ap psych unit 2 - memory, intelligence, testing - lessons 4-7
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
sensory memory
what we sense. type of memory where unattended information is lost quickly.
working memory
limited capacity. type of memory that requires rehearsals/repetition to be maintained.
long-term memory
almost limitless capacity. type of memory where some may be lost over time.
magical number seven theory
humans have an average limit of 7 (plus or minus 2) items in human short-term memory capacity.
structural encoding
processing a word based on its physical appearance.
ex. remembering a word by its font or color
phonemic encoding
processing a word by focusing on the sound of it.
semantic encoding
processing a word by focusing on the meaning of it.
ex. desert island example in class.
visual imagery
creation of visual images to represent something that needs to be remembered.
dual coding theory
humans process information through two distinct systems: a verbal system for words and a non-verbal system for images.
motivation to remember
information perceived as important is more likely to be recalled.
self referencing
how the info is being encoded affects the individual.
ex. remembering a list of words by relating each word to yourself.
central executive
the control center of working memory that directs attention and manages cognitive processes.
phonological loop
a memory component that briefly holds auditory information in short-term memory.
ex. repeating a phone number before adding it to your contacts.
visuospacial sketchpad
to remember information about objects and their relation in space.
ex. where you parked your car or the route from school to home.
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons, which can be formed in response to exercise, sleep, and nonstressful but stimulating environments.
long-term potentiation
an increase in a nerve cell’s firing after brief, rapid stimulation; a neural basis for learning and memory.
automatic encoding
process of memory where info is stored into long-term memory without effort.
ex. remembering what you had for breakfast.
implicit memory
a type of unintentional, long-term memory that influences behavior and skills without deliberate thought or awareness.
procedural memory
type of implicit memory that stores how to perform tasks and skills, allowing them to be done automatically without conscious thought.
ex. tying a shoe, riding a bike, muscle memory.
personal memory
type of implicit memory when someone remembering past events and experiences, allowing them to “re-live” past events.
ex. recalling specific details of your wedding day
explicit memory
type of long-term memory that refers to the intentional retrieval of information. It involves the ability to recall and report specific facts, events, and experiences.
flashbulb memory
type of explicit memory when remembering a dramatic, emotional event.
“I’ll never forget where I was when…”
autobiographical memory
type of explicit memory for one's personal history and memories.
ex. childhood experiences
prospective memory
type of explicit memory for actions to be performed in the future, like future events or to-do items.
semantic memory
type of explicit memory involving the ability to recall words, facts, numbers, dates, etc. Sometimes needs techniques to remember.
mnemonic devices
an aid for semantic memory that uses patterns, such as letters, rhymes, or images, to help people remember complex information.
ex. PEMS, ROY G BIV, etc.
method of loci
an aid for semantic memory that involves associating items to be remembered with specific locations along a familiar mental journey.
to do: mentally walk through a familiar place and place images of the information you want to remember along different spots on the path, and when you recall you walk the path again to get to the images.
chunking
an aid for semantic memory that involves grouping related pieces of information into larger, more manageable units
ex. phone numbers being in chunks of numbers instead of a whole sequence.
spacing effect/distributed practice
an aid for semantic memory that involves studying for something by spacing it out throughout a longer period of time instead of cramming it right before.
serial position effect
a cognitive phenomenon where individuals tend to remember the first and last items in a list better than the middle items. the first items have “primacy effect” and the last items have “recency effect,” making those terms easier to remember.
vonrenstorf effect
items that stick out are easier to remember.
priming effect
to think about a stimulus, such as a word or object, as a result of a recent exposure to the stimulus.
context-dependent memory
tendency to remember info more easily when retrieval occurs in the same setting where you originally learned the info.
ex. studying at a desk is better than studying in bed, bc test will be taken at a desk.
mood-congruent memory
phenomenon where people tend to recall memories that match their current mood.
ex. being happy makes it easier to remember happy events, being sad makes it easier to remember sad events.
state-dependent memory
the phenomenon where information is better remembered when an individual is in the same internal state as when they learned it.
ex. if you study in a relaxed state, you’ll recall better when relaxed.
measures of retention
the 3 R: recall, recognition, relearning
encoding failure
reason for forgetting in which memory code was never made/shallow memory.
storage decay
reason for forgetting in which memory fades over time if not sufficiently maintained.
retrieval failure
reason for forgetting with the inability to access or recall information that is stored in long-term memory.
ex. “it’s on the tip of my tongue”
proactive interference
reason for forgetting where previously learned information makes it harder to recall new information.
