principle of tooth preparation
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
indications for an indirect restoration (7)
missing cusp(s)
gross caries causing an unsupported cusp
protection of posterior ecodontically treated teeth
caries associated w a pre-existing indirect restoration causing weakened cusps
worn teeth w moderate to severe dentin exposure
cracked teeth (to encircle tooth)
complete crowns are indicated on teeth w 5 affected surfaces
contraindications for indrect restorations (4)
pt w uncontrolled high caries risk
to remove sound tooth structure that could be preserved w a direct restoration or be remineralized
pt w TMD symptoms (pain) should first have such concerns addressed prior to tooth preparation
teeth w a poor or guarded prognosis (e.g. loss of a tooth is anticipated within ~5 yrs due to periodontal disease)
what are the 3 things to consider in crown preparation
biologic
mechanical
esthetic
biologic considerations in crown preparations (5)
conservation of tooth structure
avoidances of over-contouring/over-prepping
supragingival margin
harmonious occlusion
protection against tooth fx
what structures should you be aware of preventing damage to during a prep
adjacent teeth
soft tissues
pulp
what is the usual cause of injury to soft and hard tissues during preps
temperature
chemical action
bacterial action
what can cause heat by friction during a crown prep
pressure
speed
bur
type
shape and size
condition- make sure not worn down
purpose of water spray
helps avoid overheating tooth
prevents tooth desiccation
removes debris, avoiding bur clogging, and avoids a reduction in cutting efficiency
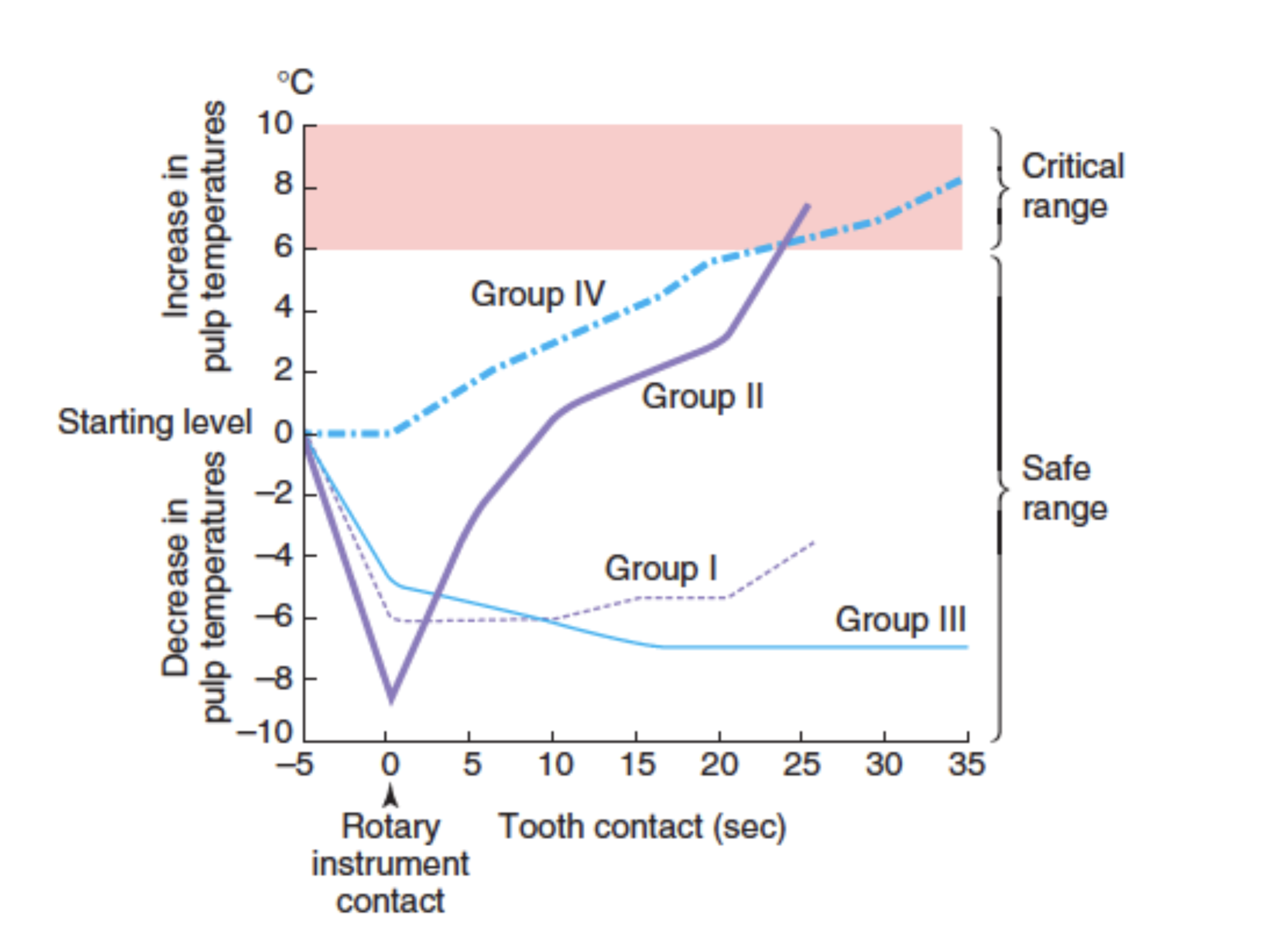
which groups can we guess used no water
Group II and IV → can notice an inc in temperature
the remaining dentin thickness is inversely proportional to the _______ _______ according to Sheltzer
the pulpal response
how do the number of dentinal tubules change as you move from the DEJ, closer to the pulp, and why is this important
