Chapter 1: Introduction to Managerial Accounting
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
managerial accounting
focuses on providing information for internal decision makers
it helps managers make decisions needed to be successful
financial accounting
focuses on providing information for external decision makers
managers use financial accounting to report monetary transactions and prepare financial statements
Financial Accounting - primary users
external — investors, creditors, and government authorities
financial accounting - Purpose of information
help investors and creditors make investment and credit decisions
financial accounting - focus and time dimension of the information
relevant and faithfully representative information and focus on the past
financial accounting - rules and restrictions
required to follow Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP); public companies required to be audited by an independent CPA
financial accounting - scope of information
summary reports prepared primarily on the company as a whole, usually on a quarterly or annual basis
financial accounting - behavioral
concern about adequacy of disclosures; behavioral implications are secondary
managerial accounting - primary users
interal — the company’s managers and employees
managerial accounting - purpose of information
helps managers and employees plan, direct, and control operations
managerial accounting - focus and time dimension of the information
relevant information and focus on the future
managerial accounting - rules and restrictions
not required to follow GAAP
managerial accounting - scope of information
detailed reports prepared on parts of the company (products, departments, territories), often on a daily or weekly basis
managerial accounting - behavioral
concern about how reports will affect employee behavior
Most companies structure their organization along ________.
departments or divisions
organizational chart
a company’s (OC) helps show the relationship between departments and divisions and the managers who are responsible for each section
board of directors
elected by the stockholders and is responsible for developing the strategic goals of the corporation
chief executive officer (CEO)
has ultimate responsibility for implementing the company’s short- and long-term plans
Each position in a company can be classified as either a line or staff position.
line positions are directly involved in providing goods or services to customers
staff positions support the line positions
planning
choosing goals and deciding how to achieve them
strategic planning
involves developing long-term strategies to achieve a company’s goals
operational planning
focuses on short-term actions dealing with a company’s day-to-day operations
directing
involves running the day-to-day operations of a business
controlling
the process of monitoring day-to-day operations and keeping the company on track
The Institute of Management Accountants (IMA) have developed standards that managerial accountants are expected to uphold when faced with ethical challenges
maintain their professional competence
preserve the confidentiality of the information they handle
act with integrity and credibility
if policies do not result in a resolution, IMA recommends discussing ethical situations with:
an immediate supervisor
an objective adviser
an attorney
principles of commitment to ethical professional practice
honesty
fairness
objectivity
responsibility
standards of ethical practice:
competence
confidentiality
integrity
credibility
Competence (CICC):
maintain an appropriate level of professional leadership and expertise by enhancing knowledge and skills
perform professional duties in accordance with relevant laws, regulations, and technical standards
provide decision support information and recommendations that are accurate, clear, concise, and timely, Recognize and help manage risk
Confidentiality (CICC):
keep information confidential except when disclosure is authorized or legally required
inform all relevant parties regarding appropriate use of confidential information. Monitor to ensure compliance
refrain from using confidential information for unethical or illegal advantage
Integrity (CICC):
mitigate actual conflicts of interest. Regularly communicate with business associates to avoid apparent conflicts of interest. Advise all parties of any potential conflicts.
