AP World unit 0 test
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Mecca
an important place for religious gathering (holds religious shrines) and trade in pre-Islamic Arabia. considered holist Islam city
Ka’aba
the shrine where worship happens
Bedouins
first to get to Arabia, nomadic, organized in tribes/clans (matriarchal), wars over land since fertile land was scarce
What was the Arabian landscape like in pre-Islamic Arabia?
mostly dry and infertile, but agriculture at coastlines
Polytheism
belief or worship of more than one god
Animism
attribution of a soul to plants, inanimate objects, and natural phenomena
Impact of Muhammad
started the spread of islam because of a vision he had from god. encouraged followers to act righteously, care for less fortunate, dismiss false deities, and submit to one god, Allah.
The Hijra
when Muhammad and followers escaped Mecca to present-day Medina where Islam is born
Quran
Muhammad’s teachings in Quran. Became known as word of god
The 5 pillars of Islam
Confession of faith (uncompromising monotheism)
Pray facing Mecca five times a day
Fast Ramadan (to commemorate Muhammad’s first revelation)
Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca to worship at Kaaba)
Give to charity, social responsibility
Purpose of 5 pillars of Islam
defined the basic identity of Muslims. Unite all under one god.
Rightly Guided Caliphs/their impact
`First four successors that led Islam after Muhammad died.
Institutionalized Islam, linked religious uprightness with empire expansion, building, appeal to all people
Jihad
religious idea of struggle by muslim solders’ desire to expand Islam faith and conquer new territories
Dar al-Islam
“world of Islam.” Any structure where Islam could be practiced freely
Dar al-Harb
“world of warfare”
Sunni Muslims
majority. believes that caliphate should be chosen by consensus (the community)
Shia Muslims
minority. believes that caliphate should be passed down through Muhammad’s bloodline
What did the split between Sunni and Shia Muslims mean?
created class division between Muslims. Resulted in an increase in tensions as well as rivalries and conflicts
What were the religions like in pre-Islamic Arabia?
polytheistic and animism
Impact of Islam through the Silk Road
spread of ideas, culture, goods, services, etc. great desire to spread islam through military conquest
Key points of the Umayyad Dynasty (661-750)
Capital: Damascus
little incentive for converts (non-Arab Muslims and non-Muslims treated as second class citizens, had to pay jizya) —> little conversion
elites (Arab Muslims) had lavish lifestyles
successful conquests in uniting via expansion
introduced gold dinar and silver dirham
made Dome of the Rock mosque
Overthrown by Abbasids because people didn’t like them
Dhimmis
non-Arabs
Key points of Abbasid Dynasty (750-1258)
overthrew the Umayyads at Battle of River Zab
capital in Baghdad
cool with converted Muslims (had equal rights and no high tax)
like Umayyads, greatly expanded empire
Introduced Ulama (Muslims scholars that interpreted Islamic law)
Al-Shafi’i was their most influential Ulama (helped develop Sharia which served as the Islamic law)
Golden age of Islam during Abbasid Rule (advancements in science, math, medicine, cultural exchange, and Baghdad as the #1 cultural center)
elites had luxurious lifestyles
flourishing arts
made Arabic language of educated class
Key points of Fatimid Dynasty (909-1171)
Shiite leader Abu Abdallah overthrew Sunni Ruler in North Africa, beginning Fatimid regime
capital in al-Qahira (Cairo)
much greater tolerance towards non-Muslims
rival to Abbasid caliphs
What is the Sharia?
Islamic law that governs practical and spiritual life including marriage contracts, trade regulations, and religious issues
Who are the Ulama?
muslim scholars that had knowledge of the Sharia. Authoritative interpreters of Islamic law
Impact of caliphates on foreign terrtories
introduced islam into new regions, direct trade, and exchange of ideas
gender rules and how they changed over time
spread of islam led to stricter gender roles
In Bedouin times, many men were traders and clans were largely matriarchal. In post-Muhammed times, women were subordinated to men and islamic empire became largely patriarchal.