number significantly increases; the more you prep → the more dentinal tubules get exposed → the more likely your pt is to experience sensitivity
what is the finish line referring to
a boundary surface of the actual tooth preperation
what is the margin referring to
the outer edge of an indirect restoration e.i. crown, inlay, onlay, etc
whenever possible, the finish line/crown margin should be _________ (subgingival/supragingival)
supragingival
advantages of placing your margin supragingival (8)
improved bonding w no cervicular seepage
preservation of cervical tooth structure maintains structural integrity of the abutment
a dental dam could be used if indicated
they can be easily finished w/o associated soft tissue trauma
more likely to be kept plaque free
impressions are more easily made, w less potential for soft tissue damage
restoration can be easily evaluated at the time of placement and at recall apts
elevation of the restorative margin eliminates potential risks of chronic periodontal complications contributed by restorative dentistry
what are the indications for subgingival margin placement (6)
dental caries, cervical erosion, or restorations extend subgingivally and crown lengthening procedure is contraindicated
proximal contact area extends apically to the level of the gingival crest
additional retention, resistance, or both are need
the margin of an esthetic restoration is to be hidden behind the labiogingival crest
root sensitivity cannot be controlled by more conservative procedures
axial contour modification is indicated
what is the biological width
dimension of the soft tissue, that is attached to the portion of the tooth coronal to the crest of the alveolar bone
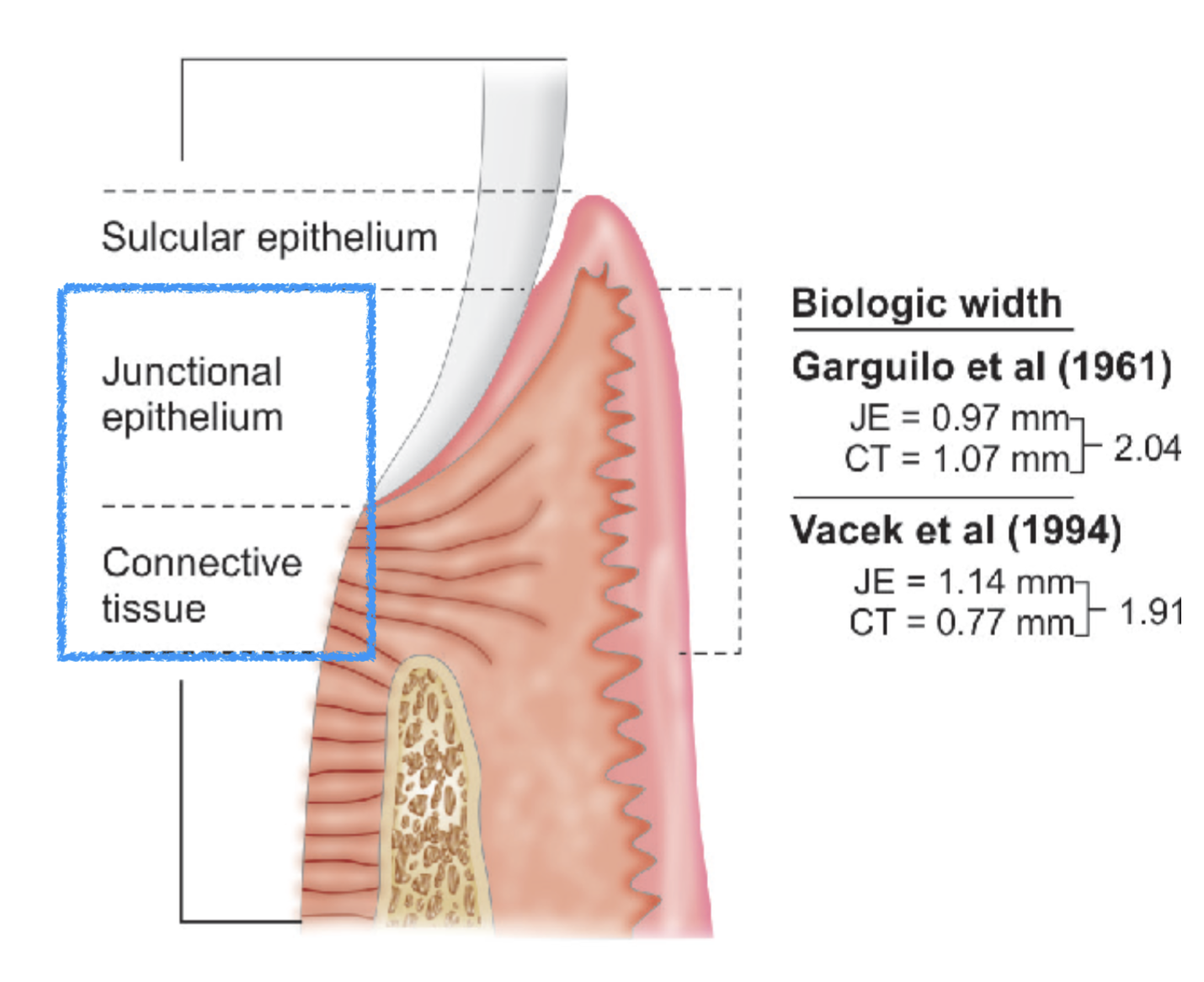
placing restorative margins within the biollgic width frequently leads to…
gingival inflammation, clinical attachment loss, and bone loss
a minimum of ____ mm of space is needed between the retorativemargins and the alveolar bone
3 mm
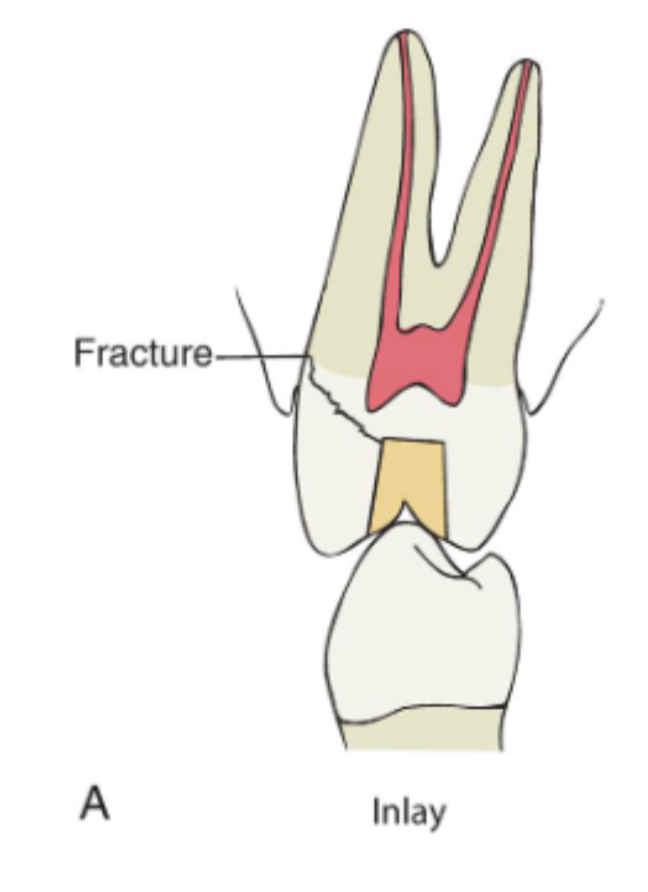
what is an inlay
an intracoronal cast restoration, does NOT include cusp coverage in restoration
