Conjunctiva & Limbus
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Conjunctiva
Thin, semi-transparent, mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the eyelids
Functions:
Lubrication (reduces friction between eyelids
Antimicrobial
Source of stem cells for corneal epithelium
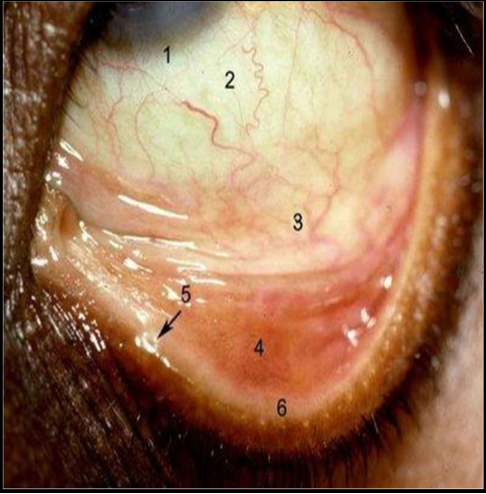
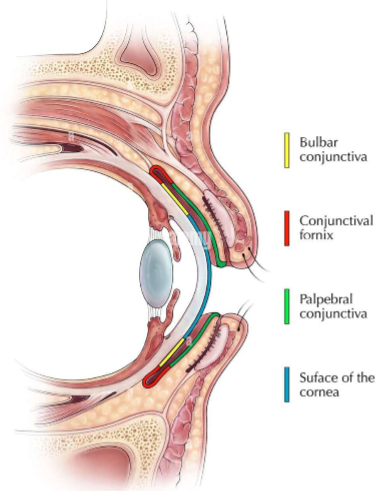
Parts of the Conjunctiva
Corneoscleral limbus
Bulbar Conjunctiva
Forniceal Conjunctiva
Palpebral Conjunctiva
Puncta
Mucocutaneous Junction
Conjunctival sac
potential space between palpebral conj and bulbar conj
Subtarsal sulcus
2mm from posterior edge of the eyelid margin
spans the inner surface of the eyelid
traps foreign particles that enter the conjunctival sac
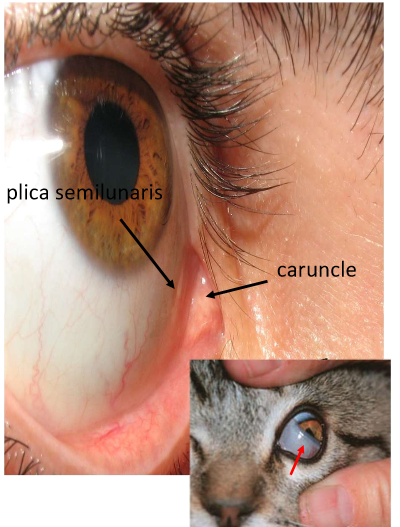
Plica Semilunaris
Crescent shaped fold of bulbar conj
unfolds when eye abducting
vestigial remnant of nicitatng membrane “third eyelid” in other species
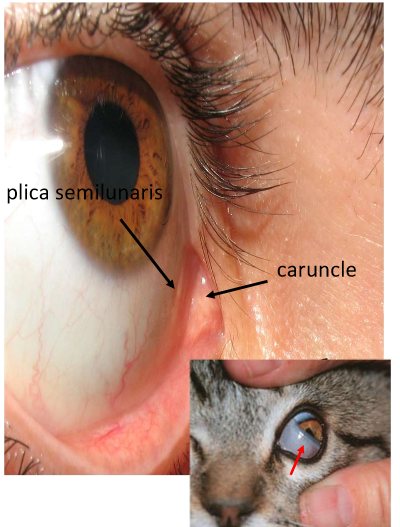
Caruncle
Nodular tissue situated between plica semilunaris and the medial canthus
Likened to non-keratinized skin
