orthopedics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
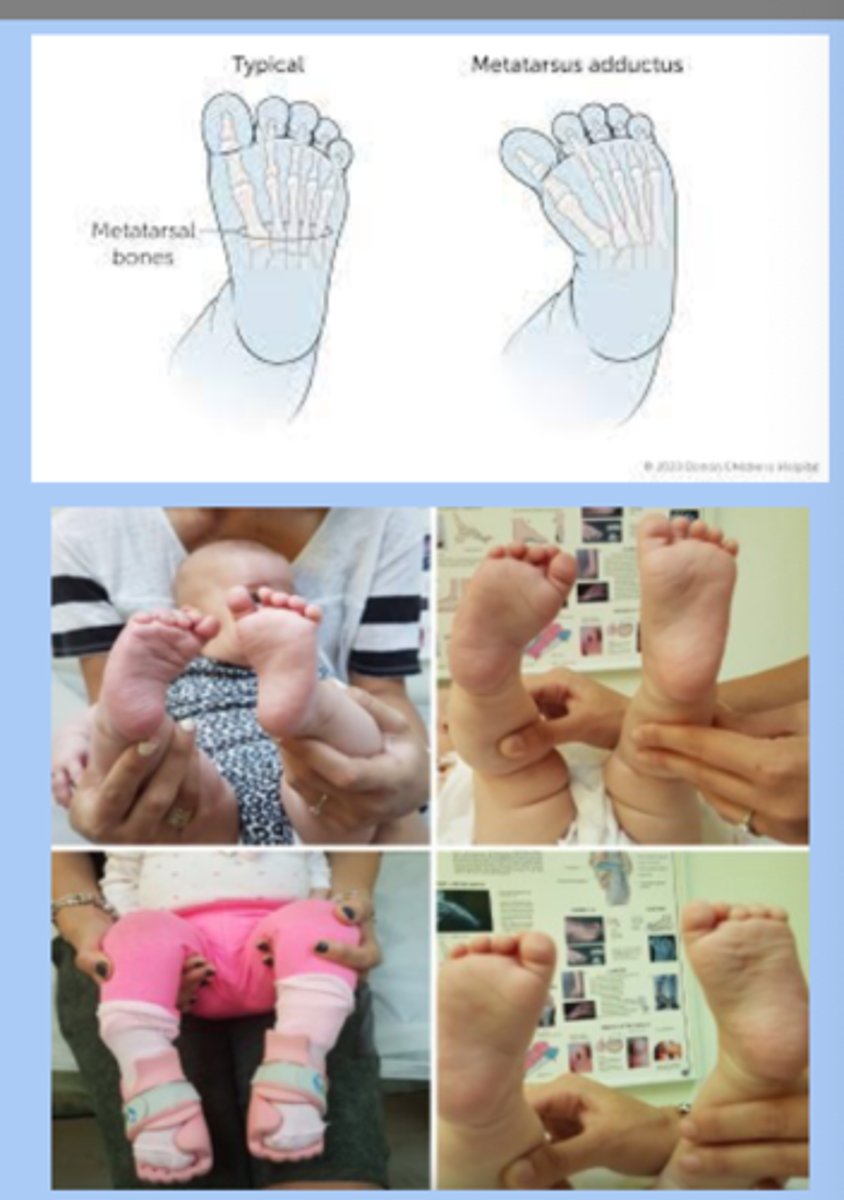
metatarsus adductus
-most common foot deformity
-inward forefoot deviation
-flexible: resolves spontaneously
-rigid: vertical creases, needs tx
-10% have hip dysplasia
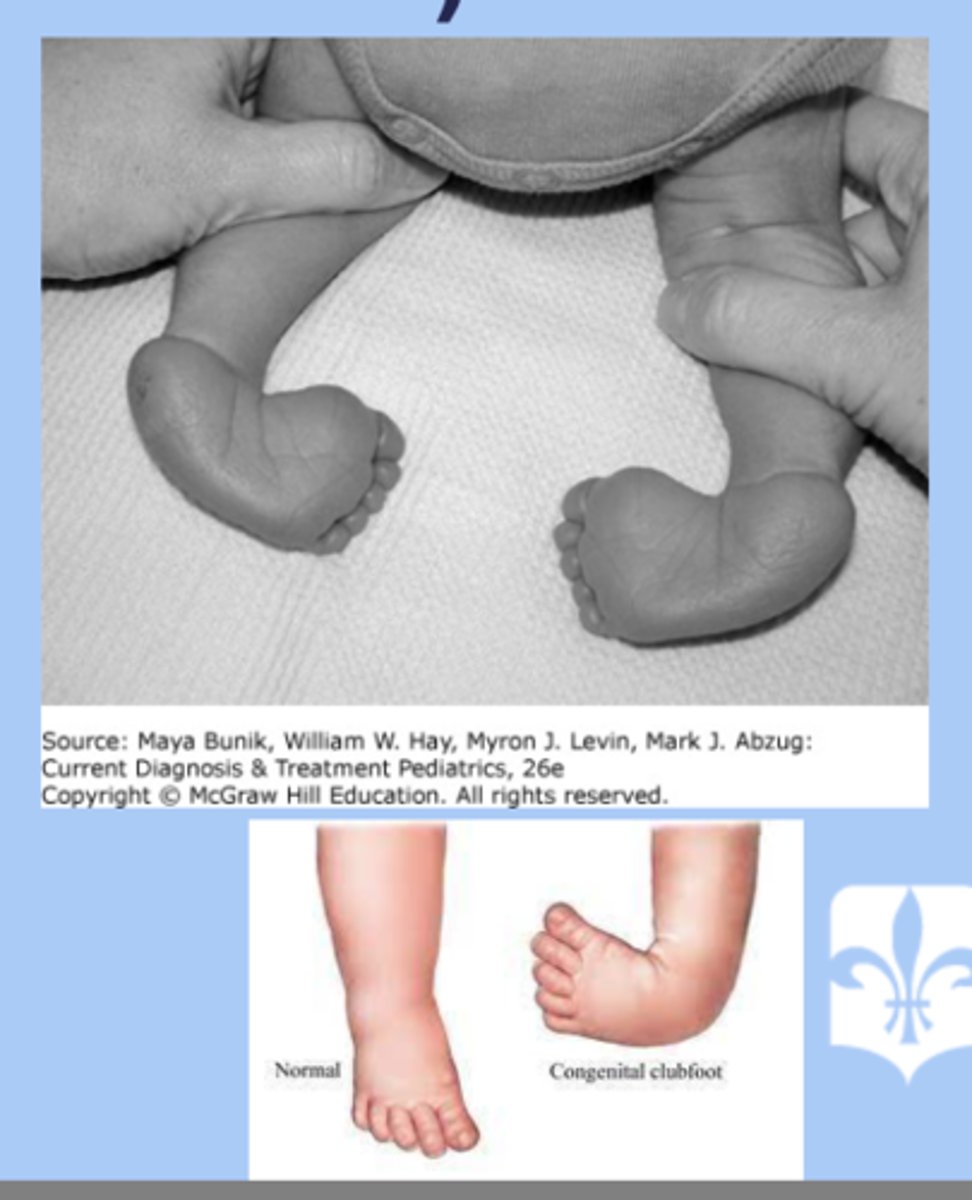
talipes equinovarus (clubfoot)
-idiopathic most common
-check spine
-dx: equinus (plantar flexion), varus (heel inversion), adductus (forefoot medial deviation)
-tx: ponseti technique, start immediately after birth
talipes calcaneovalgus
-opposite of clubfoot: excessive dorsiflexion at ankle + foot eversion
-caused by intrauterine positioning
-tx: passive streching exercises
-resolves 3-6 mons w tx
flatfoot
-universal flatfoot in new walkers
-15% do not resolve spontaneously
-sx: shortened heel cord, pain, stiffness of foot
-dx: xray
-tx: flexible= no tx, symptomatic= good shoes, severe= surgery
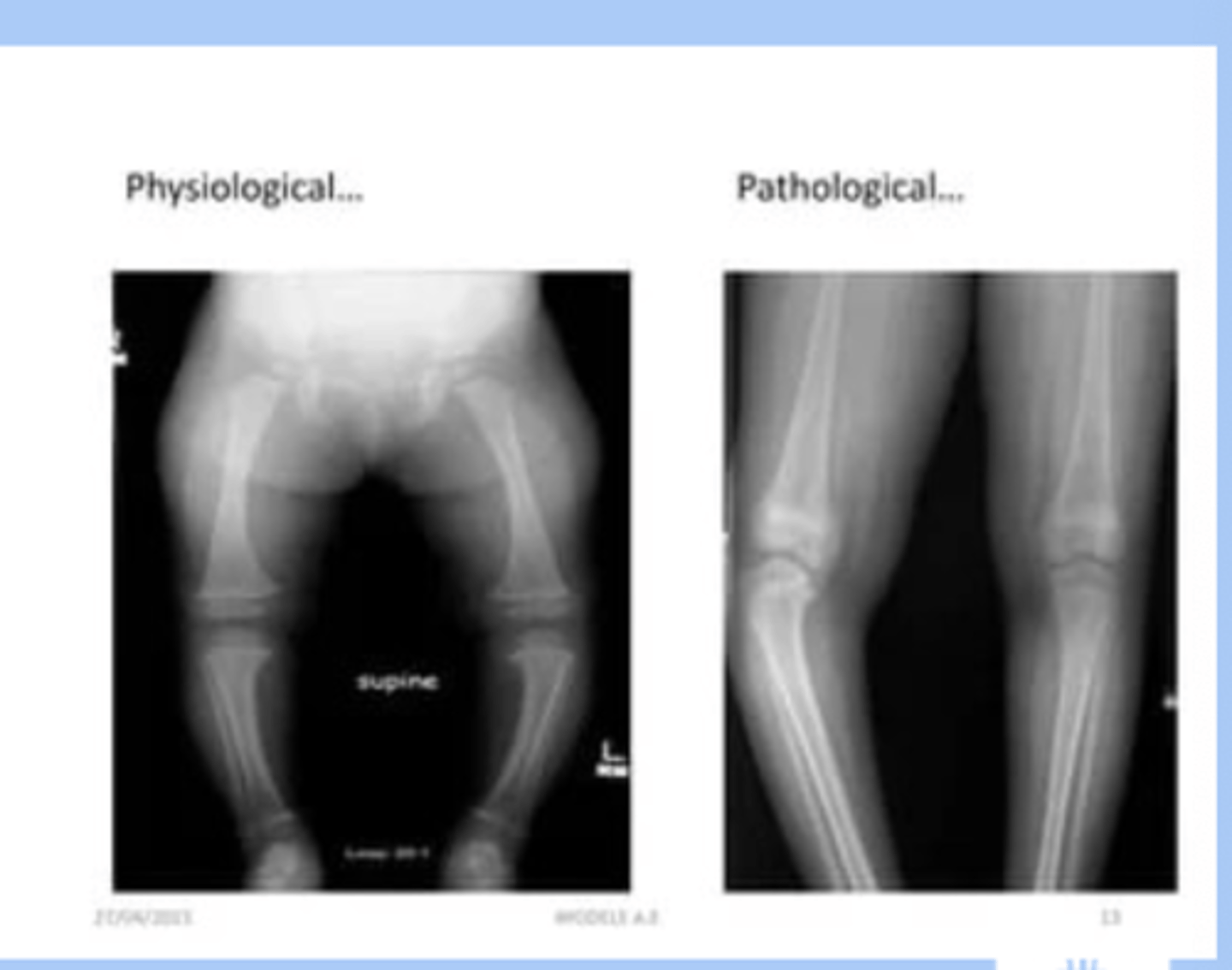
