Florida Science SSA Review
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SSA review made for concepts that I am lacking in ...
Last updated 2:42 AM on 5/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
Scientific Theory
A well-supported explanation that has been repeatedly tested and confirmed through experimentation and observation.
2
New cards
Scientific Law
Unlike theories, laws do not explain why a phenomenon occurs, but rather describe what occurs. Examples of scientific laws include the laws of thermodynamics, Newton's laws of motion, and the law of conservation of energy.
3
New cards
What are the 3 Principals of Cell Theory?
Cells are the basic unit of life
Every living thing is made up of cells
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
Every living thing is made up of cells
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
4
New cards
Levels of Organization from a cell → organism
Cell → Tissues → Organ → Organ Systems → Organism
5
New cards
List the features specific to plant cells
Cell wall provides extra support, surrounds the cell.
Chloroplast helps the plant conduct photosynthesis and gives the plant its color
Boxy in shape
One large vacuole for storage
\
Chloroplast helps the plant conduct photosynthesis and gives the plant its color
Boxy in shape
One large vacuole for storage
\
6
New cards
List the features specific to animal cells
Irregular shape
Multiple small vacuoles for storage.
Multiple small vacuoles for storage.
7
New cards
Describe homeostasis and what would happen without it
\
\
Homeostasis helps keep organisms stable and keeps cells maintained.
Homeostasis helps regulate body temperature.
Without homeostasis chemical reactions occurring withing the cell will slow down and stop.
Homeostasis helps regulate body temperature.
Without homeostasis chemical reactions occurring withing the cell will slow down and stop.
8
New cards
Scientific Method
Flashcard for Scientific Method:
Scientists ask questions, gather information, make a hypothesis (what they think the outcome could be), conduct experiments, and finally observe and record the results.
Scientists ask questions, gather information, make a hypothesis (what they think the outcome could be), conduct experiments, and finally observe and record the results.
9
New cards
Weathering
Provide instances of both chemical and physical weathering.
Provide instances of both chemical and physical weathering.
The breakdown of rocks and minerals due to wind, water, and temperature. EX: Chemical weathering, acid rain carving rock. Physical weathering, rocks breaking due to ice wedging.
10
New cards
Erosion
The gradual wearing away and moving of sediment by natural forces such as wind, water, and ice.
11
New cards
Compositional layers of Earth
How are they determined?
How are they determined?
The compositional layers of the Earth are the crust, mantle, and core.
These layers are determined by their chemical properties (their materials and elements)
These layers are determined by their chemical properties (their materials and elements)
12
New cards
Mechanical layers of Earth
How are they determined?
How are they determined?
The mechanical layers of the Earth are the lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, and the inner and outer core.
These layers are determined by their physical properties. (How they behave due to pressure and heat.)
These layers are determined by their physical properties. (How they behave due to pressure and heat.)
13
New cards
Convergent boundary → ←
A convergent boundary is a type of tectonic plate boundary where two plates move towards each other, resulting in the collision or subduction of one plate beneath the other. This can lead to the formation of mountain ranges, volcanic activity, subduction zones, earthquakes, and trenches.
\
\
14
New cards
Divergent Boundary ←→
A divergent boundary is a type of tectonic plate boundary where two plates move away from each other. This can result in the formation of rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges.
\
\
15
New cards
Transform Boundary _-
\
A type of tectonic boundary where two plates slide past each other horizontally. It causes earthquakes and can form features such as fault lines and valleys.
A type of tectonic boundary where two plates slide past each other horizontally. It causes earthquakes and can form features such as fault lines and valleys.
16
New cards
Oceanic and Continental Plates
Continental plates are thicker than oceanic plates.
Oceanic plates are dense so they subduct under continental plates. This usually results in a trench.
Oceanic plates are dense so they subduct under continental plates. This usually results in a trench.
17
New cards
Unconformities
Inclusions are younger than the rocks they cut across.
18
New cards
Mitosis
Aesexual Reproduction
Produces body cells
Identical
1 cell division
Produces body cells
Identical
1 cell division
19
New cards
Meiosis
Sexual Reproduction
23 chromosomes from each parent
Produces gametes one sperm and one egg cell.
2 cell divisions
23 chromosomes from each parent
Produces gametes one sperm and one egg cell.