contains pilosebaceous unit with cilia, accessory lacrimal gland tissue, and numerous sebaceous glands
Glands of Krause
Deep subconjunctival tissue from the superior fornix to superior border of the superior tarsal plate
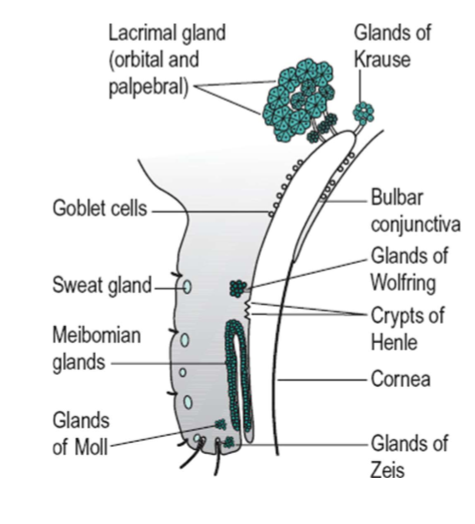
Glands of Wolfring
Larger than glands of Krause. tend to be located in the region of the tarsal plate and are more prominent nasally
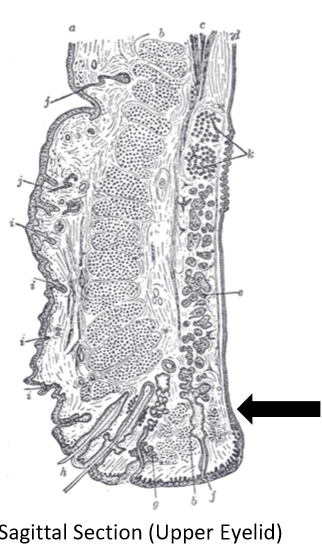
Palpebral conj (histology
stratified columnar epithelium
stratified squamous epithelium
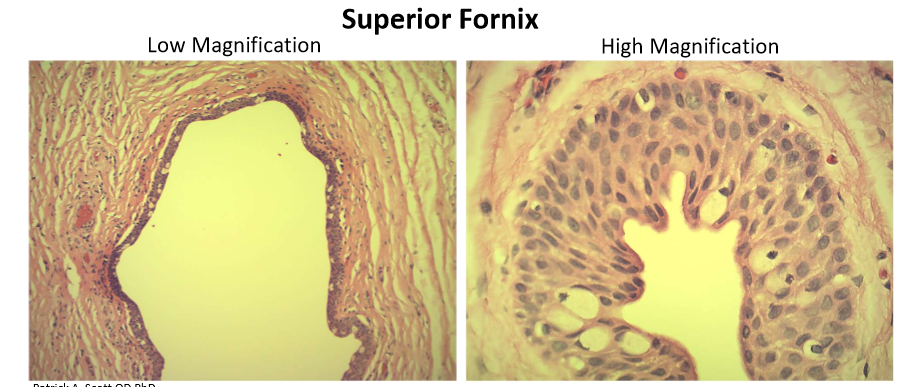
Fronix (histolgy)
stratified columnar epithelium
Bulbar conj (histology)
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Mucocutaneous junction (histology)
transitions to keratinized skin of eyelid
Serves as source of stem cells for palpebral conjunctiva
Zonula Adherens
holds neighboring cells together
Zonula Occludens (tight junctions)
seals intercellular clefts forming intercellular permeability barrier
Conjunctival Epithelium
Microvilli extend from apical surface
increase surface area for absorption and secretion
assist with stabilizing mucin layer of tear film
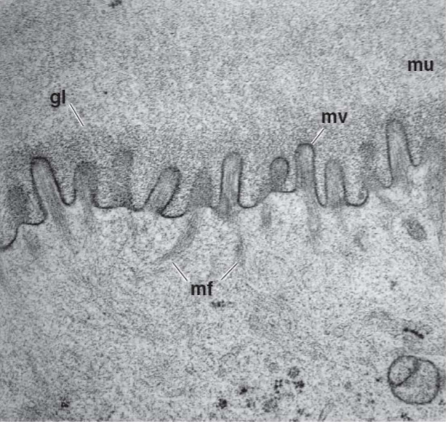