genu varum
-varum: excessive varus angulation at knee (bowleg)
-0-3yr: varum is normal
-pathologic: blounts disease (tibal rotation), obesity, early walking, genetics
-referral in persist beyond 2, bowing increases, only in one leg
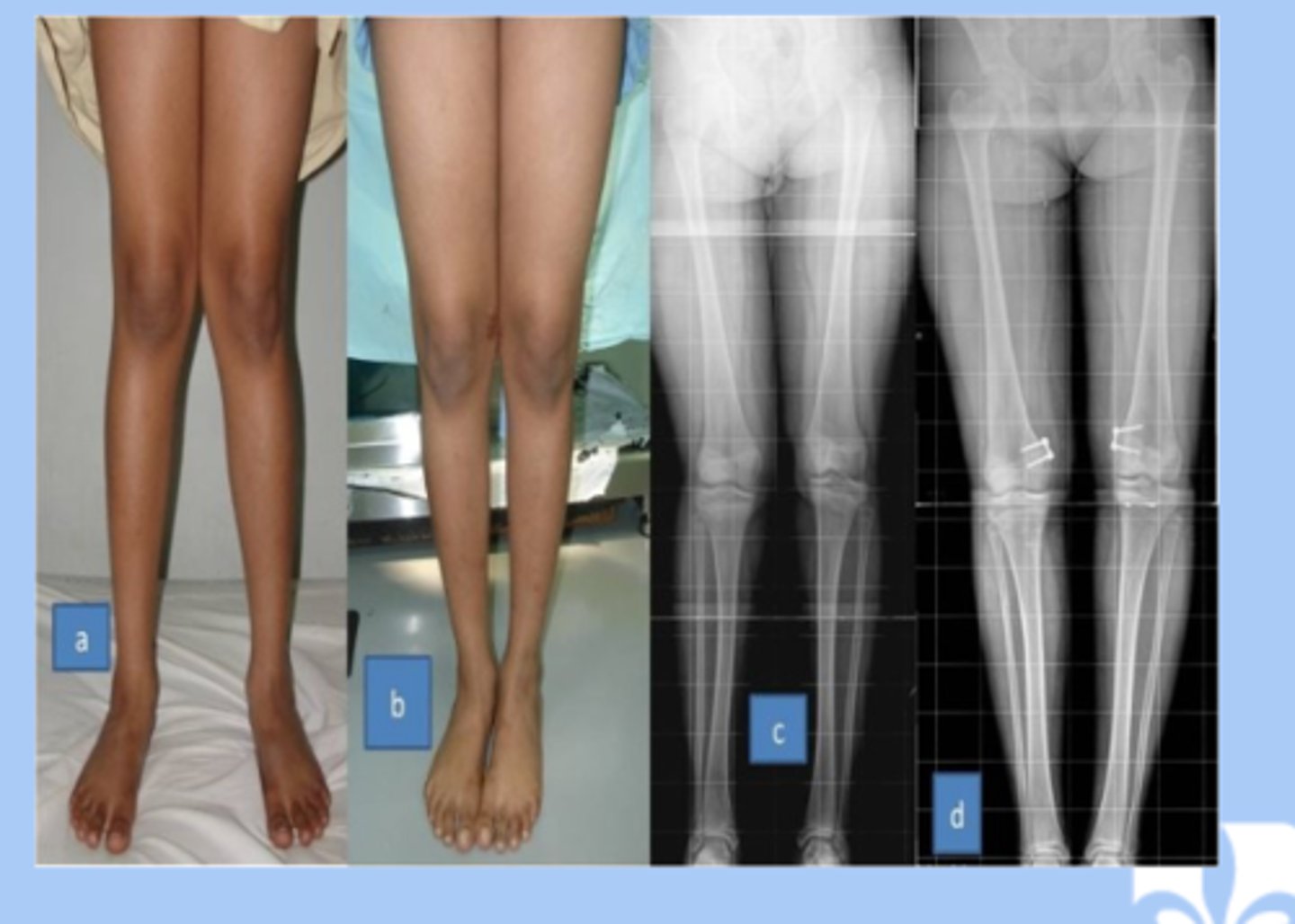
genu valgum
-valgum: excessive valgus at the knee (knock kneed)
-3-8yr: valgum is normal
-pathologic: skeletal dysplasia or rickets, obesity
-referral in short stature, function limitations or pain, persist past normal timeline
developmental dysplasia of the hip joint (DDH)
-abnormal relationship between the proximal femur and the acetabulum exists
-major risks: first born, female, breech position, family hx of DDH
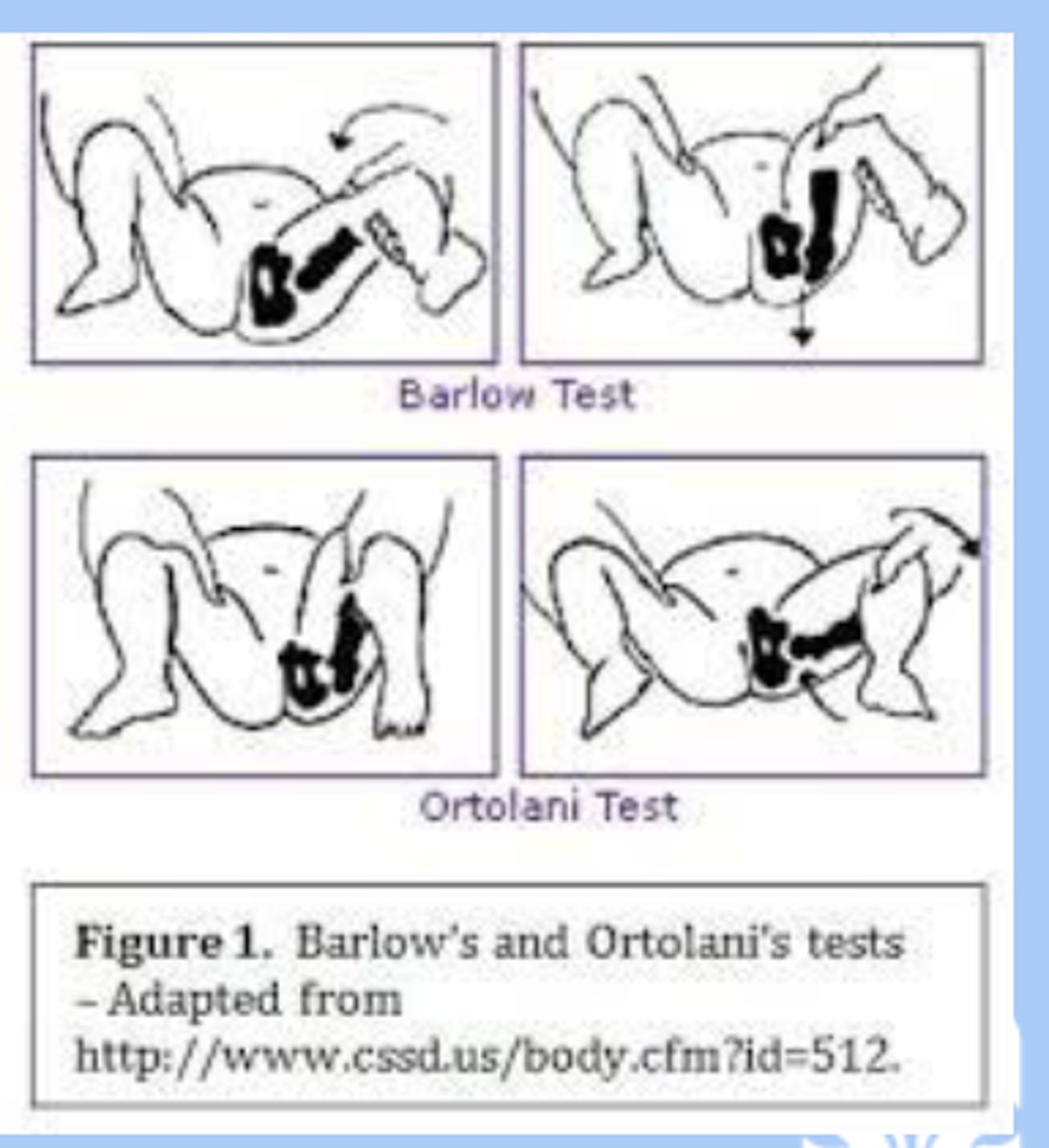
-sx: asymmetric skin folds, asymmetric knee, barlow's sign, ortolani's sign, painless limp, trendelenburg sign (dip in pelvis), bilateral DDH
-dx: ultrasonography, high risk screened for DDH w US at 6 weeks, if normal XR follow up at 6mon
