Biochemistry I Lesson 10: Evolution
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Which of the following organelles house DNA?
I. Nucleus
II. Mitochondria
III. Chloroplasts
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) i and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
The nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts all house DNA in healthy cells.
True or False? Virtually all of the mitochondria in gametes are carried in the sperm, so the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) will almost identically match the father's mtDNA.
False. Virtually all of the mitochondria in gametes is carried in the EGG, so the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) will almost identically match the MOTHER'S mtDNA. This is called Maternal Inheritance.
Which of the following principles was NOT part of Darwin's original theory of evolution by natural selection?
(A) Evolution is a gradual process that occurs over long periods of time.
(B) Variation occurs among individuals in a population.
(C) Mutations are the ultimate source of genetic variation.
(D) Individuals that possess the most favorable variations have the best chance of reproducing.
(C) Mutations are the ultimate source of genetic variation.
This was not part of Darwin's original theory of evolution.
CRB True or false? Another part of Darwin's original theory claims that those individuals with variations more suited for their environment will have more offspring, increasing these favorable traits' frequencies in future generations.
True. Another part of Darwin's original theory claims that those individuals with variations more suited for their environment will have more offspring, increasing these favorable traits' frequencies in future generations.
Explain how the 4 O'Clock tree could have white, green and varicated (speckled) leaves on different branches of the same plant.
Because the colors are due to chloroplast mutations, and chloroplast DNA is not divided evenly in cell division, an egg that had varicated leaves could unevenly divide the two types of chloroplasts early in embryogenesis. Then, different parts of the embryo/future plant will have varying colored leaves based on which embryonic cells they came from.
CRB Which of the following statements describing Evolution theories are true?
I. Darwin formulated his theories before Genetic Inheritance was widely accepted.
II. Neo-Darwinism incorporates Genetics to Darwin's theories, including Mutations being the ultimate source of variation.
III. Differential Reproduction was disproven, because some traits are advantageous and won't increase their frequency in future generations.
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
Each of the following statements are true:
I. Darwin formulated his theories before Genetic Inheritance was widely accepted.
II. Neo-Darwinism incorporates Genetics to Darwin's theories, including Mutations being the ultimate source of variation.
CRB Define Differential Reproduction. Does it relate more to Darwinism or Neo-Darwinism?
The term Differential Reproduction describes Mutations or Recombinations that lead to advantageous phenotypes (typically meant as increasing reproductive success) are more likely to be passed on to future generations.
Since this term accounts for genetics, it is more closely related to Neo-Darwinism.
Which of the following explanations best describes the endosymbiotic theory regarding mitochondria and chloroplasts?
(A) Mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent organelles, but environmental factors made them join archaea.
(B) Mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent prokaryotes, but ended up joining the ancestral eukaryotic cell
(C) Mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent prokaryotes, but over time they joined many eukaryotic and plant cells independently.
(D) Mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent organelles, but prokaryotes do not have organelles so they no longer produce these in their cellular division.
(B) Mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent prokaryotes, but ended up joining the ancestral eukaryotic cell.
True or False? The more closely related two different organisms are, the more recently they shared a common ancestor.
True. The more closely related two different organisms are, the more recently they shared a common ancestor.
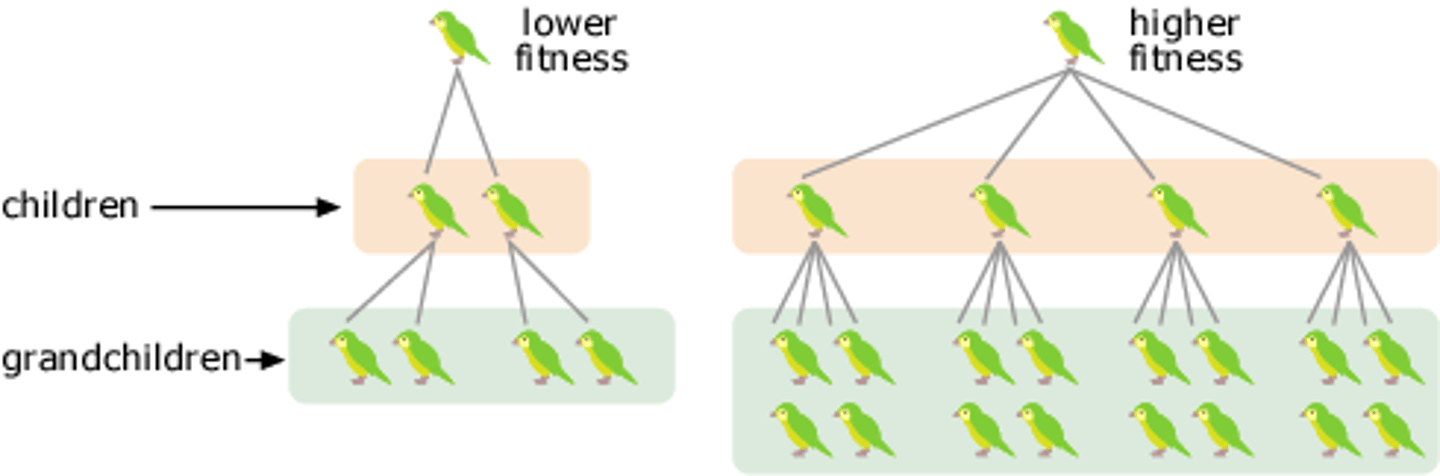
An organism's relative fitness is measured by fecundity. What does this mean?
An organism's relative fitness is measured by fecundity, which is basically the ability of one to survive and reproduce offspring. In other words, fitness is measured by the contribution to the gene pool of the next generation.

Which of the following trait types are subject to natural selection?
I. Heritable Traits
II. Acquired Traits
III. Fecundity
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(C) I and III only
Natural selection can only select for heritable traits, which contribute to the individual's fecundity.
What does fitness mean in terms of evolution and population dynamics?
Fitness refers to an organism's total ability to pass on traits to offspring.
Which of the following are driving forces of evolution other than natural selection?
I. Group selection
II. Artificial selection
III. Genetic drift
(A) III Only
(B) II and III Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
The driving forces of evolution other than natural selection are group selection, artificial selection, and genetic drift.
CRB Which of the following are other modes of Natural Selection?
I. Sexual Selection, where mates are chosen for certain traits/phenotypes, which will be more likely to be seen in future generations.
II. Kin selection, where one animal will sacrifice itself to save its genetically-similar family members or pack.
III. Visual Selection, where only the most physically appealing specimens will reproduce and have their traits seen in future generations.
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
Each of the following are modes of Natural Selection:
I. Sexual Selection, where mates are chosen for certain traits/phenotypes, which will be more likely to be seen in future generations.
II. Kin selection, where one animal will sacrifice itself to save its genetically-similar family members or pack.
How does artificial selection produce rapid changes in the phenotype of organisms?
Artificial selection produces rapid changes in the phenotype of organisms by changing the frequency of alleles and selecting for new combinations of traits.
