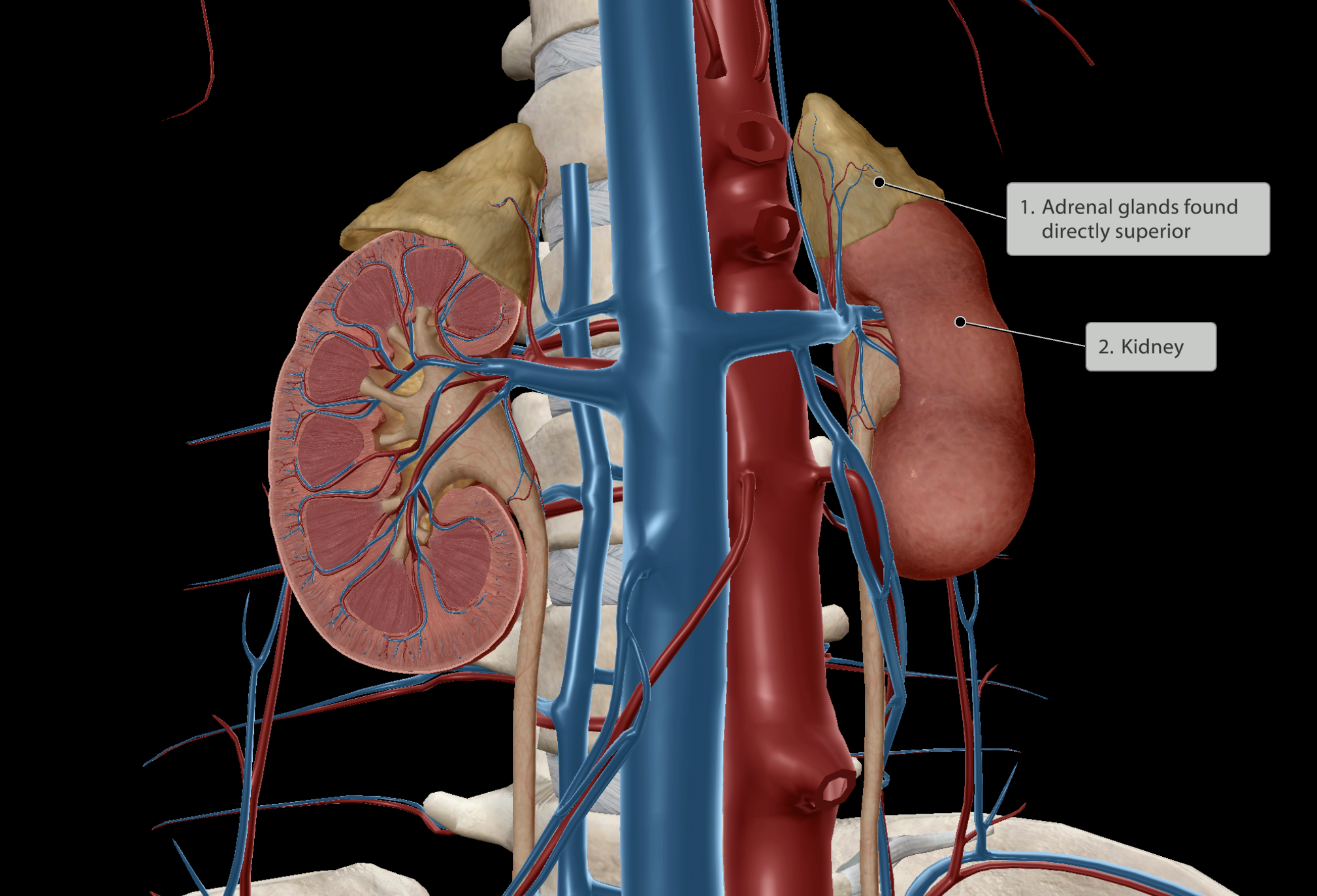
Urinary system
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
Originating from the medial aspect of the kidneys
just lateral to the vertebrae
Extending down to the posterior aspect of the bladder.
Urinary system
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
When full can hold urine in via sphincters in the urethra.
