Lecture 15- Early Hindu Architecture
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
The Rise of Hinduism
Around the time of the Gupta Empire: Buddhism merges with pre- Buddhist religious traditions to create Hinduism. Traditional Vedic practices get modernized and written down
Compare/ Contrast: Vedism vs. Hinduism
Main Focus: Vedism focused on primal ELEMENTS: fire, water, air, earth. Hinduism focused on primal DIETIES: creator, destroyer, preserver.
Texts: Vedism had a series of anonymous authorless texts collected over a period of time, Hinduism has epic texts.
Gupta Dynasty
maintained an empire over northern and parts of central and western India from the early 4th to the late 6th century CE
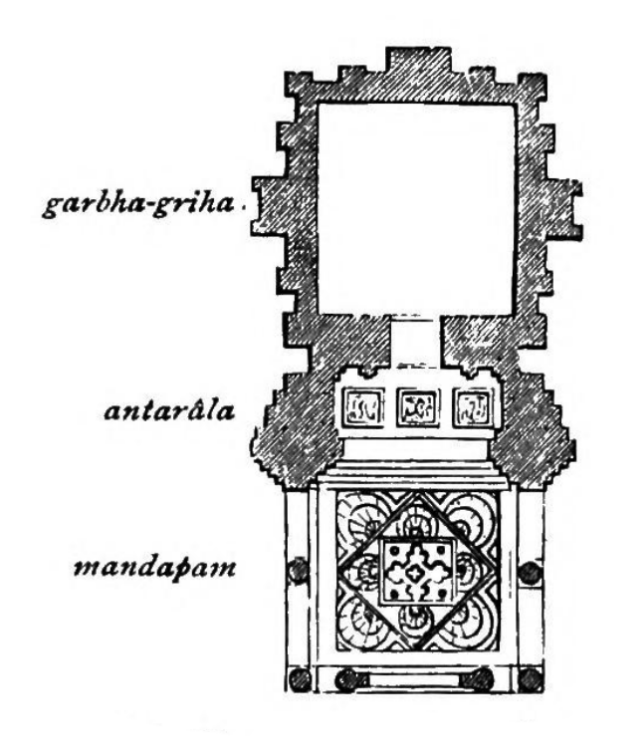
garbhagriha
A small sanctuary housing the main image or emblem of the temple deity (literally womb chamber)
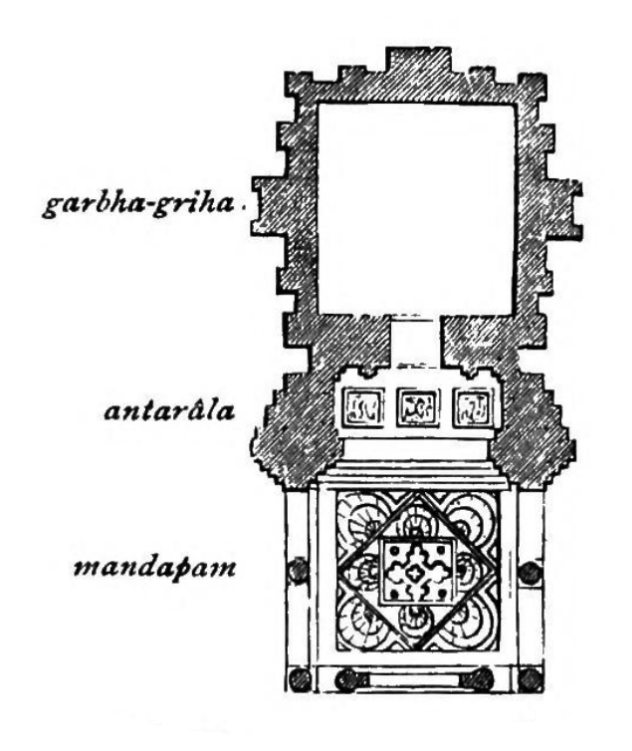
mandapa
A pillared hall in front of the temple and sometimes connected to it; if a temple has more than one mandapa, each is allocated a different function and given a name to reflect its use
