Social Psychology: Conformity, Attitudes, and Prejudice
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Social psychology
The scientific study of how a person's thoughts, feelings, and behavior are influenced by the real, imagined, or implied presence of others.
Social influence
The process through which the real or implied presence of others can directly or indirectly influence the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of an individual.
Conformity
Changing one's own behavior to match that of other people.
Groupthink
Kind of thinking that occurs when people place more importance on maintaining group cohesiveness than on assessing the facts of the problem with which the group is concerned.
Consumer psychology
Branch of psychology that studies the habits of consumers in the marketplace, including compliance.
Compliance
Changing one's behavior as a result of other people directing or asking for the change.
Foot-in-the-door technique
Asking for a small commitment and, after gaining compliance, asking for a bigger commitment.
Door-in-the-face technique
Asking for a large commitment and being refused, and then asking for a smaller commitment.
Norm of reciprocity
Assumption that if someone does something for a person, that person should do something for the other in return.
Lowball technique
Getting a commitment from a person and then raising the cost of that commitment.
That's-not-all technique
A sales technique in which the persuader makes an offer and then adds something extra to make the offer look better before the target person can make a decision.
Obedience
Changing one's behavior at the command of an authority figure.
Milgram study
"Teacher" administered what they thought were real shocks to a "learner."
Group polarization
The tendency for members involved in a group discussion to take somewhat more extreme positions and suggest riskier actions when compared to individuals who have not participated in a group discussion.
Social facilitation
The tendency for the presence of other people to have a positive impact on the performance of an easy task.
Social loafing
The tendency for people to put less effort into a simple task when working with others on that task.
Attitude
A tendency to respond positively or negatively toward a certain person, object, idea, or situation.
Components of an attitude
The three components of an attitude are the affective (emotional) component, the behavioral component, and the cognitive component.
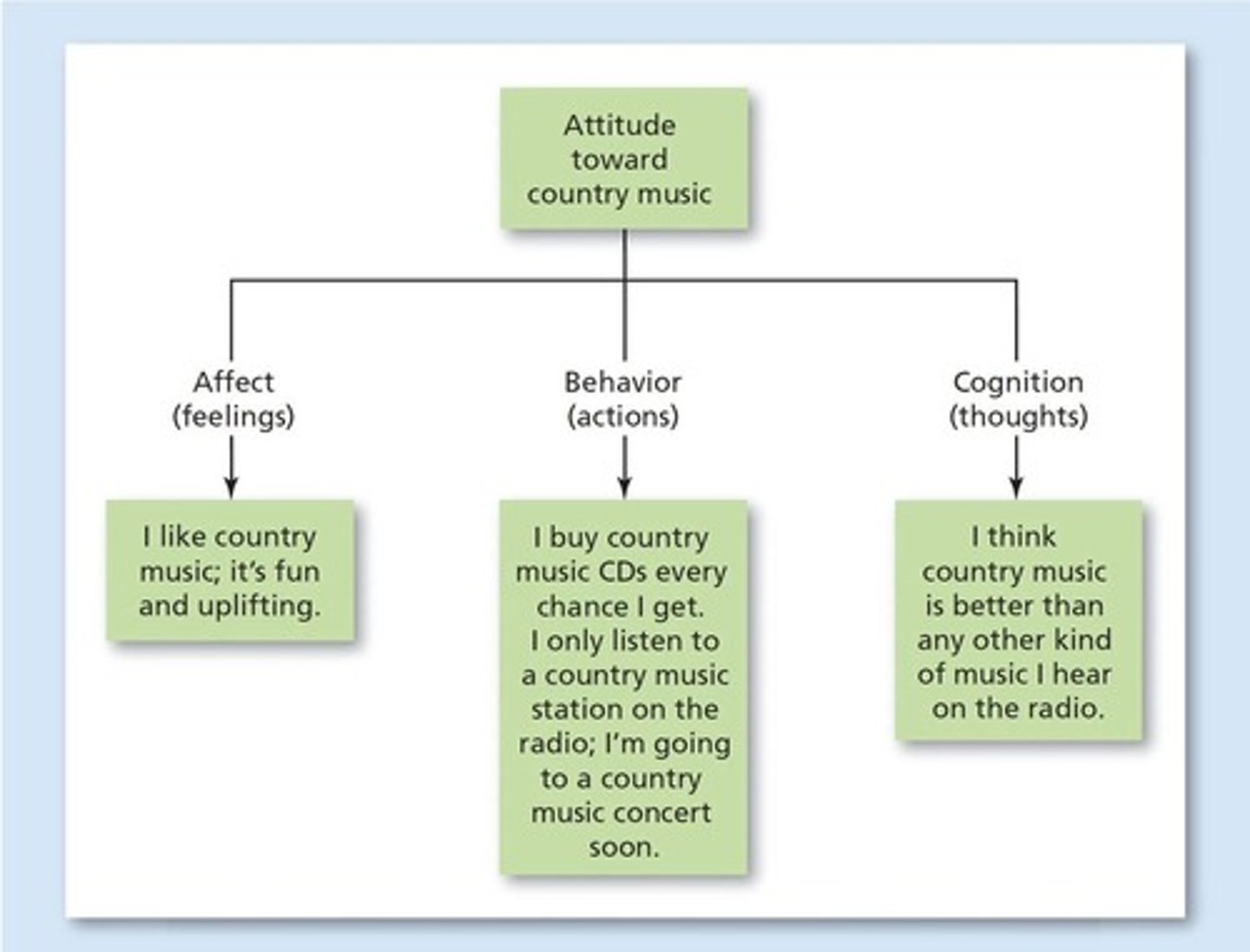
Attitude
often poor predictors of behavior unless it isvery specific or very strong.
Formation of attitudes
Direct contact with the person, situation, object, or idea; direct instruction from parents or others; interacting with other people who hold a certain attitude; vicarious conditioning.
Persuasion
The process by which one person tries to change the belief, opinion, position, or course of action of another person through argument, pleading, or explanation.
persuasion
The source of the message, the message itself, and the target audience.
Elaboration likelihood model
