Chemistry Regents Review
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Dalton's model of the atom
- atoms cannot be created nor destroyed
- mass of reactants = mass or products
Thompson's model of the atom; "Plum pudding"
- cathode ray tubes
- discovery of the electron
- positive and negative charges randomly scattered
Rutherford's model of the atom; "Nuclear model"
- gold foil experiment
- atom is mostly empty space
- positively charged center (nucleus)
- negative charges randomly scattered around nucleus
Bohr's model of the atom; "Planetary model"
- electrons revolve around nucleus, like planets to the sun
- orbitals = circular paths
Modern model; "Wave Mechanical"
- electrons have particle and wavelike properties
- orbital = location of an electron (not a circular path)
Charge, weight, and location of proton
+1, 1 amu, nucleus
Charge, weight, and location of electron
-1, 0 amu, orbitals
Charge, weight, and location of neutron
0, 1 amu, nucleus
Amount of each subatomic particle
number of protons = atomic number
number of electrons = number of protons (IF NOT AN ION)
number of neutrons = (mass number) - (number of protons)
Isotope
same element, different mass number; same number of protons, different number of neutrons
Average atomic mass formula
(% abundance as decimal)(mass) + (% abundance as decimal)(mass)
Principle energy level
orbital
- 1st p.e.l. = maximum 2 electrons
- 2nd p.e.l. = 8 electrons
- 3rd p.e.l. = 18 electrons
Valence electrons
electrons in the outermost principle energy level
The farther away an orbital is from the nucleus…
the more energy the orbital and its electrons have
Ground state
the state where the atoms are in the lowest available principle energy levels
- stable
Excited state
the state when an electron absorbs exactly the right amount of energy, jumping to a higher energy level
- unstable
- releases energy, in the form of bright line spectra, when it returns to ground state
- spectra lines are unique to each element
Pure substances
elements or compounds
- can only be broken down / changed by a chemical reaction
Elements
contains 1 type of atom, cannot be decomposed further
Compounds
contains 2 or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions
Mixtures
2 or more elements combined without a chemical reaction taking place
- can be homogeneous or heterogeneous
Separation methods of mixtures
distillation, filtration, evaporation, chromatography, desalination (all physical separation)
Filtration: small particles pass through, large particles trapped
Filtrate - substance that passes through the filter
Residue - substance trapped on the filter
Cannot be used to separate homogeneous mixtures, including solutions
Distillation: separation based on differences in boiling points
Chromatography: components of a mixture separate based on differences in the attraction from a transporting medium
Separation methods of compounds
chemical reactions; cannot be separated physically
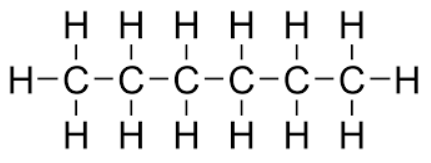
Molecular formula
shows the actual ratio of atoms (ex. C₆H₁₄)
Empirical formula
shows the ratio of atoms in simplest terms (ex. C₆H₁₄ would turn into C₃H₇)
Structural formula
shows bonding
Charge of an atom
neutral, number of protons = number of electrons
Ions
charged particles
loss of electrons = positive ion
gain of electrons = negative ion
Polyatomic ions
ions that contain more than one element
Exothermic reaction
heat is released; heat is a product (ex. breaking a bond = exothermic; “breaking glowstick releases light”)
Endothermic reaction
heat is absorbed; heat is a reactant (ex. forming a bond = endothermic)
Law of Conservation of Mass
during a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed, the number and types of atoms on both sides of the chemical equation must be the same
Synthesis
2 or more elements/compounds combine to form 1 product
Decomposition
a single compound is broken down to form 2 or more products
Single Replacement
a single element replaces another element in a compound
Double Replacement
the elements in combining compounds “switch”
An element can only replace an element that is…
less reactive
Naming ionic compounds
keepthe name of the first element, modify ending to -ide unless it is a polyatomic ion
Naming covalent compounds
follow ionic rules, then use a prefix for the amount of the first element (ex. 2 = di)
Gram Formula Mass
(amount of each individual atom) * (its weight); expressed in grams rather than amu
Percentage of Water in a Hydrate
(mass of water) / (mass of the whole compound) * 100
Mole
the number of particles (Avogadro’s number) that have a mass equal to the gram formula mass (ex. 18g of H₂O is 1 mole because H₂O has a gfm of 18g)
Phase changes
Change | Name |
solid → liquid | melting / fusion |
liquid → gas | vaporization |
liquid → solid | freezing / solidification |
gas → liquid | condensation |
solid → gas | sublimation |
gas → solid | deposition |
Kinetic Energy
energy of motion
greater the kinetic energy, the faster the particles are moving
Potential Energy
stored energy; energy of position
During phase change…
kinetic energy - constant
potential energy - changes
If heating, potential energy ↑
If cooling, potential energy ↓
There are __ phases present during phase change
2
Heat flows from…
hot → cold, until at equilibrium
Heat equations and their purposes
q = mc∆T | use when there is a change in temperature |
q = mH₁ | use when melting / freezing is taking place |
q = mH₂ | use when evaporation / condensation is taking place |
H₁ = heat of fusion
H₂ = heat of vaporization
Kinetic Molecular Theory
used to explain the behavior of gases
Assumptions:
Gas particles are in constant, random straight line motion
Gas particles collide with each other and the walls of the container (collisions are elastic - no net change in energy)
Gas particles are separated by great distances (volume of particles is negligible)
Gas particles do not attract each other
Gas Relationships
Pressure and # of particles | Direct |
Pressure and Temperature | Direct |
Pressure and Volume | Indirect |
Temperature and Velocity | Direct |
Combined Gas Law
(P₁V₁) / T₁ = (P₂V₂) / T₂
Temperature MUST be in Kelvins
If any variables are constant, cross them out in the formula
Gases behave most ideal in…
high temperature and low pressure
Most ideal gases - hydrogen, helium
Avogadro’s Law
equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and same pressure have an equal number of particles