-tx: orthopedic surgery
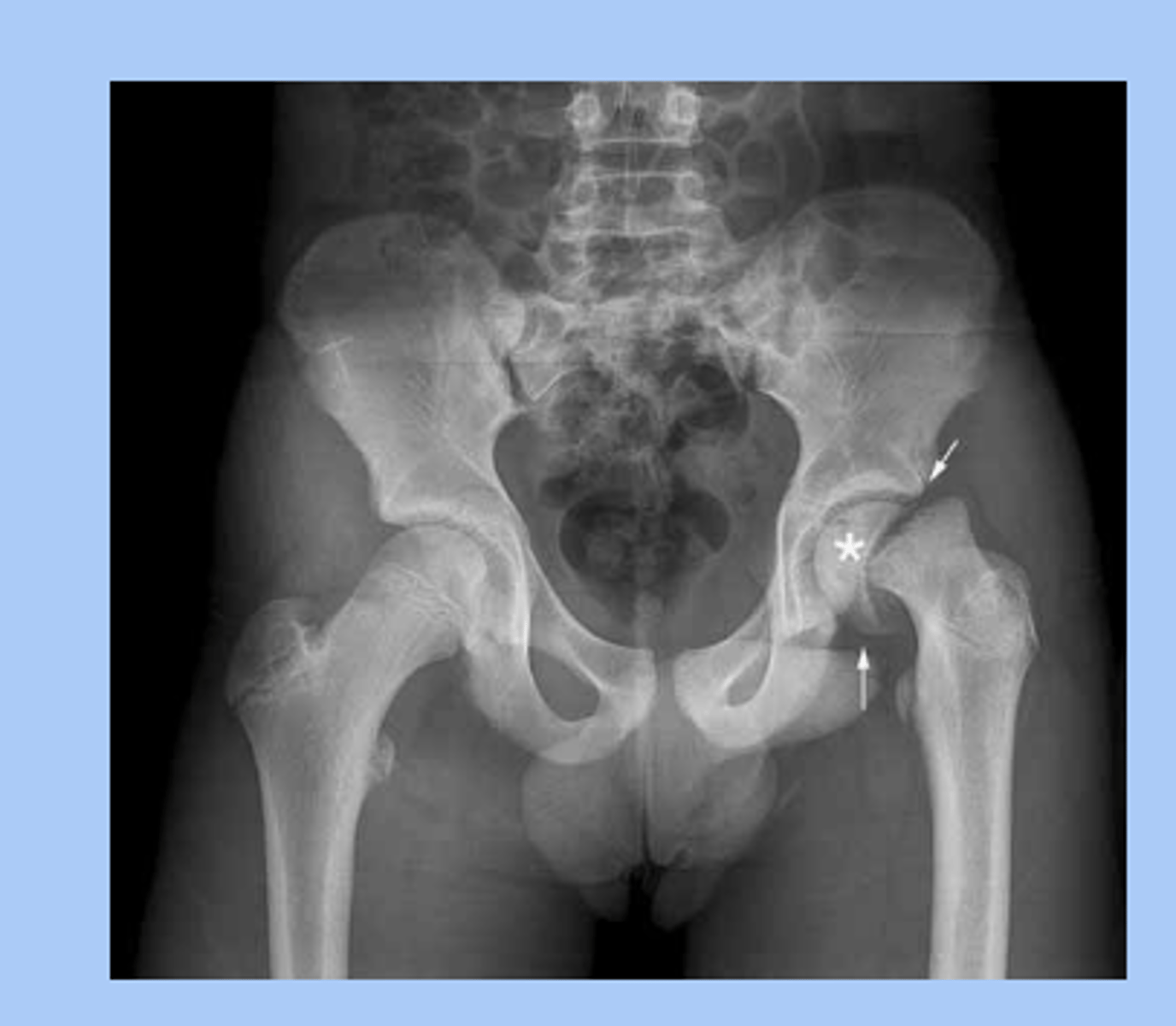
slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
-hip disorder caused by displacement of the proximal femoral epiphysis due to disruption of the growth plate
-RF: 9-16yo proceeds adolescent growth spurt, females 11.5, males 13, the big kids
-stable: bear weight
-unstable: unable to bear weight
-chronic SCFE is more common
-sx: atraumatic, pain + limp, limited internal rotation of hip
-dx: radiograph: ice cream slipping off cone
-tx: non-weight bearing on crutches, immediate referral to ortho, surgery
-development of avascular necrosis= poor prognosis
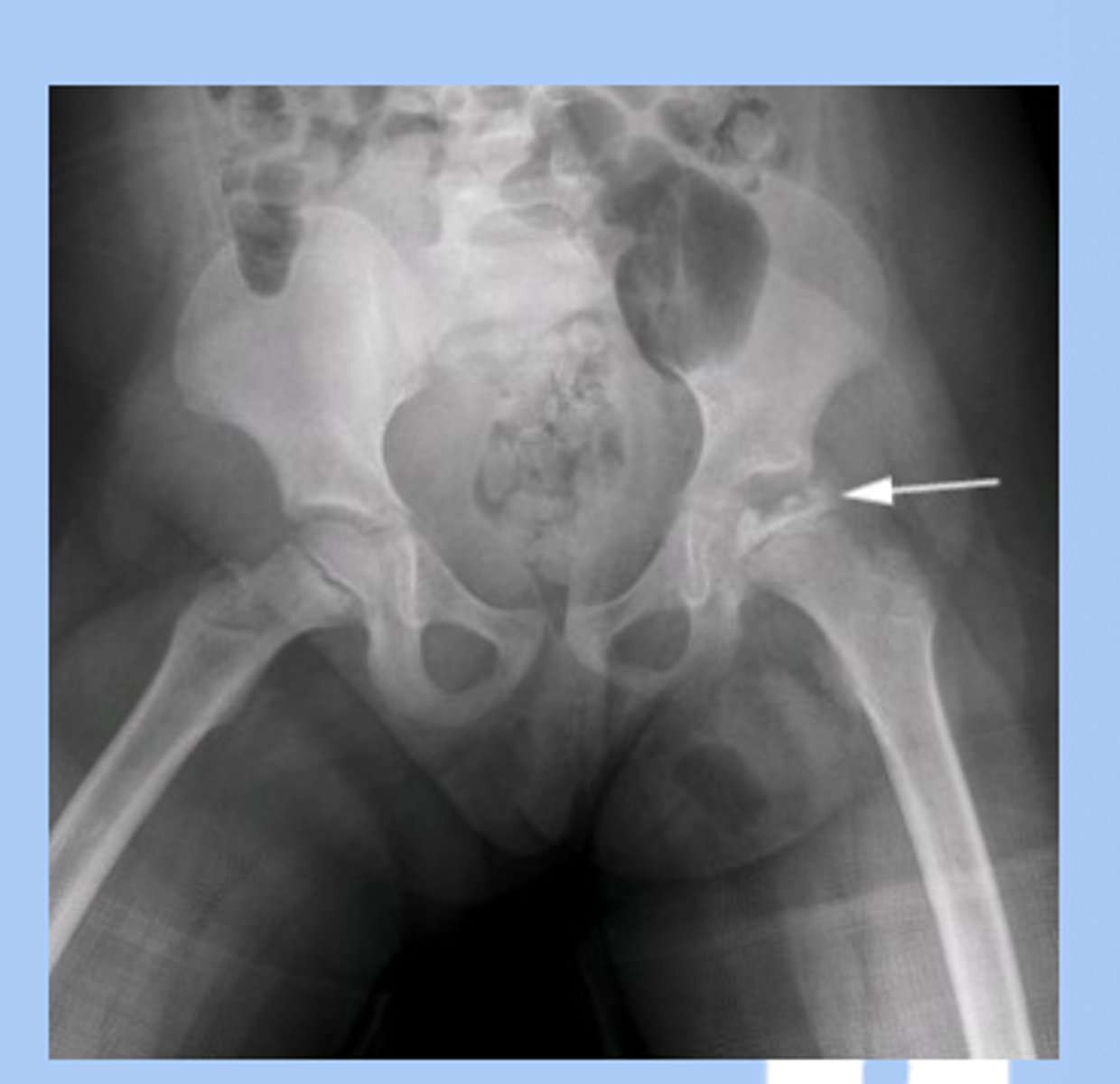
Hip Legg-calve-perthes disease
-idiopathic osteronecrosis (avascular necrosis) of the hip
-RF: 3-12yo, males, bilateral in 15%
-sx: insidious onset, painless limp
-dx: high index of suspicion, initial XR normal, as progresses XR shows fragmentation of femoral head and then healing of femoral head
