ccna networking
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
layer 1
physical (cables, hubs, etc) (uses bits)
layer 2
data link (mac addresses, switches, frames)
layer 3
network (ip addressing, routers) (uses packets)
layer 4
transport (tcp/udp, ports)(uses segments)
layer 5
session (manages sessions)
layer 6
presentation (encryption, formatting)
layer 7
application (http, dns)
how many bits does IPv4 have?
32 (ex. 192.168.1.1)
how many bits in IPv6?
128 (ex.2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334)
private ip ranges
10.0.0.0/8
172.16.0.0–172.31.0.0
192.168.0.0/16
internet
global network
intranet
internal company network
extranet
third party partners are allowed
what does dhcp do and what port is it?
assigns ip addresses automatically, port 67/68
what does a switch do?
connects multiple devices together so they can communicate
what does a router do?
connects different networks (ex. LAN to WAN)
where would LAN be used
small areas like home, office, or school
where would WAN be used?
large geographic areas like the internet or site to site VPNs
what is a firewall?
security device that filters traffic and blocks ports, IPs or protocols
RDP (remote desktop services) port?
3389
DNS port?
53
SSH port?
22
HTTP port
80
HTTPS port
443
DNS port
53
SNMP port
161
what does DNS do?
resolves domain names into IP addresses
what is tcp (transmission control protocol)
reliable, connection oriented, slow but accurate, and ordered
what is UDP (user datagram protocol)
unreliable, connectionless, fast, unordered
what are straight through cables used for
when you need to connect unlike devices (ex. switch to router)
what are crossover cable used for
when you need to connect like devices (ex. pc to pc, router to router)
T-568 B order
white orange, orange, white green, blue, white blue, green, white brown, brown
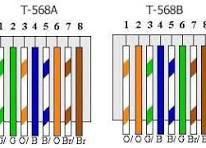
T-568 A order (hint. switch 2 and 6, 1 and 3)
white green, green, white orange, blue, white blue, orange, white brown, brown
if both ends are the same then its…
straight through
if one end is T-586 B another 586 A then its…
crossover
what is rollover cable
has no T586, used only to connect computer to the console port of a switch/router (only for configuration)
bus topology pros and cons
setup: one main cable with devices branching off it
pros: easy to set up, cheap, less cable used
cons: slow, collisions often, main cable failure = whole network down
star topology pros and cons
setup: all devices connect to a central switch/hub
pros: easy to manage, easy to add/remove devices, faster & less collisions, one device failure doesn’t impact others
cons: more cable needed, central device failure = whole network down
ring topology pros and cons
setup: devices connected in a circle, data moves in 1 direction
pros: predictable performance, no collisions
cons: one device failure breaks the network, hard to troubleshoot, slow if many devices
mesh topology pros and cons
setup: devices all connected to each other
pros: reliable, no single point of failure, high performance
cons: expensive, lots of cabling, complicated setup
cat 3 speed
10 mbps
cat 5 speed
100 mhz to 100 mbps
cat 5e speed
1 gbps
cat 6 speed
250 mhz to 10 gbps
cat 6a speed
500 mhz
what is a vpn
secure connection, lets you access a private network over the internet
what does ipconfig /displaydns do
show cached dns records
what does ipconfig /flushdns do
clears dns resolver cache
what does tracert do?
show hops
what does netstat -a do
show all active ports
what does netstat -s do
show network statistics
-t is for?
tcp ports
-a is for
showing all connections/listeners
what metric does RIP use
hop count
port for FTP
20/21
A record?
maps hostname for IPv4 address
AAAA
maps hostname for IPv6 address
802.11a frequency and max speed?
5 ghz
54 mbps
802.11b frequency and max speed?
2.4 ghz
11 mbps
802.11c frequency and max speed?
2.4 ghz
54 mbps
802.11n frequency and max speed?
2.4 & 5 ghz
600 mbps
802.11ac frequency and max speed?
5 ghz
up to 1.3 gpbs
infrastucture mode
wireless devices connect through an access point (like home wifi to a router)
what is ad hoc mode?
devices connect directly to eachother with no access point (like airdropping a picture )
what is peer to peer?
where a device acts as both a client and a server (like sharing files between home PCs without a server)
*TCP MODEL* application layer order and what it does
first, provides network services to apps (http, ftp, etc)
*TCP MODEL* transport layer order and what it does
second, host-to-host communication (tcp, udp)
*TCP MODEL* internet layer order and what it does
third, logical addressing and routing (IP, ARP)
*TCP MODEL* link layer order and what it does
fourth, physical network access and mac addressing (ethernet, wifi)
what OSI models correlate with application
session, presentation, and application