Model of persuasion stating that people will either elaborate on the persuasive message or fail to elaborate on it, and that the future actions of those who do elaborate are more predictable than those who do not.
Central-route processing
Type of information processing that involves attending to the content of the message itself.
Peripheral-route processing
Type of information processing that involves attending to factors not involved in the message, such as the appearance of the source of the message, the length of the message, and other noncontent factors.
Cognitive dissonance
Sense of discomfort or distress that occurs when a person's behavior does not correspond to that person's impression.
Impression formation
The forming of the first knowledge that a person has concerning another person.
Primacy effect
The very first impression one has about a person tends to persist even in the face of evidence to the contrary.
Social categorization
the assignment of a person one has just met to a category based on characteristics the new person has in common with other people with whom one has had experience in the past.
Stereotype
a set of characteristics that people believe is shared by all members of a particular social category.
Implicit personality theory
sets of assumptions about how different types of people, personality traits, and actions are related to each other.
Schemas
mental patterns that represent what a person believes about certain types of people. ___ can become stereotypes.
Attribution
the process of explaining one's own behavior and the behavior of others.
Attribution theory
the theory of how people make attributions.
Situational cause
cause of behavior attributed to external factors, such as delays, the action of others, or some other aspect of the situation.
Dispositional cause
cause of behavior attributed to internal factors such as personality or character.
Fundamental attribution error
the tendency to overestimate the influence of internal factors in determining behavior while underestimating situational factors.
Prejudice
negative attitude held by a person about the members of a particular social group.
Discrimination
treating people differently because of prejudice toward the social group to which they belong.
In-groups
social groups with whom a person identifies; 'us.'
Out-groups
social groups with whom a person does not identify; 'they.'
Realistic conflict theory
conflict between groups increases prejudice and discrimination.
Scapegoating
tendency to direct prejudice and discrimination at out-group members who have little social power or influence.
Social cognitive theory
views prejudice as an attitude acquired through direct instruction, modeling, and other social influences.
Social identity theory
theory in which the formation of a person's identity within a particular social group is explained by social categorization, social identity, and social comparison.
Social identity
the part of the self-concept including one's view of self as a member of a particular social category.
Social comparison
the comparison of oneself to others in ways that raise one's self-esteem.