how can fx occur in an inlay
inlays can act as a wedge during cementation or funx, but if cusps are weakened → fx will occur
what is an onlay
a cuspal-coverage restoration
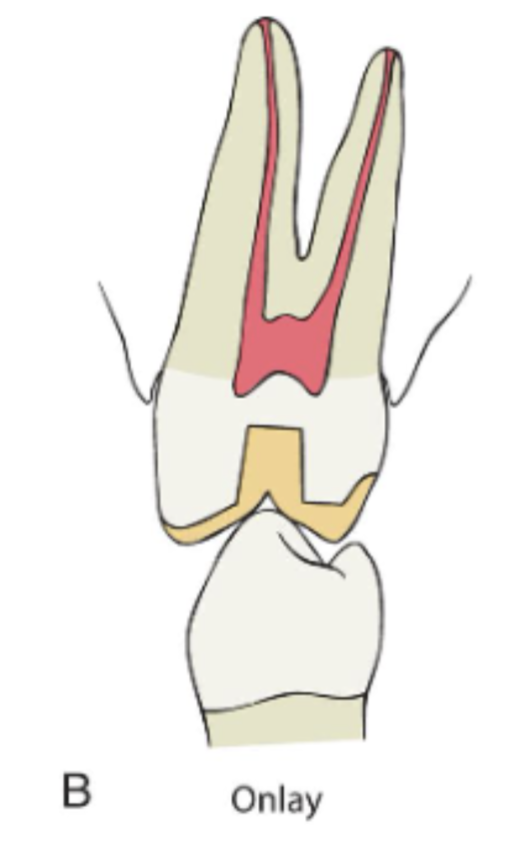
an onlay provides better ________ (retention/protection) but often lacks _______ (protection/retention)
provides better protection but often lack retention
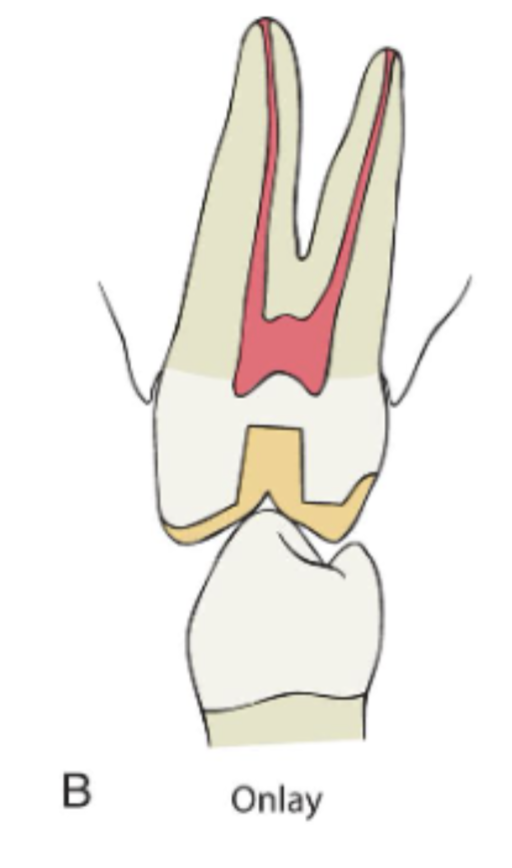
what indirect restoration provides the best protection against tooth fx AND has the best retention
complete crown
a complete crown can be associated w _______ ________ and _____ ________
associated w periodontal disease and poor esthetics
what are the mechanical considerations of tooth preps
providing retention form
providing resistance form
preventing deformation of the restoration (structural durability)
what is the path of insertion
is an imaginary line along which the restoration will be places onto or removed from the preparation
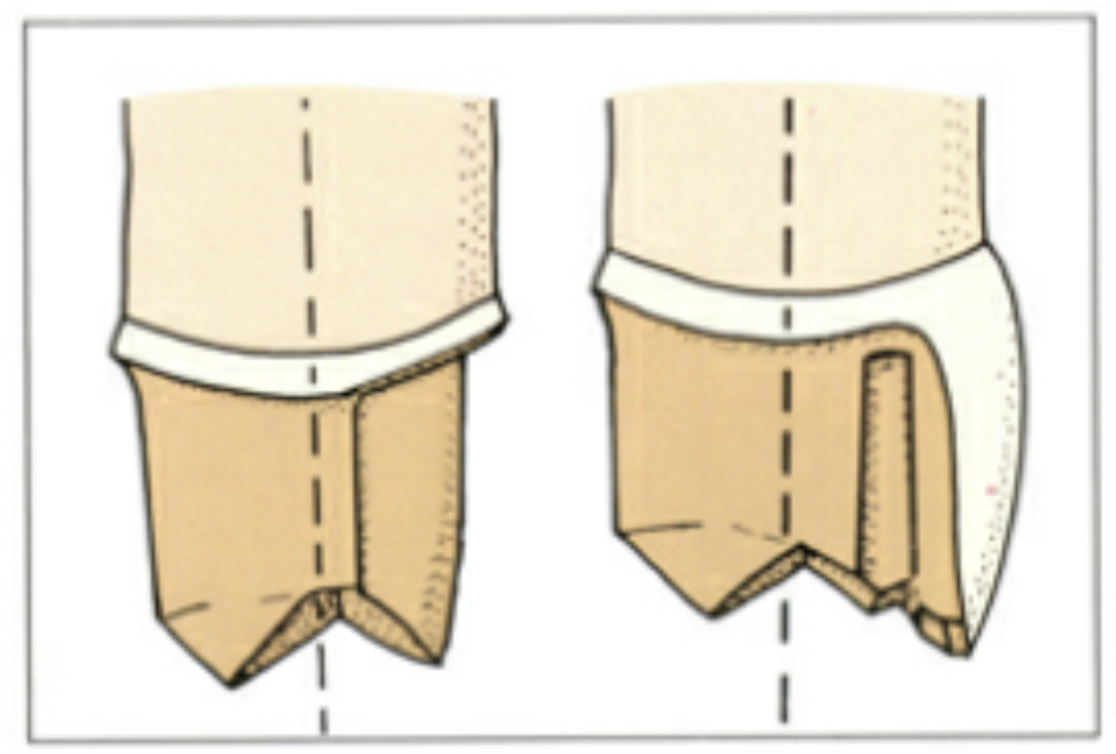
should the path of insertion be determined before or after the tooth is cut
before → this path should NOT encroach upon th epulp or adjacent teeth
what is the ideal path of insertion for a full or partial veneer crown
parallel w the long axis of the tooth
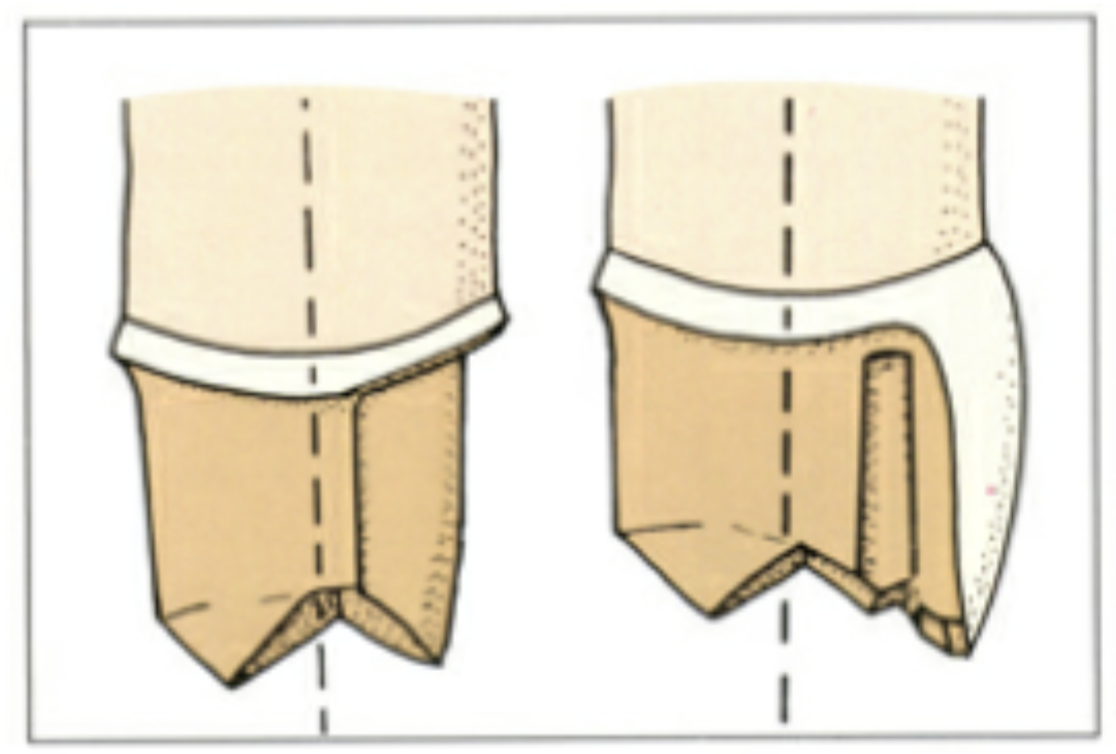
the path of insertion must be parallel to the __________ or it will be prevented from seating
parallel to the adjacent proximal contacts
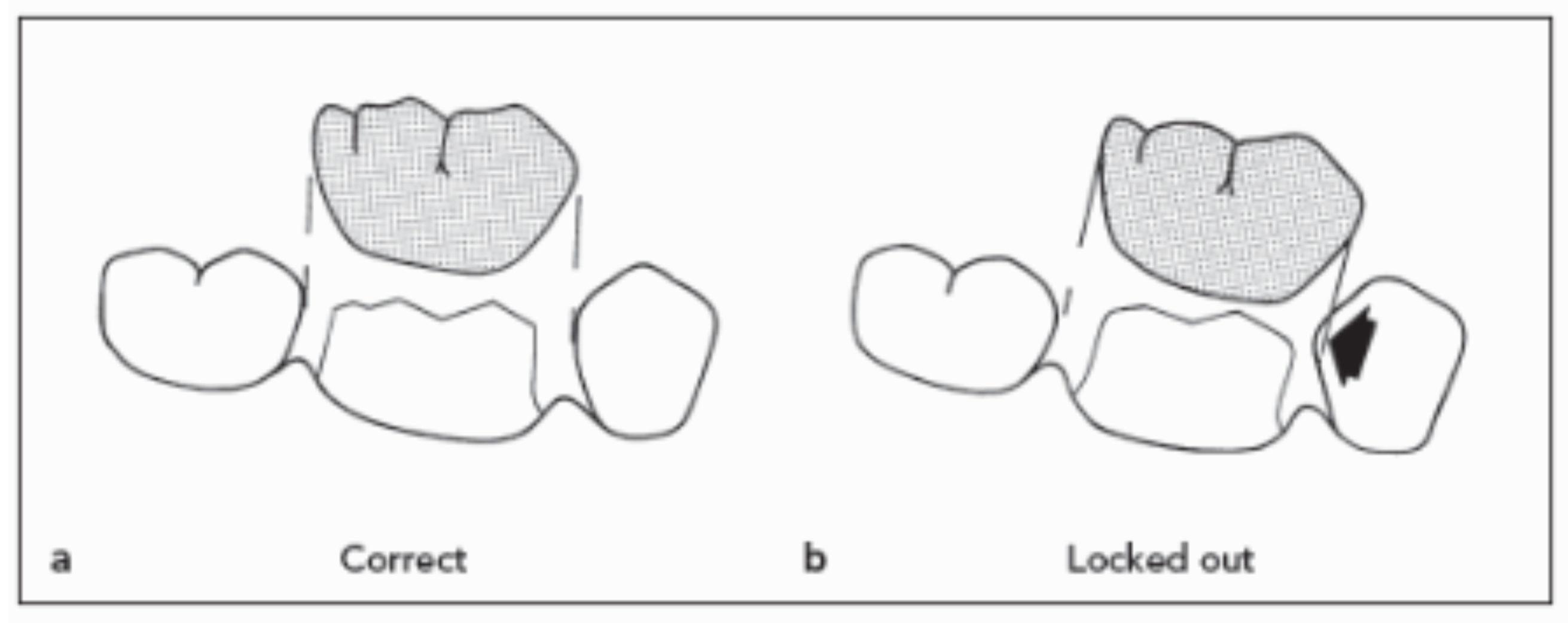
in what case would the path of insertion NOT be parallel to the long axis of the tooth
if the tooth was tilted (fig B), then the path of insertion paralleling the long axis of the tooth may be blocked by the proximal contours of the adjacent (fig C) → so path of insertion is made perpendicular to the occlusal plane (fig D)
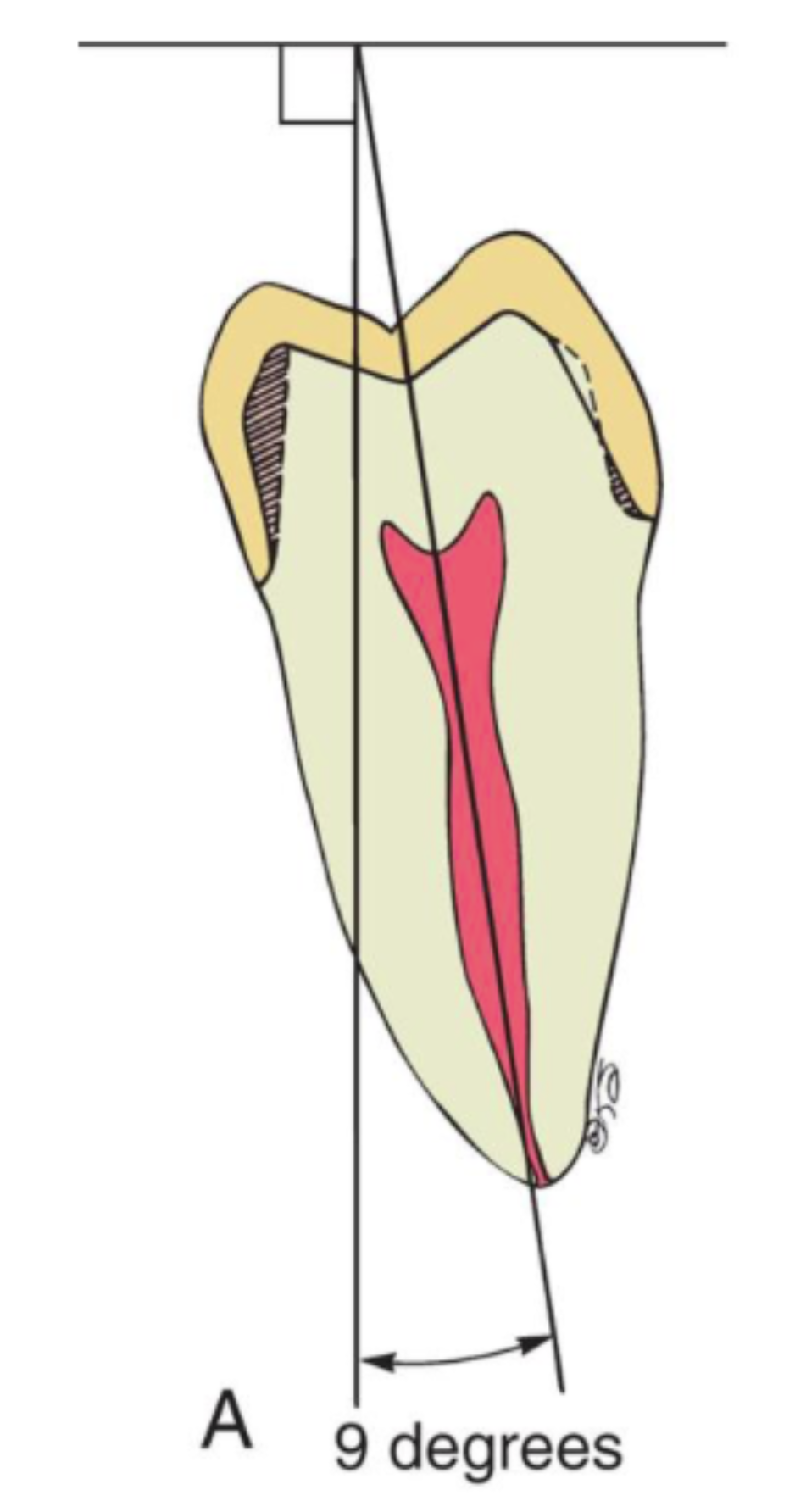
what is the typical incline of a mandibular molar
9 to 14 degrees lingually → path of insertion should coincide w this how
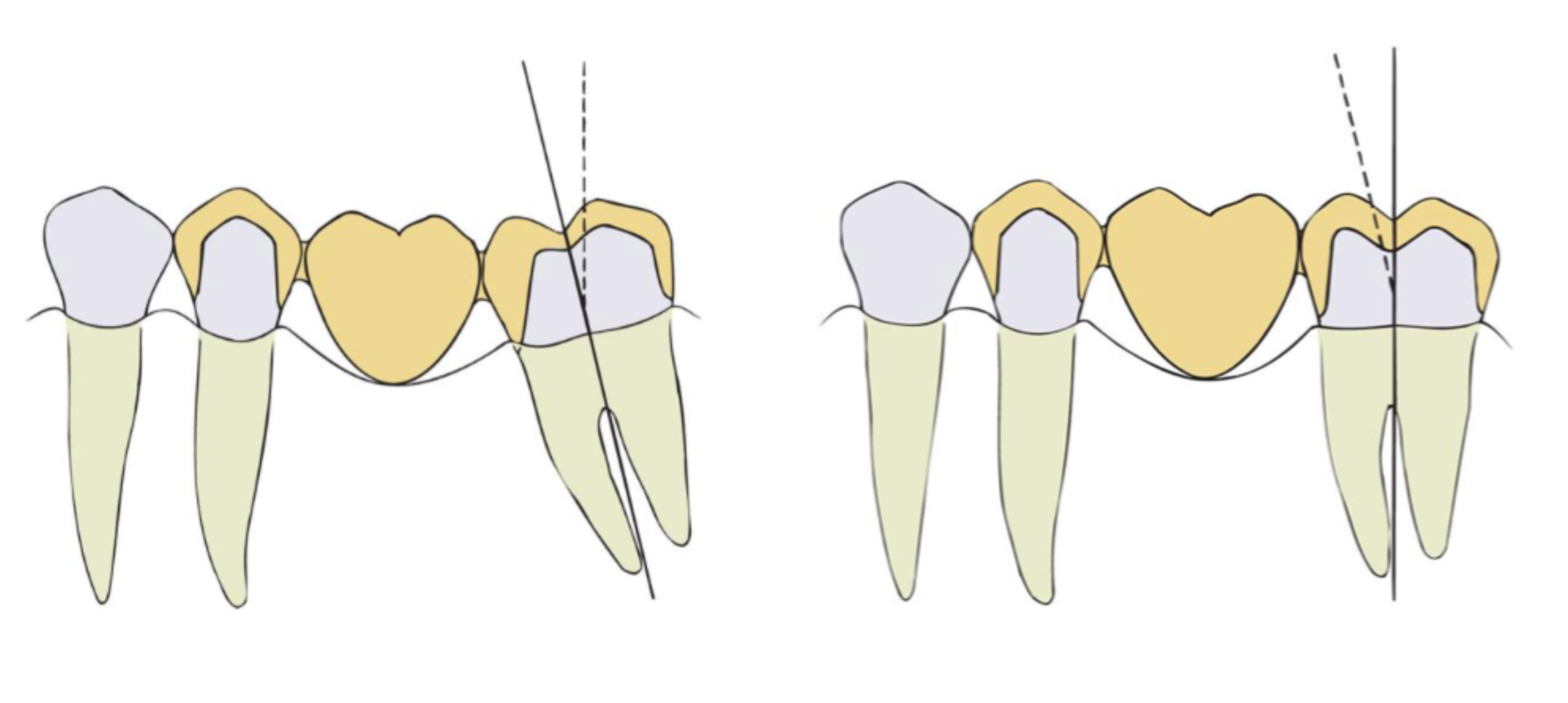