What is the difference between natural selection vs group selection vs artificial selection?
Natural selection is favoring some individual organisms over others, and leading to the evolution of traits that benefit individuals themselves.
Group selection is the idea that genetic traits that benefit the population as a whole will be selected even if it does not increase the fitness of the individual with the trait.
Artificial selection is a result of the whim of man, thus we may prefer to choose a characteristic which would have never been selected by nature.
A grandmother helps her grandchildren learn important life skills. Which type of selection would account for this?
(A) Natural Selection
(B) Group Selection
(C) Artificial Selection
(D) Inclusive Fitness
(B) Group Selection
While natural selection accounts for traits that help survival until reproduction, group selection accounts for traits that help survival even after reproduction is impossible (like the grandmother here)
The studies of changes between black and light color in populations of the Peppered moth show which of the following:
(A) Natural selection can quickly change allele frequencies and common phenotypes in a population
(B) Species can always adapt to environmental changes
(C) Predators prefer light colored moths
(D) Dark colored moths are physiologically superior to light colored moths
(A) Natural selection can quickly change allele frequencies and common phenotypes in a population.
The studies of changes between black and light color in populations of the moth show that natural selection can quickly change allele frequencies and common phenotypes in a population.
CRB True or false? The new ash-covered forests served as a Niche that the black Peppered moths was especially well adapted for.
True. The new ash-covered forests served as a Niche that the black Peppered moths was especially well adapted for.
CRB Imagine that a picture book was written about these Peppered moths, but to make it more colorful and entertaining, they made six different colors of ash, and as many colors of Peppered moths. These moths all found their niches and eventually became reproductively isolated, and over time became their own species. Which term would best describe this increase in species from a common ancestor?
(A) Polymorphisms
(B) Adaptive Radiation
(C) Evolutionary Expansion
(D) Adaptive Advantage
(B) Adaptive Radiation
Adaptive Radiation is when there is a rapid rise in the number of species from a common ancestor, as happened in this scenario.
CRB There are a few different common modes of Natural Selection. Draw out the graphs (of # of individuals vs phenotype) for each of the following:
- Stabilizing Selection
- Directional Selection
- Disruptive Selection
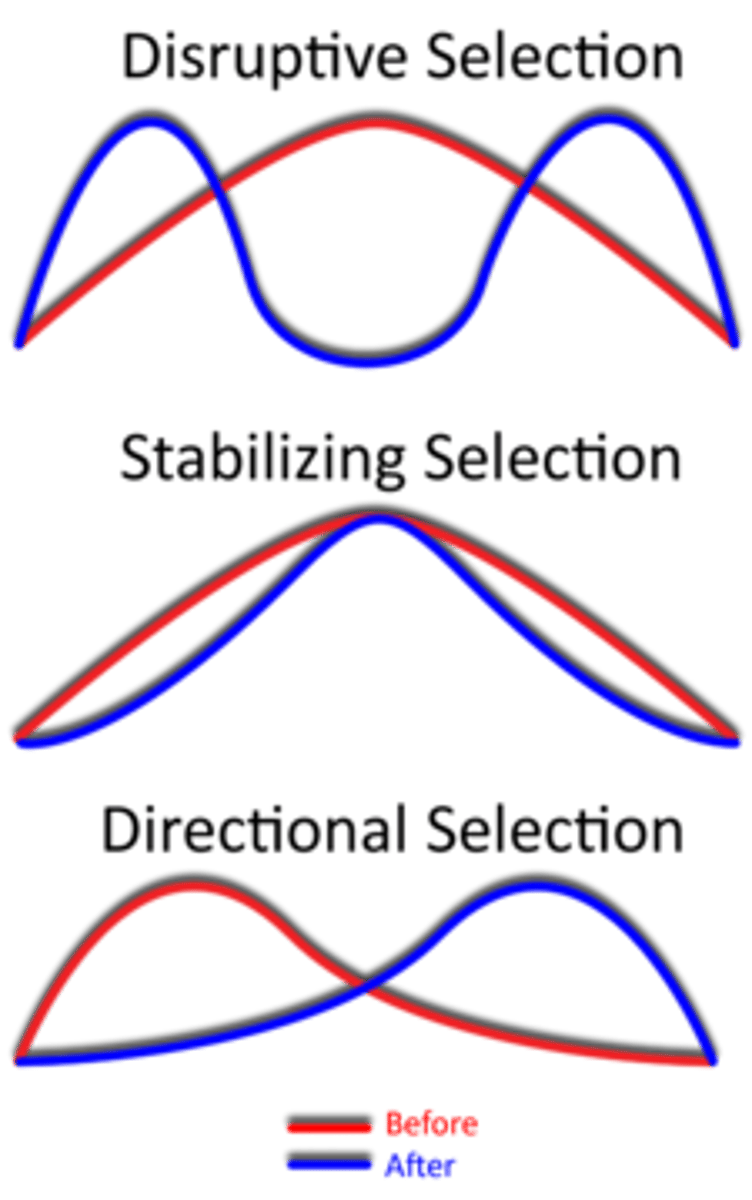
CRB Imagine that there was a species of dinosaur that varied from 4 to 10 feet tall. They had one arch-nemesis, a predator that had limited vision and neck mobility, so that they could only see the dinosaurs over 7 feet tall. Which mode of Natural Selection would expect the prey species to undergo?
(A) Stabilizing Selection
(B) Directional Selection
(C) Disruptive Selection
(D) Not enough information
(B) Directional Selection
This scenario clearly makes the shorter dinosaurs more fit for their environment, and future generations are more likely to be short. This movement in one extreme direction is best described by Directional Selection.
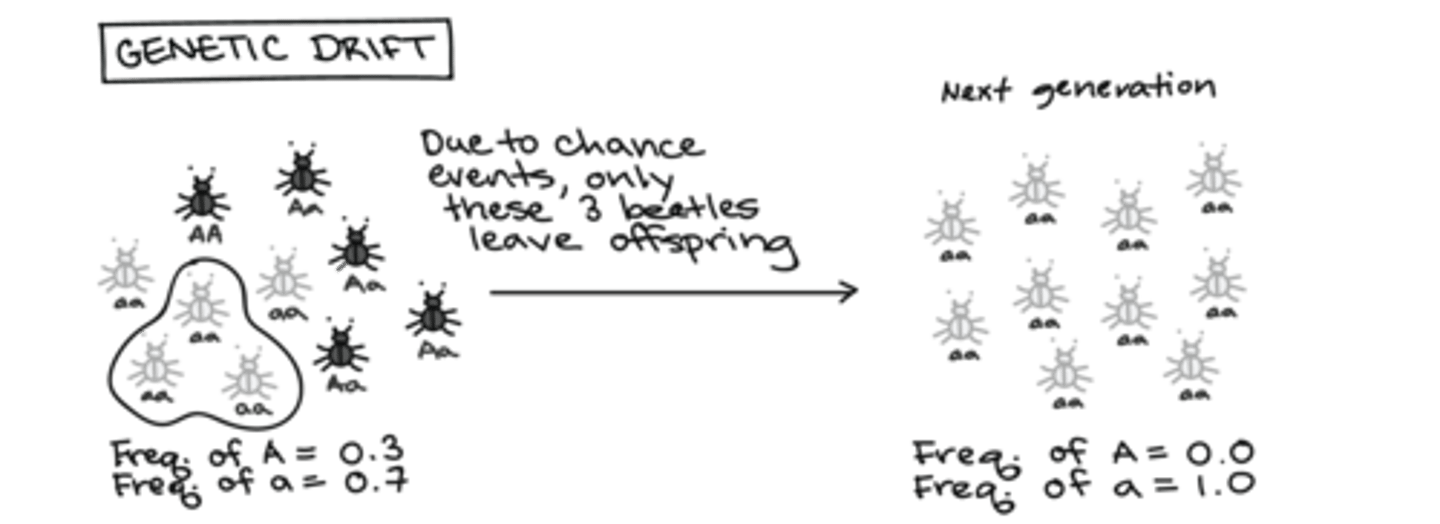
What is genetic drift?