Commercialism in the islamic world and how it impacted different regions and groups
sub-Saharan trade in Africa developed and connected to wider world due to muslim presence
commercial interactions facilitated cultural exchange between different regions, merchants shared knowledge, goods, languages, ideas, etc.
merchants became very wealthy
Abbasids used dhows (triangular shaped sail ships)
Muslims became #1 in Indian ocean trade
collaborations of Muslims with jews and Christians
expansion of knowledge in the islamic world and its significance
Translation movement: during islamic golden age, scholars translated works from other civilizations into Arabic
advancements in science, medicine, mathematics, astronomy, and chemistry
expansion of knowledge contributed to spread of knowledge with other regions
Islamic world began to expand
Feudalism
a political and economic system based on landholding and protective alliances, emerged in Europe’s class system
feudal pyramid
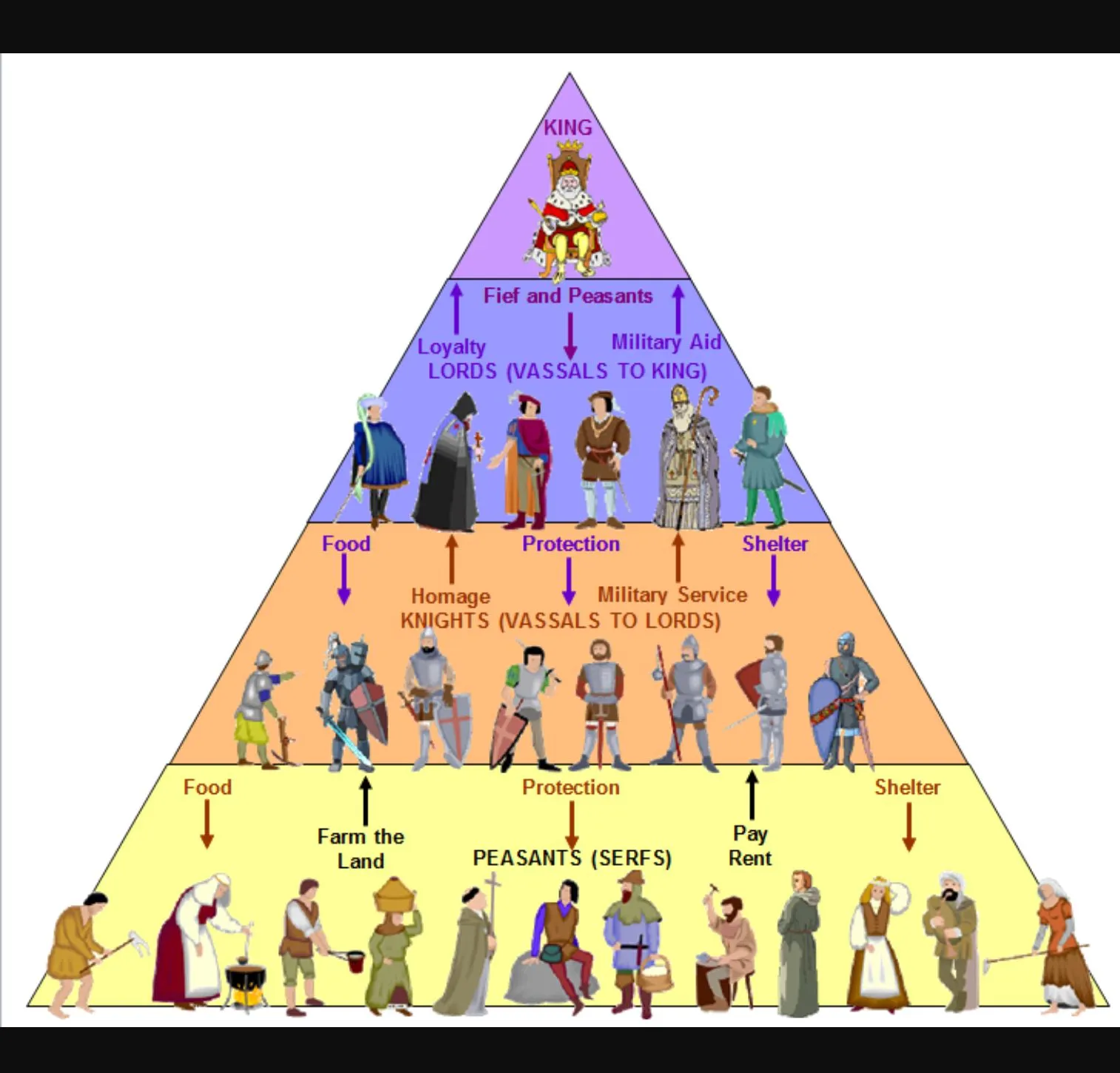
created rigid hierarchal social class structure
land/economy based on agriculture worked by labor class
established a military
Manoralism
economic system between landlords and peasants who live in estates —> led to regional monarchies with strong aristocrats
serfs gave their lord a portion of produce. lords protected serfs and provided everyday needs
Effects of manoralism
peasants/serfs generally accepted their lives to be part of God’s plan
bound peasants to the land and limited their freedom
fostered sense of self-sufficiency
ensured agricultural production and land management
increased wealth distribution
social order of feudal monarchies
those who fight: nobles and knights
those who pray: monks, nuns, leaders of the Church
those who work: peasants/serfs
expansion of feudal monarchies
After Norman invasion (1066), feudal monarchy introduced to England
Early middle ages (5th-10th century) in Europe
power struggle (uncertainty of who will rule after the roman empire falls)
rise of feudalism
rise of Christianity
everything declining (population, literacy rate, science and tech advancements, institutions)
high middle ages (10th-15th century) in Europe
slow advancements (economic and political change)
economic and territorial expansion
late middle ages (1300-1500 CE) in Europe
black plague caused war and famine
Christian faith growing and strong
trade with other countries increased (islam and mongols)
decline in feudalism
Expansion and significance of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman empire expanded in Europe mostly
Emperor Charlemagne’s land reign over most of Western Europe
Byzantine empire are opps
Pope came along by the 9th century
Charlamagne
ruler of the Franks
credited with reviving the idea of a unified Christian empire in the West
trade based on war
helped restore the Western Roman empire
