Lecture 25: Common Resources, Public Goods
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what is the problem with the Coase Theorem?
there are often impediments to negotiations; when transaction costs are high you can’t reach the socially optimal outcome
if transaction costs are ________ it doesn’t matter how the court rules
zero
what are the characteristics of public goods?
non-exclusive
non-rival
what does non-exclusive mean?
it is either impossible or very expensive to exclude someone from the benefits of the goods; impossible or extremely expensive to exclude free riders
what is an example of a non-exclusive good?
public parks
what is an example of a public good?
a lighthouse
what does it mean to be non-rival?
benefits that one person gets does not deprive someone else from the benefit
why is a pizza slice a rival?
the nutrients and tastes are going to you while you are eating it and not to someone else
a private good is
exclusive and rival
a natural monopoly is (exclusive/non-exclusive, rival/non-rival)
non-rival and exclusive
why is satellite radio non-rival and exclusive?
your use of satellite radio doesn’t affect other people but you can be excluded by not paying for the service
what kind of good is a traffic-less road in Montana (you are from CA)?
public good
what kind of good is fishing in a public lake?
common resource- when someone gets a fish they deprive someone else
what kind of a good is the Golden Gate Bridge?
private good- exclusive because you have to pay and rival because you add congestion
what is the problem created by common resources?
the incentive is to overuse the resource to a point of depletion or extinction
the MR of bonds is like the __ of buying a cow
MC
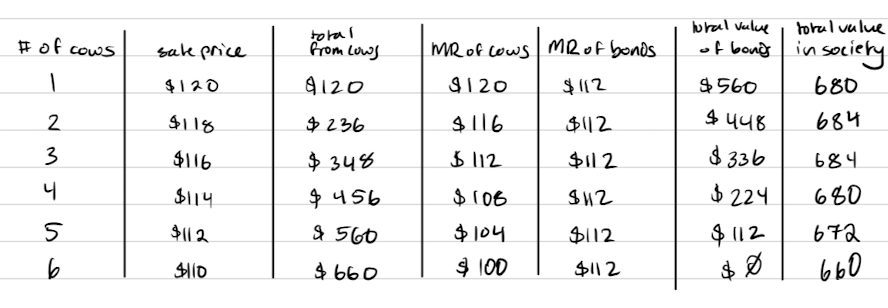
what is the end result? why is this a problem?
5 cows grazing on the commons
the optimal outcome is to have 3 cows- it gives you the highest value to society (where MR=MC)
what happens when a landowner charges rent?
they act in their self-interest but it also happens to be the socially optimal outcome
how can the problem of common resources be solved?
turn the common resource into a private good - there is no more overuse
what is the problem with the solution for common resources?
sometimes it is too expensive to turn it into a private good
if you can privatize a good it becomes
sustainable
what are the problems with public goods?
free rider problem that leads to an under/no supply of the good
free rider problem
people are benefiting from resources, goods, services, etc that they are not paying for
what is the solution to the problem for public goods?
sponsorship
tying private goods to public goods to pay for the public good
taxation
why does taxation occur?
if we rely on private markets we won’t be able to finance public goods
taxation is _________ payment
coercive
if we rely on Pareto there will be an ________/___ supply of public goods
undersupply, no
taxation achieves what kind of efficiency?
Kaldor-Hicks
rational abstention
not participating in democracy
rational to not participate because the expected benefits are less than the cost of