Stereotype vulnerability
the effect that people's awareness of the stereotypes associated with their social group has on their behavior.
Self-fulfilling prophecy
the tendency of one's expectations to affect one's behavior in such a way as to make the expectation more likely to occur.
Equal status contact
Contact between groups in which the groups have equal status, with neither group having power over the other.
Jigsaw classroom
Educational technique in which each individual is given only part of the information needed to solve a problem, causing the separate individuals to be forced to work together to find the solution.
Interpersonal attraction
Liking or having the desire for a relationship with another person.
Proximity
Physical or geographical nearness.
Reciprocity of liking
Tendency of people to like other people who like them in return.
Love
A strong affection for another person due to kinship, personal ties, sexual attraction, admiration, or common interests.
Sternberg's Triangular Theory of Love
Theory that states the three components of love are intimacy, passion, and commitment.
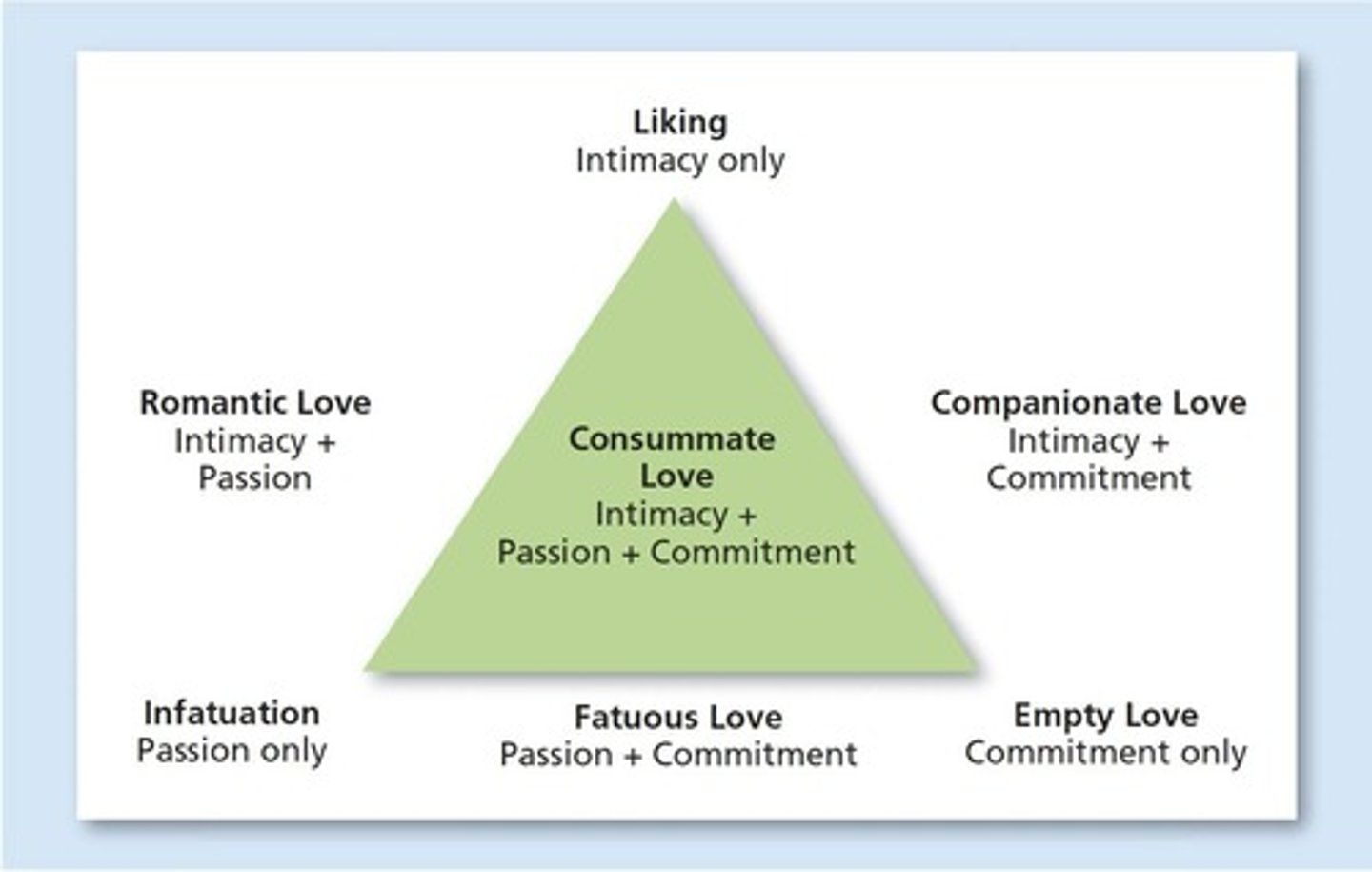
Romantic love
Type of love consisting of intimacy and passion.