facilitated in a cultural and intellectual renaissance
Impact of the Vikings
exposed Charlemagne’s weak empire
successful because of the use of ships
Schism in Chrstianity
division of Christianity into the Western Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church
Christianity in Western Europe vs. Eastern Europe
Western Europe led by Pope / East led by Patriarch
West said priests should be celibate / East said no
West wanted religion to control the state / East wanted state to control religion
West was largely Roman Christians (believing that Jesus sacrificed as payment for human guilt) / East was largely Greek Orthodoxy (believing in restoring humanity to its intended purpose of moral perfection and eternal life in union with God)
Movement of Christianity along Silk Roads and into new regions
Merchants and travelers spread Christianity into Eastern Europe and Russia
led to Kievan Rus
Kievan Rus
group of Russians (moved from Asia into Roman Empire region)P
agricultural and had villages
animism
Leaders of Kievan Rus
Vladimir I —> converts to Greek Orthodoxy, developed Russian orthodox church, forced conversions with military pressure, controlled the church
Yaroslav —> makes unifying law code (creates a golden age and education), arranged marriages with central European royalty, translates religious texts into Slavic
culture of Kievan Rus
Russian culture borrowed much from Byzantine and influenced by Greek Orthodox Church
had Boyars (like lords in feudalism but weaker)
Impact of Kievan Rus
helped facilitate cultural exchange between Byzantinesde
Decline of Kievan Rus
fell because Byzantines fell (relied on them) and invaded by Mongols
Impacts of the Sui dynasty
founded by Emperor Wendi (Yang Jain) —> unified China after period of fragmentation (after fall of Han dynasty) and wanted to consolidate power & centralize government
Sui dynasty laid groundwork for Tang dynasty after
known for canal system and rivers for population shift and transportation of goods (Yangdi’s Grand Canal)
scholar gentry
a bunch of well educated bureaucrats (state appointed officials). powerful social class in china
importance of expansion in the tang state
rise of the tang empire in China paralleled Islam’s explosion in growth and impact of Arabia, strong central government, professionally trained army, aristocratic cavalry and peasant soldiers (based on wealth status), expansion in agricultural cultivation
Minstry of rites
carry out/oversee the administration of civil service exams
Li Yuan
founding emperor of the Tang Dynasty (previously from Sui)
Tang Taizong
well known for developing more transportation systems (more roads—land-based transportation—canals—sea-based transportation). Under his reign, there was the creation of postal and messenger services which increased efficient communication through the empire.