Releases urine into the urethra
Receives urine from ureters
Location:
Posterior to the pubic symphysis
Inside the pelvis
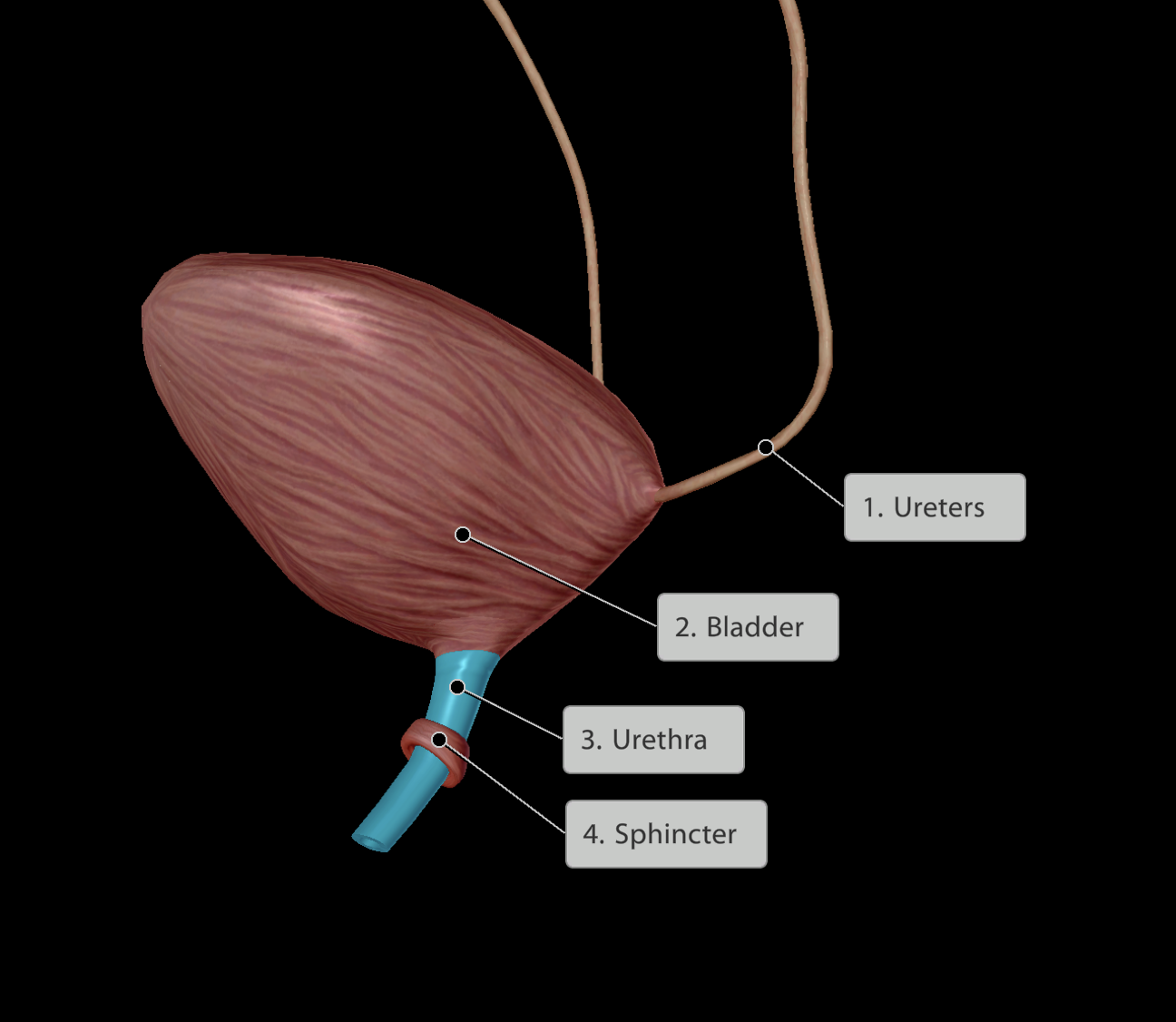
Urinary system
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
Releases urine into the external environment.
Leaves from the inferior aspect of the bladder
Travels inferior to the pubic symphysis
Longer in males than females
Thus, greater chance of infection reaching the bladder from the external environment in females
Reproductive system
Produces offspring
Passes down genetics
Gametes (sperm & ova/ovum) cause fertilisation
Ova/ovum: Female
Sperm: Male
However, there can be many variations to this binary notion, such as intersex individuals.