retroactive interference
reason for forgetting where new information makes it harder to recall previously learned information.
retrograde amnesia
physiological reason for forgetting that is the the loss of memory about something that occurred before a specific point in time, such as a traumatic brain injury or stroke
anterograde amnesia
physiological reason for forgetting that is the inability to form new memories after a specific event or injury.
ex. mr tuit had after he hit his head
infantile amnesia
immature brains can’t make memories yet.
motivated forgetting
we don’t always remember what we don’t want to remember.
memory repression
when someone goes from something traumatic, their brain prevents them from remembering to protect their mind from distress.
constructive memory
when you observe an event, you don’t store exact copy of the event in your memory. you store a simple approximation that may be reshaped with time, which can lead to disagreements.
memory consolidation
new, unstable memories are converted into stable, durable memory codes that are stored into long-term memory.
misinformation effect
someone’s memory of event becomes less accurate due to misleading info after the event.
ex. change in eyewitness memory after a car crash is described with different words.
imagination inflation
memory distortion where imagining an event increases someone’s confidence that the event actually occurred.
ex. when someone who has only imagined a childhood event, such as breaking a window, later becomes more confident that the event actually happened.
spontaneous recovery
reappearance of a previously extinguished conditioned response after a period of time, occurring without any further conditioning.
ex. when a dog, after its conditioned fear of a specific loud truck has been extinguished through therapy, suddenly shows fear again when it hears that truck after a rest period.
episodic memory
type of explicit memory with the ability to recall and relive specific personal experiences, including their context (time, place, and emotions).
ex. taste of your birthday cake.
framing
cognitive bias where people's decisions are influenced by the way information is presented.
iconic memory
the brief, highly detailed visual sensory memory that lasts for a fraction of a second, allowing us to "see" an image for a short time after it has disappeared.
ex. the momentary afterimage of a bright light, such as a camera flash or a room light that suddenly burns out.
forgetting curve
a concept showing that people forget information rapidly after learning it, with a significant portion forgotten within the first hour, though the rate of forgetting slows over time.
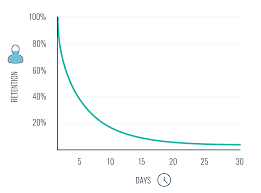
echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds.
ex. you aren’t paying attention and teacher asks “what did I just say?”
retrieval cues
stimuli, such as sights, sounds, or smells, that trigger the recall of stored long-term memories.
stanford-binet intelligence test
first test to create an IQ score. these tests only included verbal sections in english, so biased.
g factor
individual's overall cognitive ability that influences their performance across various mental tasks like reasoning, problem-solving, and learning.
WAIS
commonly used clinical intelligence test, which includes 2 sections with a variety of tasks, including nonverbal tasks, so people with less english literacy can demonstrate intelligence.
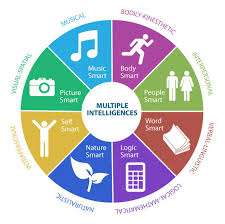
multiple intelligences
proposed by Howard Gardner, suggests that intelligence is not a single, general ability, but is a set of multiple, distinct types of intelligence.
cattell-horn-carroll theory
differentiates fluid intelligence and crystallized intelligence.
fluid intelligence
the ability to solve problems and adapt to new situations without relying on previously acquired knowledge or experience.
crystallized intelligence
stored learning that a person acquires over a lifetime.
psychometrics
the way psychologists learn to examine and assess psychological constructs.
achievement tests
tests designed to see what someone already knows.
ex. AP tests, drivers ed tests
aptitude tests
tests designed to see what a person is capable of learning - aptitude is the capacity to learn.
ex. the ASVAB
test-retest reliability
method to test the external reliability of a test:
measures the consistency of a test over time by administering the same test to the same group of people at different times.
interscorer reliability
method to test the external reliability of a test:
measures the consistency of ratings made by two or more independent raters when they evaluate the same subject or data.
split-half reliability
method to test the internal reliability of a test:
divides it into two halves (e.g., odd-numbered vs. even-numbered questions) and correlating the scores from each half.
construct validity
method to test the validity of a test:
the degree to which a test measures what it claims to measure.
ex. a scale measuring happiness has construct validity if it actually measures happiness and not something like excitement.
content validity
method to test the validity of a test:
the extent to which an assessment instrument measures all aspects of the concept it is designed to evaluate.