Goblet cells
unicellular glands secret mucus layer of the tear film via apocrine secretion
non-uniform distribution- most abundant in forniceal conjunctiva and nasal bulbar conjunctiva; sparse near limbus and lid margin
Autonomic Innervation
parasympathetic = stimulatory
Sympathetic = inhibitory
Crypts of Henle & Stieda
goblet cell-lined surface grooves the palpebral conj proposed to be part of the conj associated lymphoid tissue system
Function: trap bacteria and antigenic material, allow it to be neutralized by various defense mechanisms of the conj
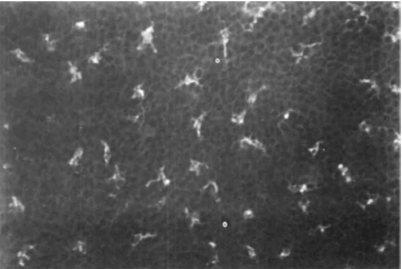
Langerhans Cells
immune cells
250-300 mm² (1/2 found in skin)
15 -20 mm² peripheral 1/3rd cornea
non in central cornea
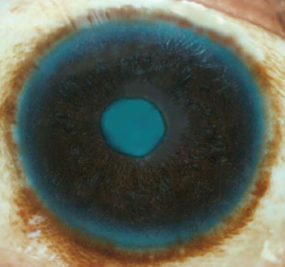
Dendritic Melanocytes
common in heavily pigmented races
produce pigmented ring at limbus
protect stem cells at limbus from UV damage
patches on bulbar conj
Corneal Stroma
Fibrovascular matrix
looser matrix in bulbar conj vs palpebral conj
attaches to underlying tenons capsule
Contains: Nerves, Blood vessels, lymphatics
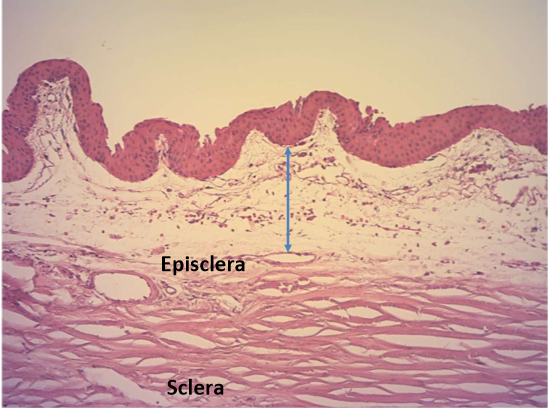
