Mismatch in V/Q. Respiratory failure
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
what is ventilation- perfusion mismatch
V/Q mismatch
represents the balance between air reaching the alveoli (V)
and blood flow to alveoli (Q)
normal V/Q ratio is approximately 0.8- 1.0
ventilation and perfusion are closely matched
what is respiratory failure
Failure to maintain adequate gas exchange
Lungs fail to oxygenate blood adequately or remove CO2
hypoxemia, PaO₂ < 60 mmHg
hypercapnia, PaCO₂ > 50 mmHg
types of respiratory failure
Acute Respiratory Failure (ARF)
Develops rapidly
requires urgent medical intervention.
Chronic Respiratory Failure (CRF)
Develops slowly
compensatory mechanisms
(PaO₂) formula
Lower limit of arterial oxygen (PaO₂)
This formula estimates normal PaO₂ levels with aging.
If PaO₂ falls below this, ARF is suspected.
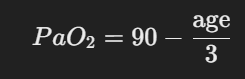
Mechanisms Leading to Respiratory Failure
Ventilation-Perfusion (V/Q) Mismatch
most common cause of hypoxemia
Airflow and blood flow are not matched
Low V/Q
⇓ ventilation,
normal perfusion
pneumonia
pulmonary edema.
High V/Q
normal ventilation
⇓ perfusion
pulmonary embolism
Altered Diffusion
Impaired O2 transfer
across the alveolar-capillary membrane
Causes:
increase diffusion distance
Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary fibrosis
reduced alveolar surface area
emphysema
Disruption in gas exchange
Abnormal Hb binding affinity
CO poison
Alveolar Hypoventilation
Reduced air movement into the lungs
CO₂ retention
hypercapnia
Causes:
CNS depression
opioid
brainstem injury
Neuromuscular disorders
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
Pathogenesis of Acute Respiratory Failure
Type 1: Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
PaO₂ < 60 mmHg (low oxygen levels)
Develops over hours to days
Caused by: V/Q mismatch
Shunt
(blood bypasses ventilated alveoli)
(e.g., ARDS)
Impaired diffusion
Compensation: hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV)- alv/cap reflex
Type 2: Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure
PaCO₂ > 50 mmHg (high CO₂ levels)
Develops abruptly
drunk like, vessels in eyes
Life-threatening if untreated
respiratory acidosis
Common mechanisms:
Alveolar hypoventilation
⇓ respiratory drive
muscle weakness.
Airway obstruction (e.g., COPD, asthma)
V/Q mismatch
⇓air reaching alveoli
CO₂ ⇑
Etiology of Acute Respiratory Failure
Airway Abnormalities
Obstruction → foreign bodies, severe asthma, anaphylaxis.
Air trapping → COPD, cystic fibrosis
CNS Abnormalities
Brainstem damage (stroke, trauma, tumors).
Drug overdose (opioids)
Chest Wall Abnormalities
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (restricted lung expansion)
kyphoscoliosis
fractured ribs
Neuromuscular Conditions
Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
progressive nerve degeneration
Chronic Respiratory Failure (CRF)
Develops over months to years
compensatory mechanisms to take effect.
Three Stages of CRF Progression
Bronchopulmonary syndrome
persistent respiratory symptoms.
Dyspnea, wheezing
b/p syndrome
compensation
HR increases
angiogenesis
⇑ erythropoietin
Neuropsychiatric syndrome
Chronic hypoxia + hypercapnia
affected the brain and heart
confusion, memory loss
chronic pul. hypertension
results in cor pulmonale
Hypercapnic encephalopathy
Blood Gas Changes in Respiratory Failure
Type 1 (Hypoxemic R/F):
↓PaO₂
normal or ↓PaCO₂.
Type 2 (Hypercapnic R/F):
↓PaO₂,
↑PaCO₂
respiratory acidosis.
explain the stages of CRF and what leads to what?
Chronic Respiratory Failure (R/F)
|
V
Stage 1: Initial Disease
|
V
Initial Symptoms
|
V
Stage 2: Compensation
|
V
Body Compensates for R/F
|
V
Stage 3: Complications
|
V
Complications Develop
|
V
Symptoms of Complications