-tx: non weight bearing, immediate referral
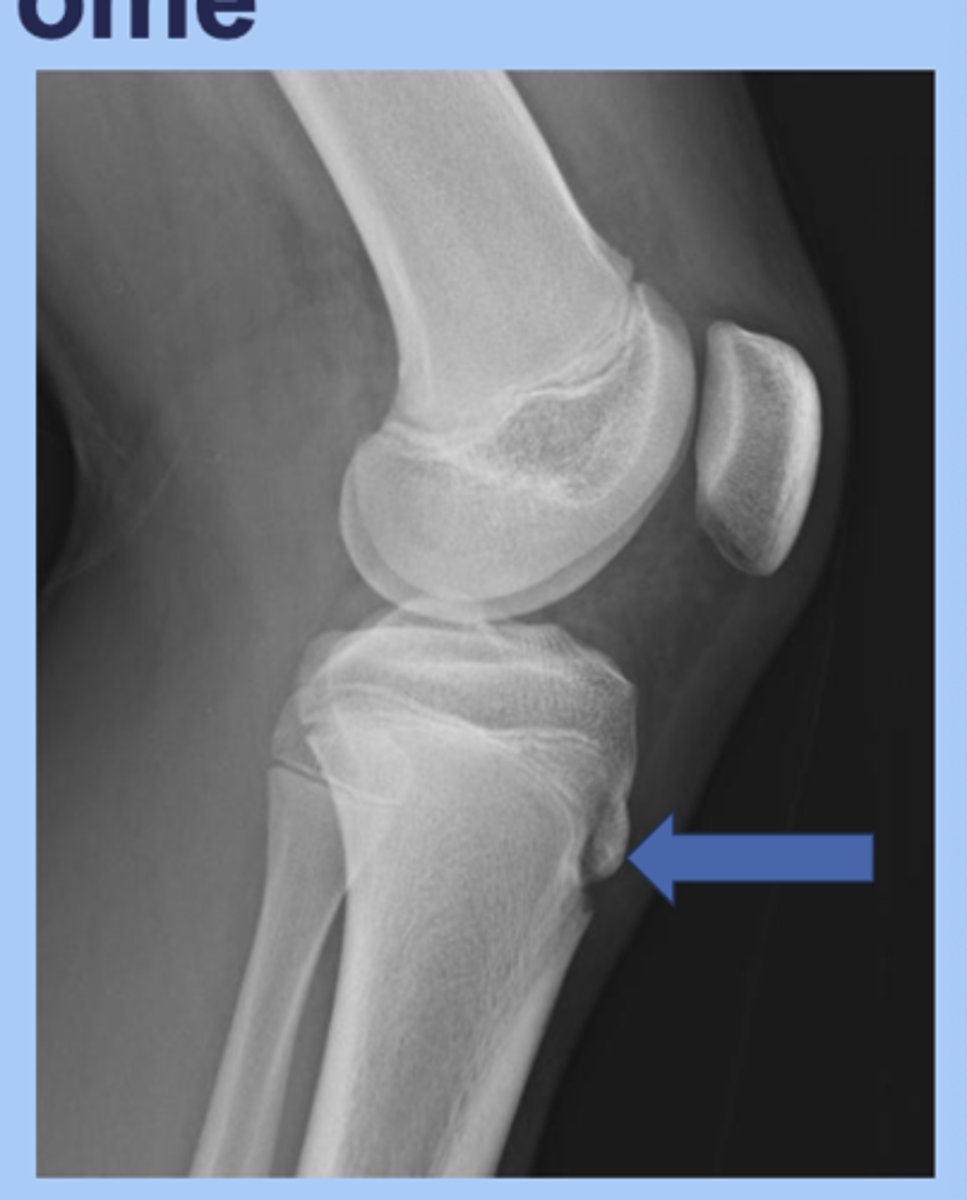
osgood-schlatter syndrome
-tibial tuberosity apophysitis (inflammation of tibial plate)
-common in active adolescents
-repetitive stress activities
-sx: knee pain with activity, improves with rest, palpable tibial tuberosity
-dx: XR may show fragmentation
-tx: rest, activity modification
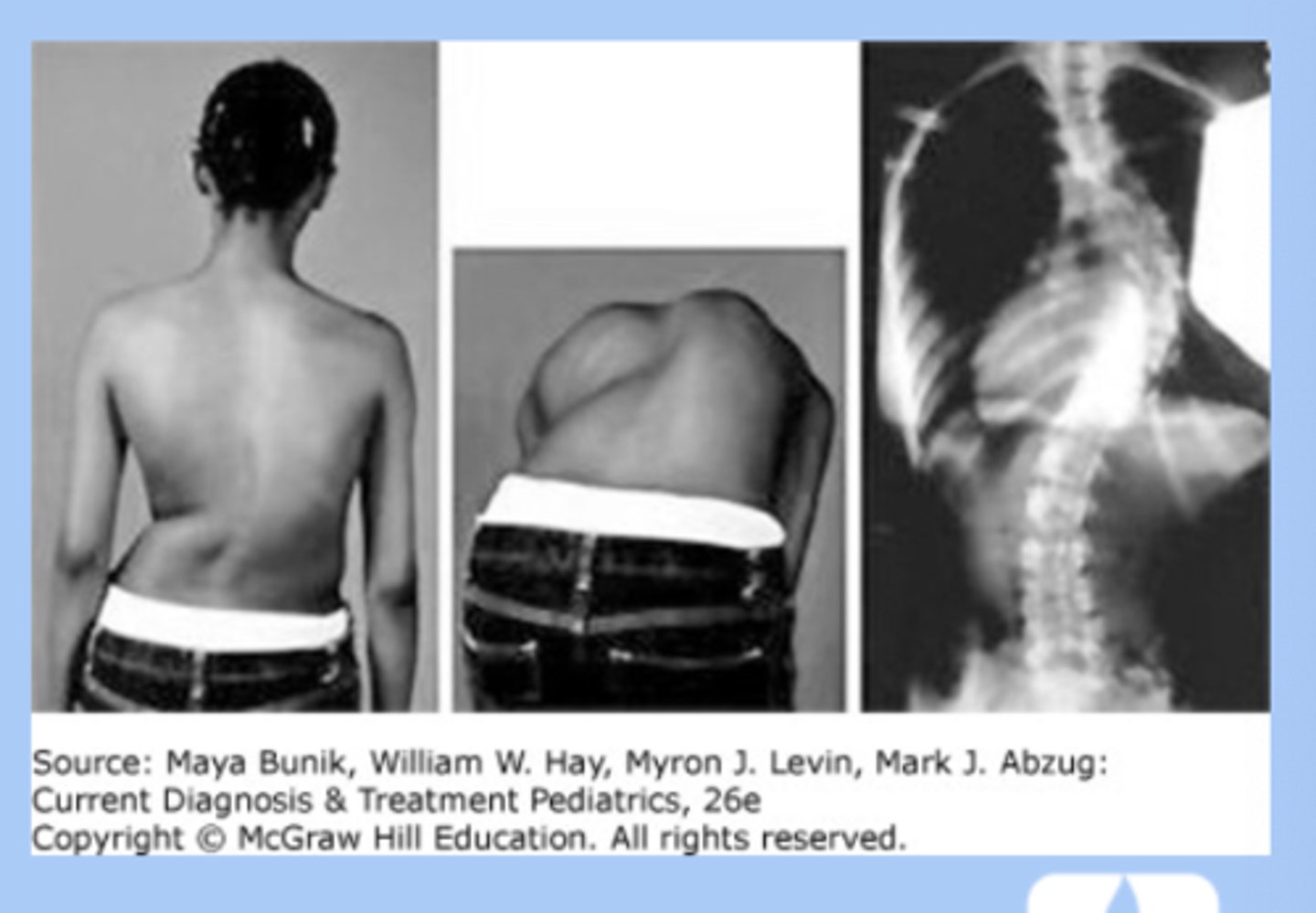
scoliosis
-lateral spine curvature + vertebral rotation
-location thoracic
-idiopathic (80%), girl 10-12
-sx: usually painless, deformity of rib cage, scapular wing
-screening: adams forward bend test at age 9
-dx: XR
-tx: waitful watching, bracing, surgery
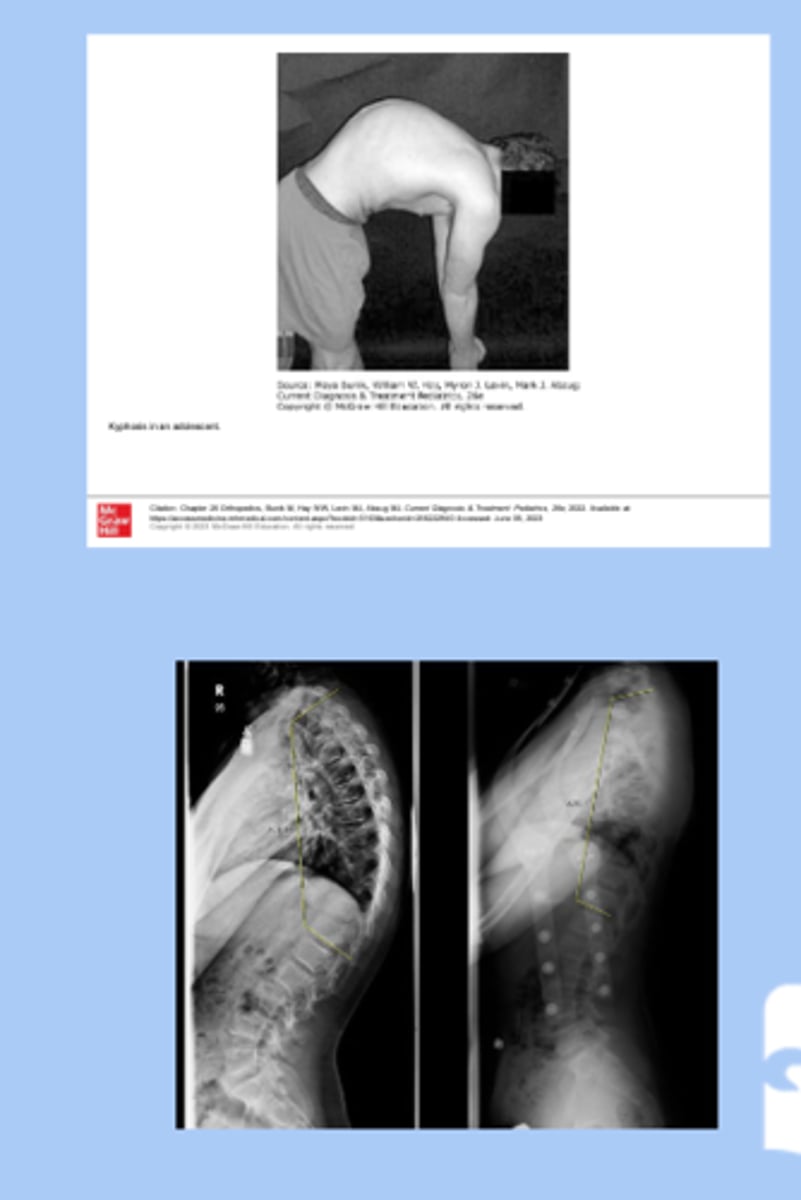
kyphosis
-exaggerated posterior convexity of thoracic region
-associated with scoliosis
-sx: deformity visible on back
-dx: standing AP and lateral XR
-tx: mild bracing, surgical
