Geologic Time
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
It is known that Rock A is older than rock B but younger than rock C. It would then be accurate to say that rock __________ is the oldest, followed by rock __________, with rock __________ being the youngest.
C; A; B
Sedimentary rocks cannot be used to determine dates on the geologic time scale because the numerical age?
Is the age of the igneous rocks that make up the sediment.
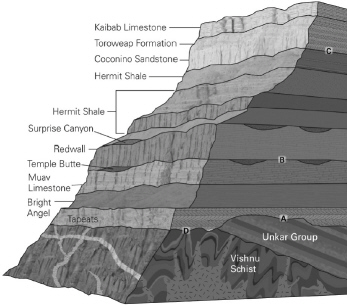
In the following image of the Grand Canyon, identify the nonconformity.
D
Buried erosional surfaces between parallel sedimentary strata are termed?
Disconformities
In the following image of the Grand Canyon, identify the angular unconformity.
A
A tilted sequence of sedimentary rocks violates which principle?
Original horizontality
How is the half-life of a radioactive parent isotope defined?
The time it takes for half of the parent isotope to decay to daughter isotope
A(n) __________ contact surrounds a pluton.
Baked
Within the world’s sedimentary rocks, fossils?
Occur in an ordered sequence
In an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rocks, younger layers overlie older layers, according to the principle of?
Superposition
If an igneous dike cuts across a sequence of sedimentary beds?
The beds must be older.
If a sandstone lies on top of a shale?
The shale must be older, according to the principle of superposition
The geologic time scale is broken into a series of eras, epochs, and periods based mainly on the fossils found in each section. This is an example of __________ dating.
Relative age
Which type of unconformity requires there to have been little to no deformation in the rocks before and after the unconformity was created?
Disconformity
Two atoms of a single element that differ in number of neutrons are said to represent two distinct __________ of that element.
Isotopes
If the relative ages of two formations are known, their __________ can be inferred.
Relative positions in a sequence of rock layers
If horizontal sedimentary strata overlie tilted strata (and no fault is present), the eroded surface between the horizontal and tilted strata must be a(n)?
Angular unconformity
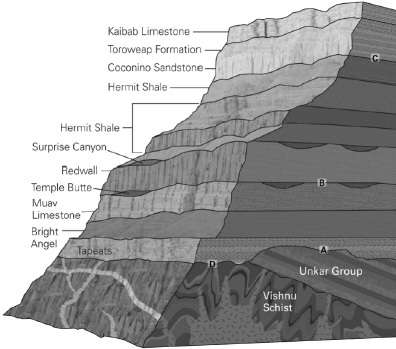
In the following image of the Grand Canyon, identify the disconformity.
B
Uniformitarianism is succinctly summarized by which phrase?
The present is the key to the past.
If the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes is 25:75, how many half-lives have passed?
2
The surface below sedimentary rocks that overlie igneous or metamorphic rocks is termed a(n)?
Nonconformity
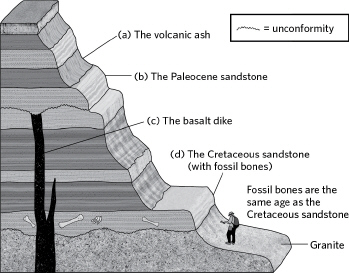
Which of the units in the following image would be least useful for obtaining a numerical age?
B
Several geologic principles are used to determine __________ ages.
Relative
A basaltic lava flow contains fragments of sedimentary rocks. Which of the following statements is true regarding their relative ages?
The lava flow is younger than the sedimentary rock
If a basalt body cuts across a fault, what are the relative ages of the basalt and the fault?
The fault must be older, according to the principle of cross-cutting relationships.
Unconformities represent __________ in the rock record.
Erosion or nondeposition
An erosional surface between two sequences of flat-lying sedimentary rocks is called a(n)?
Disconformity.
Relative ages expressed on the geologic time scale primarily resulted from the study of?
Fossil content and spatial relationships among sedimentary rocks.
Which of the following is always the same for different isotopes of a single element?
Atomic number
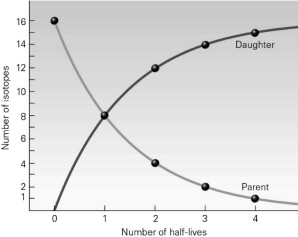
According to the following image, after one half-life has passed, what is the ratio of parent isotopes to daughter isotopes?
8:8
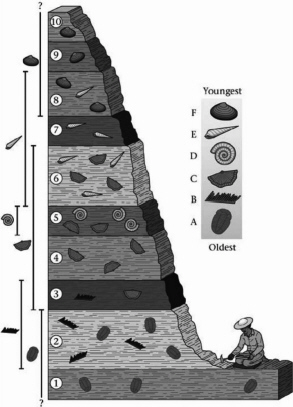
Based on the following figure, what is the age of layer 7 relative to layer 3?
Layer 7 is younger than layer 3.
Stratigraphic correlation is conducted by matching __________ and __________.
lithologic layers; fossils
Two layers of rock contain trilobites that have the same body morphology; however, one rock layer is a shale and the other is an ironstone. Can these two layers be used for correlation?
Yes, if the trilobites are the same, then the layers were formed at the same time.
Relative ages expressed on the geologic time scale primarily resulted from the study of?
Fossil content and spatial relationships among sedimentary rocks.