Homologous structures: Although physically structured differently, these structured developed from the same embryological origin, thus have comparable functions
Reproductive system
Scrotum/Labia majora
Spongy urethra/Labia minora
Foreskin/Prepuce
Body of penis/Body of clitoris
Glans of penis/Glans of clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian tubes/ductus deferens or vas deferens
Ovaries/testicles & epididymis
Both serve to protect delicate genitalia from the external environment
Scrotum:
Holds subcutaneous (just under skin) tissue
Holds testicles
Labia majora:
Protect the female genitalia
Ensure adequate temperature is maintained

Reproductive system
Scrotum/Labia majora
Spongy urethra/Labia minora
Foreskin/Prepuce
Body of penis/Body of clitoris
Glans of penis/Glans of clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian tubes/ductus deferens or vas deferens
Ovaries/testicles & epididymis
Both are hairless.

Reproductive system
Scrotum/Labia majora
Spongy urethra/Labia minora
Foreskin/Prepuce
Body of penis/Body of clitoris
Glans of penis/Glans of clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian tubes/ductus deferens or vas deferens
Ovaries/testicles & epididymis
Further protective structures for underlying glands.
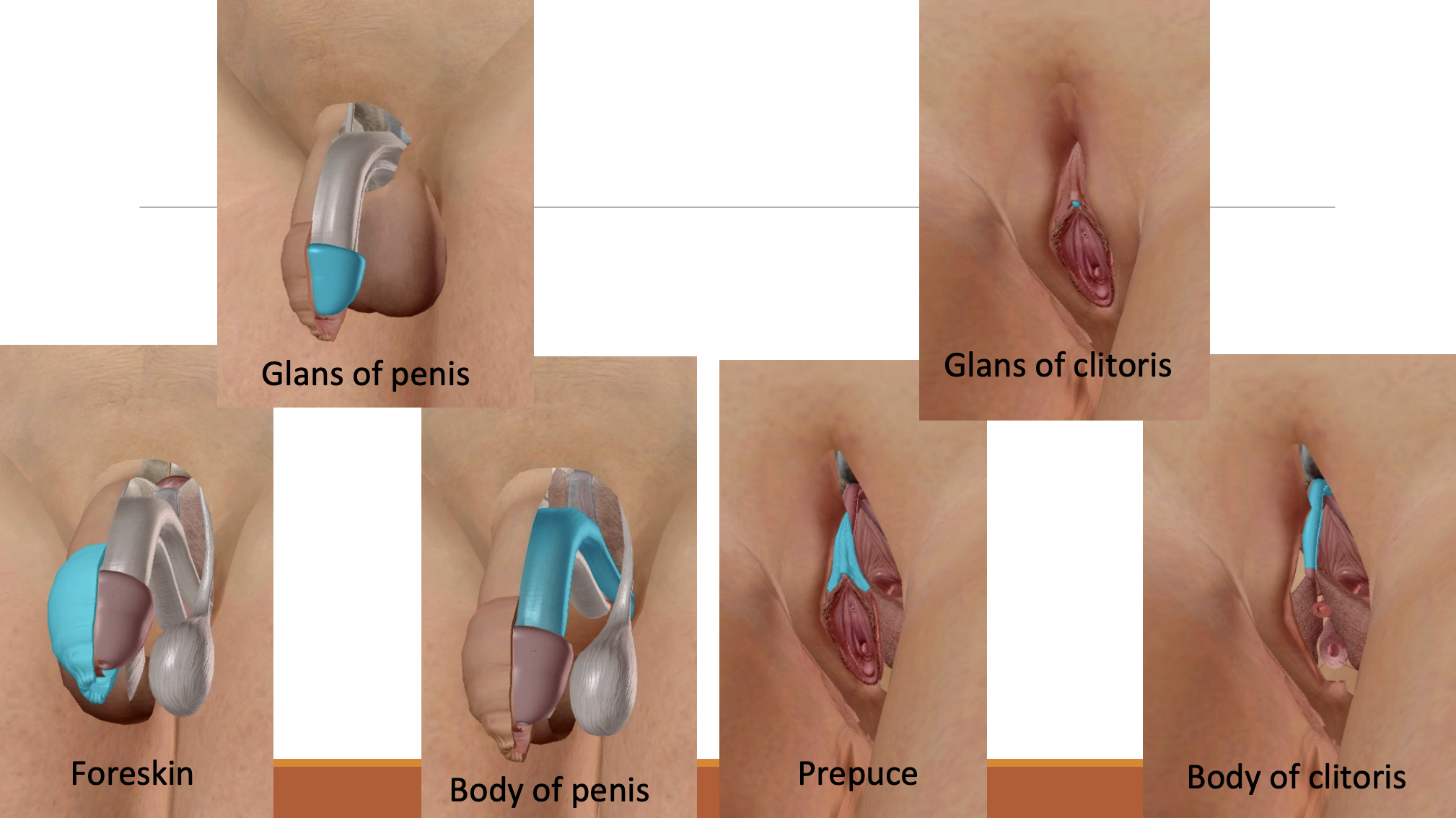
Foreskin:
Protects the penis & glans of penis
Prepuce:
Protects clitoris & glans of clitoris
Shape varies between individuals.