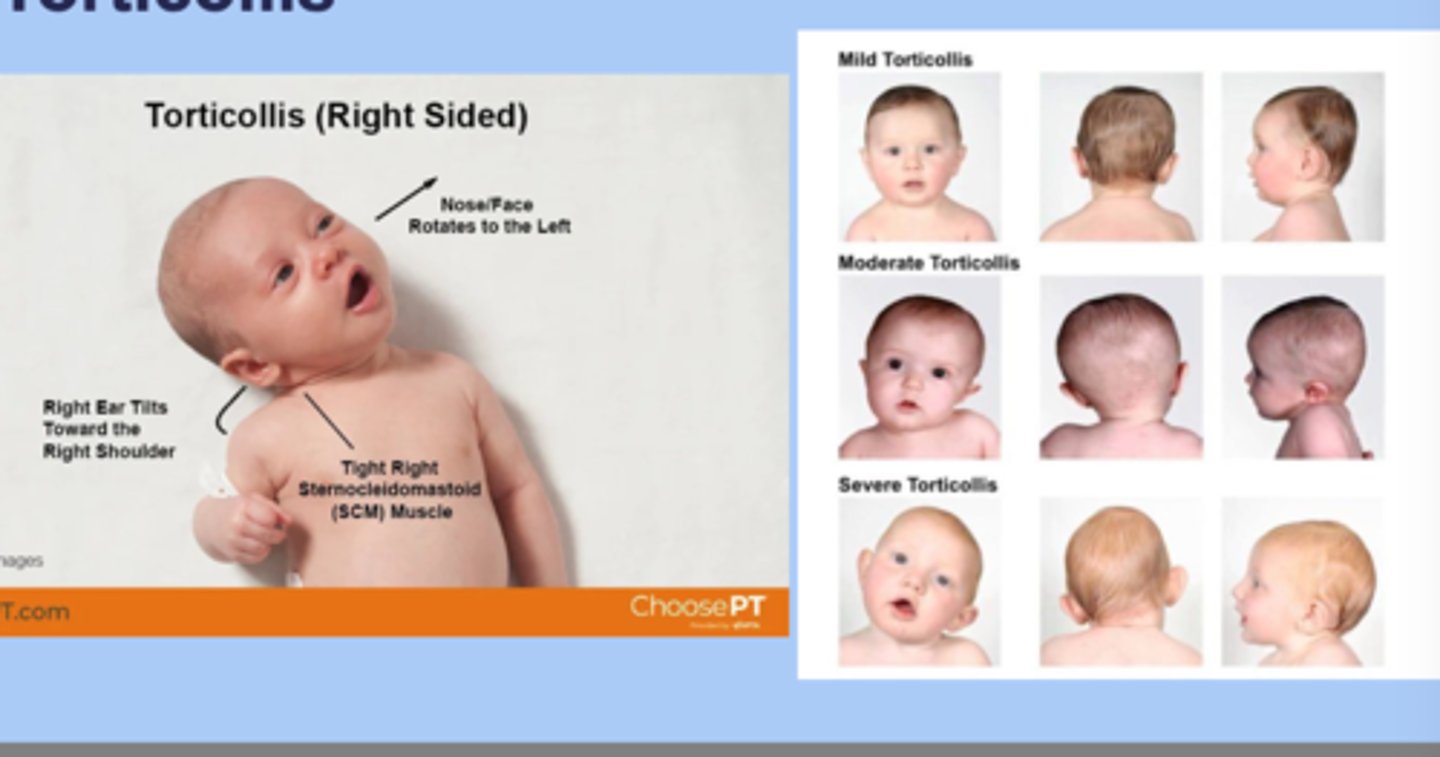
torticollis
-lateral twisting of the neck that causes the head to tilt to one side with the chin turned to the opposite side
-congenital: most common arises from muscular fibrosis of the SCM
-acquired: secondary to other
-sx: chin OPPOSITE side of affect muscle, head TOWARD affected muscle
-dx: 20% associated with DDH, evaluate for plagiocephaly
-tx: passive stretching
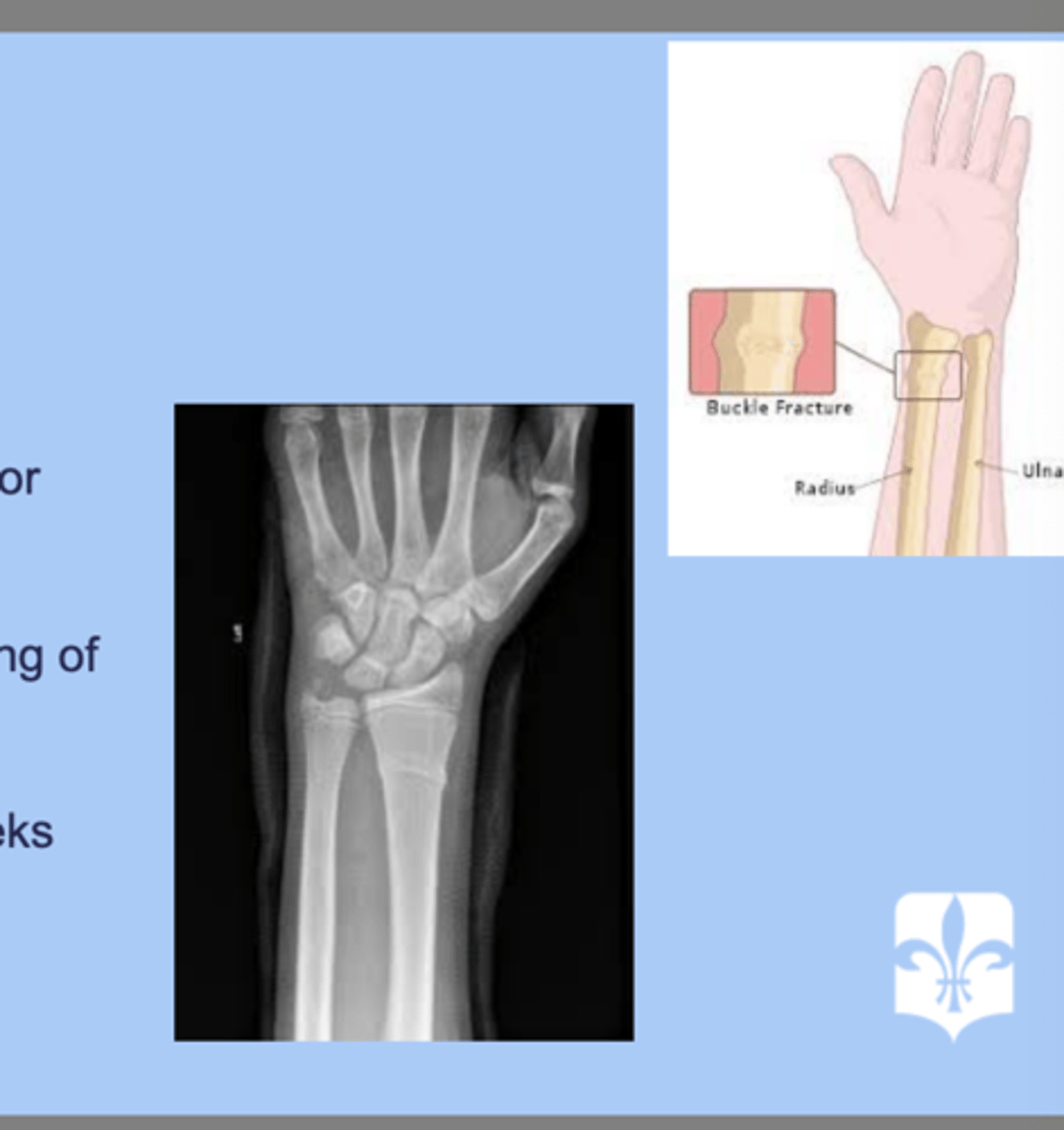
torus fracture
-buckling of the cortex due to compression of the bone
-distal radius or ulna
-dx: XR= bulking of bone
-tx: alignment with cast for 3 weeks
greenstick fracture
-frank disruption of the cortex on one side of the bone but no discernible cleavage plane on the opposite side
-txL reduction and casting, repeat XR -7-10 days
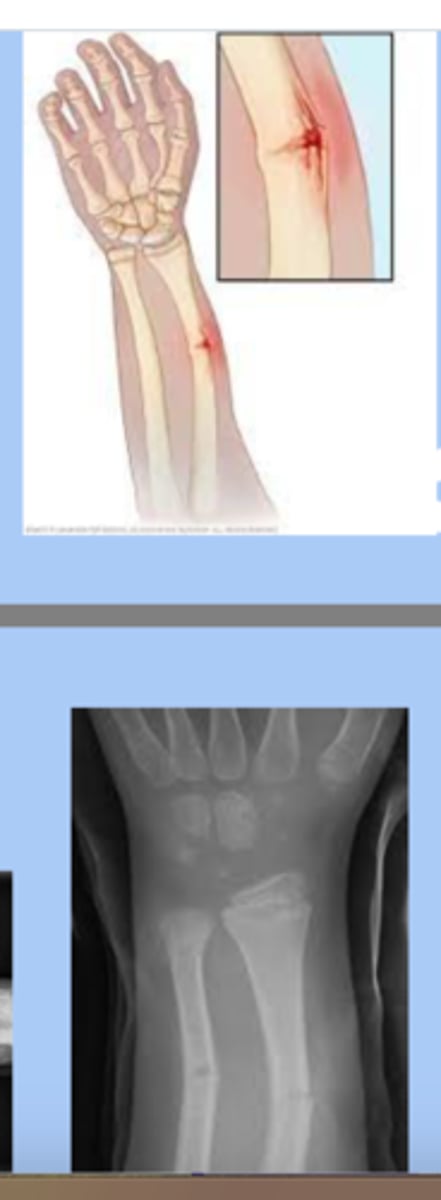
supracondylar fractures
-superior to the humeral condyles
-children 3-6yr
-proximity of the brachial artery in the distal arm creates a potential danger when dealing with these
