Antibiotics
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What do class do the following drugs belong to?
Penicillin G
Penicillin V
Amoxicillin
Cephazolin
Cephalexin
Ceftriaxone
Vancomycin
a) DNA synthesis inhibitors
b) Cell wall synthesis inhibitors
c) Protein synthesis inhibitors
b)
What do class do the following drugs belong to?
Doxycycline (30S)
Erythromycin (50S)
a) DNA synthesis inhibitors
b) Cell wall synthesis inhibitors
c) Protein synthesis inhibitors
c)
What do class do the following drugs belong to?
Ciprofloxacin
Sulfamethoxazole + Trimethoprim
a) DNA synthesis inhibitors
b) Cell wall synthesis inhibitors
c) Protein synthesis inhibitors
a)
Which of the following is a protein synthesis inhibitor drug for 30S?
a) Erythromycin
b) Doxycycline
c) Ciprofloxacin
d) Ceftriaxone
b)
Which of the following is a protein synthesis inhibitor drug for 50S?
a) Erythromycin
b) Doxycycline
c) Ciprofloxacin
d) Ceftriaxone
a)
Goal of Chemotherapy?
Kill or Inhibit a pathogenic organism without harming the patient
What are the different types of chemotherapy?
Antimicrobial agents
Antineoplastic agents
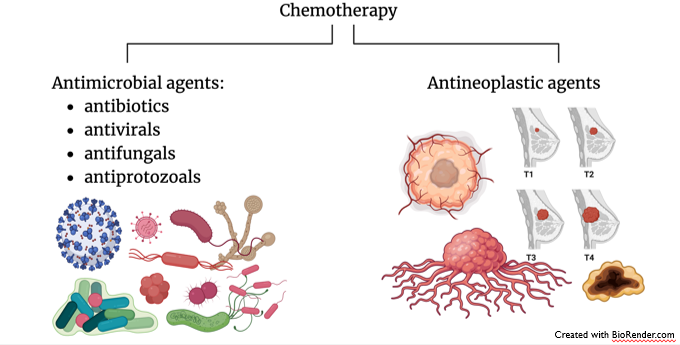
History of Chemotherapy:
What did Ancient China use?
a) Chaulmoogra oil to treat leprosy
b) Chenopodium to treat intestinal worms
c) Cinchona bark for fevers
d) Moldy soybean curd on boils
e) Mercury for syphilis
d)
History of Chemotherapy:
What did Ancient India use?
a) Chaulmoogra oil to treat leprosy
b) Chenopodium to treat intestinal worms
c) Cinchona bark for fevers
d) Moldy soybean curd on boils
e) Mercury for syphilis
a)
History of Chemotherapy:
What did 16th century Greece use?
a) Chaulmoogra oil to treat leprosy
b) Chenopodium to treat intestinal worms
c) Cinchona bark for fevers
d) Moldy soybean curd on boils
e) Mercury for syphilis
e)
History of Chemotherapy:
What did 17th century use?
a) Chaulmoogra oil to treat leprosy
b) Chenopodium to treat intestinal worms
c) Cinchona bark for fevers
d) Moldy soybean curd on boils
e) Mercury for syphilis
c)
Development of ______ to _____ and characterize microbes and mammalian cells
dyes to stain
Arsenical agents
Atoxyl for sleeping sickness
Arsphenamine in 1906
Neoarsphenamine in 1909 for syphilis
if certain dyes could selectively stain microbes, could they could also be selectively toxic to these organisms.
Who said this?
a) Paul Ehrlich
b) Gerhard Domagk
a)
In 1935, _____ demonstrates antibiotic properties of Prontosil, a sulfonamide dye, in pyogenic infection.
a) Paul Ehrlich
b) Gerhard Domagk
b)
Do we need the whole structure? the PABA and the dye?
No! Active moiety is para-amino benzene sulfonamide
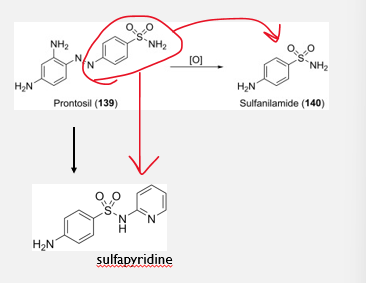
______ was the first sulfonamide to be marketed in 1938.
Sulfapyridine
Different ways of Organizing Antimicrobials:
Chemical structure
Azide, sulfonamide, etc.
