Bell Palsy, GBS, chronic fatigue, chronic spacity, RLS
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Bell Palsy
onesided facial weakness, paralysis
viral infx
HSV most common
Symptoms of bell palsy
cant close eye
secretion issue (tears, saliva)
expresions are difficult
pain on ear, headache, jaw
sagging, weakness, paralysis on one side
Non pharm bell palsy
Protect the eye
eyepatch at night, tape eyelid closed
sunglasses, goggles in day
eyedrops to keep mois
drops in day
eye ointment at night
Bell Palsy tx
for all - want early tx within 72 hours of onset with CS
prednisone 60-80mg/day for 1 wk
prednisolone 60mg/day 5 days, reduced by 10mg daily UF
no effect in children.
If severe, antiviral tx
Bell palsy is common in
pregnant women - 3rd trimester
acetaminophen and non drug tx
CS - caution, clef palate risk in 1st trimester
Breastfeeding
CS ok, antivirals preferred.
monitoring bell palsy
facial expression, function - want full recovery with treatment
monitor CS side effects
do GBS pts resolve?
yes, most can walk independently at 6 months - 1 year after dx
no cure, just supportive measures.
Tx for GBS
plasma exchange - remove aby that do nerve damage (AE: sepsis, hypotension)
High dose immunoglobulin tx (preferred) - neutralize aby
both best if started 2-4 weeks of neuropathic symptoms
GBS symptoms
initially bilateral weakness, burning, tingling in legs and arm, upper body, face
severe, delayed:
breathing issue, swallowing, irregular HR, BP, bladder issue, walking issue
Can you get GBS from injection
1 / 1 million get it
if got GBS from vaccine and need more vaccines in that series do not complete series
withhold all imunnizations for a year after onset of GBS
GBS
autoimmune disease - body immunse system attack peripheral nervous system
triggered by infection → weakness and parlysis of limbs (from attack of mylein sheath)
Weakness, tingling of legs
Chronic fatigue syndrome
resting doesnt improve symptoms
Chornic fatigue presentation
muscle, joint pain
headahce
sleep dysfunction
cognitive issue
GI abnormality, HR, hypersensitivity to light and sound
Assessment for chronic fatigue
SCHOLARE the symptoms
more testing for differential diagnosis