-severe swelling
-tx: casting, surgery
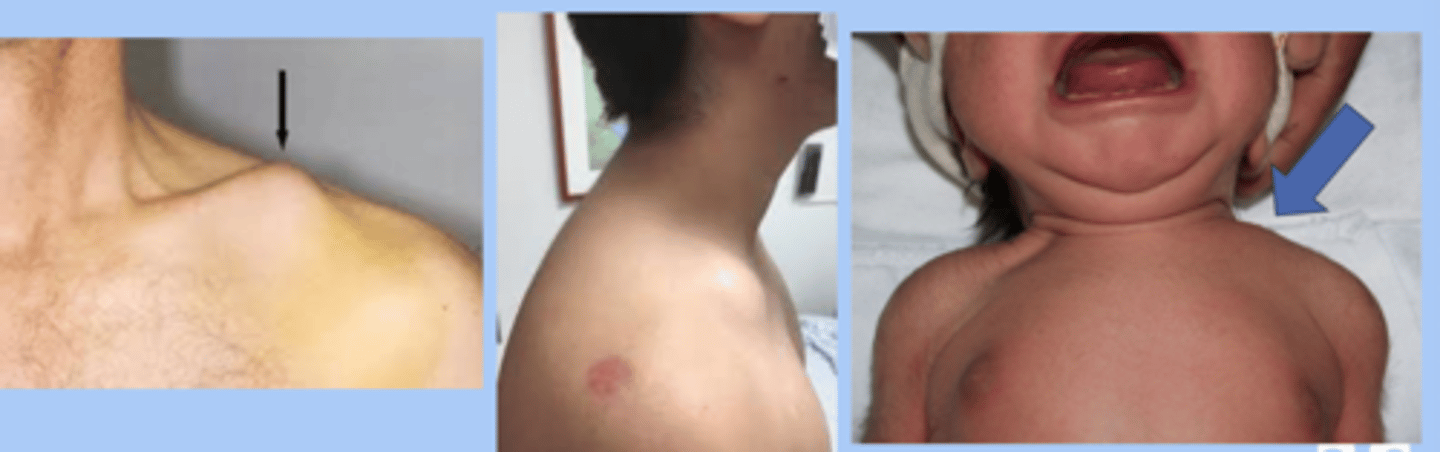
clavicular fractures
-caused by fall onto shoulder or difficult vaginal birth
-midshift: pain the middle 1/3, snapping at time of injuru, local swelling, tent of skin, creptitus
-distal 1/3: confused with AC, pain and tenderness around AC joint, swelling
-proximal 1/3: least common
-infants: crepitus, edema, lack of movement, asymmetrical bone contour, crying with passive motion
-tx: immobilization vs casting
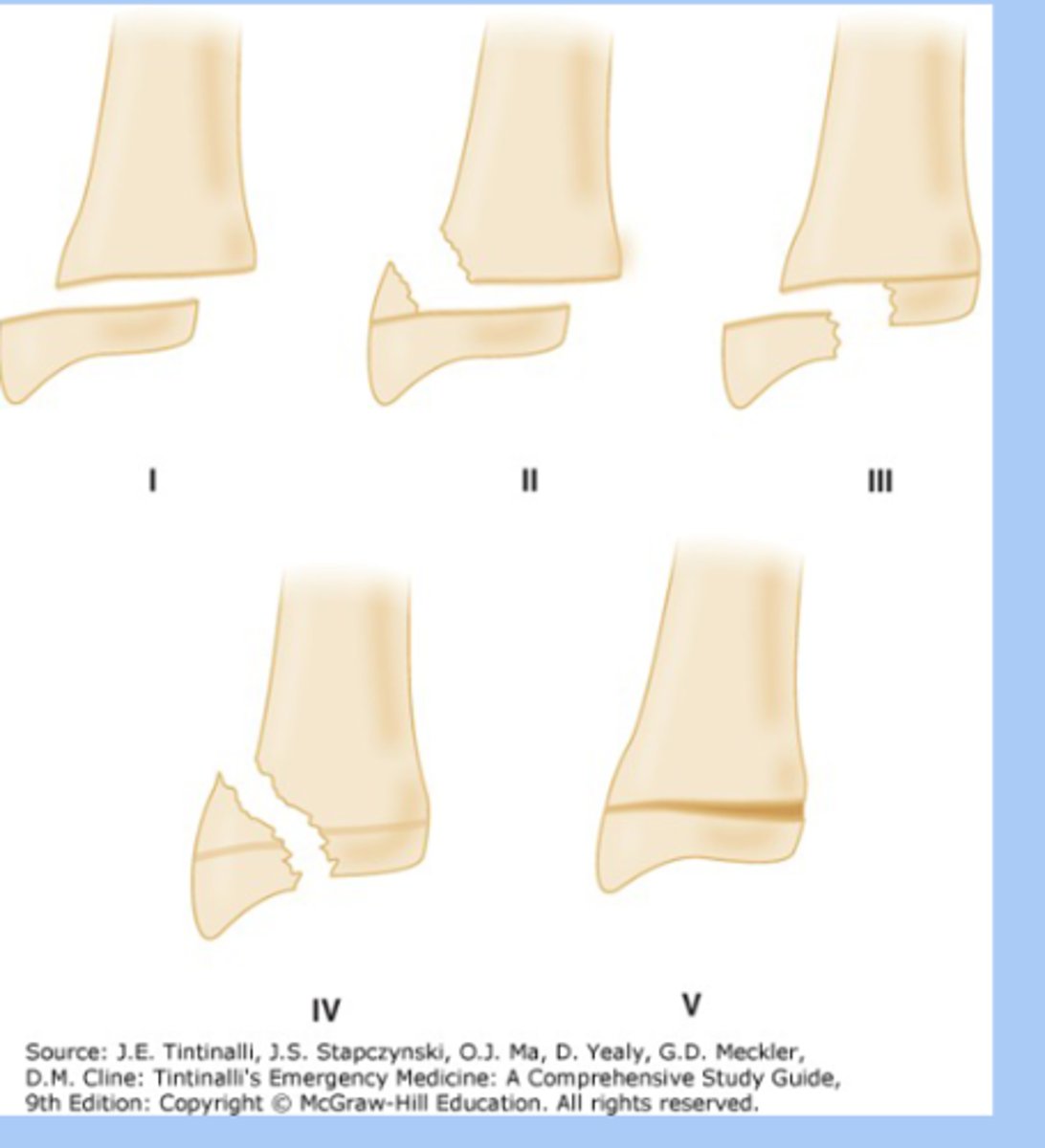
salter harris fractures
-fracture involving epiphyseal plate
-type 1: physis fracture
-type 2: metaphysis and physis
-type 3: epiphysis and physis
-type 4: epiphysis and metaphysis
-type 5: crush fracture
-dx: XRay
-tx: splinting, immobilization, surgery
-permanent growth arrest
toddlers fracture
-rotational injury of the tibia resulting in spiral fracture