Conjunctival stroma (histology)
firmly adherent to tarsal plate (cant be moved)
stroma in palpebral conj has abundance of lymphoctyes and plasma cells that secret IgA
sometimes organize to form follicles
vascular structures in conj surrounded by mast cells that release granules containing histamine
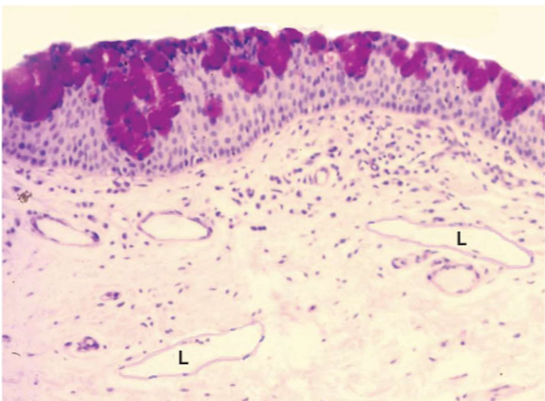
Conjunctiva Stroma (Lymphatics)
not appreciated in vivo
lymphangiectasis may occur with chronic irritation of the conjunctiva
Surgical limbus
transitional area of 1-2 mm in width where conrea merges with sclera
appears as a blue-grey ring
anterior margin of limbus corresponds to peripheral termination of descmet’s membrane (Schwables line)
posterior margin where coloration gives way to white sclera responds to posterior limit of Schlemm’s canal at the scleral spur
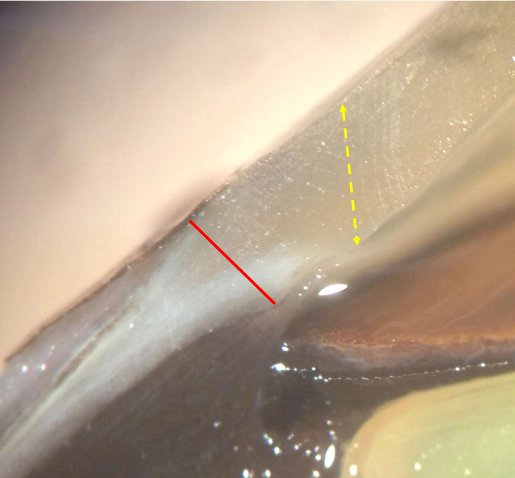
Palisades of vogt
conj epithelium transitions into corneal epithelium
8-10 layers thick
stem cells for bulbar conj epithelium and conreal epithelium reside
radial folds increase surface area for basal cell proliferation
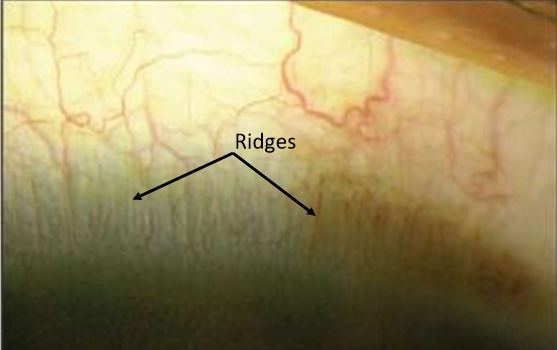