what is the common clinical error that results in additional unecessary removal of tooth structure (cross-hatched area)
preparing such a tooth w a path of placement that is perpendicular to the occlusal plane of the mandibular arch
how can ortho aid in crown preparation
ortho repositioning can help the crown prep be more conservative
definition of retention
prevents removal of the restoration along the path of insertion or long axis of the tooth preparation
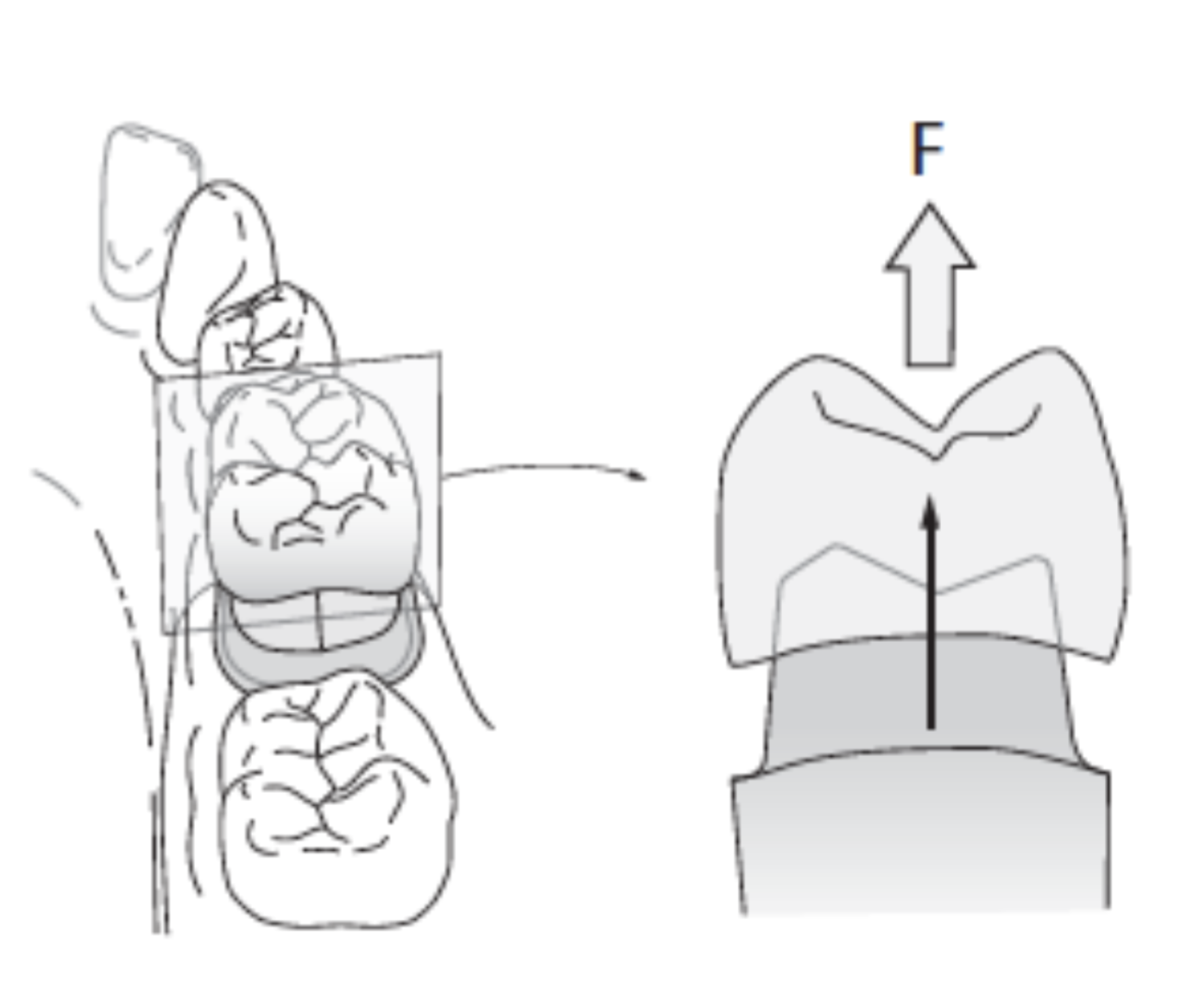
what is the essential element of retention
the two opposing vertical surfaces of the same preparation such as the buccal and lingual // mesial and distal walls
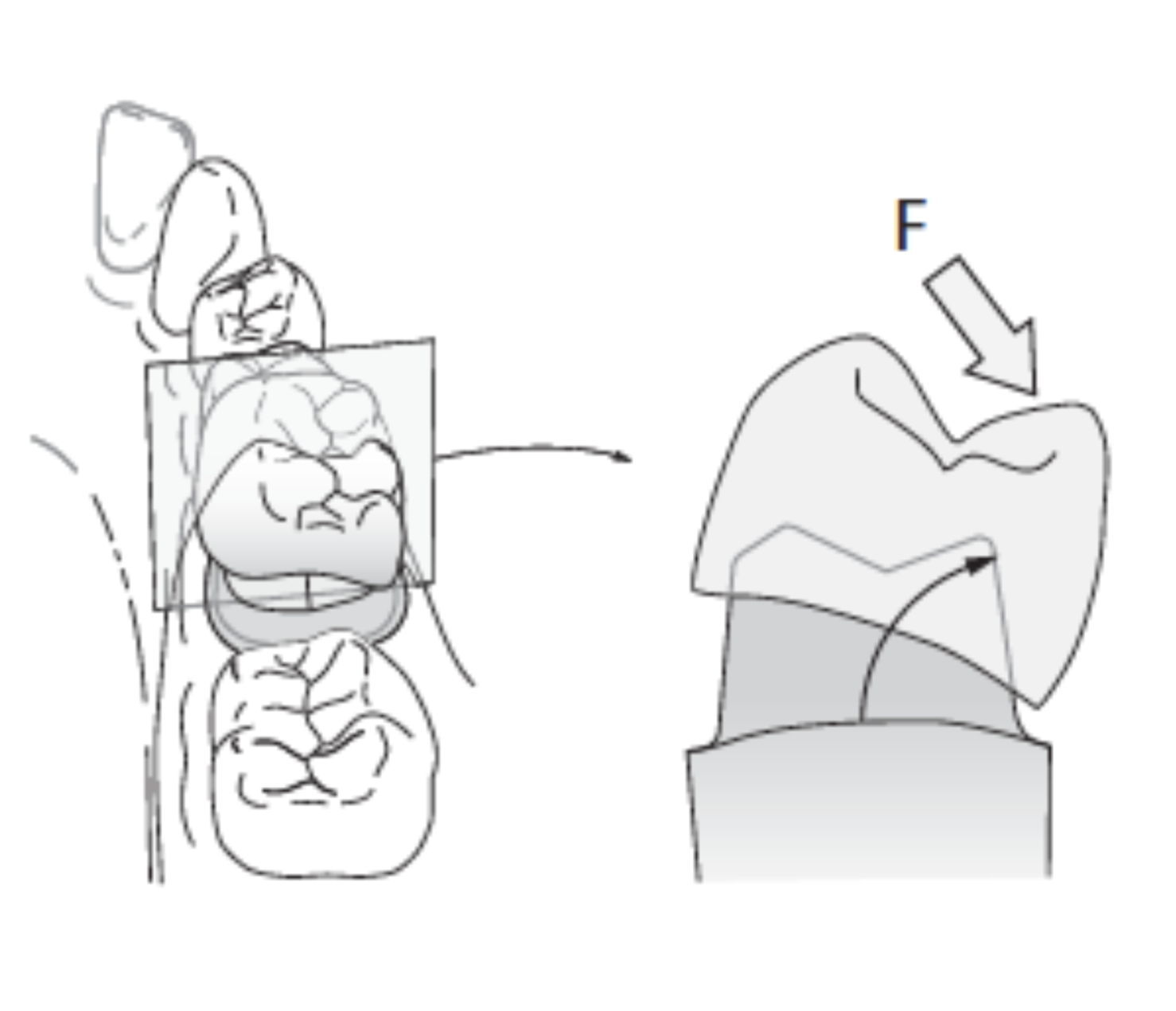
definition of resistance
prevents dislodgment of the restoration by forces directed in apical or oblique direction and prevents any movement
retention and resistance are ______, so they are often inseparable qualities
they are interrelated
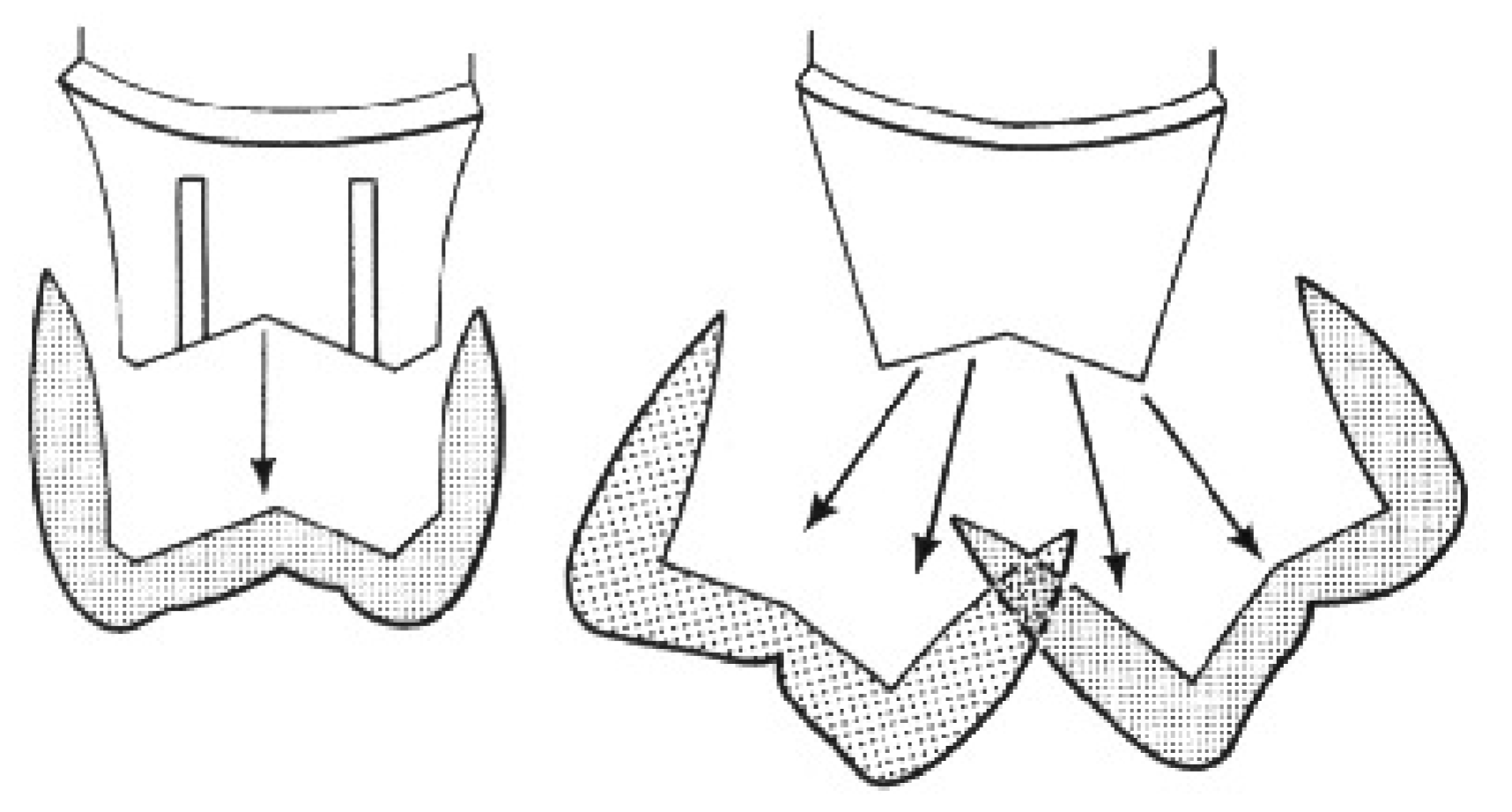
what are the factors influencing retention for a given fixed restoration in order (5)
magnitude of dislodging force
geometry or tooth preparation
roughness of the fitting surface of the restoration
material being cemented
film thickness and properties of the luting agent
forces that tend to remove a cemented restoration along is path of placement are very _____ (big/small) compared to ones that seat or tilt
v small
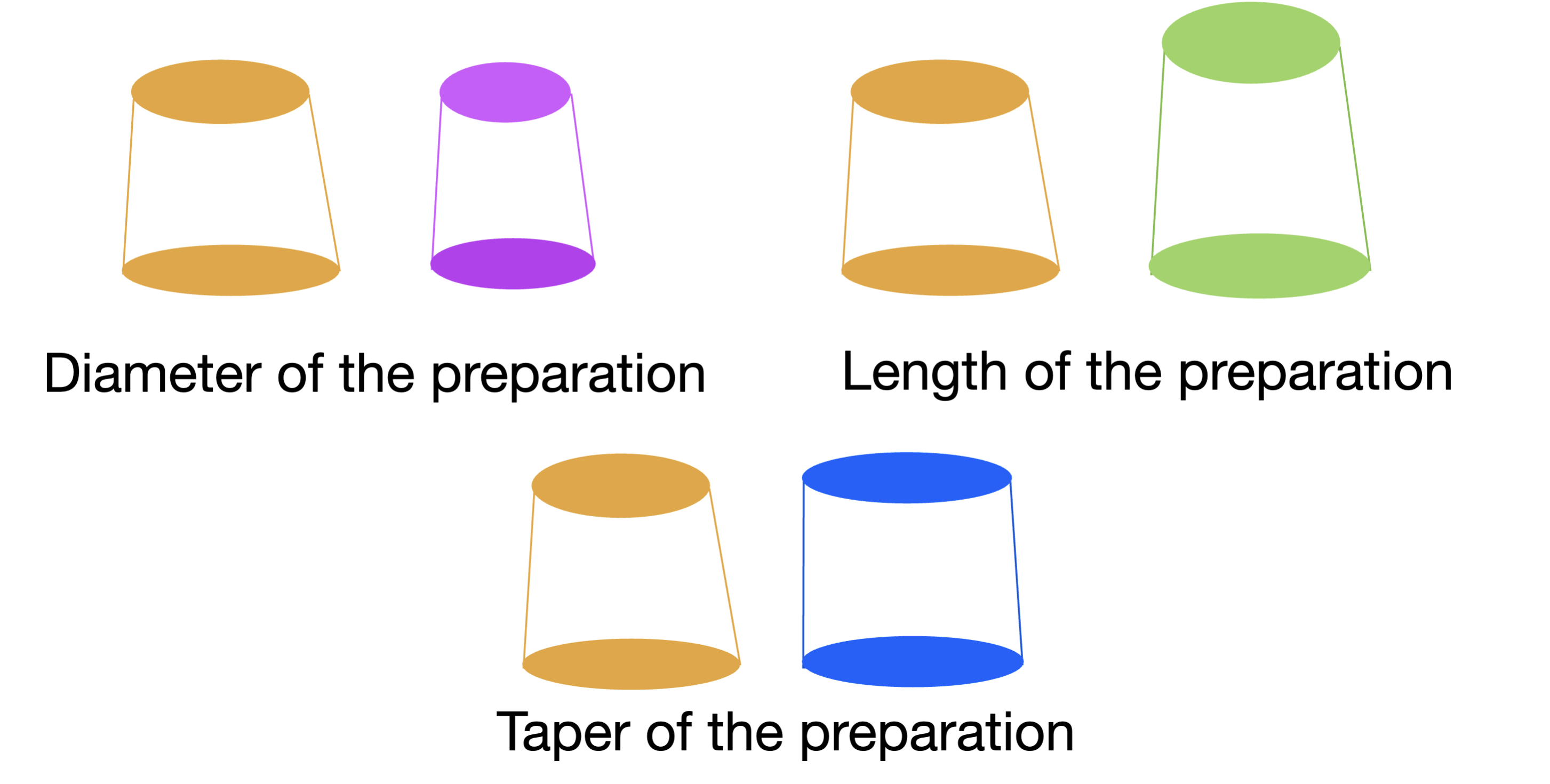
what are the 3 properties of retention-geometry of the prepared tooth
diameter of the preparation
length of the preparation
taper of the preparation
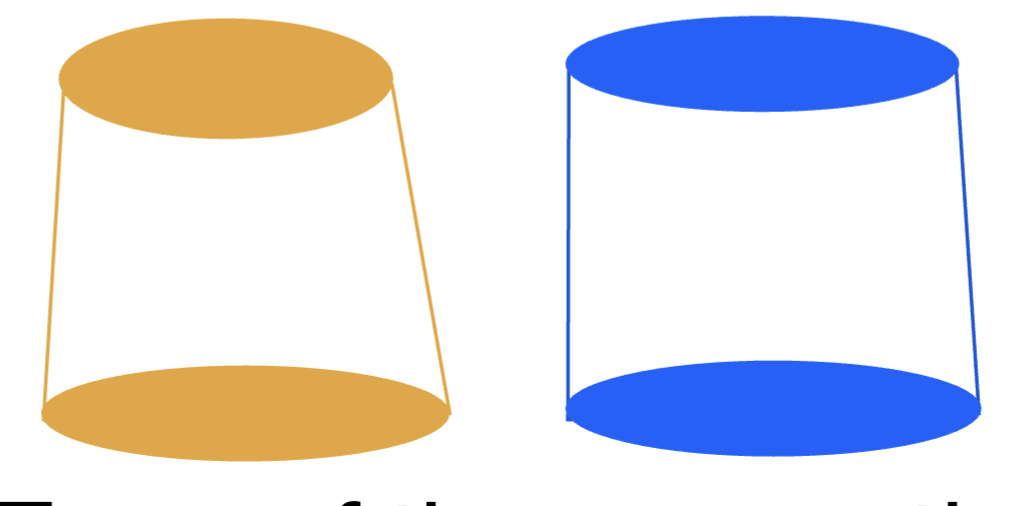
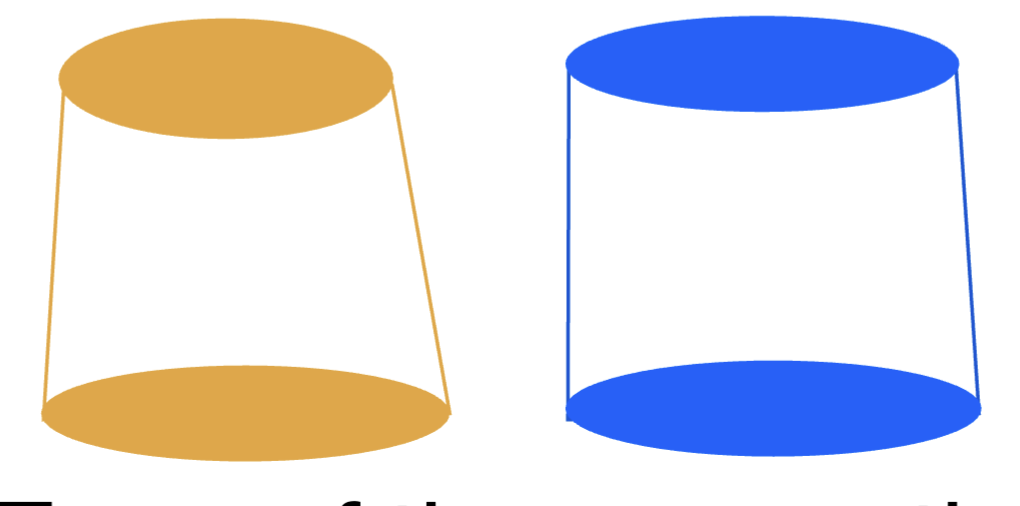
what will inc retention:
a slightly tapered wall
a slightly parallel wall
slightly parallel wall
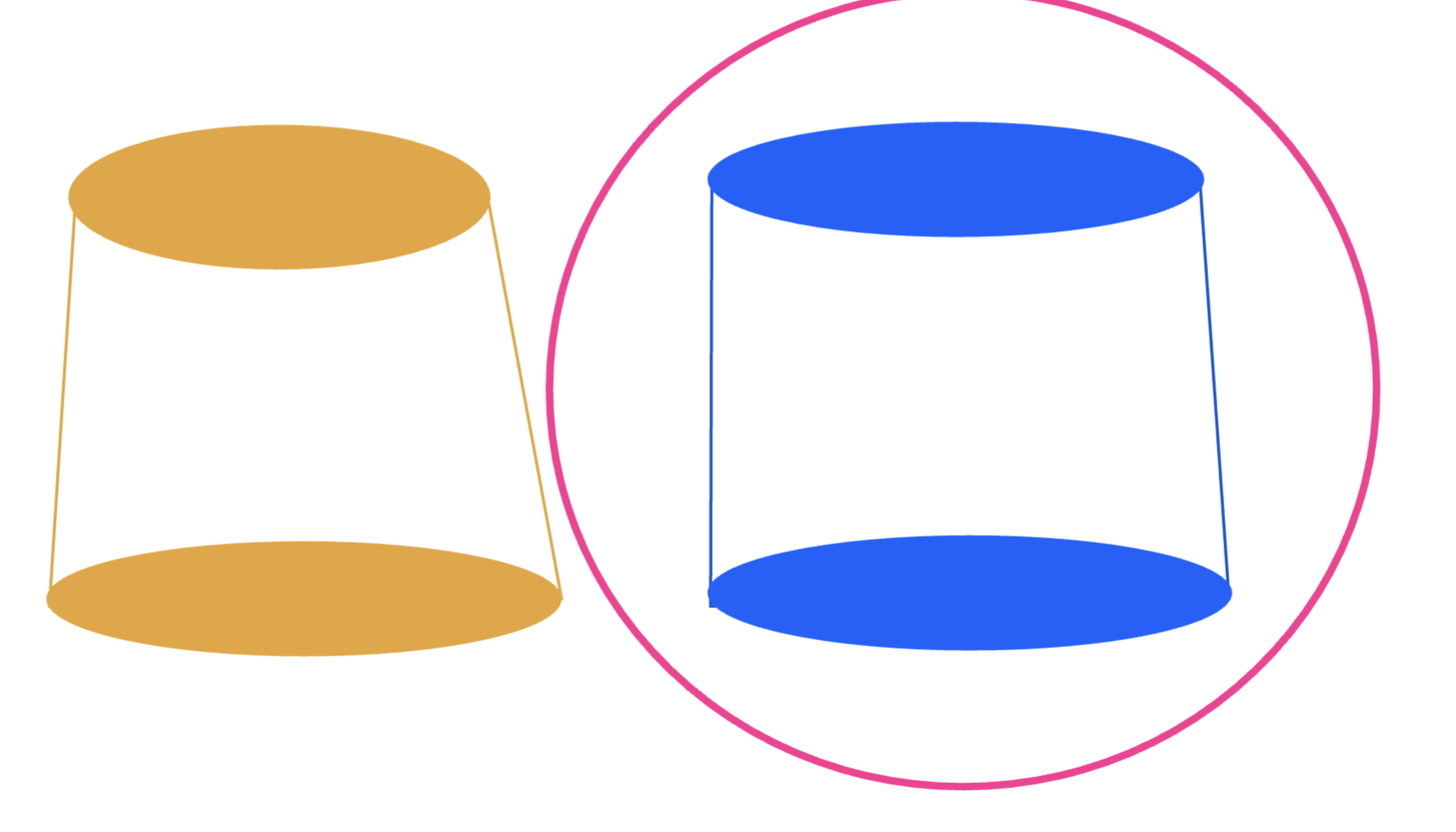
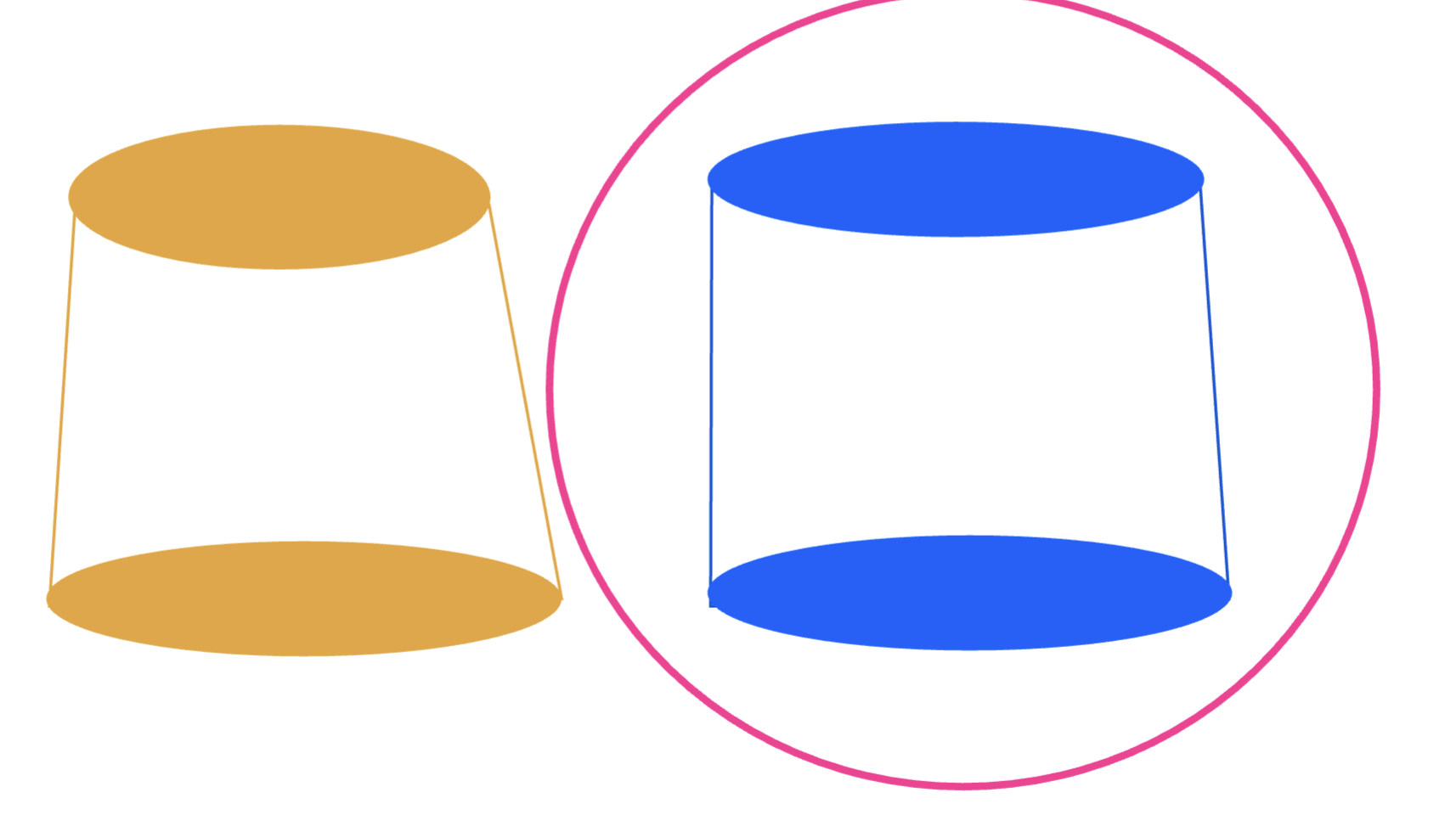
which would inc resistance:
a slightly tapered wall
a slightly parallel wall
a slightly parallel wall
definition of taper
the convergence of two oppsoite external walls of a crown preparation as viewed in a given plane