2 cell divisions
20
New cards
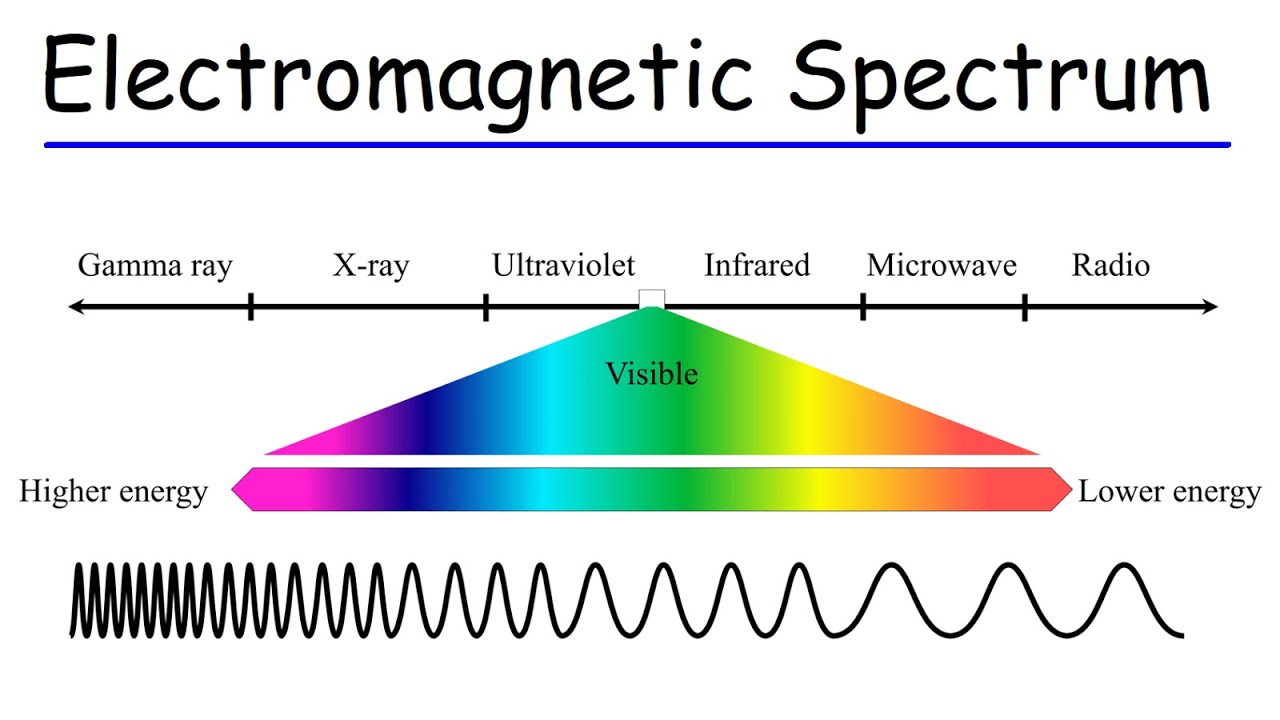
Electromagnetic spectrum
Radio waves have the lowest frequency, longest wavelength, and the lowest energy.
Ultra-violet waves have the highest frequency, shortest wavelength, and the highest energy.
Ultra-violet waves have the highest frequency, shortest wavelength, and the highest energy.
21
New cards
Properties of protons, neutrons and electrons.
PROTON- Middle mass, positive charge and located in the nucleus
NEUTRON- Most mass, neutral/no charge and located in the nucleus
ELECTRON- Least mass, negative charge, and located around the nucleus.
*You can find the amount of neutrons by subtracting the atomic number from the mass.*
\
NEUTRON- Most mass, neutral/no charge and located in the nucleus
ELECTRON- Least mass, negative charge, and located around the nucleus.
*You can find the amount of neutrons by subtracting the atomic number from the mass.*
\
22
New cards
Mnemonic device for the planets behind the Sun
My very educated mother just served us noodles !!!!!
23
New cards
Recite Newtons laws
1. An object at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force ( something will not move until a force such as gravity or friction causes it to move)
2. Force is equal to the mass multiplied by the acceleration ( heavier objects will require more force for higher acceleration)
3. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction ( think tug of war)