Genetic drift is the variation in the frequency of different genotypes in a small population due to chance events.
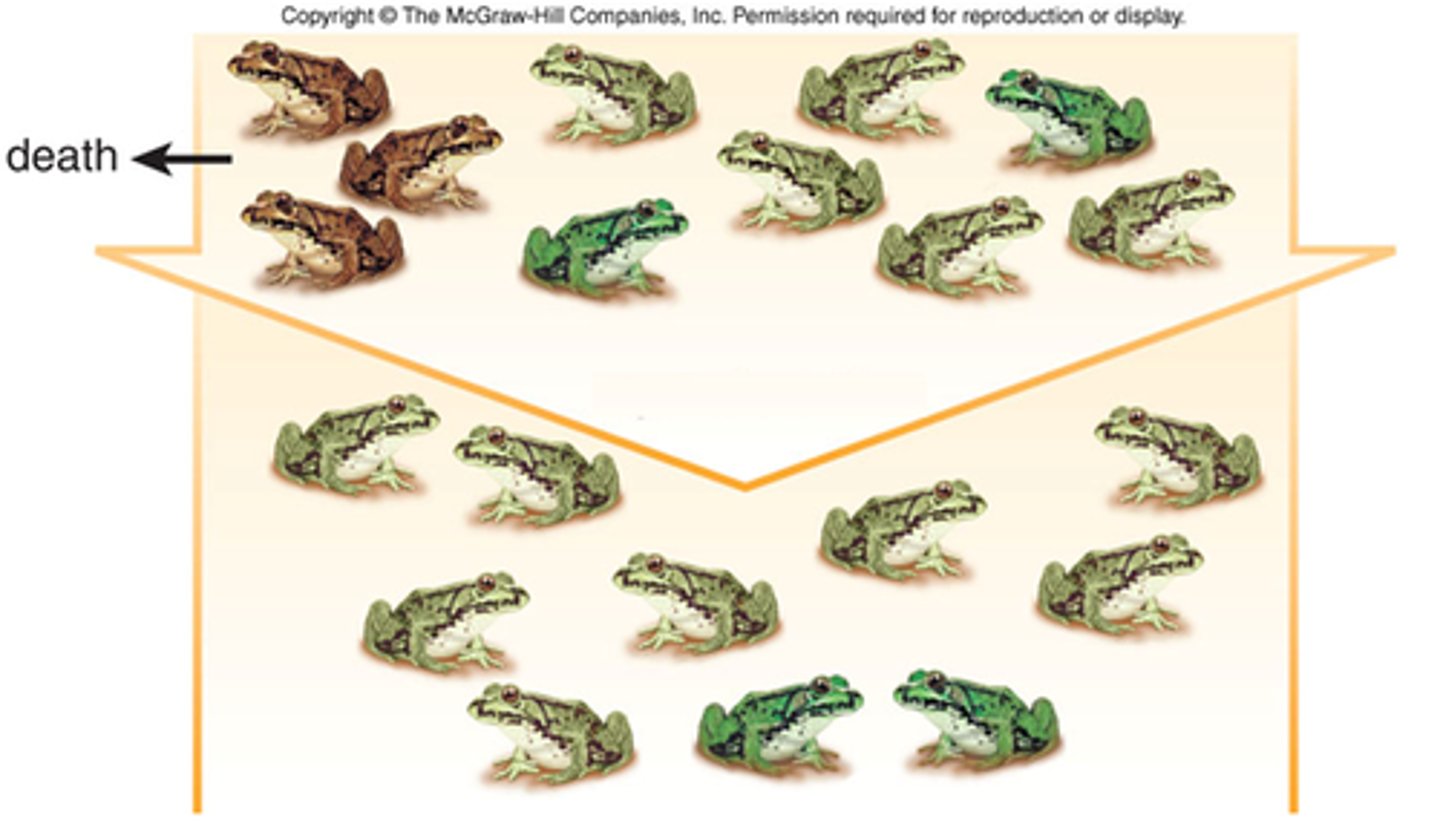
What are the two types of genetic drift that can cause extreme reductions of diversity in a population?
(A) Bottleneck effect and the founder effect
(B) Bottleneck effect and the gene flow
(C) Genetic isolation and the founder effect
(D) Genetic isolation and the gene flow
(A) Bottleneck effect and the founder effect
Bottleneck effect and the founder effect are two types of genetic drift that can cause extreme reductions in diversity in a population.
Genetic drift will increase or decrease genetic diversity in dynamic population?
