Ch9: Islands on Dry Lands/Invasive Species
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Dr. Thomas Lovejoy
decided to gain insight of habitat fragmentation on species of the rainforest in the Amazon
cattleman were asked to clear forests and got stipends from the government in doing so
they left some areas in tack, creating “islands”
dr’ Lovejoy wanted to study these areas and protect them
found that some species will go extinct in the areas of islands, there is a biodiversity loss
thanks to his work, over 50% of the rainforest is protected
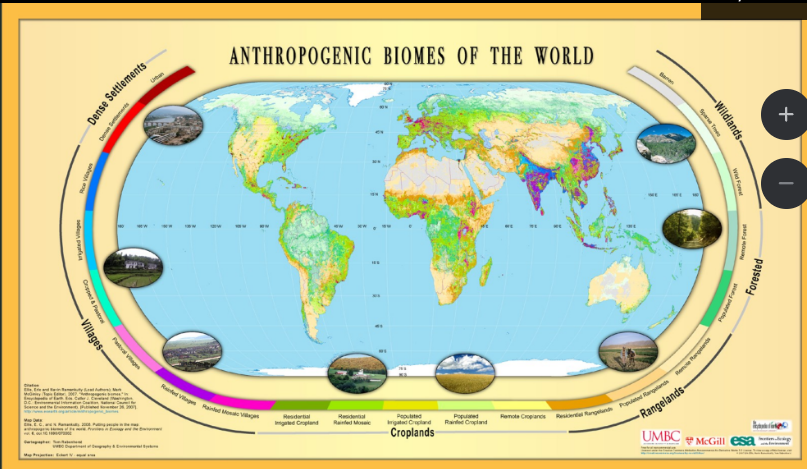
biome
definition: a region or global land area that is characterized by its plants or animals that is specific to that areas ex: dessert, rainforests, etc
difference between biome and anthrone is the way that humans are able to change the world to suite us
only species that are able to do this
biomes give us knowledge on how the area once was, that animals are found three, etc
anthromes are how humans have taken the area and transformed it
brazil biomes
tropical rainforest makes of majority, ~60%
dense and heavy rainforest
savannah’s ~20%
plains in a subtropical area
how land is used rn
across the world, there are 50 million square miles of land that are ice free
used as the baseline for human impacts
humans have directly transformed 50% of this
crops, pastures, logging, minings, cities
only 23 million square miles left
of that, 3/5 is the forests
this is not even pristine due to lines, pipelines, etc.
number of species in the amazon
over 1300 bird species
probably even more due to different bird calls
collected by a ring and free technique
plots themselves recorded 1400 species of trees
refuge effects
as the forest decreases, the species will temporarily gain population, and then they will start to decrease
relaxation effects
when you lose one species it starts to affect other species
the vulnerable species start to loose numbers and get more prone to disease and other effects
they are not able to survive these impacts anymore but would’ve been if they had the correct numbers
fragmentation
dividing the region into smaller fragments
in a fragmented region, the larger area of a habitat has been exposed to damaging outside influences like pollution
sustainability of the ecosystem is now reduced because of the fragmentation
species with large area and doesn’t have a lot of space to live
diversity is self enforcing
high species diversity thrives because there is a lot of competition
leads to evolutionary instincts because they have to fight to survive more and get more specialized
when you remove these conditions, they become more vulnerable
when plains disappeared in north America, species got his such as bisons and 50% of birds
biodiversity loss in African continent in the 21st century
Millennium ecosystems assessment, inc
Assessed impacts on terrestrial biodiversity using biodiversity intactness index
Predicts 21st century declines 2-3x greater than past 300 years
Urgent need for better aligning biodiversity conservation and development priorities in, and across, regions
Human population increase correlates to biodiversity loss
Have to look at much wider ranges, what happens to land, etc, much more accurate on whats going to happen instead of focusing on one specific animal
Army ants, eciton burchellii
Carnivorous
Always on the move
Build living bivouacs
Can consume 30,000 prey/day
Natives in areas have used ants for natural stitches
The ants bite the wound and then chop the head off
Hydrological cycles. Are we at the tipping point?
Air and moisture comes up out of the air and travels for miles, then will come down in rain
When you defragment the land, at what point do you reach the tipping point that the clouds won’t happen anymore, which is the center of life for the rainforest
Time lapse land defragmentation in southern brazil
Soil isn’t as rich, therefore not as good for crops
Sahara desert was one a green oasis in the center of civilization
It is thought that humans tipped the balance to make the sahara a desert
Biodiversity loss greatest since end-cretaceous extinction?
E.O. wilson in 1980s calculated extinction rate was 10,000X greater than naturally occurring background
Takes time for extinction, but incurs ‘extinction debt’
Regrowth always at play
Observational flaws
ex: conservation status, known is ~1% of known invertebrates
We don’t really observe everything that is going extinct
food web
Start with a primary produces which is fed upon a primary consumer
Tertiary producer and consumer are at the top
Global warming: On the move
Defragmentation
Ocean acidification
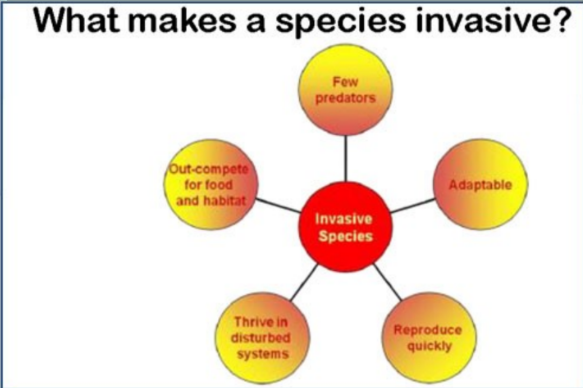
Invasive species
U.S. has a lot of threats to invasive species
Ecological imbalance
These invasive species are going into an area that has never been there before
It really thrives and takes over, outcompeting other species
Asian carp and killer frogs
Killer frogs are in florida that is large and can kill cats and dogs
End up in an area without a natural predator
These are killing off native species, destroying the ecosystem etc