-sx: 9mon-3yr, unwilling to bear weight, localized tenderness
-dx: xray= subtle, oblique, nondisplaces fracture
-tx: immobilzation for 4 weeks
-often associated with abuse
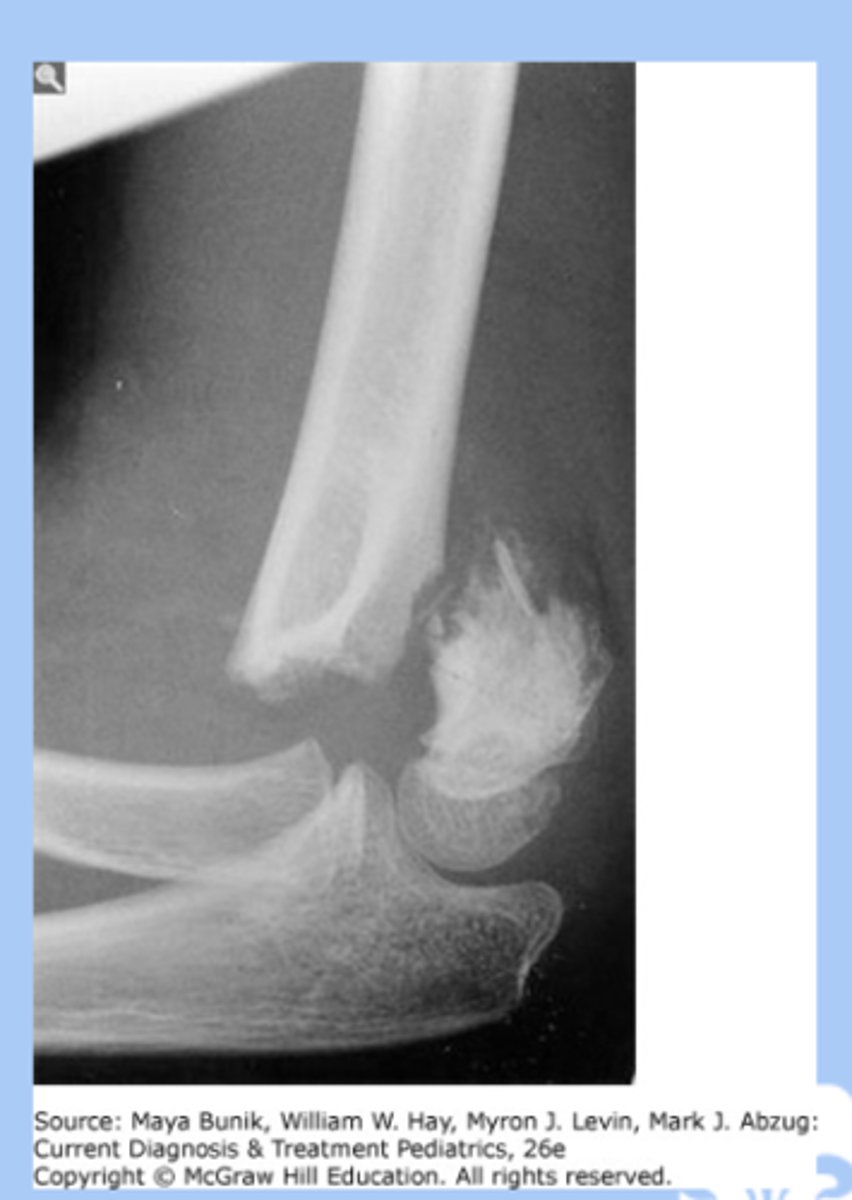
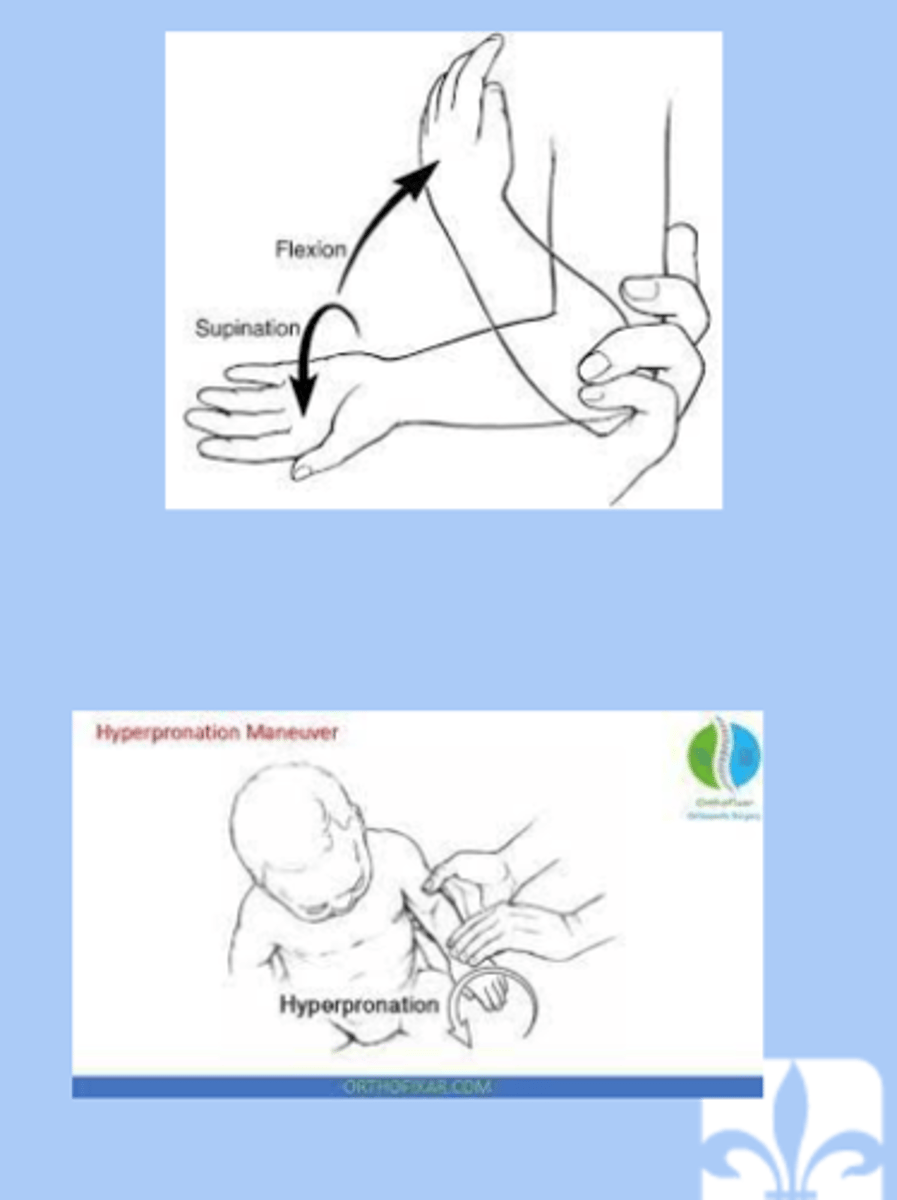
nursemaids elbow
-subluxation of the radial head resulting in trapping of the annular ligament
-lifted or pulled by the hand
-sx: child will not bend elbow, pain, not reach for things
-dx: radiograph= normal, point tenderness over the radial head
-tx: placing elbow in full supination and slowly moving the arm from full extension to flexion or hold elbow at 90 angle of flexion then slowly hyperpronated the wrist to complete reduction
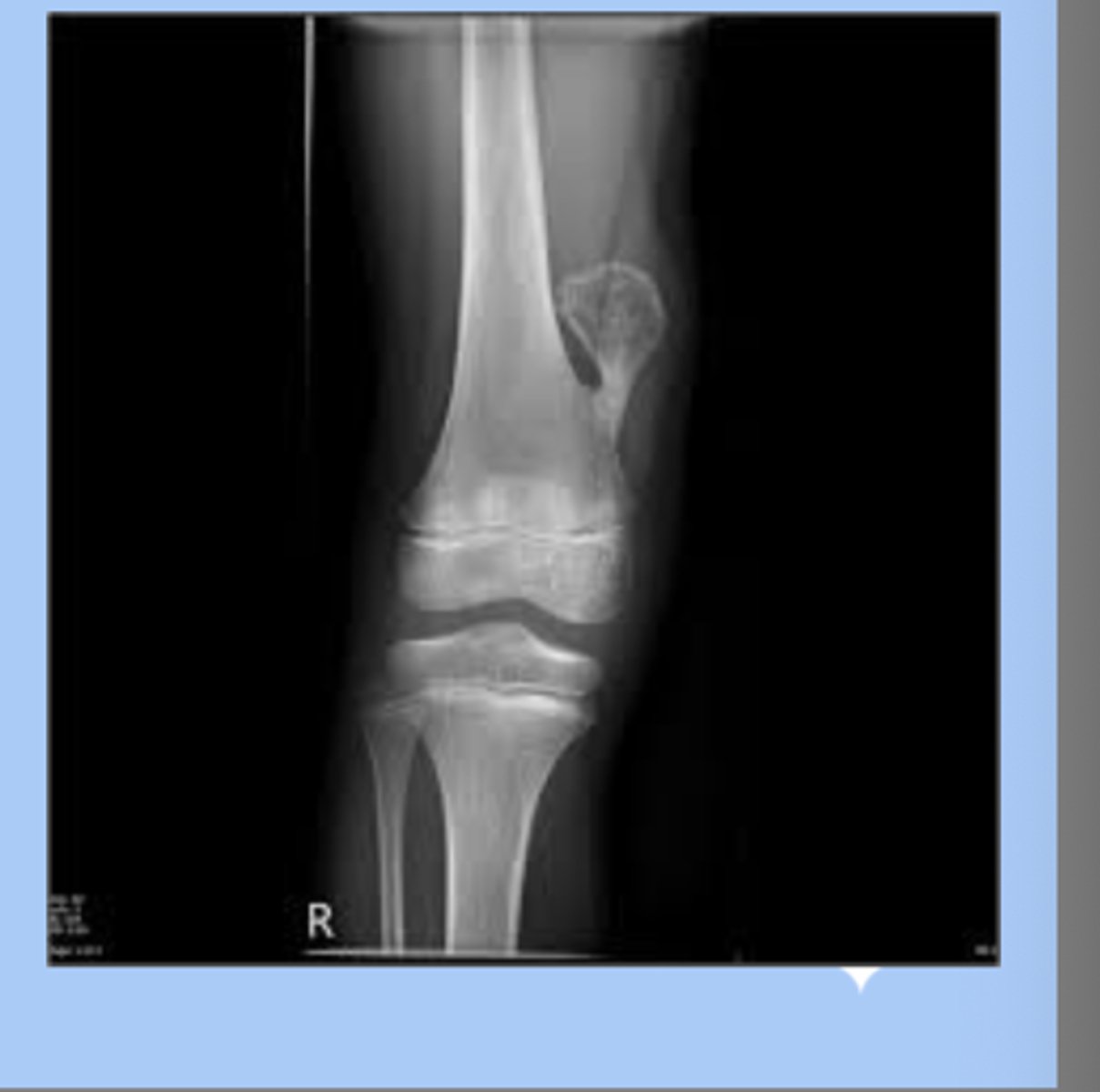
osteochondroma
-most common benign tumor in children
-males
-lesion is a bone mass capped with cartilage, grow in porportion to childs growth
sx: pain free mass
-dx: radiograph metaphyseal region
-tx: excision if interferes with function