Genetic drift decreases genetic diversity
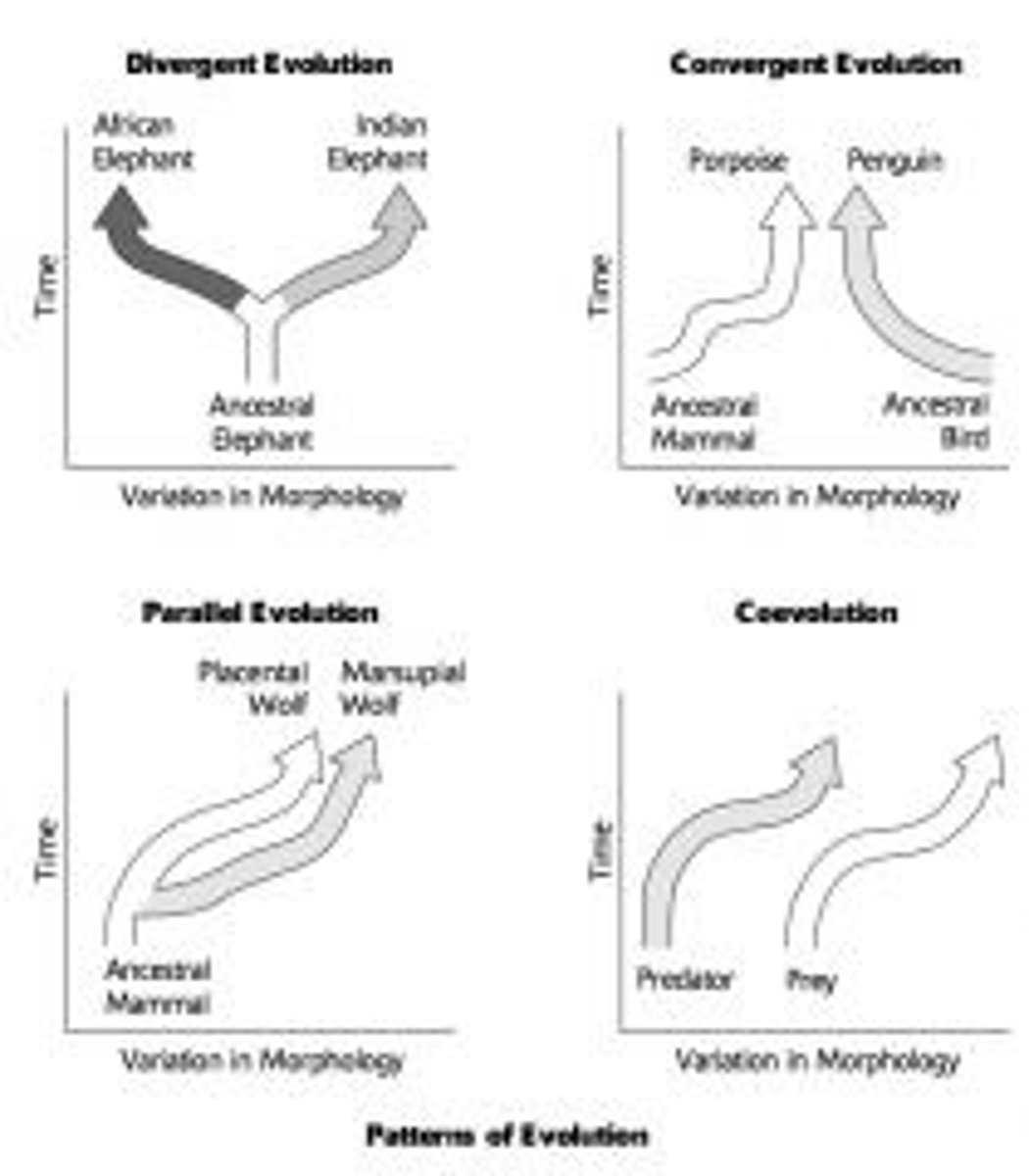
CRB There are different patterns of evolution when comparing species. Compare Divergent, Parallel and Convergent Evolution.
Divergent Evolution is when species develop dissimilar characteristics.
Parallel evolution is when related species evolve similarly over a long period of time, and is usually related to facing similar environmental pressures.
Convergent evolution is when multiple species develop similar characteristics, even if they did not have a common ancestor with these characteristics.
CRB Imagine that aliens were found on another planet filled with water, and their life forms looked a whole lot like Earth's fish. Which type of evolution would this most be like?
(A) Divergent Evolution
(B) Parallel Evolution
(C) Convergent Evolution
(D) I will go read about the 3 main patterns of evolution and come back!
(C) Convergent Evolution
There is no reason to assume that these aliens and Earth's fish are related, so the fact that they have evolved similar characteristics should be chalked up to Convergent Evolution.
Gene flow will increase or decrease genetic diversity in dynamic population?
Gene flow will increase genetic diversity in a population
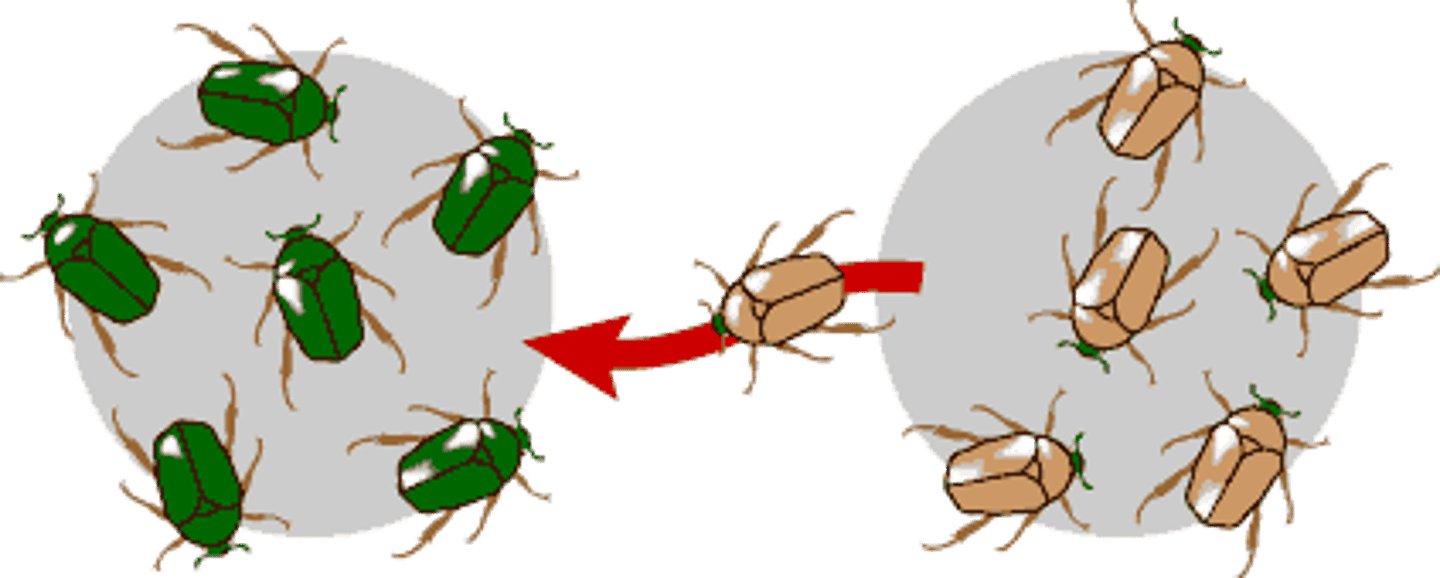
Genetic drift is increased by all of the following EXCEPT:
(A) Small population size
(B) Bottleneck effects when the population size is greatly reduced then recovers
(C) Founder effects when a small number of individuals are isolated and reproduce to form a new sub-population
(D) Movement of individuals from one isolated population to another
(D) Movement of individuals from one isolated population to another
Genetic drift is increased by all the following except the movement of individuals from one isolated population to another.