Describe how fossils can be used to interpret the geologic history of an area.
Fossils are evidence of past life and therefore will show what types of organisms inhabited an area. This can determine what type of environments have existed during geologic time. For example, we know that certain types of dinosaurs live only on land; thus, if we find evidence of a land-dwelling dinosaur we know that the area was above sea level sometime between 299 and 65 Ma. If the particular dinosaur has been dated, we can narrow the age range even more.
Fossil succession is the idea that life evolves over time and that once a species goes extinct, it does not reappear. Is this an example of unidirectional change or cyclic change? Why?
Unidirectional change involves transformations that never repeat, like the existence and extinction of species. Cyclic changes repeat the same steps over and over. Fossil succession is thus an example of unidirectional change.
How do gradual change and catastrophic change impact the Earth system? Provide an example of each.
Gradual change happens slowly over long intervals of geologic time (millions to billions of years). Catastrophic change takes place relatively rapidly (seconds to millennia). The growth of a mountain belt is an example of gradual change; whereas, a meteorite impact is an example of catastrophic change.
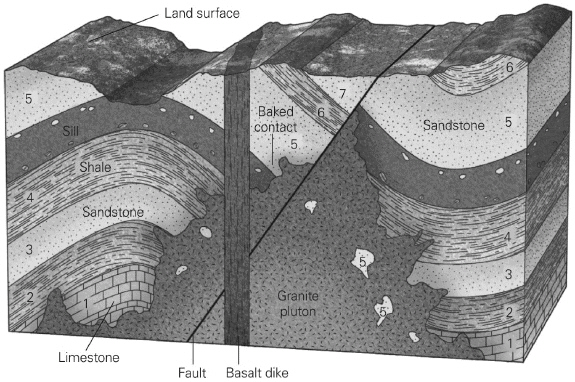
Place the layers and geologic events in order from oldest to youngest. Make sure to include all of the layers and events, including the top surface. (There will be one event/layer per line when complete.)
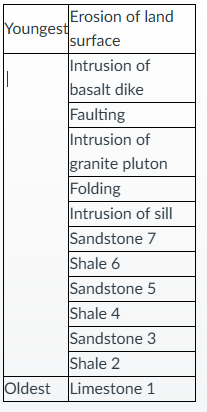
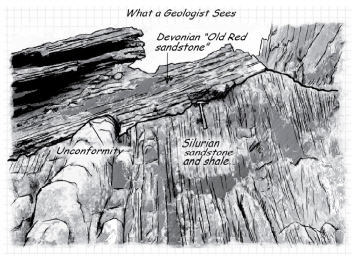
Describe the plausible geologic history of the rocks in the diagram below.
The sediments that make up the sandstone and shale were most likely deposited along a coast. The sediments were buried, lithified, uplifted, and tilted. The top of the sandstone and shale package was eroded away and then the sediments of the Old Red Sandstone were deposited in a subaerial environment, buried, oxidized, and lithified. The entire package of rocks was then uplifted, tilted, and eroded to its present state.
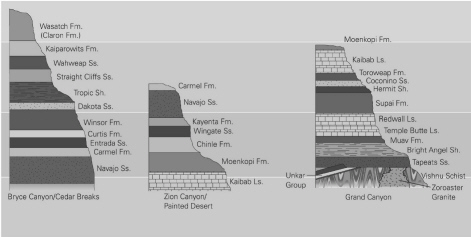
Correlate the layers in the following three stratigraphic columns by drawing lines from the top and bottom of matching formations. What is the oldest unit in this region? The youngest unit?
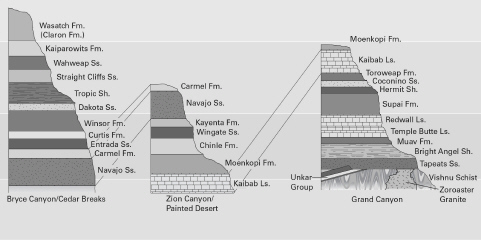
Discuss what the numerical age represents when radiometrically dating a basalt, a gneiss, and a quartz sandstone.
The numerical age of a basalt gives the age that crystals formed and the rock cooled from magma/lava. The numerical age of a gneiss gives the age of metamorphism of the rock. The age determined from a sandstone gives the age of cooling or metamorphism of the quartz crystals within the sandstone.
What is the principle of uniformitarianism? How does this principle apply to our understanding of the Earth system? How is this useful in the context of relative dating?
Uniformitarianism states, “The present is the key to the past.” This principle means that physical processes operating in the modern world also operated in the past, at roughly the same rates. We can use this principle to help us interpret the information found in the rock record. It also alludes to the vastness of geologic time, reminding that change in the Earth system can happen very slowly.
How is a relative age different from a numerical age? How are each of these determined?
A relative age compares the age of one geologic feature in a sequence with respect to another. This is deduced using observations and geologic principals. A numerical age is the age of a rock in a specific number of years; this is calculated using isotopic dating.
Do the fossils preserved in the rock record accurately and completely represent the entire extent and biodiversity of life on Earth? What does it take to create and preserve a fossil?
Only an exceedingly small number of living organisms become fossils when they die, so the fossils preserved in the rock record represent only a very small sampling of life on Earth. To make and preserve a fossil, at least one of the following must take place: (1) an organism must die in an anoxic environment, (2) the remains must be buried rapidly, and/or (3) there must be hard parts present.