Companionate love
Type of love consisting of intimacy and commitment.
Aggression
Behavior intended to hurt or destroy another person.
aggression
bio influence: May include genetics, the amygdala and limbic system, and testosterone and serotonin levels.
Social role
The pattern of behavior that is expected of a person who is in a particular social position.
Prosocial behavior
Socially desirable behavior that benefits others.
Altruism
Prosocial behavior that is done with no expectation of reward and may involve the risk of harm to oneself.
Bystander effect
Referring to the effect that the presence of other people has on the decision to help or not help, with help becoming less likely as the number of it increases.
Diffusion of responsibility
Occurring when a person fails to take responsibility for actions or for inaction because of the presence of other people who are seen to share the responsibility.
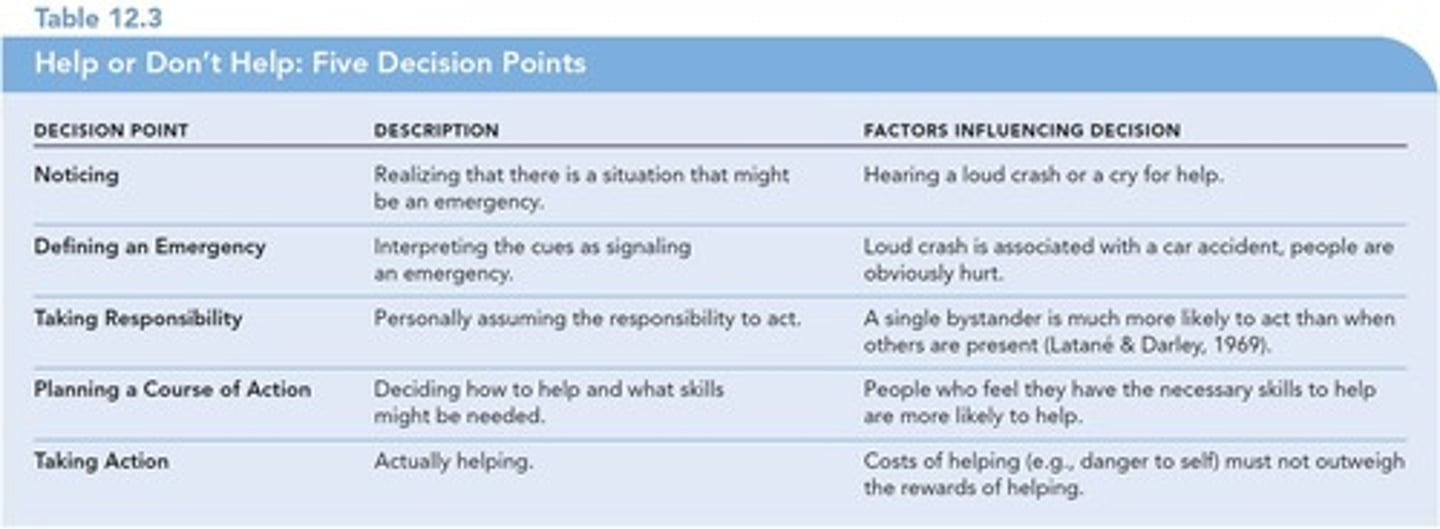
Five Steps in Making a Decision to Help
1. Noticing 2. Defining an emergency 3. Taking responsibility 4. Planning a course of action 5. Taking action.
Cults
Groups that people join, often characterized by stress, unhappiness, gullibility, and idealism, using love-bombing, isolation, rituals, and activities to keep recruits from questioning.