Palisades of vogt (histology)
radially oriented fibrovascular channels between ridges of thickend conjunctival epithelium
fibrovascular channels contain, arterial, venous, and lymphatic vessels
more prominent at superior and inferior limbus
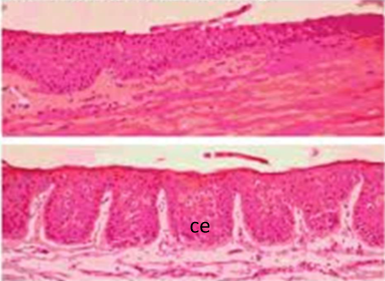
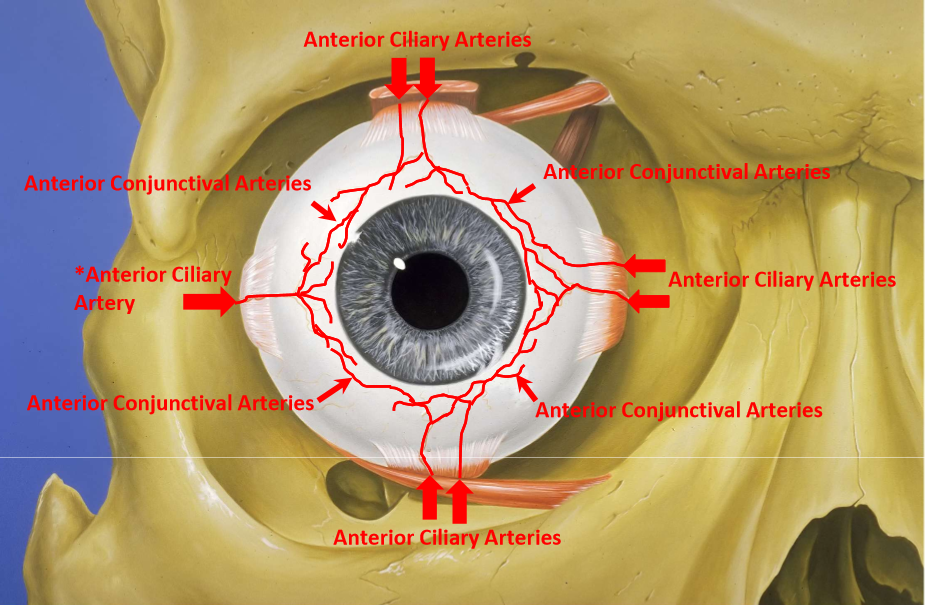
Blood supply
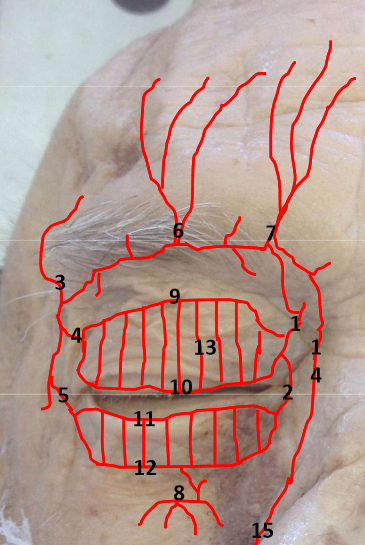
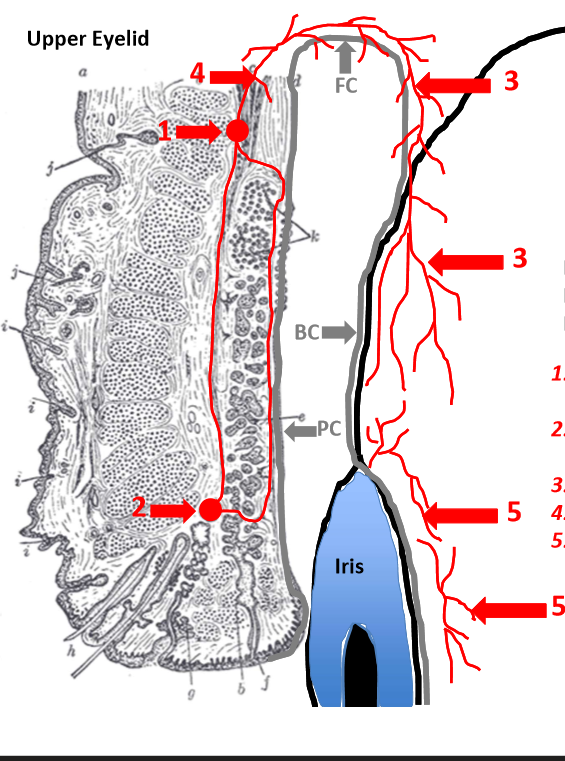
Palpebral conj - marginal and peripheral palpebral arcades (artery)
palpebral arteries originate from medial and lateral palpebral arteries and anastomose in eyelid
small collateral branches connect arcades to the tarsal plate
collateral arteries give it pinkish-red color
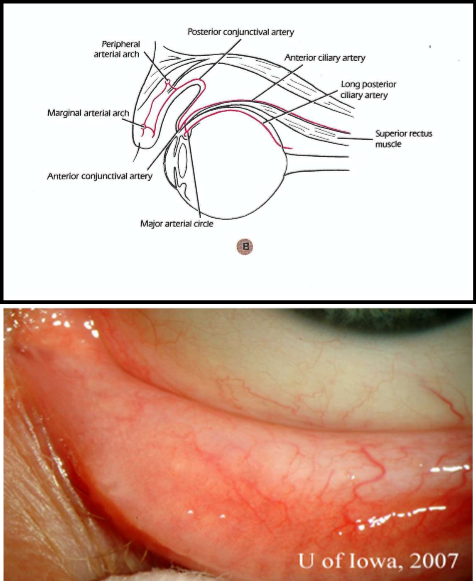

Vasculature of Bulbar conj
Posterior conj arise from peripheral palpebral arcades
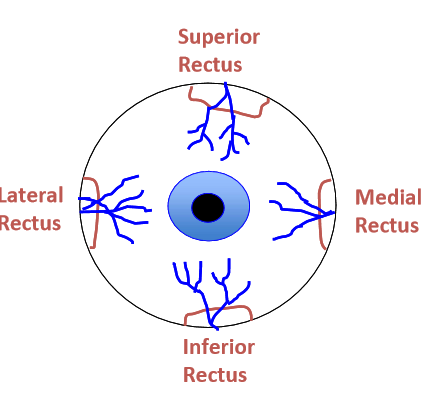
anterior conj vessels arise from anterior ciliary arteries (7 total) which branch from muscular arteries to each rectus muscle
supply bulbar conj up to limbus
from superficial pericorneal vascular plexus (fenestrated)
Anterior Conj Arteries
lateral rectus only has 1 anterior ciliary artery