Mechanism of action
Receptor inhibitor, enzyme inhibitor, cell wall disruptor, etc.
Target organisms
Bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc.
Spectrum of activity
Narrow, extended, broad
Effect on the microbe
-cidal (kills the bug) or static (stops bug growth)
Drug source/origin
Bacteria, fungi, plant, synthesized
Antibiotics Go Hand In Hand with Bugs and Infections:
Which of the following is best described?
Classification
Genetics
Pathogenesis
Diagnostic Techniques
a) Infectious Diseases
b) Antibiotics
c) Bacteria
c)
Antibiotics Go Hand In Hand with Bugs and Infections:
Which of the following is best described?
Classification
MOA
Spectrum
PK/PD
Side effects
Clinical uses
a) Infectious Diseases
b) Antibiotics
c) Bacteria
b)
Antibiotics Go Hand In Hand with Bugs and Infections:
Which of the following is best described?
Presentation
Diagnosis
Management
a) Infectious Diseases
b) Antibiotics
c) Bacteria
a)
Common Infections:
Which of the following is best described?
Infective endocarditis
Bone and joint
Bacterial meningitis
Derm/soft tissue infections
a) Mostly Gram (+)
b) Mostly Gram (-)
a)
Common Infections:
Which of the following is best described?
Pneumonia
UTI
STI (plus protozoa, spirochetes, viruses)
Bacterial meningitis
a) Mostly Gram (+)
b) Mostly Gram (-)
b)
Biological Approaches:
Which is best described?
Bacitracin, Vancomycin, Daptomycin, Streptogramins, Linezolid
Mostly used for ____: PCNs
a) G (+) only
b) G (-) only
c) Broad-spectrum
d) Bactericidal
a)
Biological Approaches:
Which is best described?
Aztreonam
Mostly used for ____:
Extended-spectrum PCNs, 3rd gen cephalosporins, Aminoglycosides
a) G (+) only
b) G (-) only
c) Broad-spectrum
d) Bactericidal
b)
Biological Approaches:
Which is best described?
Carbapenems, Tetracyclines, Macrolide, Chloramphenicol, Clindamycin, anti-folates, Quinolones
a) G (+) only
b) G (-) only
c) Broad-spectrum
d) Bactericidal
c)
Biological Approaches:
Which is best described?
Cell wall inhibitors, Tigecycline, Aminoglycosides, Streptogramins, TMP/SMZ, Quinolones
a) G (+) only
b) G (-) only
c) Broad-spectrum
d) Bactericidal
d)
Empiric Therapy:
Treatment plan based on _______, _____ lab results confirming the identity of the microbial pathogen
a) infection type, before/ prior to lab results
b) infection type, after lab results
a)
Empiric Therapy:
Pneumonia: ______
a) Cell wall inhibitor
b) Cell wall inhibitor + Protein synthesis inhibitor
c) Anti-folate