if everything normal → chronic fatigue
non pharm for chronic fatigue
symptomatic management of the symptom that bothers them the most
no cure to chronic fatigue
Sleep hygiene
CBT
graded exercise
Activity pacing
balanced diet
Pharm tx for chronic fatigue
Sedatives
antihistamine (dozylamine)
hypnotic at lowest dose
Rituximab?
*****Stimulannts and TCA NOT RECOMMENDED
Chronic spasticity
increased in muscle tone - stiff, tighten
imbalanced of excitatory and inhibitory input
chronic spacicity
issue with reflexes, involuntary mvt
, limited mvt
deformity,
skin brkdwn
in spasticity do we treat it?
can worsen gait and mvt by unmasking weakness in limbs
only tx if cause pain and interfere with daily function
nonpharm for chronic spasticity (tailor to pt)
functional electrical stimulation
braces
daily stretching and exercise
Pharm tx (only if affecting daily life)
Focal (in one area)
botulinum toxin or phenol injection (Q6months
surgery to cut off nerve to muscle
General spasticity
baclofen
tizanidine
gabapentin
THC/CBD spray
BZD
baclofen intrathecal
Baclofen sudden d/c can lead to
seizure, hallucination, confusion
need to taper.
(dont use in <12)
Tizanidine
don’t use in <18
spasticity improves with
hours to days of starting meds
RLS symptoms
worse at night and inactivity
improve with activity
want to move leg and have sensation of tugging or pulling (burning, nagging, aching, electric, itching)
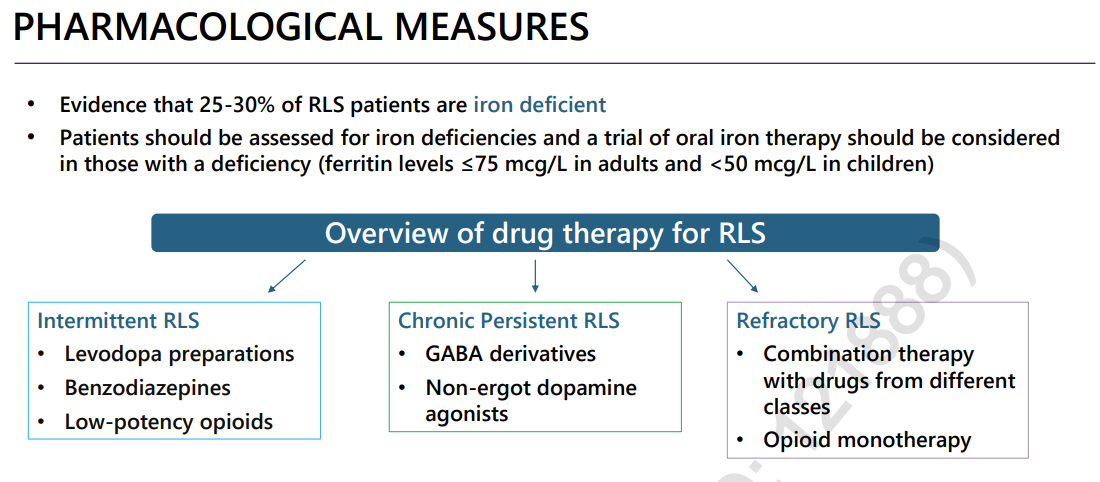
medically induced RLS
iron deficiency most common
MS
PDDM
ESRD
venous insufficiency
Drugs that worsen RLS
EtOH
caffiene
nicotine
anti-depressants (minus bupropion)
antipsychotics
antiepileptics (topiramate)
1st gen antihistamines
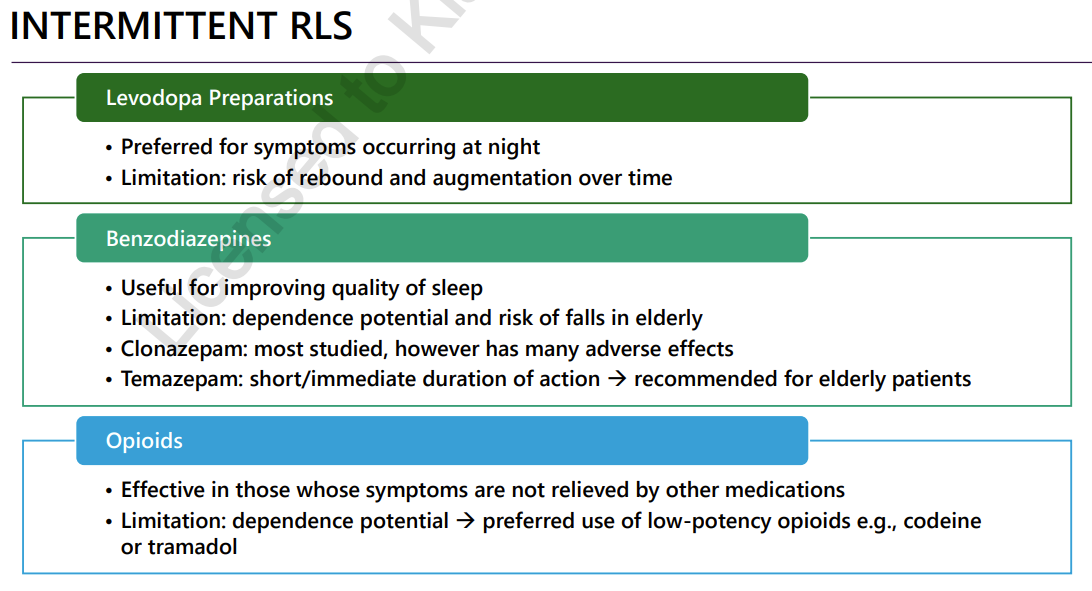
intermittent RLS
<2x week, PRN tx
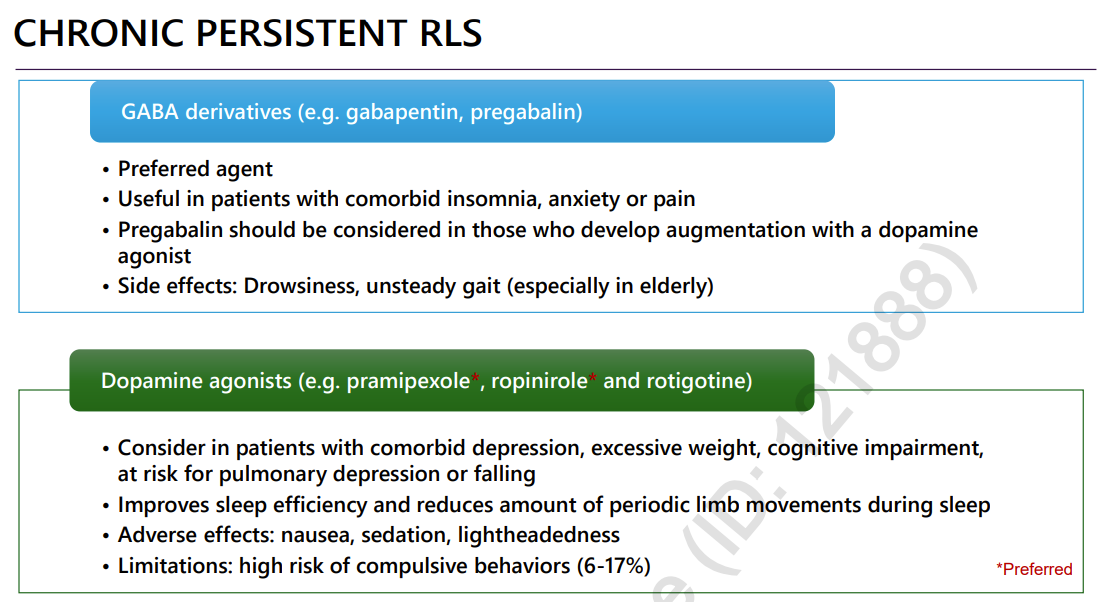
chronic persistent RLS
>2x a week, mod-severe, need daily tx
refractory RLS
unresponsive to max dose of 1st line, inadequate response →augmentation
nonpharm for RLS
mental stimulation (puzzle) to remove boredom
avoid ETOH, caffeine, nicotine
stretching, massage
hot bath
min aggrevating factor
INtermittent RLS tx
summary of RLS treatment
chronic RLS tx