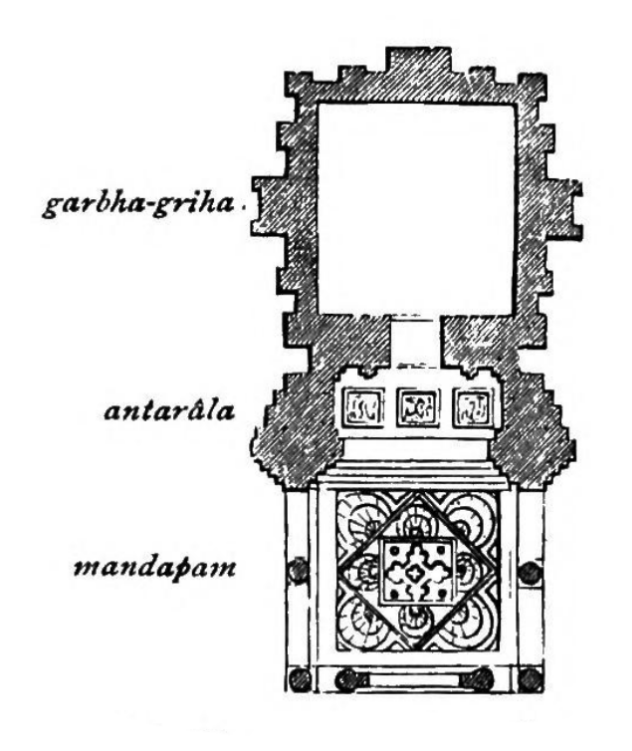
antalara
An open or closed vestibule connecting the garbha-griha to one or more adjoining pillared mandapas
mandala
A type of sacred, and often complex, symbolic diagram, used, especially in Tantric ritual, as an aid to visualization and a way of manifesting the deity, or group of deities, represented at its centre. The mandala itself is thought to be a twodimensional representation of the cosmos, and as such can contain potentially anything
shikhara
A superstructure, tower, or spire above the garbha-griha