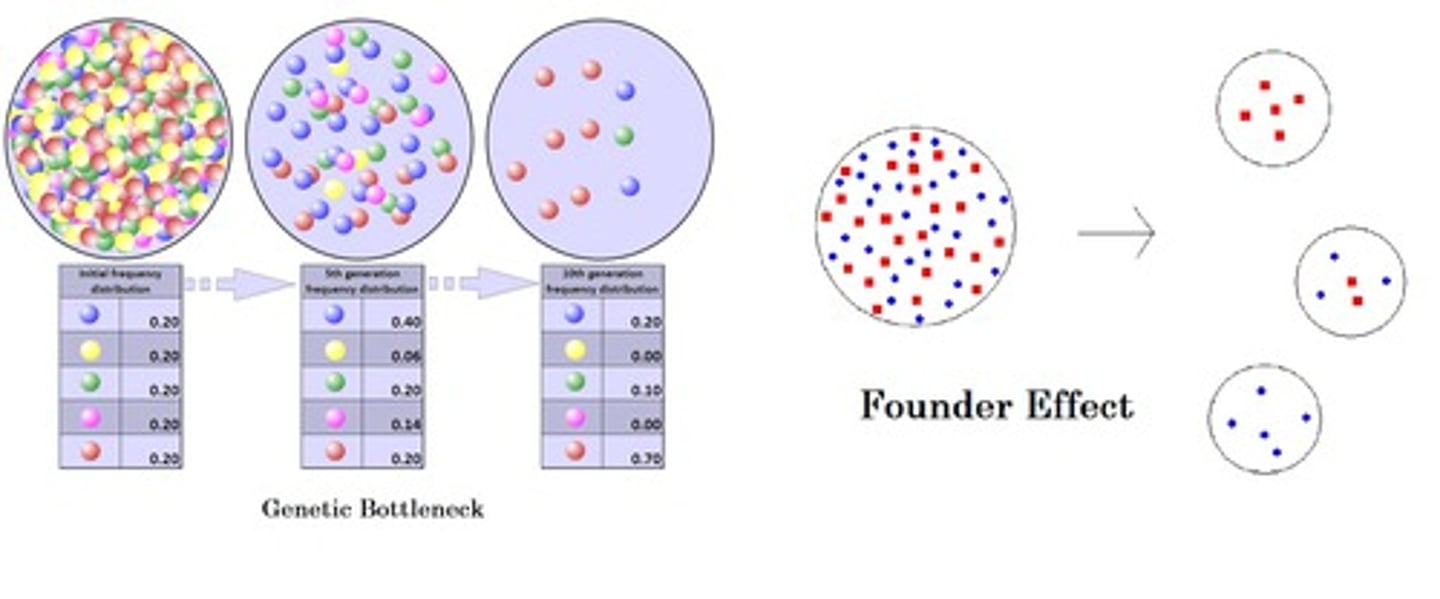
What is the difference between bottleneck effect and the founder effect?
The bottleneck effect is the reduction of the population size due to a natural disaster thus leading to a new genetic variation in a population.
The founder effect is the loss of genetic variation when a new colony is established by a very small number of individuals away from a larger population.
The seal population was reduced by overhunting to 20 individuals in the 1890s. Although the population had rebounded to over 30, 000 individuals by 1974, only 24 were found to be homozygous recessive by genetic testing. What is this an example of?
(A) Founder Effect
(B) Genetic Drift
(C) Gene Flow
(D) Bottleneck Effect
(D) Bottleneck Effect
This is an example of the bottleneck effect because there was an external factor (hunting) leading to a smaller population size of seals thus leading to a change in frequency of genotypes.
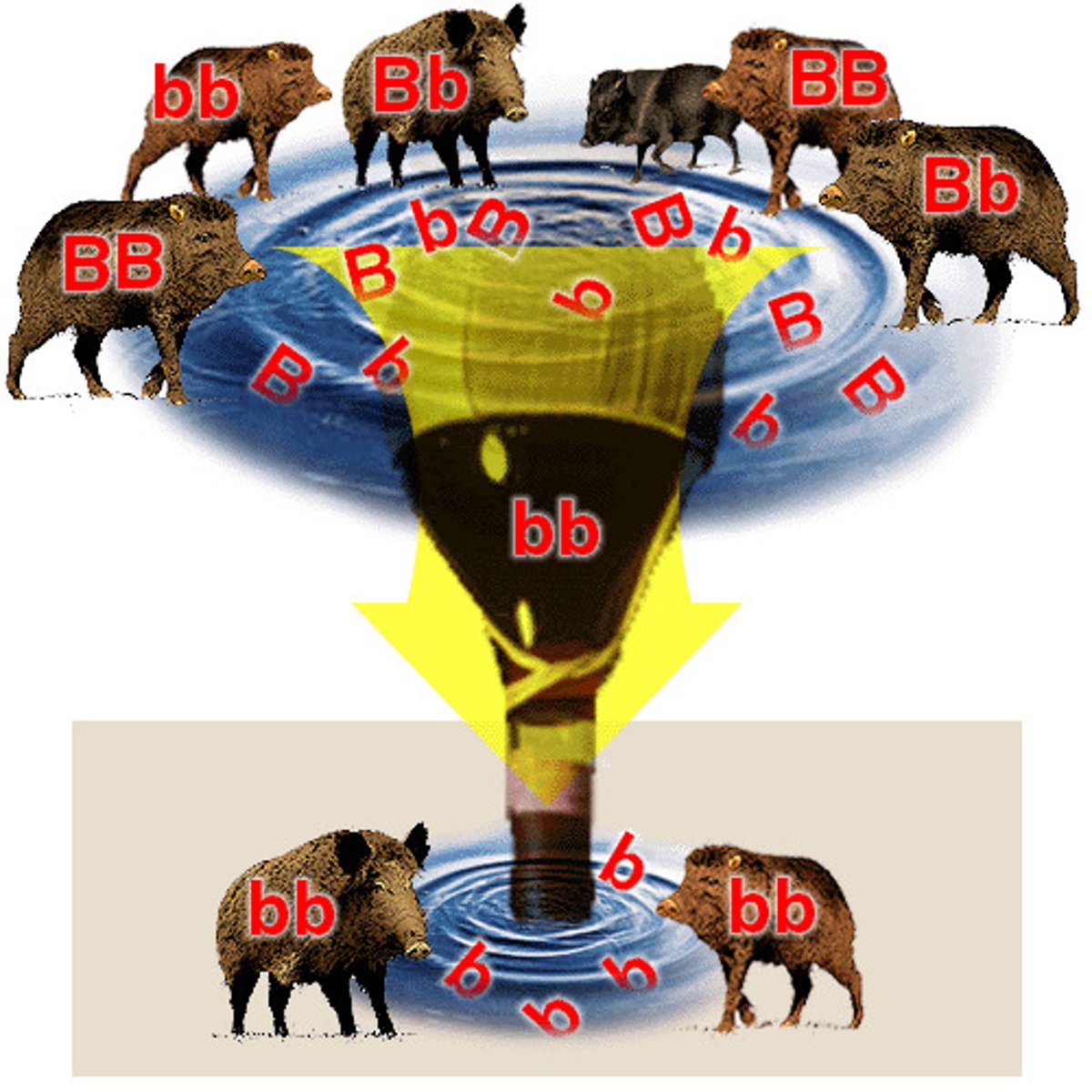
Which of the following is NOT true of a genetic drift?