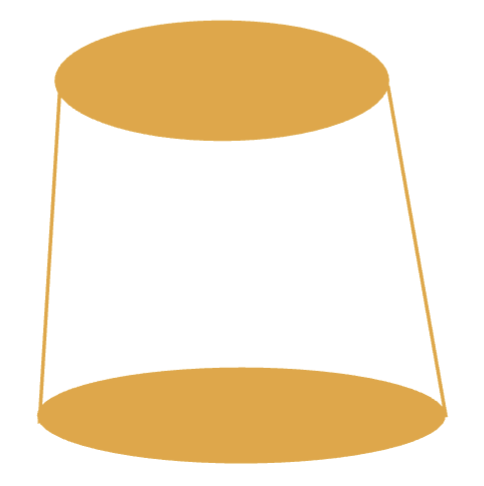
what is the angle of convergence/ total occlusal convergence (TOC)
the extension of the two opposite-facing external walls in a given plane forming an angle
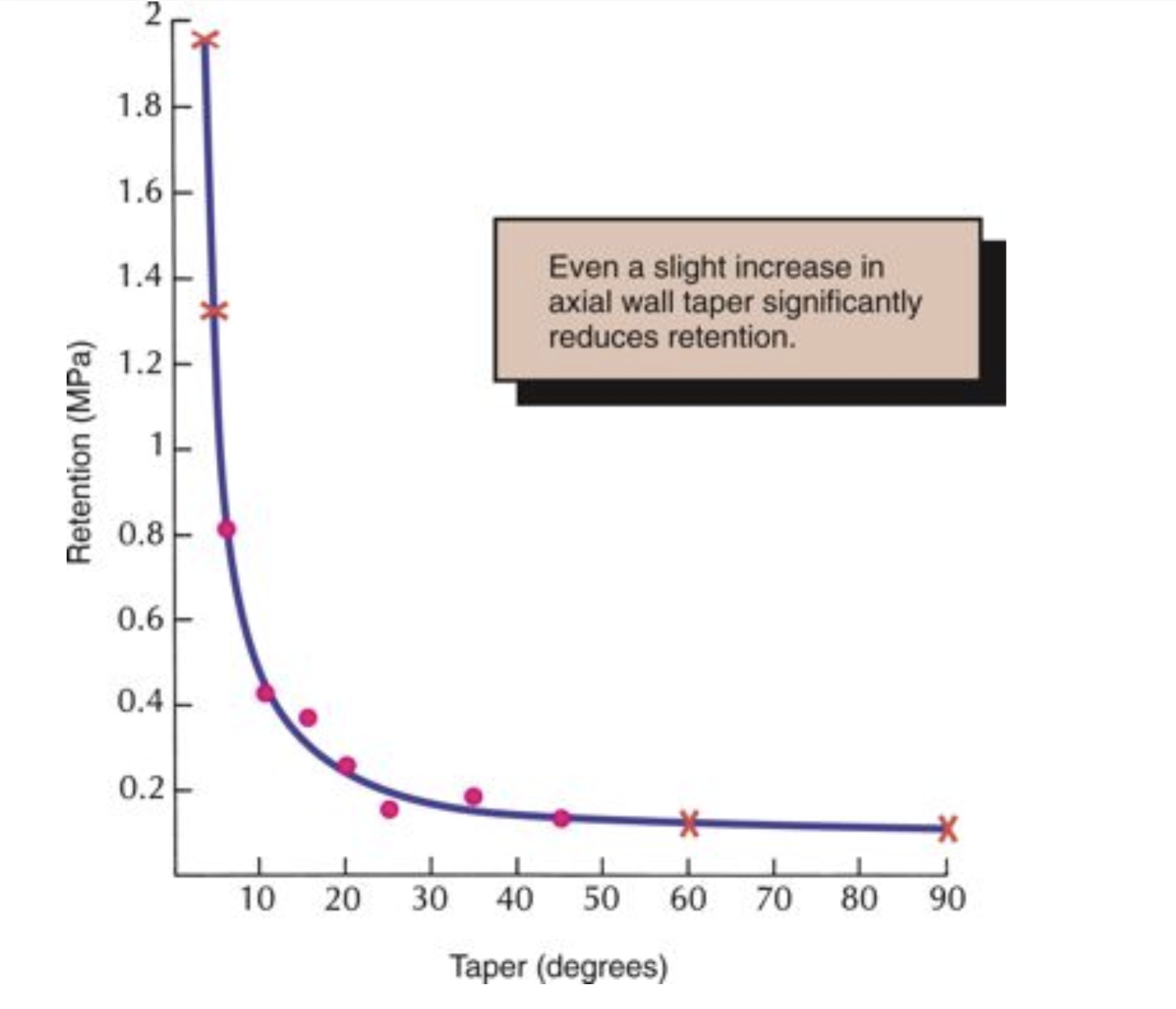
what effect does even a slight taper have on retention
significantly reduces retention
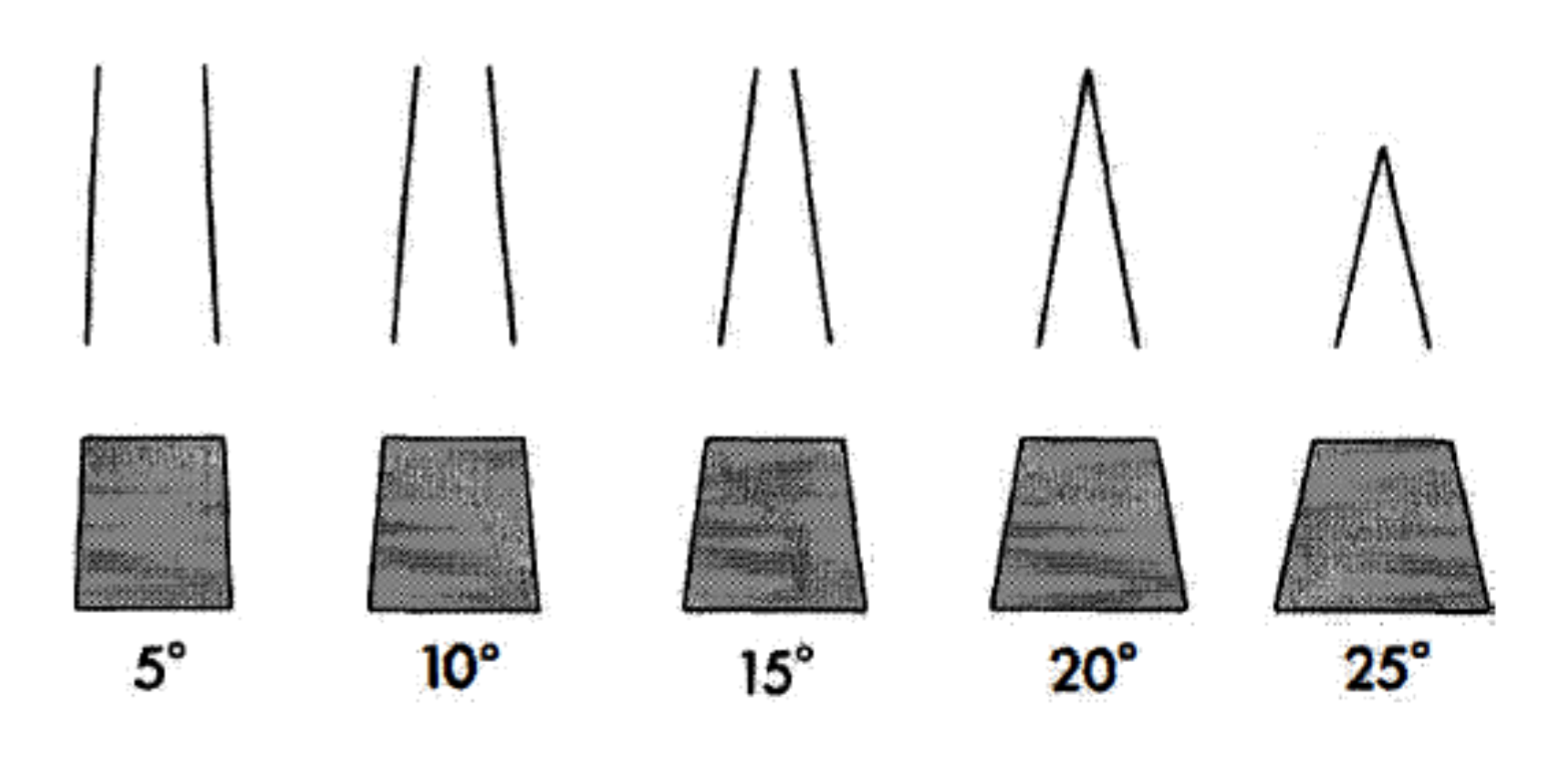
the recommended convergence between opposing walls is ____ degrees, which has been shown to optimize retention for _____________ cement
6 degrees; zinc phosphate cement
what is a clincially acceptable taper range for a complete crown
range from up to 5-20 degrees
why can the TOC not be as parallel as possible
to allow escape of excess luting agent during seat of the crown
slight undercuts are often present in preparations that are too cylindrical and prevent the restoration from seating
definition of undercut on a complete crown preparation
any irregularity in the wall of a prepared tooth that prevents the withdrawal or seating of a wax pattern of crown
how can undercuts be present
can be present whenever two axial walls face opposite directions
divergence is inadvertently created between opppsite-facing external axial wall, or wall segments in a cervico-occlusal direction
how do you evaluate preparation taper to ensure all negative taper/undercuts are eliminated
view w one eye from a distance of approximately 30 cm or 12 inch
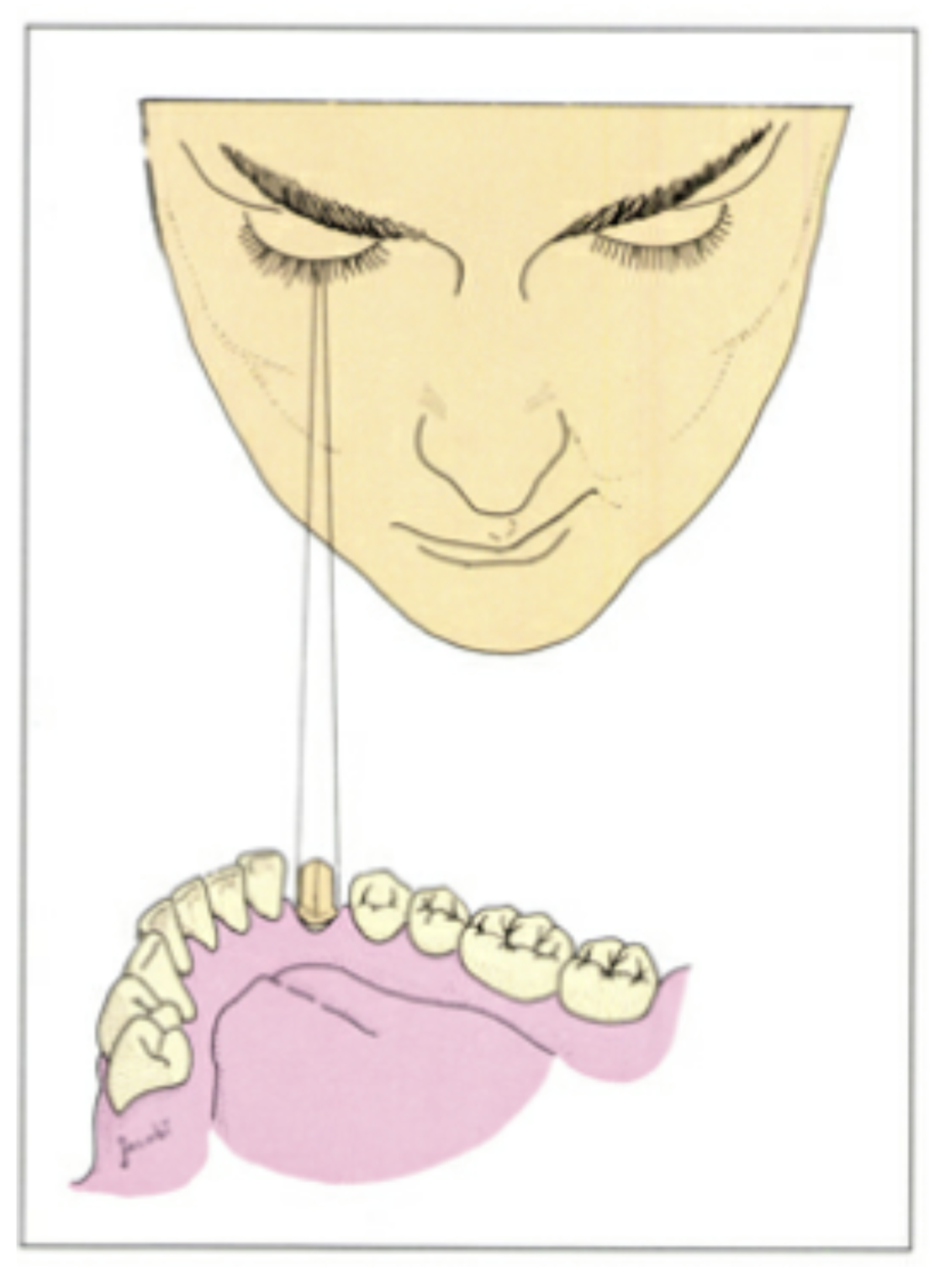
why do we only use one eye during evaluation of preparation taper
an undercut as great as 8 degrees can be overlooked if both eyes are used
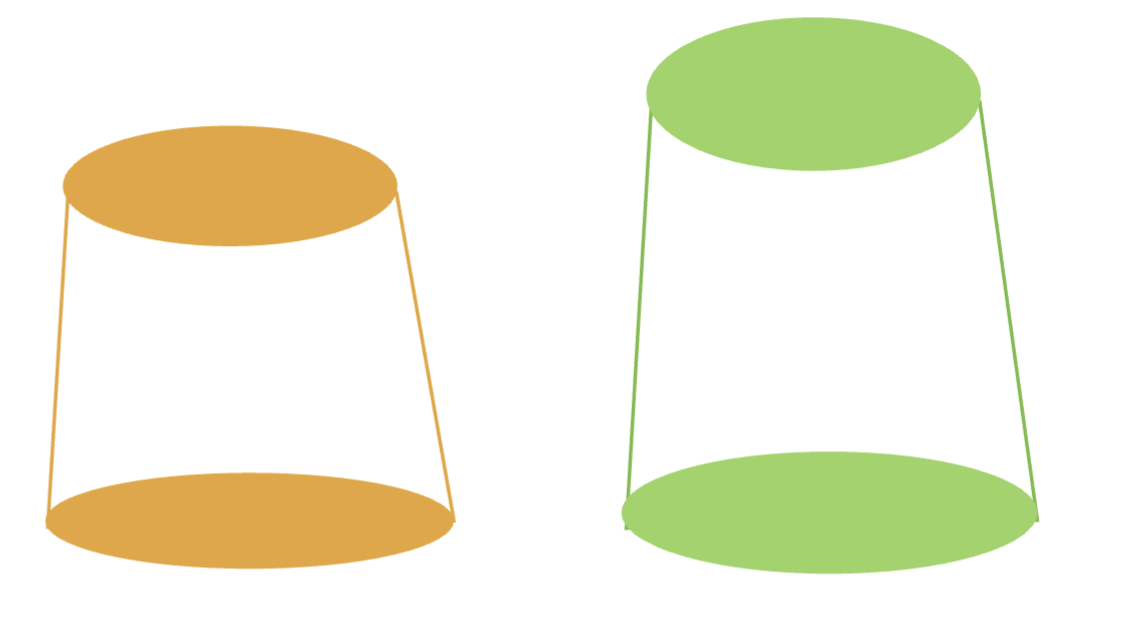
what will inc retention:
dec in height
inc in height
taller preps help retain crowns better, but beyond a certain height, the extra retention gain is less significant
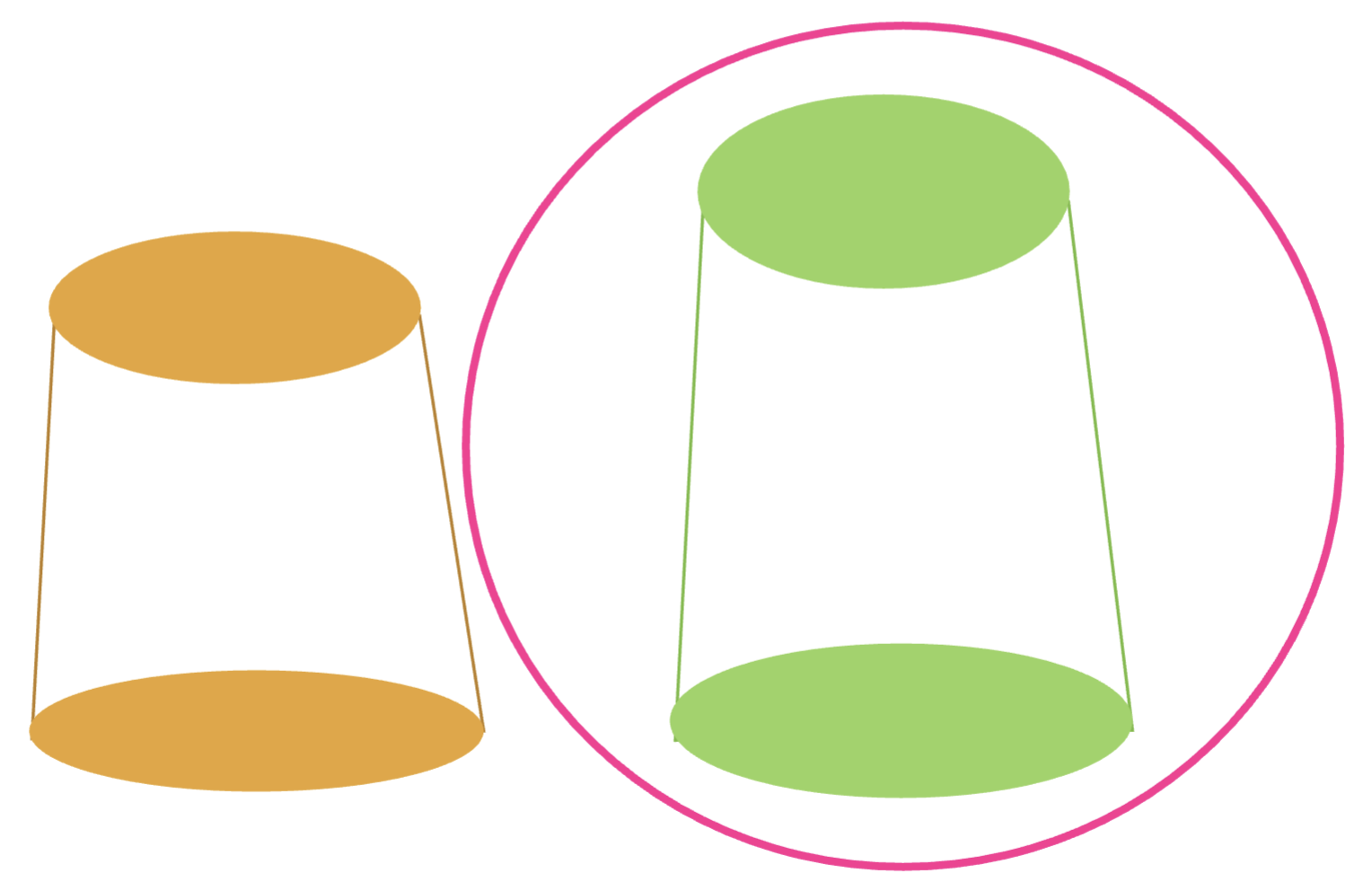
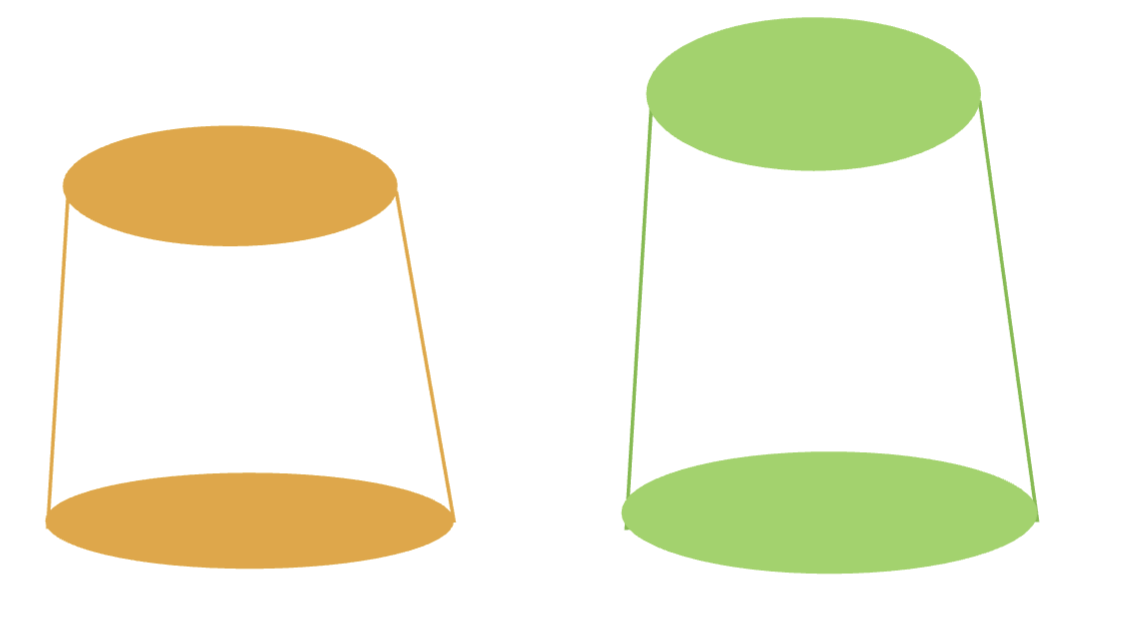
what will inc resistance:
dec height
inc height
inc height
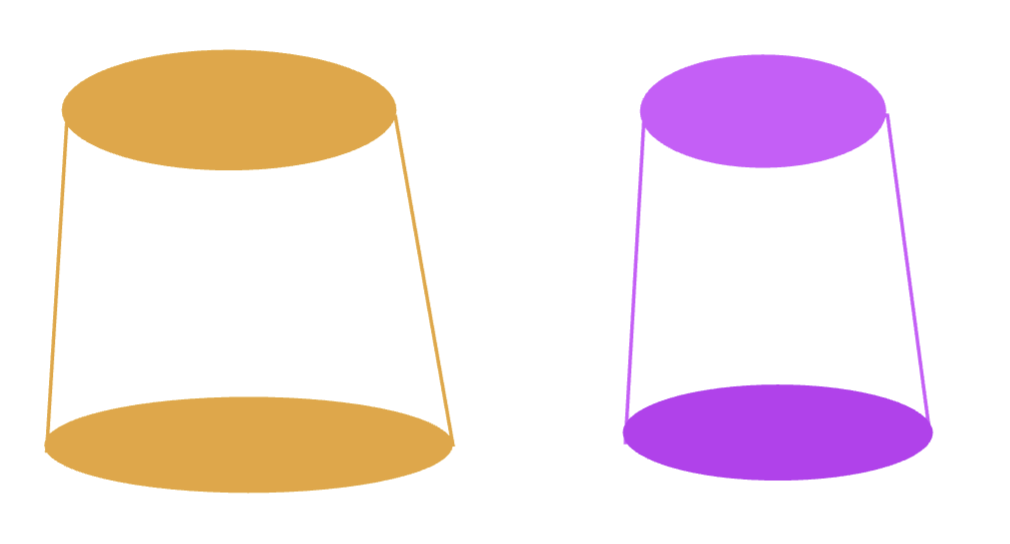
what will inc retention:
dec in diameter
inc in diameter