Different components of the Tang state (type of gov, economy, religions and their significance, culture)
Capital: Chang’an
Government: centralized bureaucracy that employed merit-based service exam system to select officials (rooted in Confucian beliefs)
Economy: experienced a period of economic prosperity. Agricultural development, strategic location along Silk Road, good trade
Religions: Buddhism, Daoism, Confucianism are primary religions. created differing views/view on religion varied from emperor to emperor
BUDDHISM: more of a philosophical/ideological concept rather than a religion. Follows the Four Noble Truths: to live is to suffer, to suffer is caused by desire, suffering can terminate, and the solution is the Noble Eightfold Path
DAOISM: emphasis on harmony with natural and spiritual practices
CONFUCIANISM: a philosophy based on mutual respect and kindness toward others. ethical practices
Culture: time of Tang dynasty referred to as the Golden Age of Chinese civilization
Civil Service exam and what it did for china
written civil exam to ensure appointed officials were qualified so only the best could work —> recruited officials based on qualifications and knowledge on Confucianism, rather than aristocratic birth
Empress Wu and her significance
badass
dominated tang dynasty (609-705)
uses her beauty and and intelligence to gain prominence and becomes empress after her husband, Emperor Gaozong dies
expanded military force & forced secret police
ordered scholars to write biographies of famous women
encouraged buddhism over daoism as the favored state religion (buddhism reached its highest point)
impact of buddhism
united the Chinese people into a community of believers
helped the people overcome a period of war and unrest
was important for the spread of ideas and beliefs on the Silk Road
How did people feel about Buddhism overtime?
Anti-Buddhist campaigns —> claimed Buddhism conflicted native traditions
Han Yu is responsible for destroying thousndads of monasteries, and temples
By mid-19th century, Buddhism is openly persecuted
Han Yu
Confucian Chinese scholar who believed Buddhism threatened Chinese traditions and values and believed it was a foreign doctrine
Chan/Zen
new form of buddhism that focuses predominantly on meditation
Sinification of Korea
China had an influence on the Silla —> rigid hereditary social structure
once the tang dynasty began to fall and imperial system began to crumble, silla fell too (they had similar system)
Autonomous government (self-governing)
expansion of chinese culture to other regions in Asia
Umma
Arab Muslims
who founded Kievan Rus?
Prince rurik
Sinification of Japan
Soga kinship group rises to power and took control of japanese courts
Pirnce Shotoku —> introduces Buddhism to Japan and promoted both Buddhism & Confucianism. Influenced the Shinto cults
The Nakatomi family rises to power (645 CE) and overtakes Prince Shotoku
reflected Confucian principles
autonomous government
Chinese culture spreads even more and becomes intertwined into these societies
Which groups of people led to the fall of the Tang Dynasty?
Muslims forces drove the Tang from Turkistan in 751 — Battle of Talas River
Sogdians and Tibetans (challenged the Tang)
Tang group retreated back to original heartlands (Yellow and Yangtze Rivers) and it weakened the empire until it finally ended in 907 CE
Chronological order of the emperors of Tang Dynasty
Li Yuan —> Li ShiMin —> Gaozong —> Empress Wu