d) Cell wall inhibitor, viral DNA polymerase inhibitor
b)
Empiric Therapy:
Infectious Endocarditis: ______
a) Cell wall inhibitor
b) Cell wall inhibitor + Protein synthesis inhibitor
c) Anti-folate
d) Cell wall inhibitor, viral DNA polymerase inhibitor
b)
Empiric Therapy:
Bone and Joint: ______
a) Cell wall inhibitor
b) Cell wall inhibitor + Protein synthesis inhibitor
c) Anti-folate
d) Cell wall inhibitor, viral DNA polymerase inhibitor
a)
Empiric Therapy:
UTI: ______
a) Cell wall inhibitor
b) Cell wall inhibitor + Protein synthesis inhibitor
c) Anti-folate
d) Cell wall inhibitor, viral DNA polymerase inhibitor
c)
Empiric Therapy:
STD: ______
a) Cell wall inhibitor
b) Cell wall inhibitor + Protein synthesis inhibitor
c) Anti-folate
d) Cell wall inhibitor, viral DNA polymerase inhibitor
d)
Empiric Therapy:
Bacterial meningitis: ______
a) Cell wall inhibitor
b) Cell wall inhibitor + Protein synthesis inhibitor
c) Anti-folate
d) Cell wall inhibitor, viral DNA polymerase inhibitor
a)
Empiric Therapy:
Skin infections: ______
a) Cell wall inhibitor
b) Cell wall inhibitor + Protein synthesis inhibitor
c) Anti-folate
d) Cell wall inhibitor, viral DNA polymerase inhibitor
a)
Case Example: Treating Pneumonia in Adults
Common pathogens: Strep (+), Hemophilus, Moraxella
Atypical bacteria: Legionella, Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Pseudomonas
Mainly ______
Mainly cell wall inhibitors (block transpeptidase/PBP) ± protein synthesis inhibitor (30S/50S)
Case Example: Treating Pneumonia in Adults
Common pathogens: Strep (+), Hemophilus, Moraxella
Atypical bacteria: Legionella, Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Pseudomonas
Mainly cell wall inhibitors (block transpeptidase/PBP) ± protein synthesis inhibitor (30S/50S)
Empiric treatment approach:
Community: ______
a) Piperacillin/Tazo ± vancomycin ± gentamicin
b) Ceftriaxone + Azithromycin
b)
Case Example: Treating Pneumonia in Adults
Common pathogens: Strep (+), Hemophilus, Moraxella
Atypical bacteria: Legionella, Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Pseudomonas
Mainly cell wall inhibitors (block transpeptidase/PBP) ± protein synthesis inhibitor (30S/50S)
Empiric treatment approach:
Hospital-acquired: ____
a) Piperacillin/Tazo ± vancomycin ± gentamicin
b) Ceftriaxone + Azithromycin
a)
Case Example: Treating Pneumonia in Adults
Empirical therapy: cover ______
G (+) and G (-)
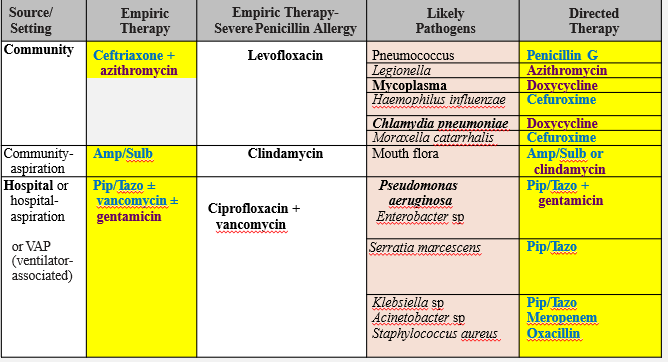