Reproductive system
Scrotum/Labia majora
Spongy urethra/Labia minora
Foreskin/Prepuce
Body of penis/Body of clitoris
Glans of penis/Glans of clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian tubes/ductus deferens or vas deferens
Ovaries/testicles & epididymis
Both contain erectile tissue.
Receives increased blood flow when sexually aroused.
Difference:
Penis contains the urethra, through which both urine and semen exit
Clitoris has no opening
Reproductive system
Scrotum/Labia majora
Spongy urethra/Labia minora
Foreskin/Prepuce
Body of penis/Body of clitoris
Glans of penis/Glans of clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian tubes/ductus deferens or vas deferens
Ovaries/testicles & epididymis
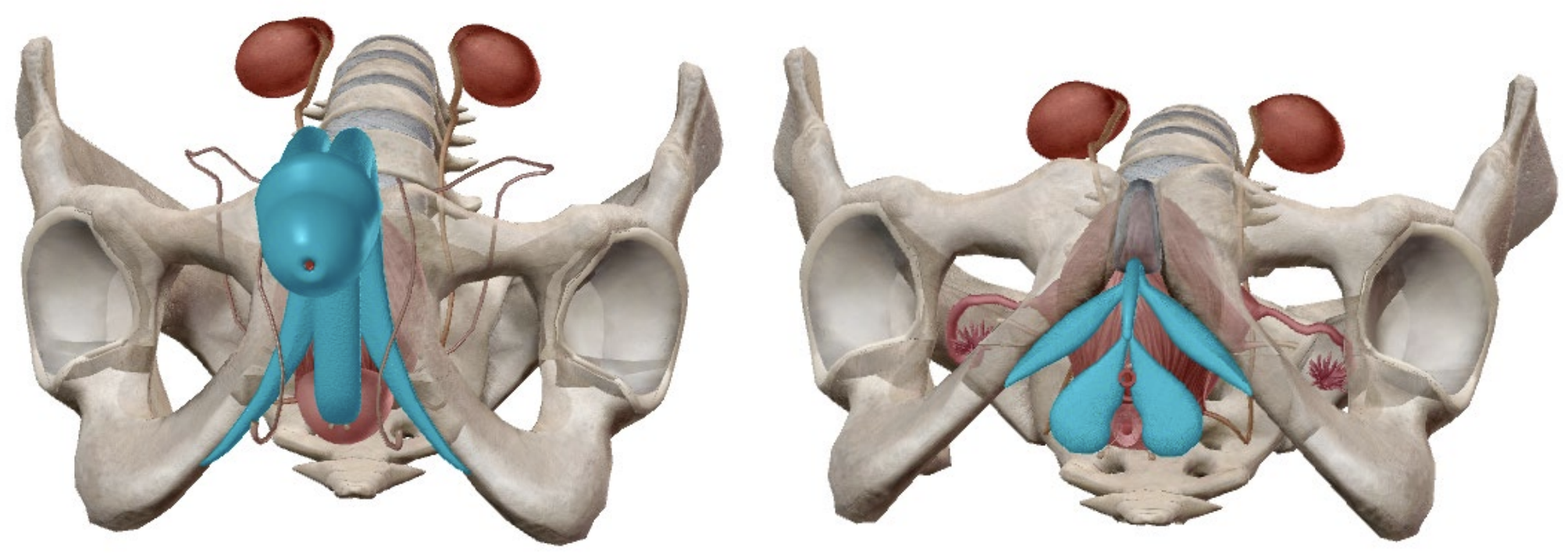
Both contain erectile tissue.
Receives increased blood flow when sexually aroused.