(A) genetic drift results in the passing on alleles from parents to offspring due to chance events.
(B) genetic drift can increase genetic diversity.
(C) genetic drift can lead to fixed alleles in a population.
(D) genetic drift can lead to a loss of alleles in a population.
(B) genetic drift can increase genetic diversity.
Genetic drift of a population does NOT increase the genetic diversity of a population.
In South Africa, there is a population that has a much higher frequency of a rare disease than other regions across the world. The cause is that this population is most likely descended from a small subset of European colonists. What explains the phenomenon observed in this South African population? Why?
(A) Founder Effect
(B) Genetic Drift
(C) Gene Flow
(D) Bottleneck Effect
(A) Founder Effect
The founder effect explains this phenomenon because it described how a new population is started by a small group from a larger population and displays certain genetic biases.
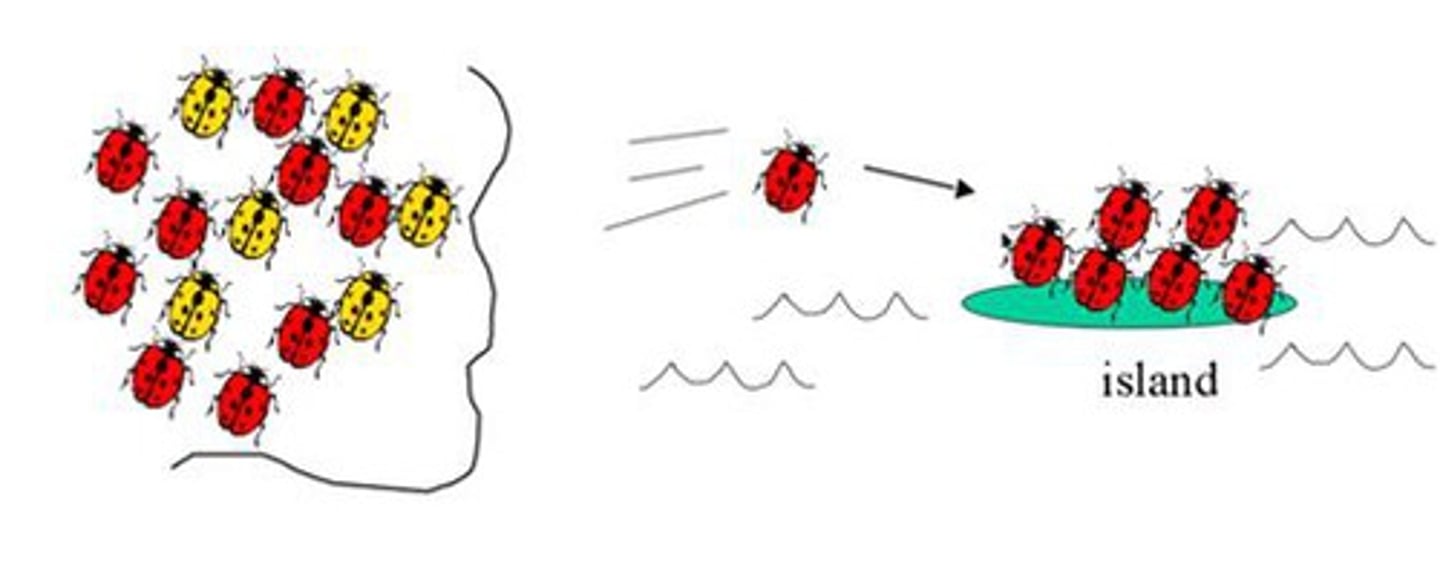
Which of the following is most likely to result in the loss of rare alleles?
(A) Founder Effect
(B) Genetic Drift
(C) Gene Flow
(D) Bottleneck Effect
(B) Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is most likely to result in the loss of rare alleles because if an allele has a high frequency at baseline, the chance of it being passed down to subsequent generations is higher than alleles at a lower frequency. The Founder Effect and Bottleneck Effect are specific examples of genetic drift.
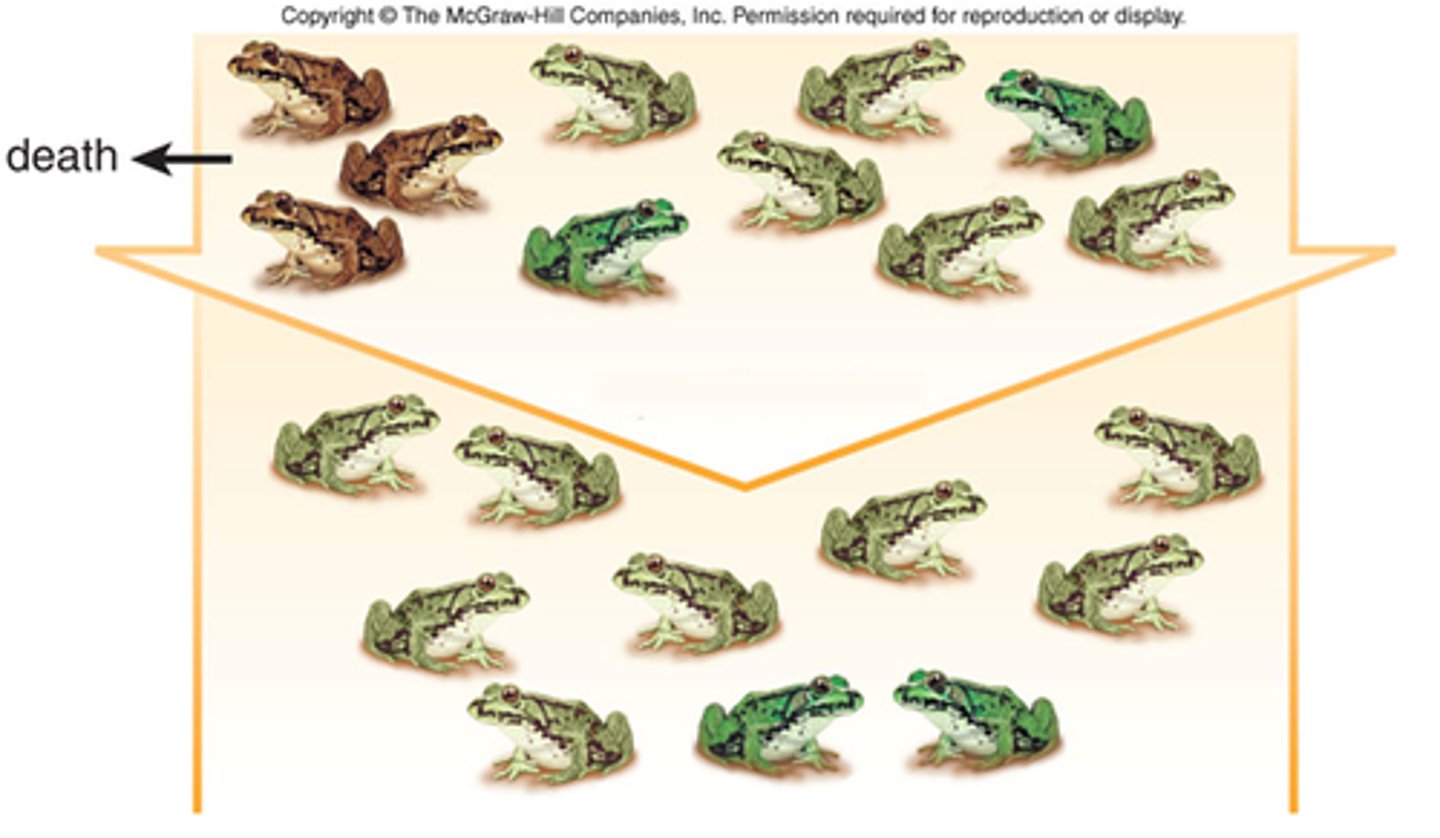
What is the only factor that can change allele frequencies in populations to produce adaptive evolutionary change?