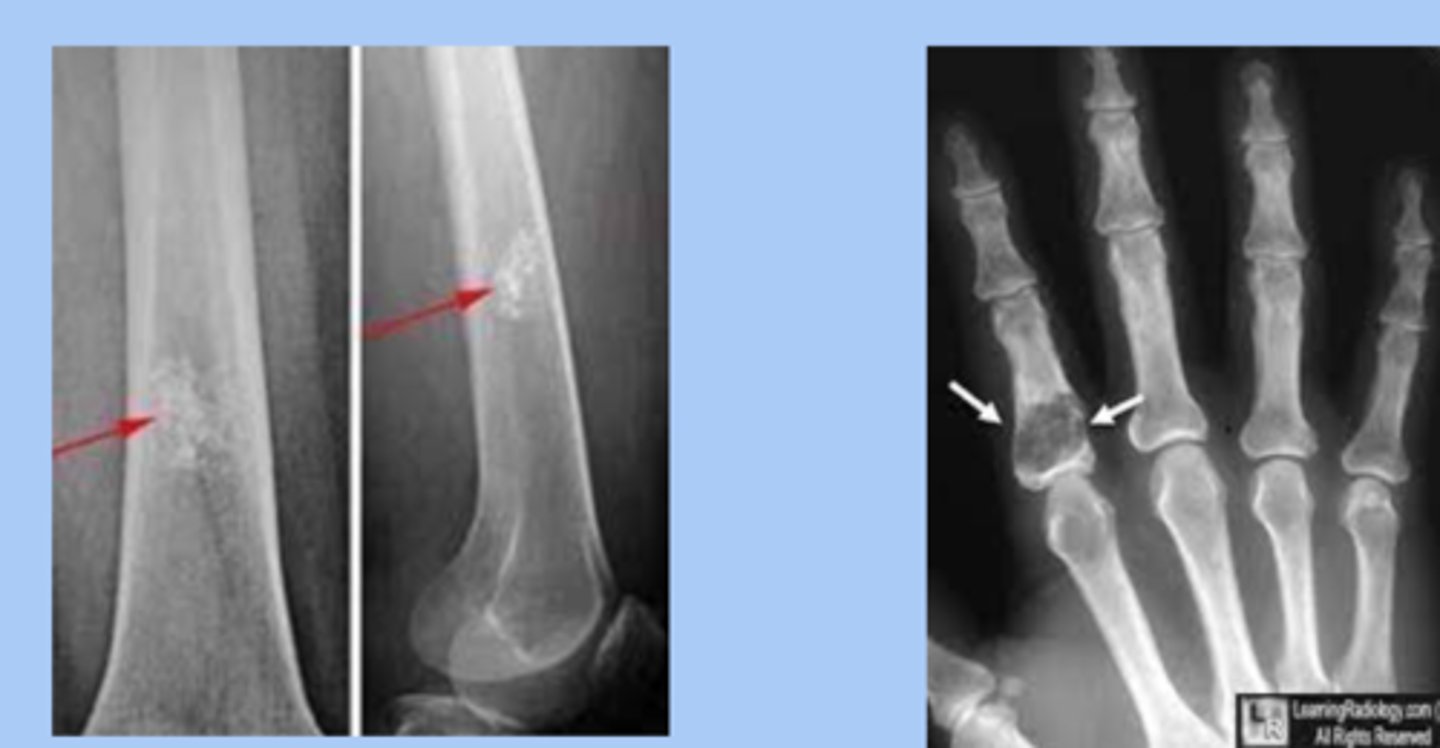
enchondroma
-nest of benign cartilage within long bone
-silent lesion unless produces fracture
-dx: radiograph= fingernail through clay appearance
-tx: surgical curettage and bone grafting when indicated
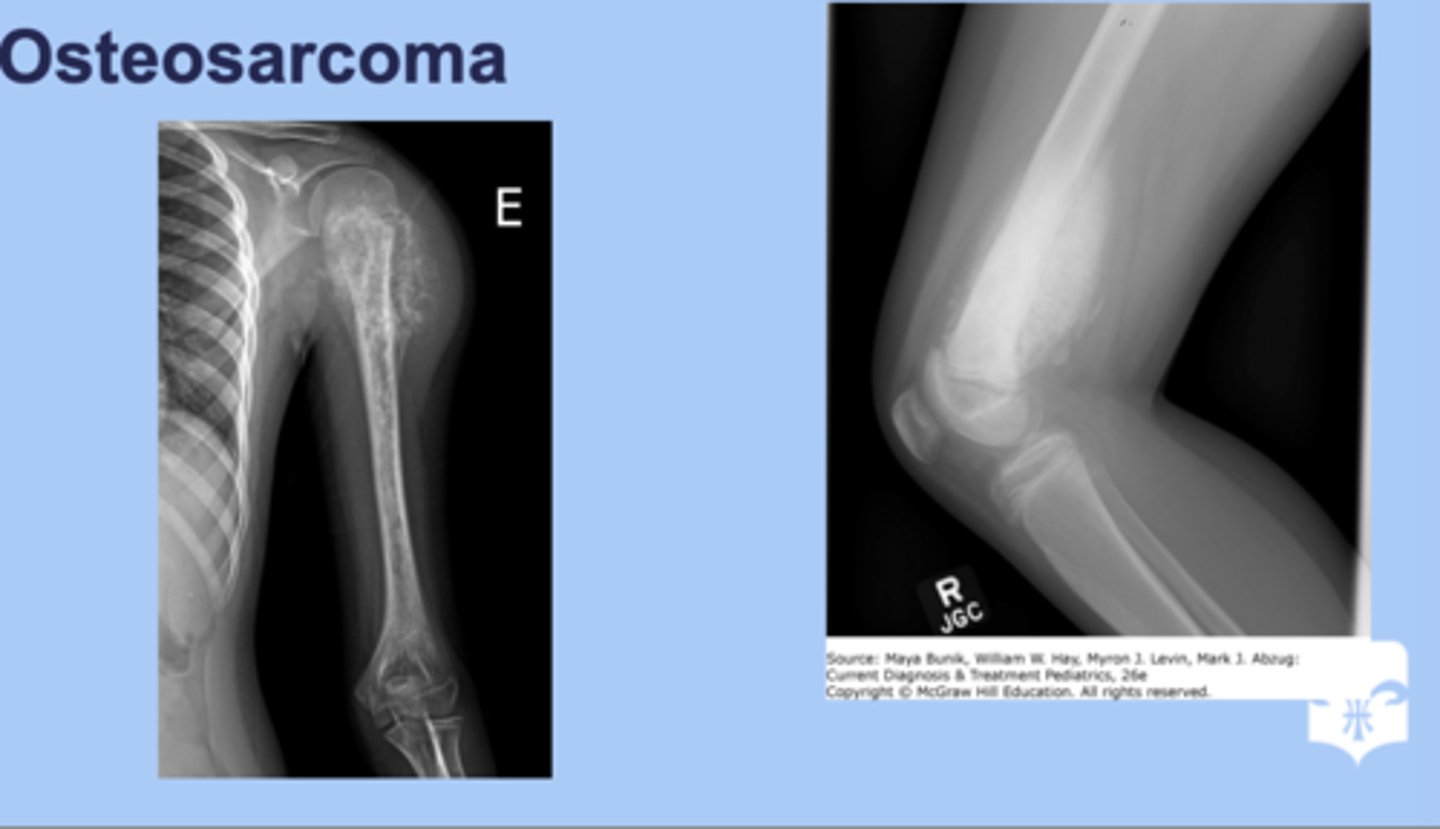
osteosarcoma
-aggressive form of cancer
-femur, tibia, humerus, other long bones usually affected
-sx: pain in the long bone
-dx: Xray= sunburnt appearance
-tx: surgery, chemo and rediation
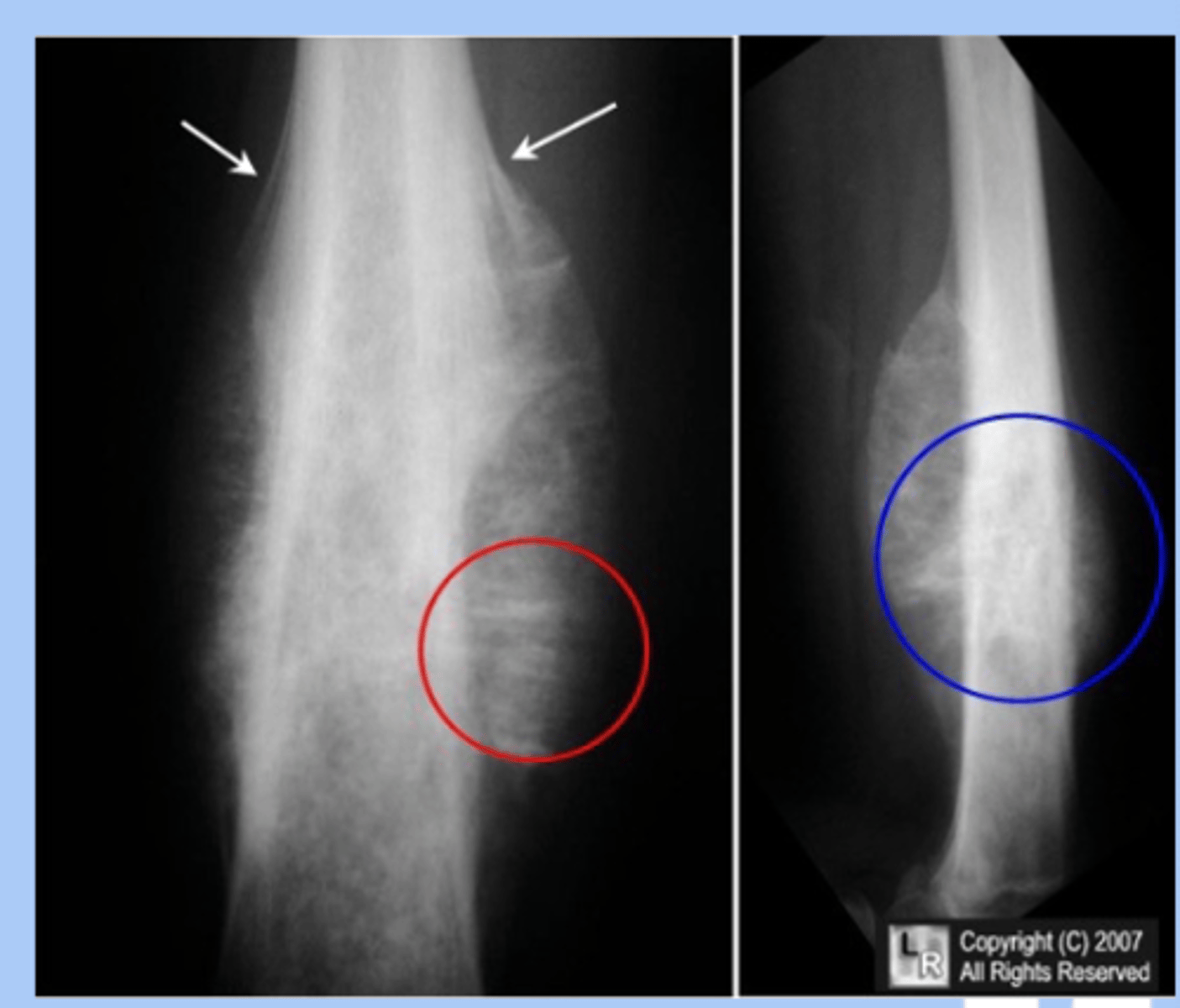
ewing sarcoma
-rare malignany presents as undifferentiated primary bone tumor
-sx: pain and tenderness, fever, leukocyotis
-dx: Xray= onion skin layering
-tx: chemo, radiation, surgery
sports physical
-cardiac death younger than 50 should be documented
-careful respiratory and cardiac exam looking for exercise induced bronchospam or anatomic heart disease
-not indicated for routine screening
-should not replace yearly WCC