BSTAT Exam 2
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
College of the Ozarks Fall 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the components of central tendency
Mean, median, and mode
Variation is measured using:
range, interquartile range, variance, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation.
Range
largest # - smallest #
Interquartile range
Quartile 3 - Quartile 1
Coefficient of variation =
Standard deviation/mean

sample mean
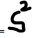
Sample Variance
S
Sample Standard Deviation
𝜇
population mean
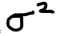
population variance
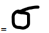
Population standard deviation
n
sample size
N
population
Sample computed measurement =
statistic
population computed measurement =
parameter
What does the 5-number summary consist of?
smallest number
Quartile 1
Median
Quartile 3
Largest Number
these convert a number to be expressed as standard deviations
z-scores (z-score of 2 means our number is two standard deviations away from the mean)
how to find z-score on excel
=STANDARDIZE(x,mean,standard dev)
How is an outlier determined?
if it is at least 3 standard deviations away from the mean.
NOT normally distributed
Chebyshev’s theorem
in Chebyshev’s theorem, what % of the data must be withing 2 standard deviations of the mean?
75%
in Chebyshev’s theorem, what % of the data must be withing 3 standard deviations of the mean?
89%
in Chebyshev’s theorem, what % of the data must be withing 4 standard deviations of the mean?
94%
According to the Empirical Rule, what % of the data must be within 1 standard deviation of the mean?
68%
According to the Empirical Rule, what % of the data must be within 2 standard deviation of the mean?
95%
According to the Empirical Rule, what % of the data must be within 3 standard deviation of the mean?
99.7%
Normally distributed with 0 skewness
Empirical Rule (Bell-shaped)
Discrete Random variable
a random variable that may assume a finite number of values
Finite =
Discrete
Probability Distribution
A list or function that shows all the possible outcomes of a random event and their corresponding probabilities.
E(x) =
average or mean
Calculate probability distribution:
Mean = x*f(x)
Standard Deviation
Sum(x-E(x))² f(x) FORMULA WILL BE ON TEST
4 Properties of binomial distribution
the experiment consists of a sequence of n identical trials
the outcomes are possible on each trial. We refer to one outcome as a success and the other outcomes as a failure.
the probability of a success (p), cannot change from trial to trial. and the probability of a failure, (1-p) does not change from trial to trial
the trials are independent
the probability of a success =
p
the probability of a failure =
1-p
Properties of Poisson distribution
Events are independence
Constant rate
Discrete events (two events cannot occur at the same time)
mean=variance
STANDARD DEVIATION = the mean
The Standard Deviation of a poisson distribution =
Mean