ex. a driving test that covers all aspects of traffic rules
predictive validity
method to test the validity of a test:
the extent to which a test accurately predicts future outcomes, behaviors, or performance.
flynn effect
the observed rise in average IQ scores across generations, with each new generation scoring higher than the last.
heritability
a biased and inaccurate explanation in between-group differences in highly heritable traits:
observed differences in a trait among people in a population due to genetic differences.
socioeconomic status
an explanation in between-group differences in highly heritable traits:
measure of someone’s social and economic position in society, including income, education, occupation, etc.
encoding specificity principle
the idea that cues and contexts specific to a particular memory will be most effective in helping us recall it.
ex. context-dependent memory
interleaving
learning strategy where students mix different topics or skills during a single study session, instead of focusing on one topic at a time.
ex. mixing different types of math problems during a study session.
positive transfer
when previous learning helps or facilitates the learning of a new, related skill.
ex. already knowing latin so learning french is easier.
repression
defense mechanism where the mind unconsciously pushes anxiety-inducing thoughts, memories, or feelings out of conscious awareness.
ex. thinking you ate 6 cookies, when in reality you ate 15.
reconsolidation
a process in which previously stored memories, when retrieved, are potentially altered before being stored again.
ex. telephone game
factor analysis
a statistical method used to identify underlying relationships between variables by grouping them into broader factors.
savant syndrome
a condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill, such as in computation or drawing.
triarchic theory
theory that proposes three reliably measured intelligences.
-analytical (academic problem-solving) intelligence
-creative intelligence
-practical intelligence
emotional intelligence
critical part of social intelligence that consists of 4 abilities: the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions.
testing bias
an explanation in between-group differences in highly heritable traits:
when a test systematically favors one group over another due to factors unrelated to the trait being measured.
stereotype threat
an explanation in between-group differences in highly heritable traits:
fear that people might experience if they believe that their performance on tests might confirm negative stereotypes about a group they’re a part of.
stereotype lift
someone from a group has improved self-esteem due to being reminded of a positive stereotype from their group.
ex. man is reminded that men are stronger than women, so he is motivated to lift heavier.
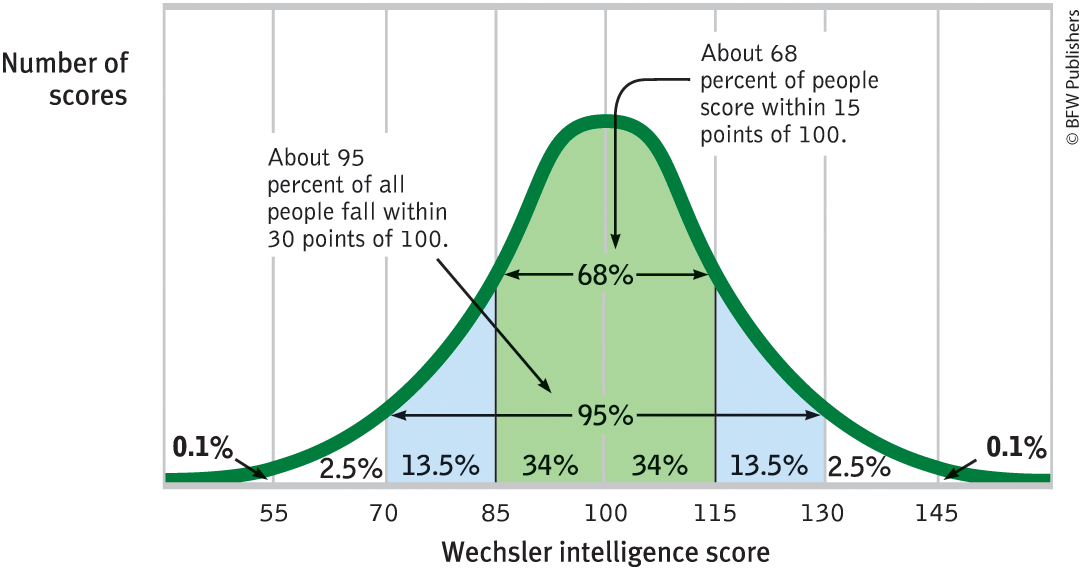
normal curve
a symmetrical, bell-shaped graph showing a frequency distribution where most scores cluster around the mean.
cohort
a group of people sharing a common characteristic, such as from a given time period.
longitudinal study
research method that involves observing the same group of participants over a long period to track changes and developments over time.
cross-sectional study
a type of observational research that analyzes data from a population at a single point in time