inc in diameter gives a linear inc in retention
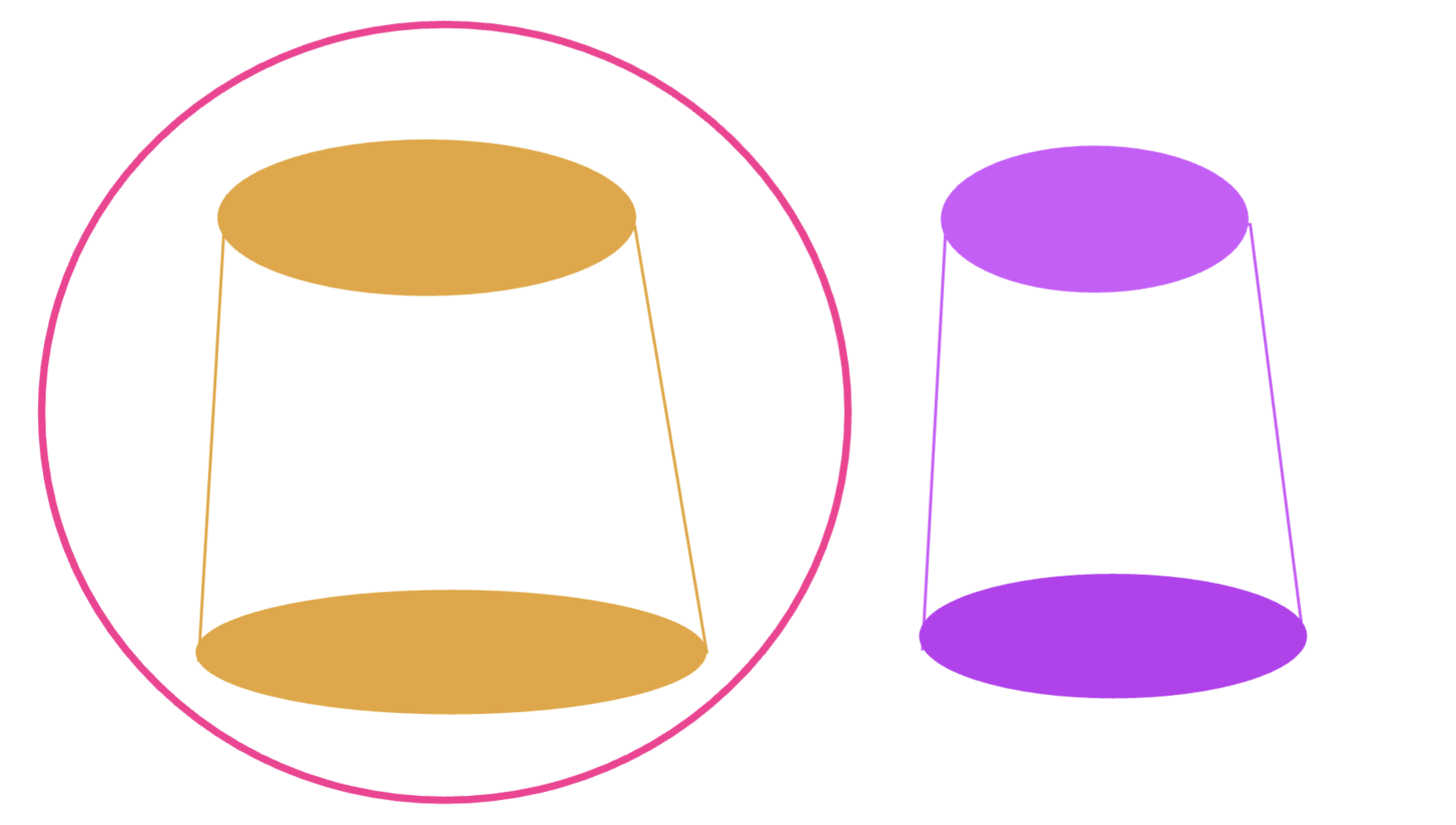
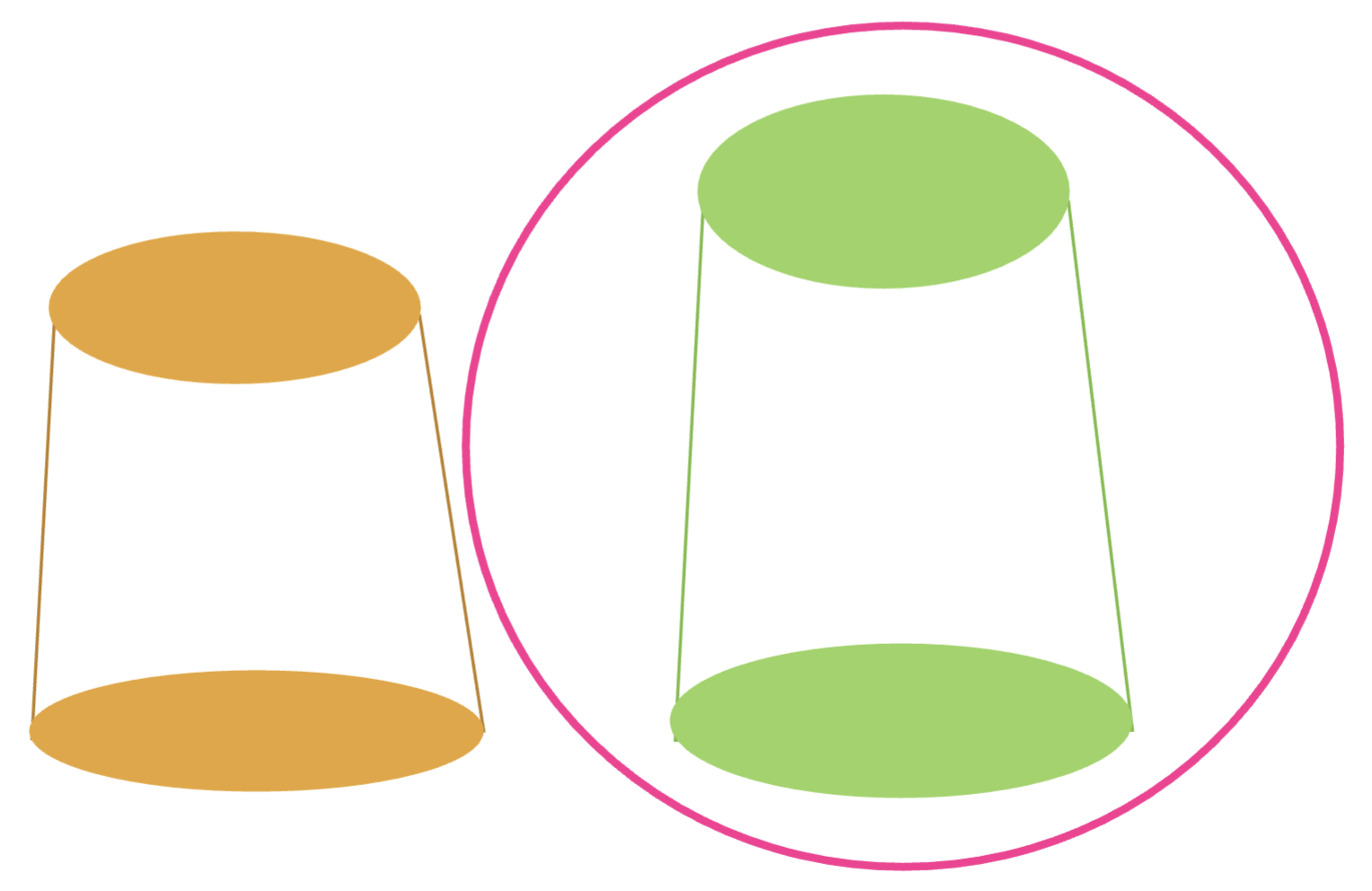
what will inc resistance:
dec in diameter
inc in diameter
dec in diameter
__________ ___________ is an important factor in both retention and resistance
occlusogingival length
what is the minimal incosocervical dimension of incisors and premolars when prepared w 10-20 degrees of TOC
3 mm
what is the minimal occlusocervical dimension of molars when prepared w 10-20 degrees of TOC
4 mm
what helps in adequate clearance and does not require excessive tooth reduction
an anatomically prepared occlusal surface
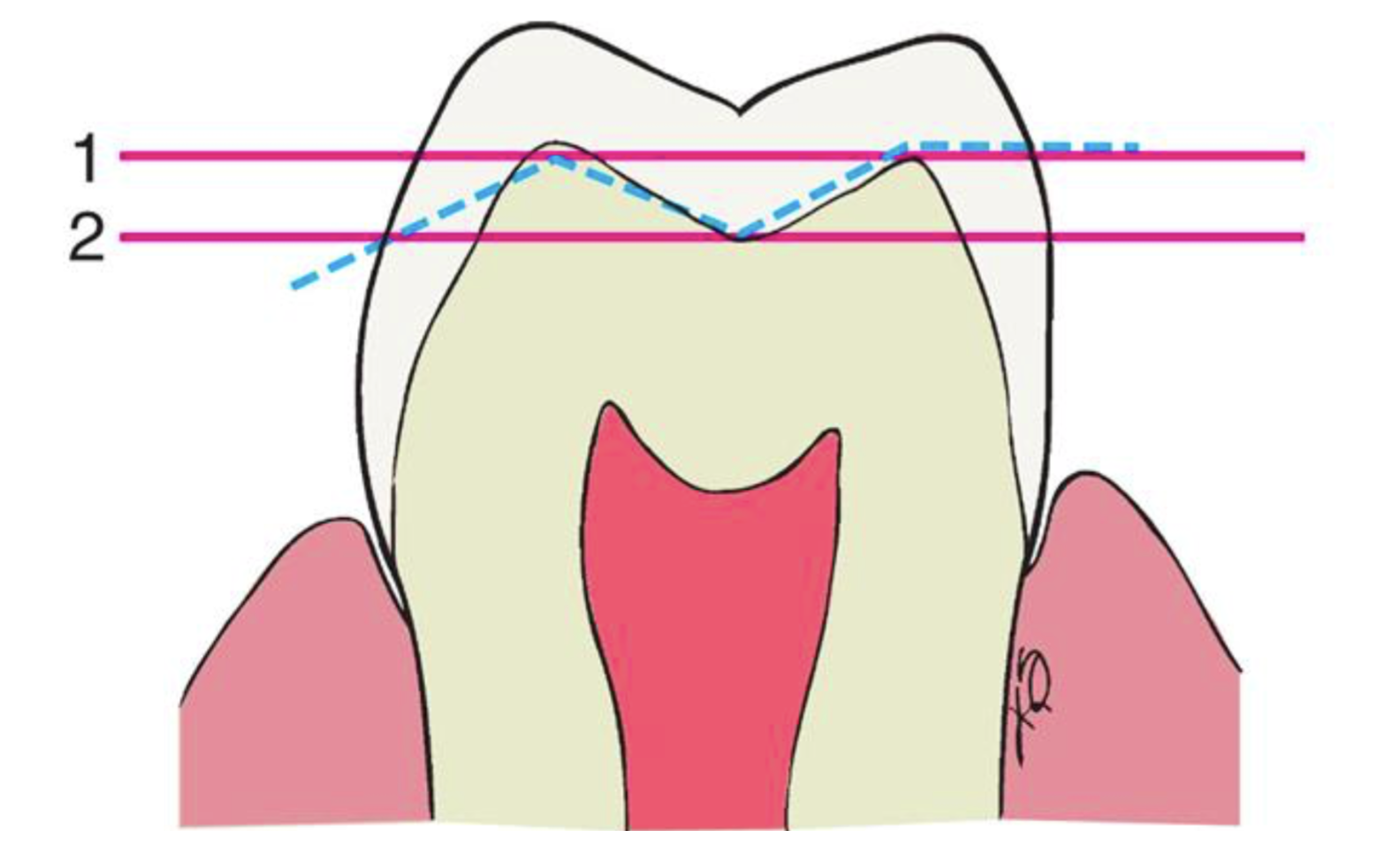
what can a flat occlusal surface preparation result in (2)
insufficient clearance
or an excessive amount of reduction
what factors are affected (2) of the occlusal surface if the preparation does NOT follow the contour of the unprepared tooth
height dec
surface area dec (friction)
metal castings are most effectively prepared by…
airborne particle abrading the fitting surface w 50 microns of alumina
______ _______ of the fitting surface of restorations can improve retention w certain luting agents
acid etching
overall, roughening the tooth preparation has what influence on retention and is it recommended
hardly influences retention, NOT recommended
how is evidence supporting: retention is affected by both the type of castign alloy and any core buildup material that is present on the axial walls of the crown prep
clinical significance is not confirmed
conflicting results w different in vitro studies
how is evidence supporting: the effect of inc thickness of the cement film on retention of a restoration
conflicting evidence
what 6 factors influence retentive properties of a restoration
taper
surface area
type of preparation
surface texture
film thickness
luting agent
rank these factors from greater retentive properties to lesser:
6 degree taper
parallel
excessive taper
parallel > 6 degree > excessive taper
rank these factors from greater retentive properties to lesser:
small surface area
large surface area
large > small surface area
rank these factors from greater retentive properties to lesser:
smooth surface texture of intaglio of restoration
rough surface texture of intaglio of restoration
rough > smooth
retentive effect of film thickness
effect uncertain
rank these factors from greater retentive properties to lesser:
glass ionomer luting agent
polycarboxylate/zinc oxide-eugenol luting agent
adhesive resin luting agent
zinc phosphate luting agent
adhesive resin > GI > polycarboxylate/zinc oxide-eugenol > zinc phosphate
adequate resistance depends on what 3 things
magnitude and direction of the dislodging forces
geometry of the tooth preparation (primary and secondary retentive features)
physical properties of the luting agents
resistance is a funx of the relationship between what factors
axial wall taper
preparation diameter
preparation height
what factors can interfere w rotational radius of a tooth preparation
tooth diameter
occlusal-gingival length
amount of taper
retentive features (bow, groove)
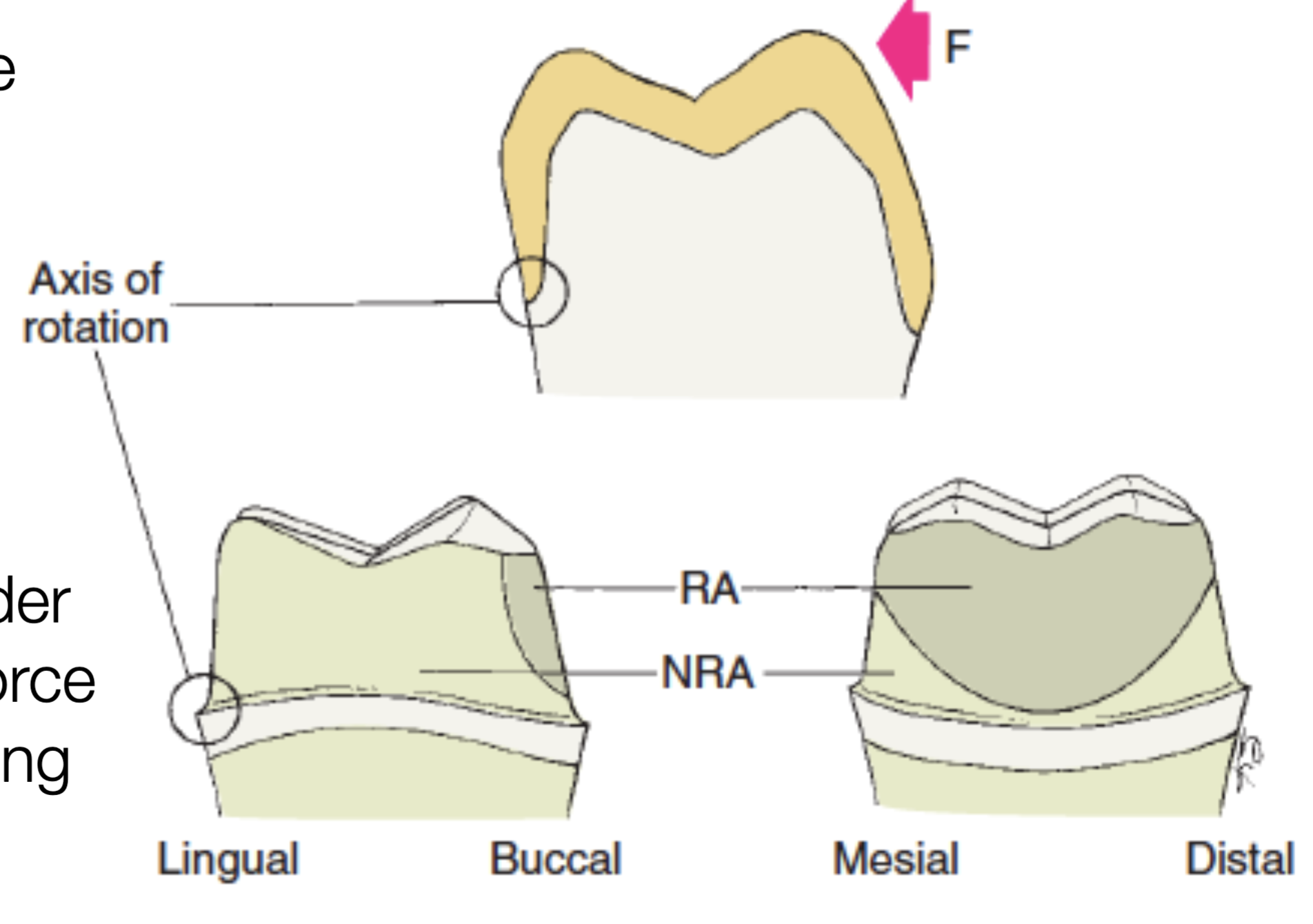
how can lateral forces displace a restoration, specifically talking about the rotational radius
causes the rotation around the gingival margin, effectively tipping the crown off its preparation
what area of a complete crown is placed under compression when a lateral force is applied
the resistance area (RA)
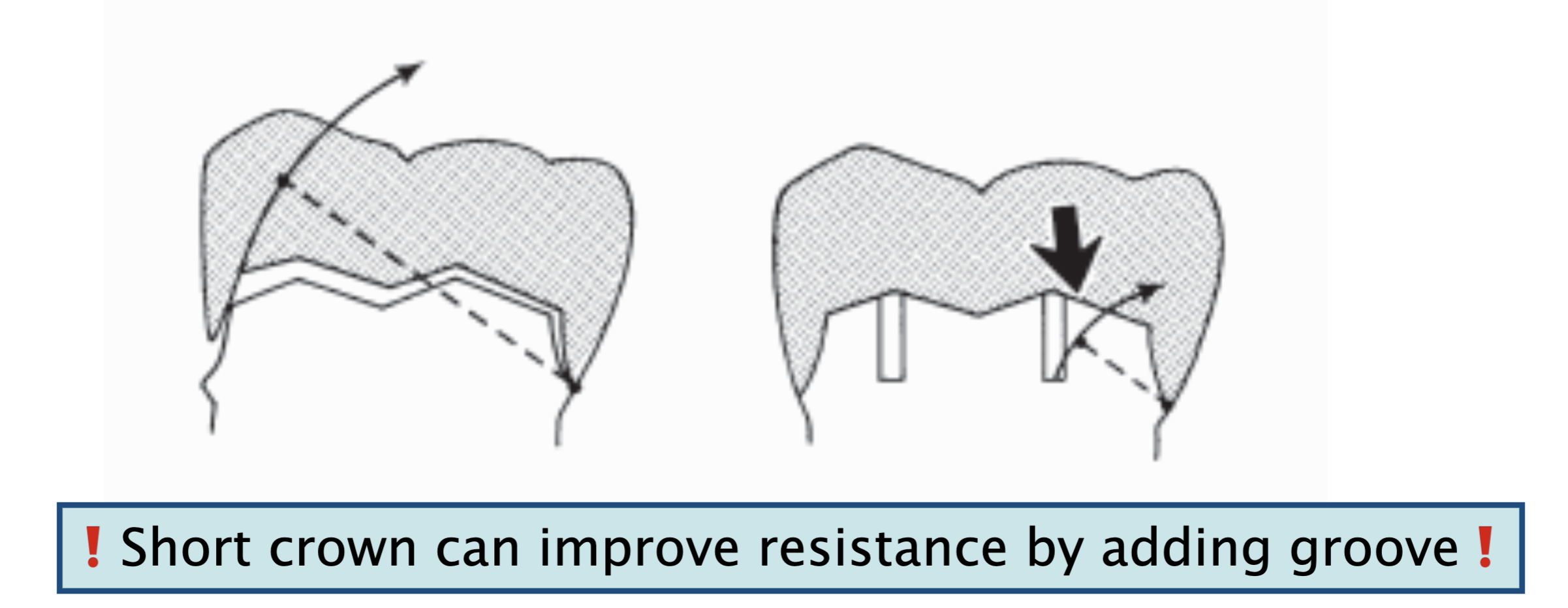
______ (short/tall) tooth preparations w ________ (small/large) diameter were found to have very little resistance form
short tooth preparations w large diameter
which teeth require a more parallel preparation than other teeth to achoeve adequate resistance form
molar teeth require more than premolar or anterior teeth
why does retention inc when the diameter is larger
bc this inc surface area
why does resistance inc when the diameter is smaller
bc the shorter rotational radius for the arc of displacement
what can be placed in healthy tooth structure that are effective in enhancing the resistance form of crown preparations