the rest have 2
Sub conjunctival hemorrhage
rupture of a posterior or anterior conj artery
typicall benign only require palliative treatment
associated with valsalva, blood thinners, constipation, straining
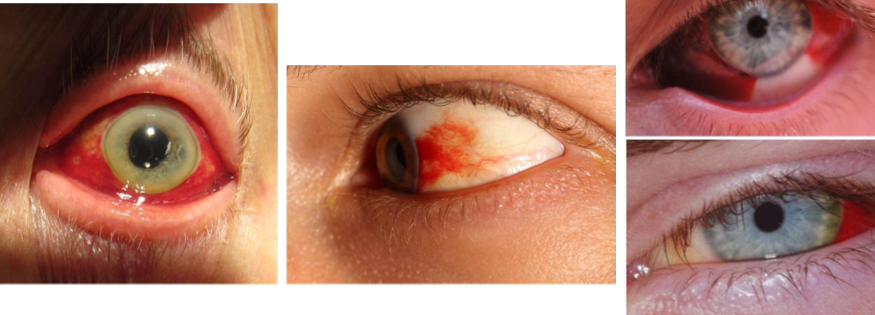
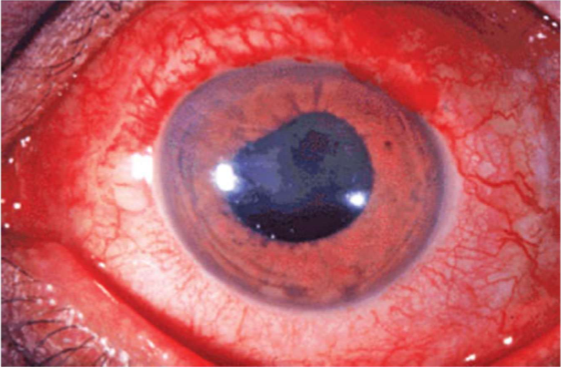
Ciliary injection
inflammation in deeper structures such as iris or ciliary body (uveitis)
perforating anterior ciliary arteries that supply major arterial circle of iris become congested and show injection of perilimbal vascular plexus
peripheral bulbar conj not injected as perilimbal region
Venous Drainage
more numerous than the arteries
Palpebral Veins or anterior ciliary veins —> muscular veins —> superior or inferior ophthalmic vein
lymphatic drainage
lymph from lateral conj drains into preauricular lymph nodes
lymph from medial conj drains into submandibular lymph nodes
Innervation palpebral conj
Upper palpebral conj
CN V1 - Ophthalmic Division
Lacrimal Nerve
Supraorbital nerve (From frontal nerve)
Supratrochlear nerve (from frontal nerve)
Lower Palpebral conj
CN V2 - Maxillary Division
Infraorbital nerve