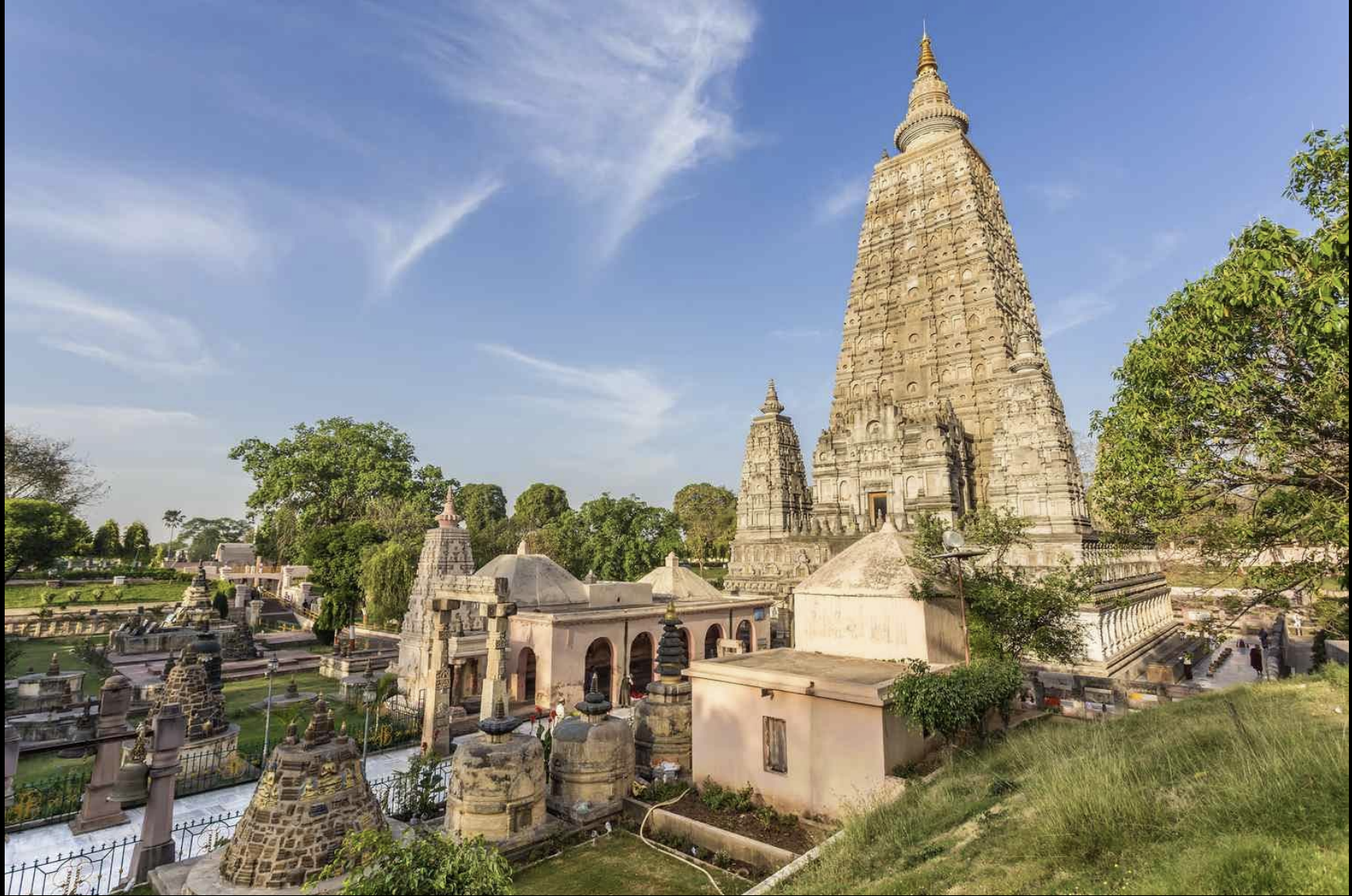

Site/ Location/ Built
Site: Mahabodhi Temple
Location: Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India
Built: ca. 5th to 6th century CE
Compare: Bhitargaon vs. Mahabodhi Temple
Compare: Buddhist vs. Hindu Cave Temples
both used rock cut architecture
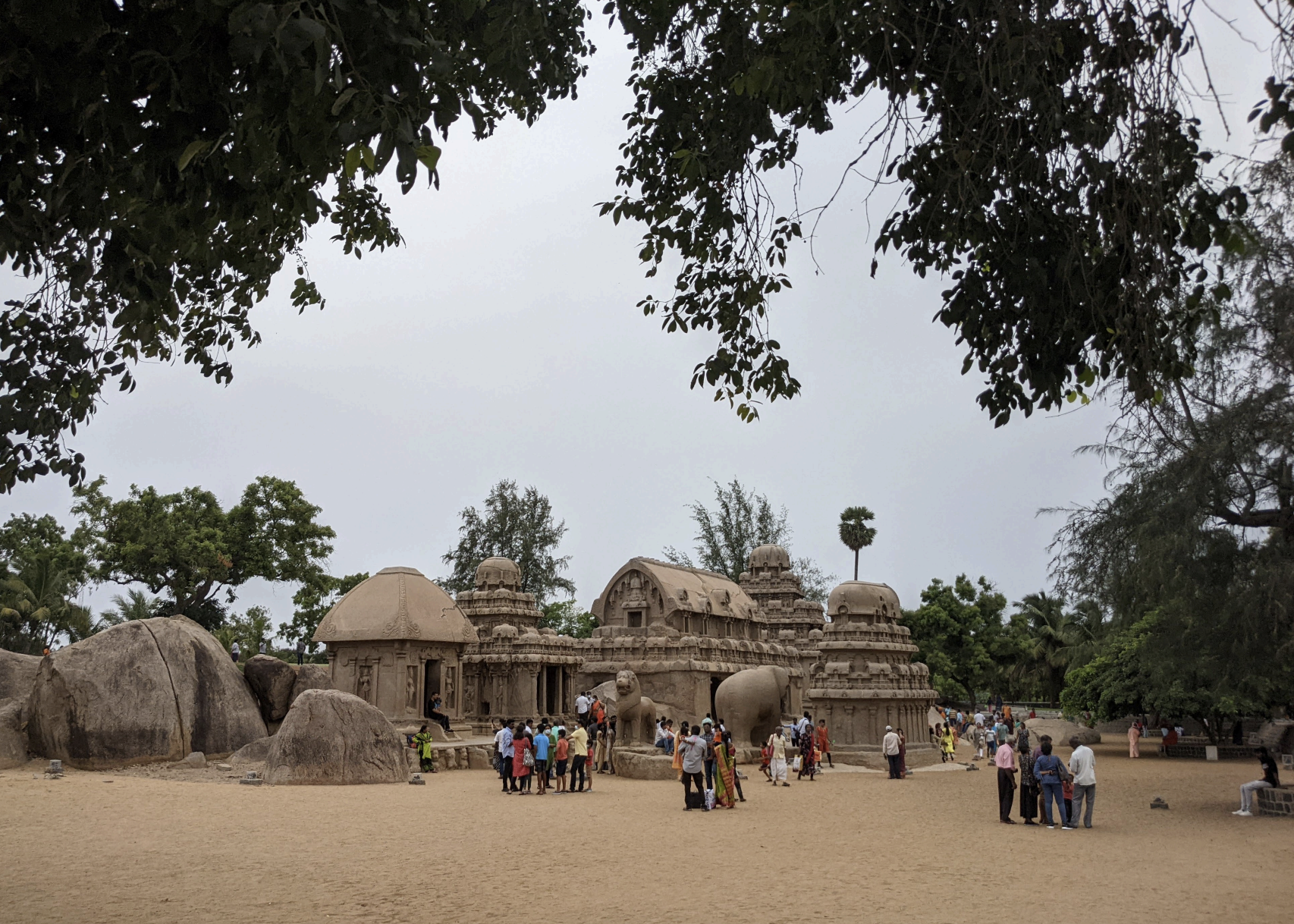

Site/ Location/ Built
Site: Five Rathas (Pancha Rathas)
Location: Mahabalipuram (Mamallapuram), Tamil Nadu, India
Built: ca. 650–700 CE
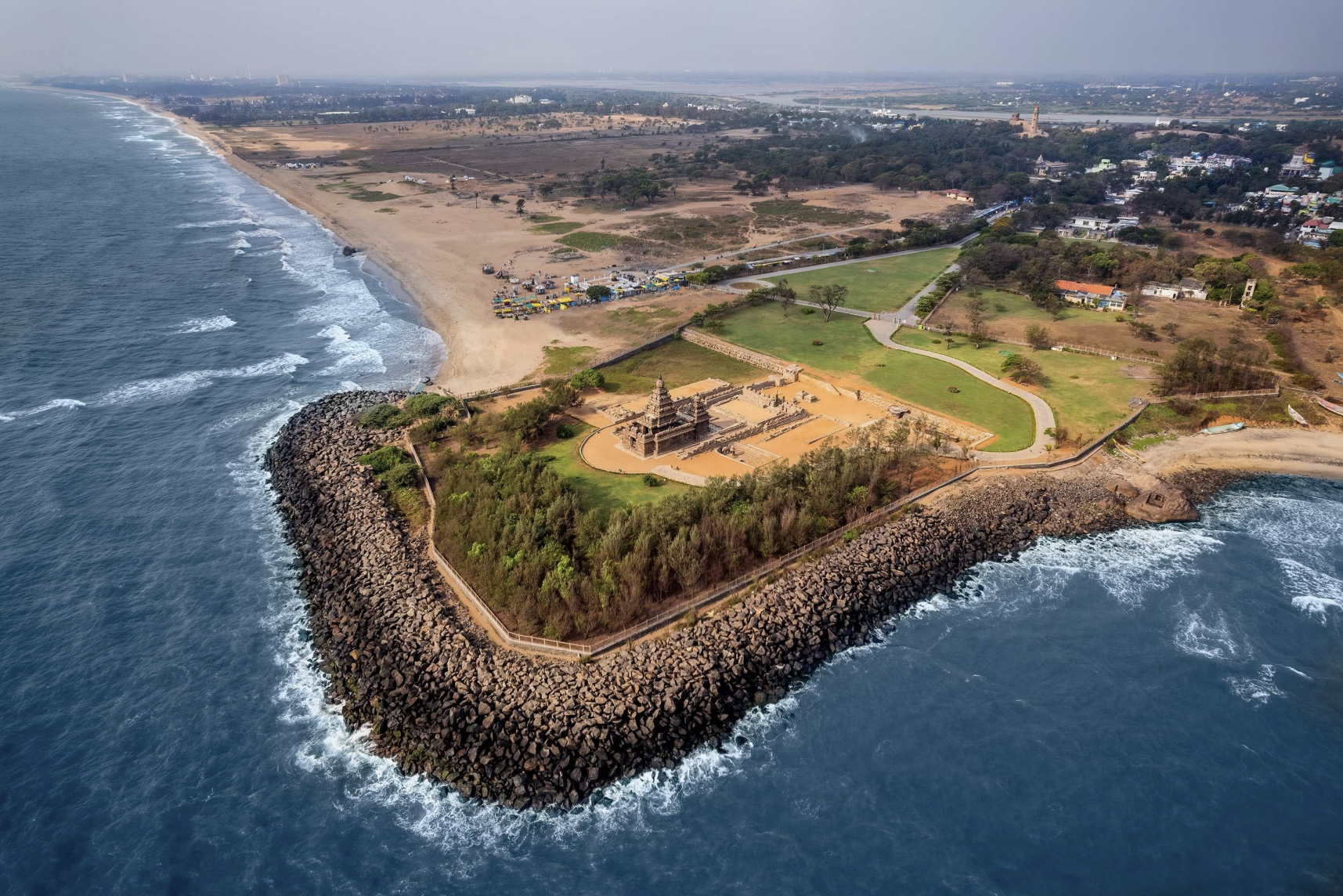

Site/ Location/ Built
site: Shore Temple