(A) Gene flow
(B) Non-random mating
(C) Genetic drift
(D) Natural Selection
(D) Natural Selection
Natural selection is the answer because the question asks about producing adaptive evolutionary change.
CRB Describe the relationship between Evolution and Natural Selection.
Natural Selection is one mechanism that Evolution can occur through, but Evolution can occur through other mechanisms too. This means that Natural Selection and Evolution are NOT synonymous.
Why can inbreeding be problematic for autosomal recessive diseases?
Inbreeding can be problematic because it can lead to an increased chance that the mating partner might also be a carrier. This leads to diseased children, since most autosomal recessive diseases do not show symptoms and carriers are not generally aware of their status.

Compare the two major categories of reproductive isolation between species: pre-zygotic and post-zygotic isolation. Give examples of each type of isolation.
Pre-zygotic forms of isolation will prevent organisms of two species from successfully creating an embryo, and causes can include temporal/habitat isolation, behavioral isolation (how species attract mates), mechanical isolation (being physically unable to mate), or gametic isolation (if gametes do not meet, they cannot successfully form zygote)
Post-zygotic forms of isolation mean that zygote formation was possible, but the outcome will not produce a fertile offspring. A few examples are zygote mortality, hybrid inviability (the offspring will have high mortality rate or won't reach adulthood) and hybrid sterility (the offspring will be unable to successfully mate/produce offspring, even if it reaches adulthood).
What is animal foraging? How does this relate to evolution?
Foraging describes an animal's behavior when searching for wild food resources. Foraging affects an animal's fitness because it plays an important role in an animal's ability to survive and reproduce.

What is the difference between the two main foraging strategies that an animal can use - solitary foraging vs. group foraging?
The two main foraging strategies that an animal can use are:
- solitary foraging (finding food alone)
-group foraging (finding food in groups)
What are the advantages and disadvantages of group foraging over solitary foraging?
Advantage = it allows animals to work together, which can result in less threat from predators
Disadvantage = it can lead to competition between animals
True or False? Genetics is the only force that drives foraging behavior in animals.
False. Several factors drive foraging behavior in animals, including:
- genetics
- animal learning (the kids learn from their parents how to hunt and what to hunt)
What are some of the main reasons why animals communicate?
to attract mates
defend their territory
warn animals within the same species that a predator is near
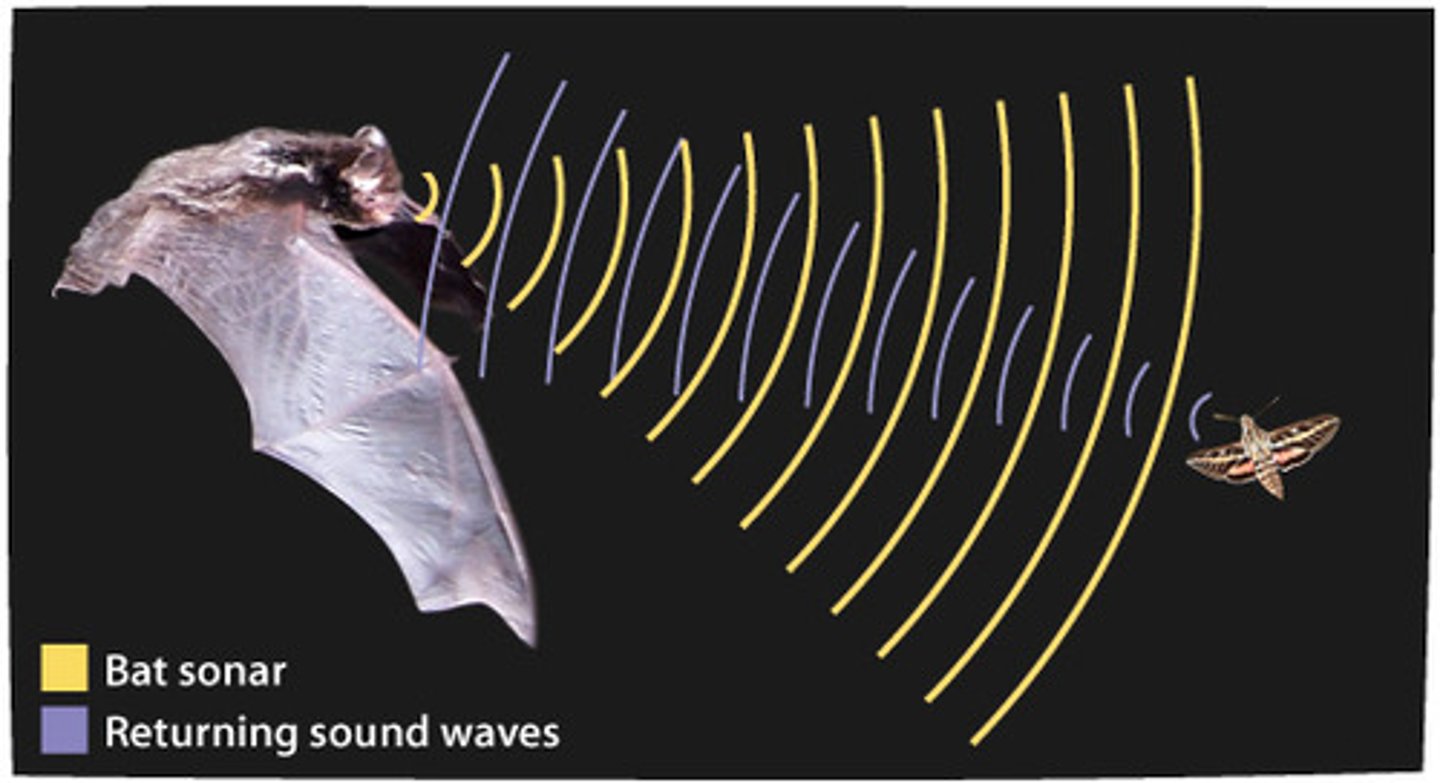
What is echolocation? Provide an example of echolocation and explain how it can relate to foraging.