Refrain from engaging in any conduct that would prejudice carrying out duties ethically
abstain from engaging in or supporting any activity that might discredit the profession
contribute to a positive ethical culture and place integrity of the profession above personal interests
Credibility (CICC):
communicate information fairly and objectively
provide all relevant information that could reasonably be expected to influence an intended user’s understanding of the reports, analyses, or recommendations
disclose delays or deficiencies in information, timeliness, processing, or internal controls in conformance with organization policy and/or applicable law
communicate professional limitations or other constraints that would preclude responsible judgement or successful performance of an activity
service companies
sell their time, skill, and knowledge
merchandising companies
resell products they previously bought from suppliers
manufacturing companies
use labor, equipment, supplies, and facilities to convert raw materials into finished products
manufacturing companies have three kinds of inventory:
raw materials inventory (RM)
work-in-process inventory (WIP)
finished goods inventory (FG)
Raw Materials Inventory
includes materials used to make a product
work-in-process inventory
includes goods that are in the manufacturing process but are not yet complete
finished goods inventory
includes completed goods that have not yet been sold
direct cost
a cost that can be easily and cost-effectively traced to a cost object
cost object
anything for which managers want a separate measurement of cost
indirect costs
costs that cannot be easily or cost-effectively traced directly to a cost object
Direct materials (DM)
raw materials used in production
direct labor (DL)
labor of employees working on the products
Manufacturing overhead (MOH)
the indirect product costs associated with production, including:
indirect materials
indirect labor
factory costs for rent, utilities, insurance, etc. (other MOH)
prime costs
combine the direct costs of direct materials and direct labor
conversion costs
combine direct labor with manufacturing overhead
product costs
include the costs of purchasing or making a product
direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead
period costs
non-manufacturing costs
selling and administrative expenses and other expenses such as taxes and interest
balance sheet:
service companies carry no inventories on their balance sheets
merchandising companies record the cost of inventory purchased as an asset, Merchandise Inventory, on their balance sheet
manufacturing companies keep track of costs using three inventory accounts: Raw Materials Inventory, Work-In-Progress Inventory, and FInished Goods Inventory
Income Statement:
service companies only record period costs such as salaries expense and rent expense
merchandising companies and manufacturing companies report Cost of Goods Sold as the major expense
because a manufacturer makes the product it sells, the calculation of cogs is different for manufacturing companies than for merchandising companies
Cost of Goods Manufactured
the manufacturing costs of the goods that finished the production process in a given accounting period
three calculation steps for COGM
calculate direct materials used
calculate total manufacturing costs incurred during the year
calculate cost of goods manufactured
(Manufacturing) Cost of goods sold represents the _____________ inventory that has been sold.
Finished Goods Inventory
amount used, manufactured, or sold =
beginning balance + additions - ending balance
unit product cost =
cost of goods manufactured / total units produced
business trends that are affecting managerial accounting:
shift toward a service economy
global competition
time-based competition
Enterprise Resource planning (ERP) systems integrate companies’ data
e-commerce allows companies to sell products to customers around the world
Just-in-Time (JIT) Management is an inventory management tool
advances in technology
Total Quality Management (TQM)
a philosophy of continuous improvement in products and processes
it creates a value of cooperation
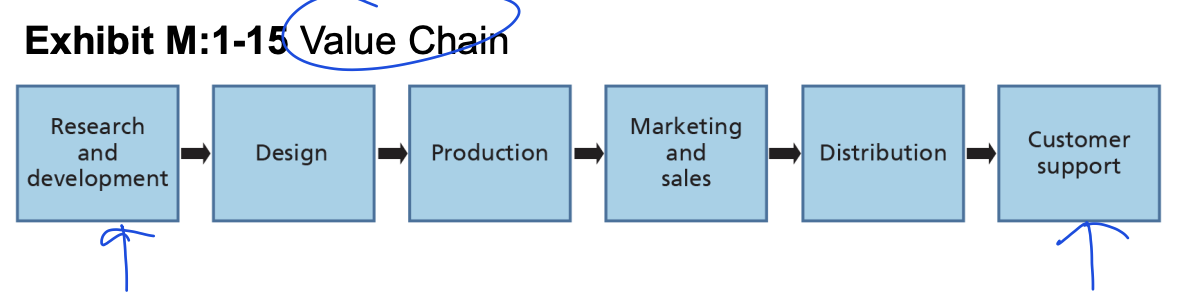
each step adds value to the end product (aka the value chain)
Value Chain
Triple Bottom LIne
the economic, social, and environmental impact of doing business, and includes:
profits
people
planet
customers and stockholders are choosing to support companies based on:
their labor practices, community service, and sustainable environmental practices
how is managerial accounting used in service and merchandising companies?
managers of service and merchandising organizations make decisions on pricing based on cost per service or cost per item
unit cost per service =
total operating costs / total number of services provided
unit cost per item =
total cost of goods sold / total number of items sold