Both are connected to the pelvis
Both contain a shaft originating posteriorly, extending anteriorly along the midline
Difference:
Penis contains the urethra, through which both urine and semen exit
Clitoris has no opening
Reproductive system
Scrotum/Labia majora
Spongy urethra/Labia minora
Foreskin/Prepuce
Body of penis/Body of clitoris
Glans of penis/Glans of clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian tubes/ductus deferens or vas deferens
Ovaries/testicles & epididymis
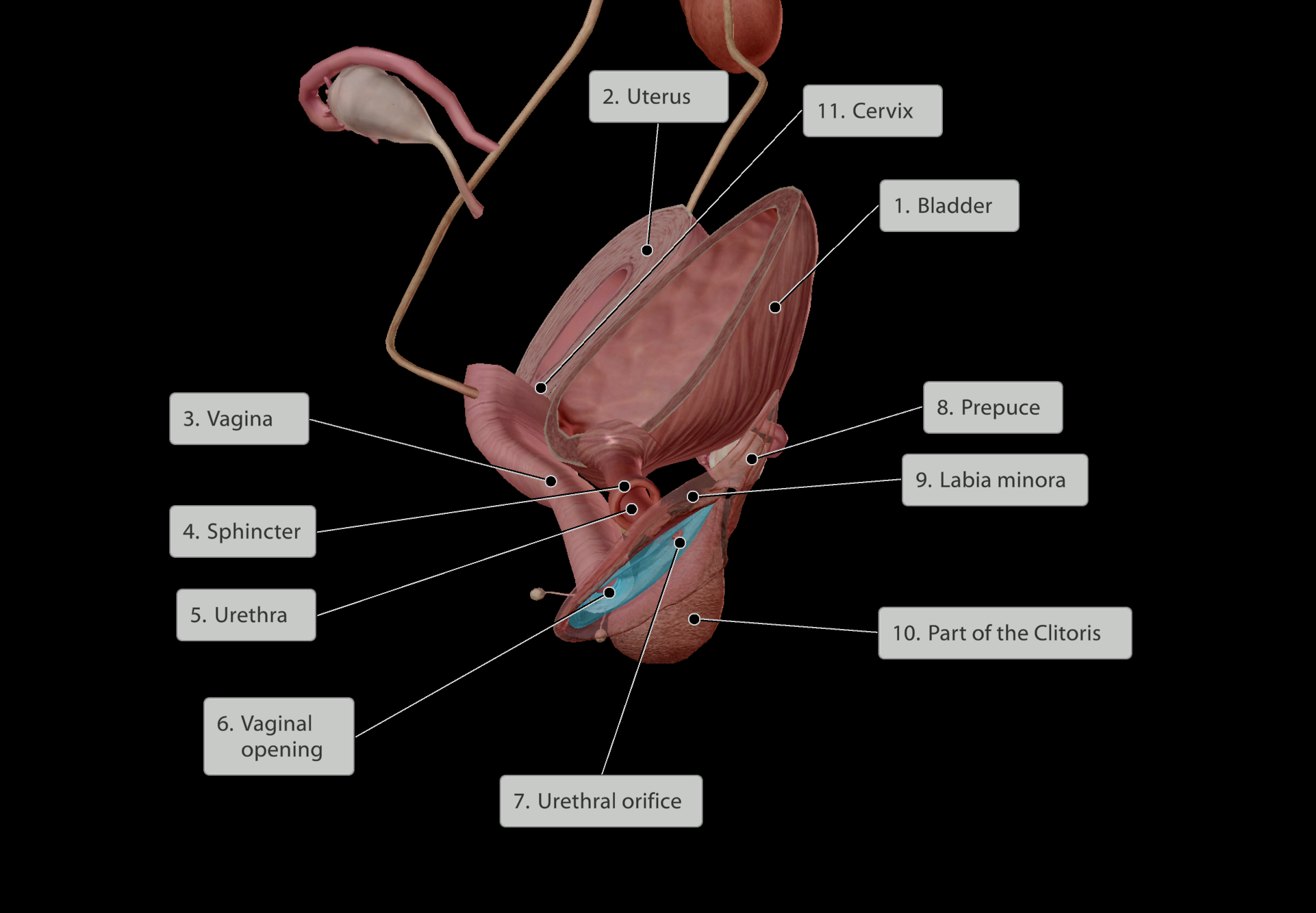
Passageway for sexual intercourse
Where menstrual flow exits
Where child exits during childbirth
Location:
POSTERIOR to the urethra
However, the vagina extends posteriorly AND superiorly to the bladder, connecting with the CERVIX & UTERUS, which is located SUPERIOR to the bladder.