proximal grooves or boxes
why does proximal grooves or boxed improve resistance
these interfere w rotational movement (tipping) of the crown and thereby subject additional areas of the luting agent to compression
resistance to deformation is affected by physical properties of…
the luting agent, such as compressive strength and modulus of elasticity
what are the 6 factors that influence resistance
dislodging forces
taper
diameter
height
type of preparation
luting agent
rank these dislodging forces from most to least resistant:
habits
anterior guidance
eccentric interferences
habits > eccentric interferances > anterior guidance
rank these from most to least resistant:
minimum taper
excessive taper
6 degrees
minimum > 6 degrees > excessive
rank these from most to least resistant:
small diameter premolar
large diameter molar
premolar > molar
rank these from most to least resistant:
average height
large height
short height
long > average > short
rank these from most to least resistant:
onlay
partial coverage
complete coverage
complete coverage > partial > onlay
rank these luting agents from most to least resistant:
glass ionomer
adhesive resin
polycarboxylate
zinc oxide
zinc phosphate
adhesive resin > GI > zinc phosphate > polycarboxylate > zinc oxide
how can you prevent deformation of a restoration
adequate tooth reduction
what are the 3 componenets of adequate tooth reduction
occlusal reduction
functional cusp bevel
axial wall reduction
what can be made before tooth preparation to facilitate evaluationof tooth reduction uniformity
putty index
the finish line design requires a design that can provide enough …. to resist deformation
must provide enough bulk of the material
what are the 2 finish line designs we practice
chamfer (what we doing now)
shoulder
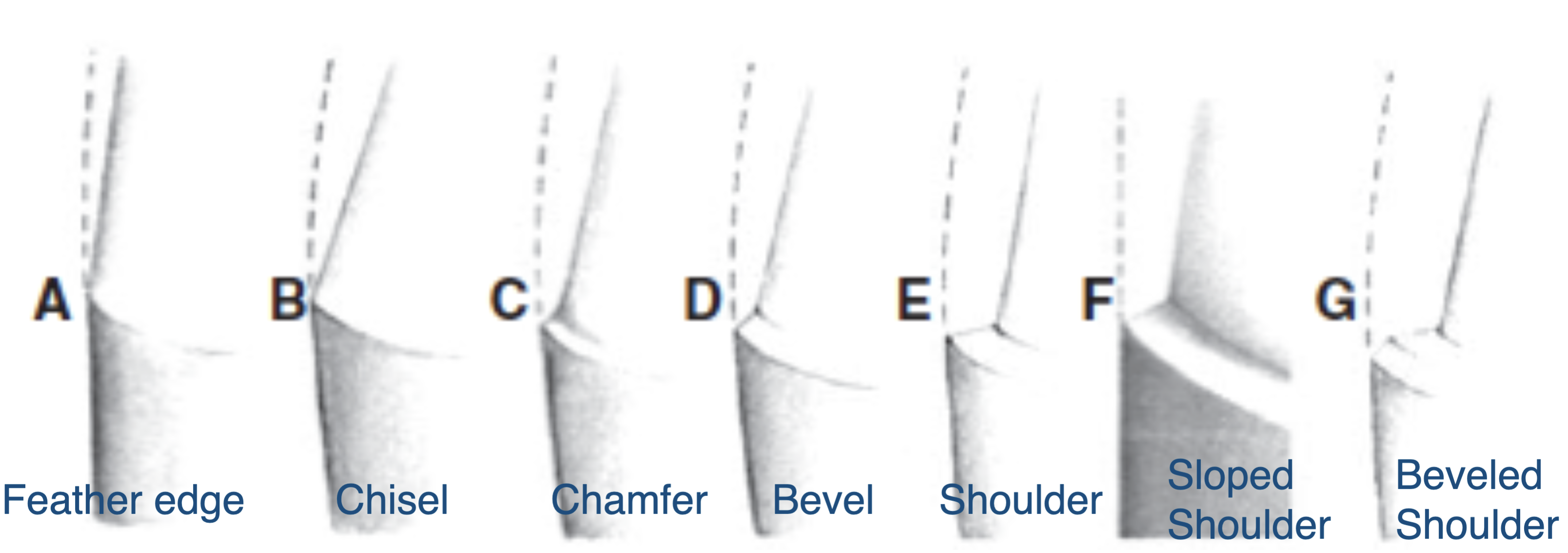
advantages of chamfer margin design
distinct margin, adequate bulk, easier to control
disadvantages of chamfer margin design
care needed to avoid unsupported lip of enamel