Location: Mahabalipuram (Mamallapuram), Tamil Nadu, India
Built: ca. 700–728 CE
lingam
Literally, ‘phallus,’ but also ‘mark’ or ‘sign’; the symbol for Shiva
yoni
The symbol of the goddess Shakti, the feminine generative power and, as a goddess, the consort of Shiva
gopura
Tall ornate gateway to a Hindu templeenclosure
Compare: Christian Church vs. Hindu Temple
…
Compare: Kailasanathar vs. Virupaksha Temple
…
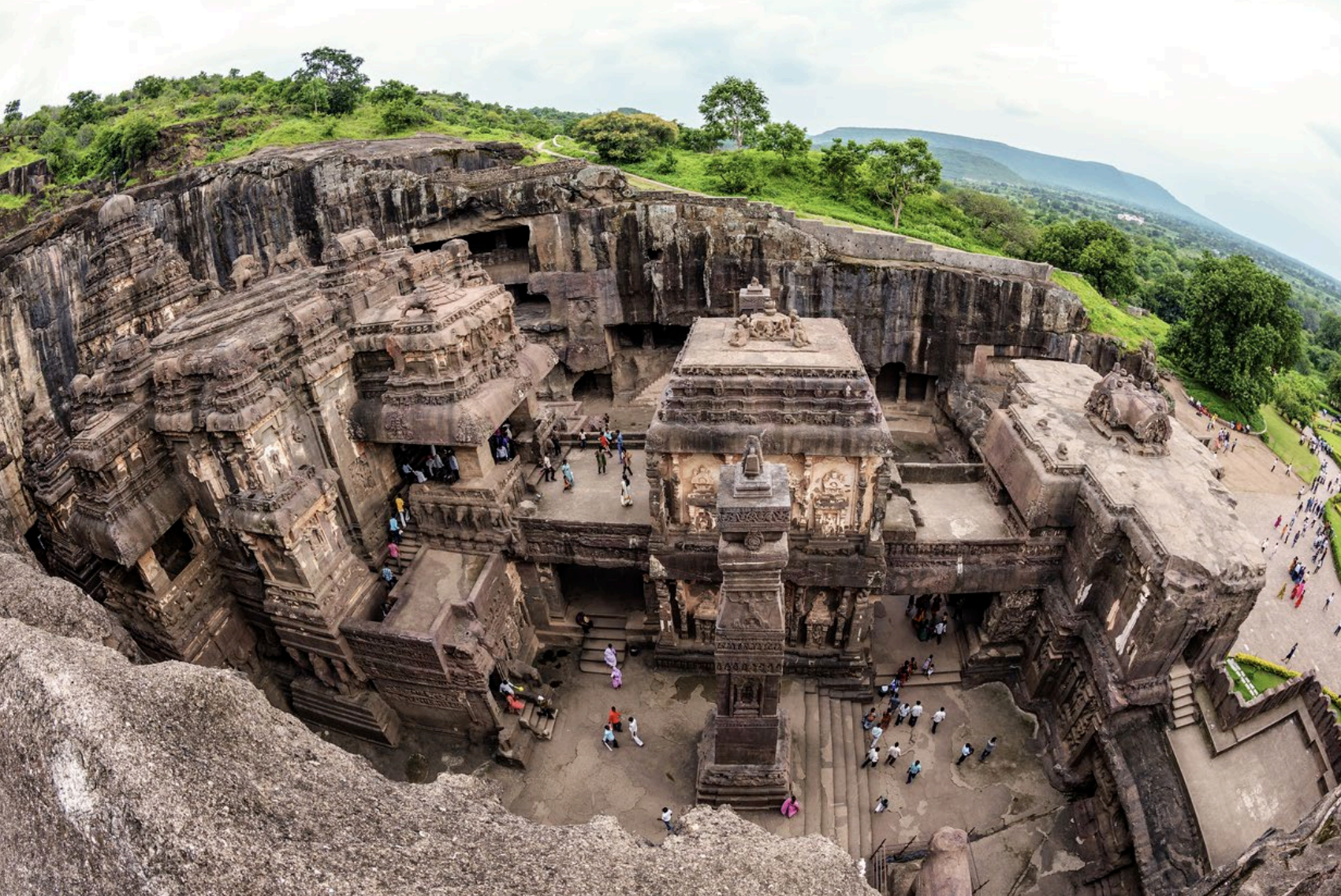

Site/ Location/ Built
Site: Kailasa (Kailasnath) Temple at Ellora
Location: Maharashtra, India
Built: ca. 750–800 CE