ib chem 15/16 common questions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
would confirmation of the rate expression prove its correct
no because diff mechanisms can have the same rate expression
state the meaning of Ea
minimum energy that colliding molecules need to have to successfuly collide, leading to reactions
why does increase in temp increase rate of reaction (3)
more frequent collisions per unit time
increase kinetic energy
greater proportion of molecules have energy greater than or equal to activation
why does increasing particle size of solid reactant decrease rate
less surface area, $ of collisions decrease
2 situations where rate = constant
zero order
every conc is 1 mol
describe collision theory (2)
particles must collide at ccorrect orientation
particles must have sufficient energy to be greater or equal to Ea
how and why does rate change with time (3)
conc of rxts per unit volume decrease, making collision less frequent = decrease reaction rate
in some cases, increasing conc of reactant doesnt increase rate. how may this occur
reactant is not involved in the rate-determining step
how can the Ea be determined (3) graph
determine the rxn rate at a range of temperatures
calulate k for each temperature
graph ln k with 1/t
in another experiment something was added while all conc remained unchanged. why did color change occur faster and how to confirm hypothesis (2)
more rapid = catalyst is the thing
see if the thing comes out at the end of the reaction
define activation energy Ea
minimum energy requried for reactants to successfully collide/react/transitionstate
on the graph sketch line you would expect if catalyst is added (arrhenius graph)
any line is ok as long as line is less steep
how to determine the order of experiment
do many experiments at same temperature but diff concs of reactant, plot conc/time graph and calculate initial slope of eachcurve at the start and then deduce relationship between rate and conc
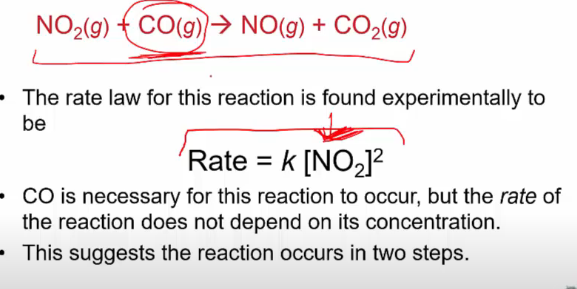
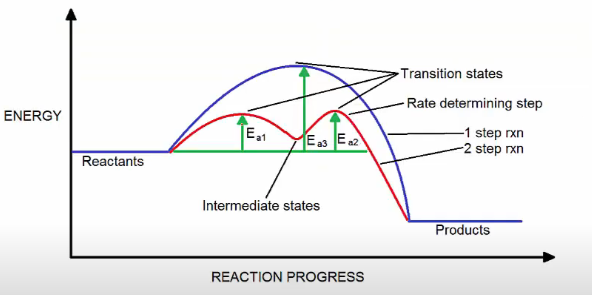
intermediate vs transition state graph
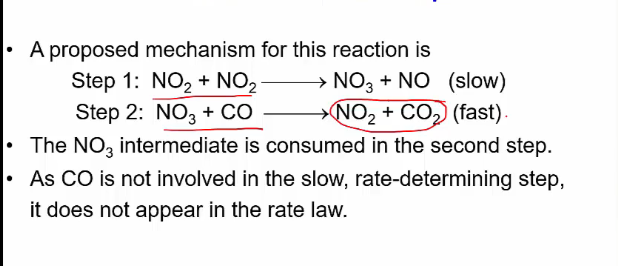
guessing RDS steps
determine possible mechanism and see which one fits the rate equation
eg. a + b + c = abc, rate = k [a][b]
try: a + b = ab, then ab + c = abc
or try a + c = ac then ac + b = abc etc…
the first one is more likely with the first reaction as the RDS