Echolocation is a type of animal communication with their surrounding environment in order to receive information for themselves. Echolocation is the use of sound waves and echoes to determine where objects are in space. For example, bats use echolocation to navigate and find food in the dark. (There can be many other examples such as dolphins, whales, shrews and some birds).
What is anthropomorphism?
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, and intentions to animals and other non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology.
Ants produce scents as a signal to give directions about a location, which explains how assiduous ants exercise remarkable cooperation in building a colony. What is this signal called?
(A) Gustatory compound
(B) Pheromone
(C) Seismic communication
(D) Olfactory compound
(B) Pheromone
This scent signal is called a pheromone and is a type of chemical communication in animals.

What is seismic communication?
Seismic communication is a type of somatosensory communications that is a process of conveying information through mechanical vibrations.

What is the key feature of visual communication in animals that is not found in other types of communication?
Visual communication allows the animal to deliberately not communicate with other animals (think of camouflage!)
Coral polyps disperse their sperm into the ocean currents. Contact with an egg in another coral is completely up to chance. What type of mating behavior is this? Why?
(A) Assortative mating
(B) Disassortative mating
(C) Allusive mating
(D) Random mating
(D) Random mating
This is called random mating because a population that is randomly mating will not make choices in mates that have any advantage in behavior, appearance, or social aspects.
Large blister beetles tend to choose mates of large size and small blister beetles tend to choose small mates. What type of mating behavior is this called? Why?
(A) Assortative mating
(B) Disassortative mating
(C) Allusive mating
(D) Random mating
(A) Assortative mating
This is called assortative mating because individuals tend to choose mates similar to themselves.

Two animals with completely different traits are mating. What is this type of mating behavior called? Why?
(A) Assortative mating
(B) Disassortative mating
(C) Allusive mating
(D) Random mating
(B) Disassortative mating
This is called disassortative mating in which individuals with dissimilar genotypes/phenotypes mate with one another.

Which type of mating behavior would result in fewer heterozygous individuals? Why?
(A) Assortative mating
(B) Disassortative mating
(C) Allusive mating
(D) Random mating
(A) Assortative mating
Assortative mating would result in fewer heterozygous individuals, because mating individuals with similar phenotypes would also have similar genotypes.
Which of the following is NOT true of assortative mating?
I. Assortative mating increases the likelihood of harmful recessive traits be passed along to offspring
II. Assortative mating alters allelic frequencies
III. Assortative mating tends to weaken a population
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) III Only
(D) I and II Only
(B) II Only
Assortative mating does not alter allelic frequencies.
A gene seeks only to be passed along to offspring if there are other copies of the gene in other individuals and the success of other individuals to reproduce. What does this concept illustrate?
(A) Natural Selection
(B) Group Selection
(C) Artificial Selection
(D) Inclusive Fitness
(D) Inclusive Fitness
This concept illustrates concept of inclusive fitness: a theory suggesting that the genetic success of an organism is dependent upon cooperation with other individuals in a population. A gene will be more prevalent in future generations if all individuals who carry that gene are successful at reproducing, rather than just one individual with that gene.
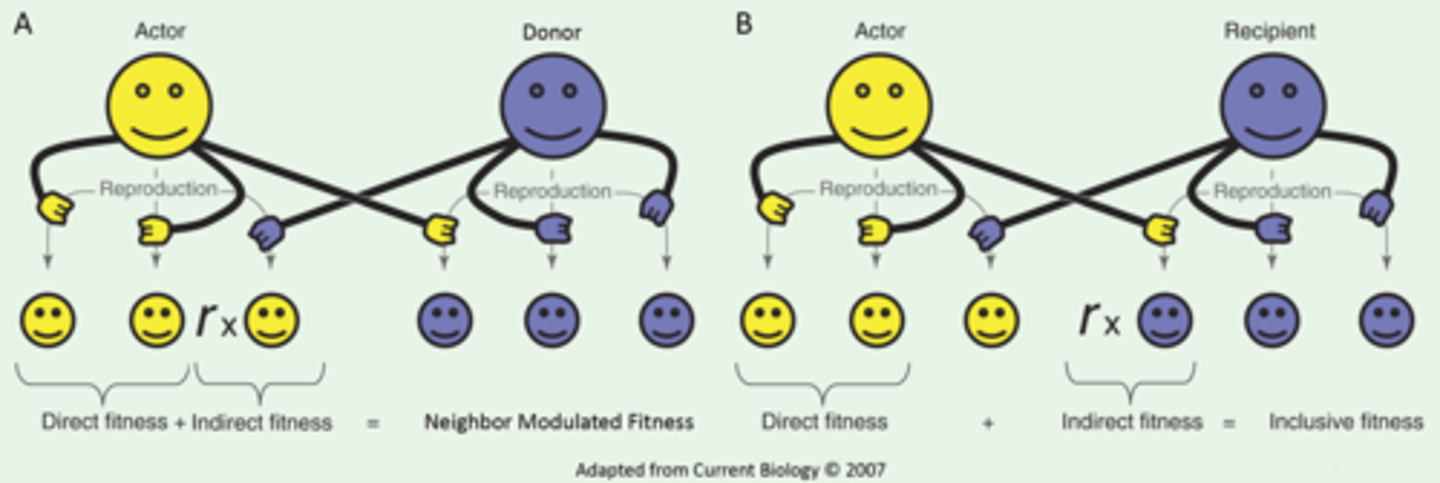
How does altruism fit into natural selection?
Altruism is the idea that an individual may act in a self-detrimental way for the good of the greater group/species. An example of this is a monkey screeching to alert others of a predator. This is actually an evolutionary stable strategy, increasing the fitness of the community as a whole.
CRB Eldrige and Gould had their own theory of evolution, based on fossil records showing little change over long periods, followed by short periods with lots of increased diversity and evolutionary changes. Which of the following is the name of their theory?
(A) Differential Evolution
(B) Epochal Evolution
(C) Punctuated Equilibrium
(D) Differential Equilibrium
(C) Punctuated Equilibrium
The Theory of Punctuated Equilibrium is based on the idea that changes in species occur in rapid bursts, not evenly over time (like Darwin had suggested).
CRB In spite of Punctuated Equilibria, the Evolutionary Clock Model equates the similarity of species' genomes with the time passed since the two species diverged from their last common ancestor. Would 2 species with more or less genomic similarity have a more recent last common ancestor?
Species that have had a more recent last common ancestor should have more genomic similarities.