Innervation of Bulbar Conj
Sensory
CN V1 - Ophthalmic
Nasociliary Nerve
Long Posterior Ciliary nerves
Autonomic
Postganglionic Sympathetics from carotdi plexus (constriction)
Postganglionic Parasympathetic fibers from pterygopalatine ganglion
Sensory to caruncle
CN V1 - Ophthalmic Division
Nasociliary nerve
Infratrochlear nerve
Hyperemia
looseness of substantia propria in the forniceal conj permits fluid accumulation (edema) accumulation of mast cells, lymphocytes, etc. in substantia propria
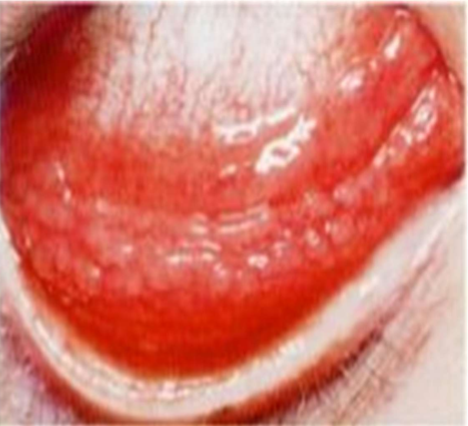
Follicles
lymphoid germinal centers vessels around the base
Viral = lymphadenopathy
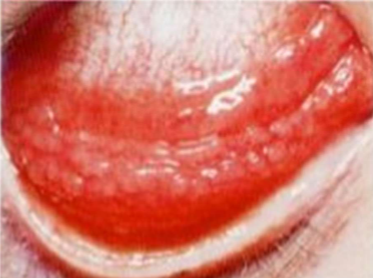
Papillae
swelling of conj
fibrovascular core central vessel
nonspecific, mechanical + Allergic
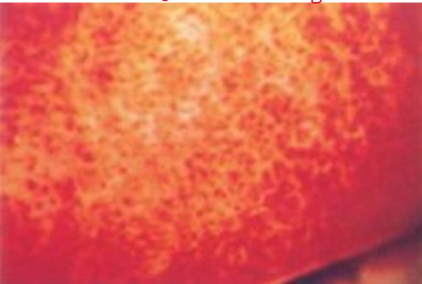
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis
Contact lens induced
Verneal (seasonal) keratoconjunctivitis
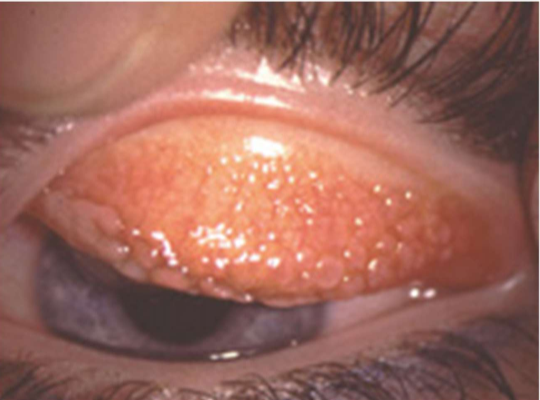
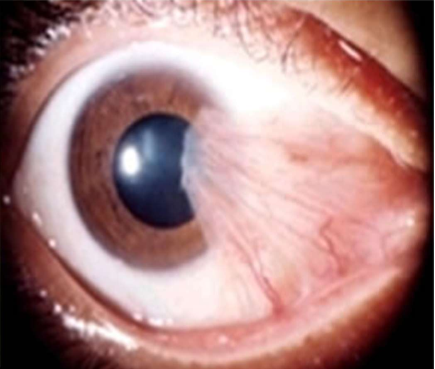
Pinguecula
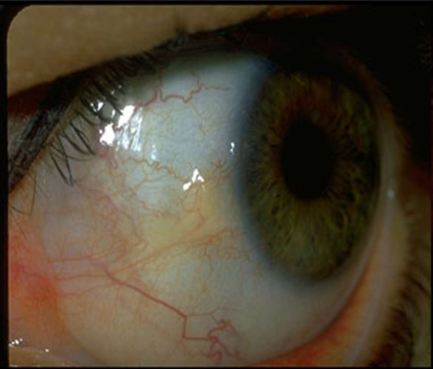
Pterygium
when removed they often come back
can cause induced astigmatism