Thus, when a woman is pregnant, the weight of the foetus presses DOWN onto the bladder due to gravity, causing her to be able to hold less urine, and need the toilet more often.
Reproductive system
Scrotum/Labia majora
Spongy urethra/Labia minora
Foreskin/Prepuce
Body of penis/Body of clitoris
Glans of penis/Glans of clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian tubes/ductus deferens or vas deferens
Ovaries/testicles & epididymis
‘cervix’ means ‘Neck’
e.g “cervical vertebrae”
The cervix is the joining between the uterus and the vagina
Reproductive system
Scrotum/Labia majora
Spongy urethra/Labia minora
Foreskin/Prepuce
Body of penis/Body of clitoris
Glans of penis/Glans of clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian tubes/ductus deferens or vas deferens
Ovaries/testicles & epididymis
Uterus:
Holds the child during pregnancy
Fallopian tubes:
Location of fertilisation and conception
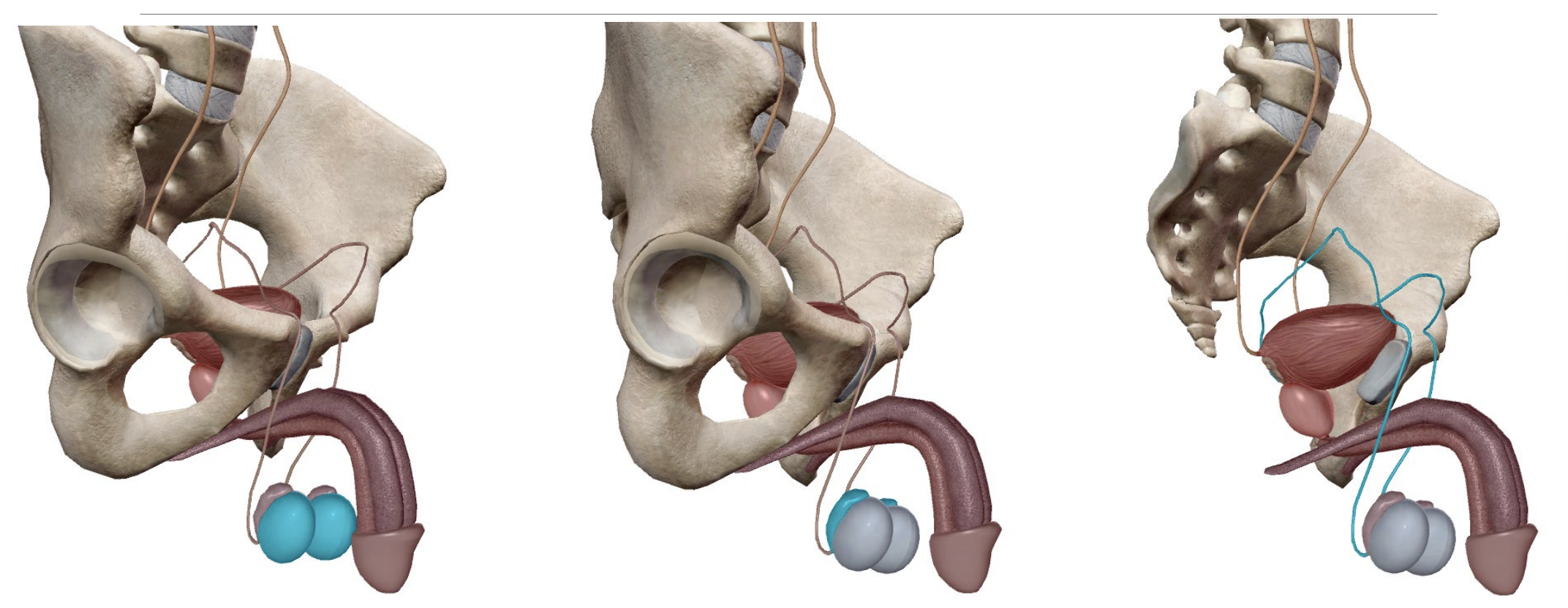
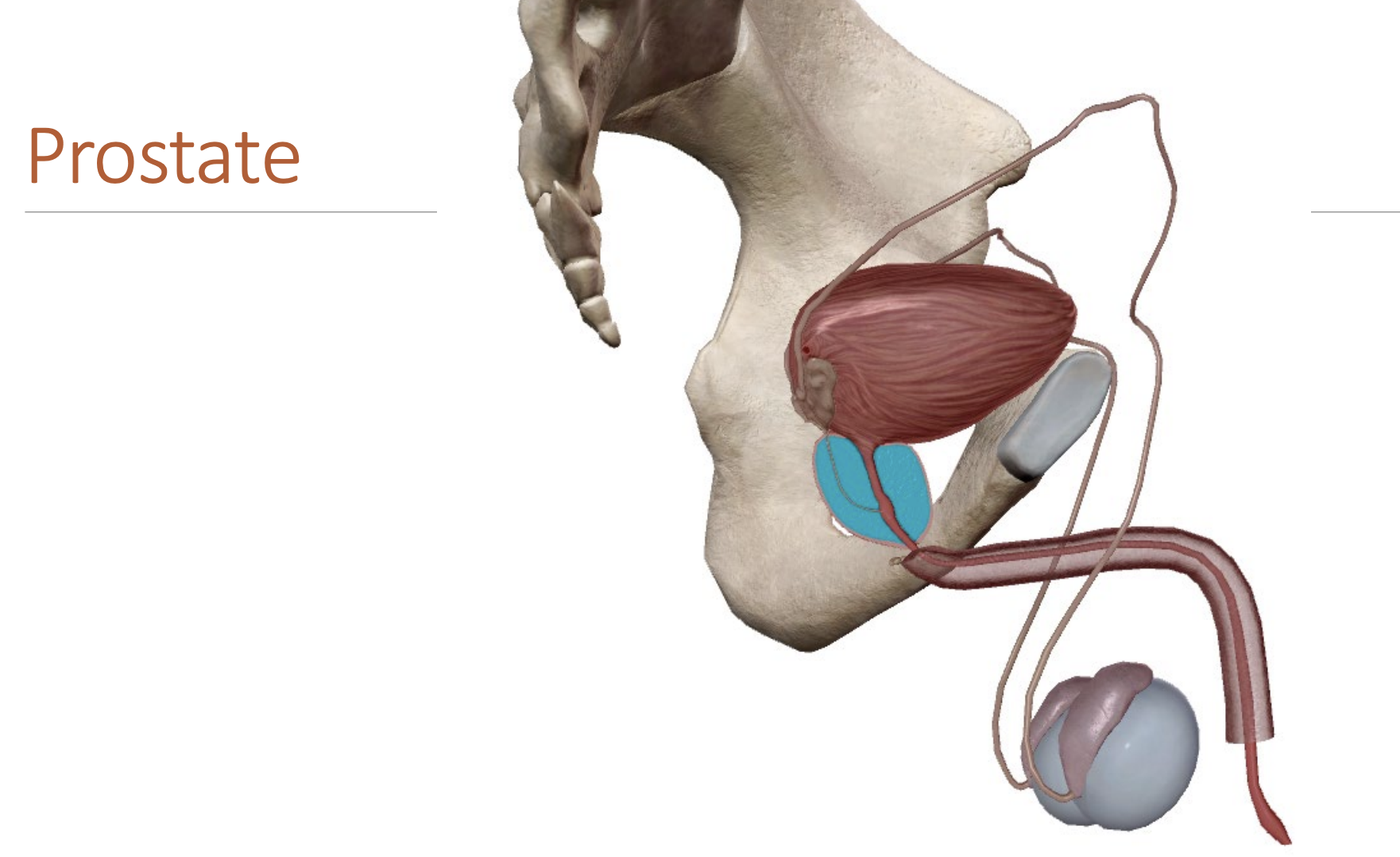
Ductus deferens/vas deferens:
Tubes through with mature sperm travel to reach the penis.
Runs posterior to the bladder, entering the urethra via the prostate.
Reproductive system
Scrotum/Labia majora
Spongy urethra/Labia minora
Foreskin/Prepuce
Body of penis/Body of clitoris
Glans of penis/Glans of clitoris
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian tubes/ductus deferens or vas deferens
Ovaries/testicles & epididymis
Ovaries:
Contains the lifetime supply of ova.
Testicles:
Contains the lifetime supply of sperm.
Immature sperm matures within the epididymis