Case Example: Treating Pneumonia in Adults
Empirical therapy: cover G (+) and G (-)
G (-) cocci: Moraxella, Hemophilus= ______
2nd/ 3rd gen cephalosporins
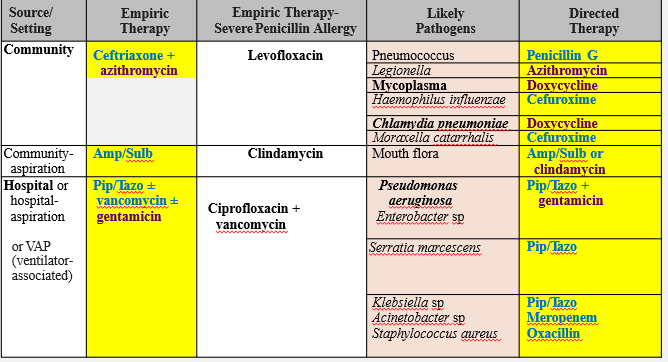
Case Example: Treating Pneumonia in Adults
Empirical therapy: cover G (+) and G (-)
G (-) cocci: Moraxella, Hemophilus= 2nd/ 3rd gen cephalosporins
Atypical bacteria (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia): ______
Doxycycline (30S inhibitor)
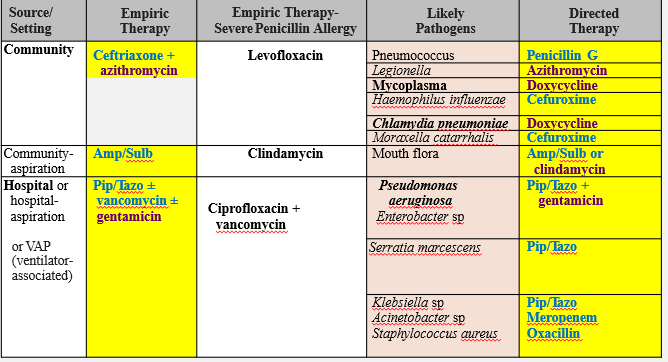
Case Example: Treating Pneumonia in Adults
Empirical therapy: cover G (+) and G (-)
G (-) cocci: Moraxella, Hemophilus= 2nd/ 3rd gen cephalosporins
Atypical bacteria (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia): Doxycycline (30S inhibitor)
Legionella: _____
Azithromycin (50S inhibitor)
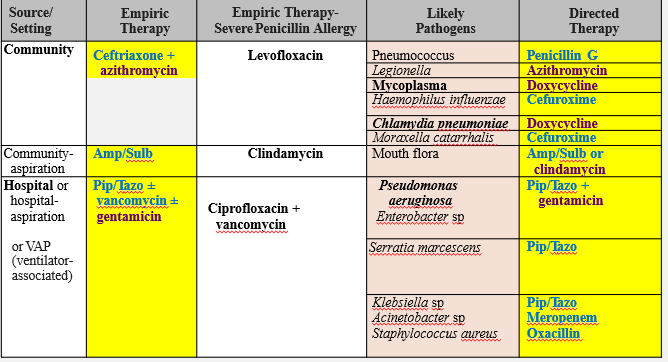
Case Example: Treating Pneumonia in Adults
Empirical therapy: cover G (+) and G (-)
G (-) cocci: Moraxella, Hemophilus= 2nd/ 3rd gen cephalosporins
Atypical bacteria (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia): Doxycycline (30S inhibitor)
Legionella: Azithromycin (50S inhibitor)
Pseudomonas: _______
Anti-pseudomonal PCN + Beta-lactamase inhibitor (cell wall inhibitor) + aminoglycoside (30S inhibitor)
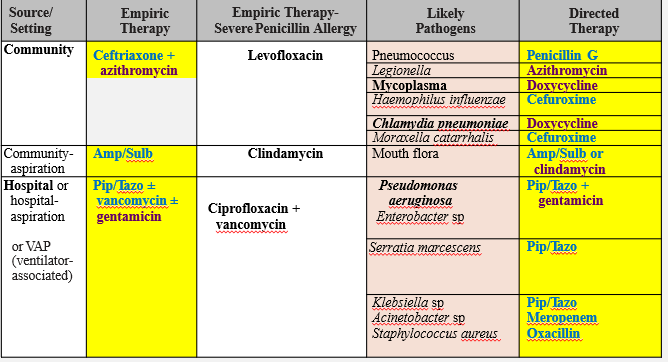
Case Example: Treating Pneumonia in Adults
Empirical therapy: cover G (+) and G (-)
G (-) cocci: Moraxella, Hemophilus= 2nd/ 3rd gen cephalosporins
Atypical bacteria (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia): Doxycycline (30S inhibitor)
Legionella: Azithromycin (50S inhibitor)
Pseudomonas: Anti-pseudomonal PCN + Beta-lactamase inhibitor (cell wall inhibitor) + aminoglycoside (30S inhibitor)
PCN allergy: use ______
Quinolones (DNA gyrase inhibitors)
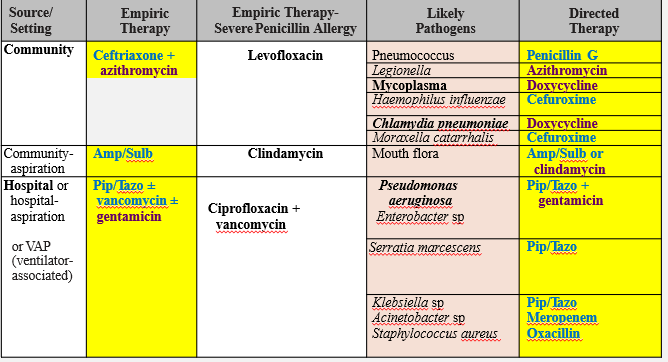
Case Example: Bacterial Meningitis in Adults
Common pathogens:
_______
N. meningitis (Gram-negative cocci)
Streptococcus pneumoniae (Gram-positive cocci)
H. influenza (Gram-negative coccobacillus)
Listeria (Gram-positive bacillus)
P. aeruginosa (Gram-negative rod)
Case Example: Bacterial Meningitis in Adults
Common pathogens:
N. meningitis (Gram-negative cocci)
Streptococcus pneumoniae (Gram-positive cocci)
H. influenza (Gram-negative coccobacillus)
Listeria (Gram-positive bacillus)
P. aeruginosa (Gram-negative rod)
Mainly ______
Empiric
Community: _______
Mainly cell wall inhibitors
Empiric
Community: Ceftriaxone + Vancomycin