UTS MIDTERMS
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
UTS derives its perspective from
Western and Eastern Perspective
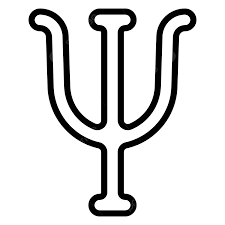
What does this symbol mean
psi (psychology)
According to Magalona, how did he define the self (1)
The self is thinking and feeling being within us and within ourselves.
According to Magalona, how did he define the self (2)
The self is the distinct identity which is a summation of the experiences of an individual.
According to Magalona, how did he define the self (3)
The self is commonly defined by the following characteristics: separate, self-contained,
independent, consistent, unitary, and private.
The search for the self is a process of
Learning, Relearning, and Unlearning
This model was developed in 1955 at the University of California Los Angeles
The Johari Window
Who created the Johari Window
Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham
Johari Model (Open)
Information you know and others know
Johari window (hidden)
Information you know but others dont
Johari Window(Blind)
Information you dont know but others do
Johari Window (Unknown)
Information that neither nor others know
Mother of all science
Philosophy
Under social science is
Philosophy
The self is divided into
Material, Spiritual, Physical, Digital, Sexual
Etymological definition of philosophy (philos)
love
Etymological definition of philosophy (sophia)
wisdom
Philosophy is also known as
Inquisitive mind
Philosophy is part of
Social science and natural science
Socrates (470-499 bc) is known famously for the phrase
Know thyself
Socrates taught?
Plato
“An unexamined life is not worth living”
Socrates
Goal of the socratic method
Better quality of life through self examination
“True knowledge exist in knowing that you know nothing”
Socrates
The dichotomous realm is divided into
Physical and Intellectual self
The physical self refers to the
Body (changeable), physical realm
Intellectual self
Soul, Truth, Goodness, Beauty
Key to virtuous life
Constant self-examinatio/introspection
St. Augustine (AD 354-430)
The self has an immortal soul
Self presentation leads to (St. Augustine)
Self Realization
God is the (St. Augustine)
Source of truth and reality
Mind is superior over the (St. Augustine)
Body
Through self knowledge, knowing God will eventually lead to (St. Augustine)
Happiness
One of the realm of thought (St. Augustine)
Sinfulness of man
Disordered love
man loves the wrong things which he believes will give him happiness
Love of physical objects
Greed
Excessive love for people
Jealousy
Love for self
Pride
Role of love
All things are worthy to love but they must be loved properly. If man loves God,
first, and everything else to a lesser degree then all will fall into rightful place.
Franz Boa (1858 - 19420) German born - American Anthropologist, is known as
Father of Anthropology
Franz Boa is known for his theory of
Cultural Relativism
Sociology
Human societies and interactions that preserve and change them
Dynamics of constituent parts of society
Institutions, communities, population, gender
Racial groups, age
Social status/stratification
Social movement/change
Disorder (crimes and revolutions
Anthropology
Study of human beings, culture, behavior, beliefs
Fields under Anthropology
Archaeology, linguistics, Physical and Cultural Anthropologyu
Ethnography
Writtings of anthropologist
“If we were to select the most intelligent, imaginative, energetic, and emotionally stable third of mankind, all races would be present.."
Franz Boa
Margaret Mead (1901 - 1978) is known for her theory
Theory of Imprinting (Children learn by watching adult behavior)
Who is the teacher of Margaret Mead
Franz Boa
Margaret Mead applied the principles of social science and anthropology to
Social Problems (World hunger, childhood education, and mental health)
Assigned to do note taking at an early age and is known for the quote “Always remember that you are absolutely unique. Just like everyone else." and “What people say, what people do, and what they say they do are entirely different things.”
Margaret Mead
George Herbert Mead (1863 - 1931) Massachusets, what is his concept of self?
A dimension of personality that is made up of individual’s self-awareness and self-image and the self cannot be separated from the society
Preparatory Stage (0-2 years old)
No sense of self at birth but develops over time based on social interaction and experience. Children behavior are primarily based on IMITATION
Play stage (3-6 years old)
Language and symbols of communication is the basis for socialization. Children learns to roleplay and widens perspective
Game stage (7 years old onwards)
Sees the perspective of others. Understands the concept GENERALIZED OTHERS (expected norms, values behaviors), MULTIPLE ROLES (pertains to a person), SIGNIFICANT OTHERS (people who take care of them)
Charles Cooley (1864 - 1929) American sociologist is known for the theory
Looking glass self
Charles Cooley’s proposed how the sense of self is formed
By one’s actual experiences and by what others ideas of one oneself to be
“ I am not what I think I am, I am not what you think I am, I am what I think you think I am”
Charles Cooley
How is the sense of self / self image achieved?
A person imagines how he appears to others, how others judge/perceive them, develops a reaction or identity based on other’s thought
Carl Rogers (1902-1987) is among the founders of
Humanistic approach in psychology
Carl Rogers self concept
Image of oneself
Humans are always striving for (Carl Rogers)
For self - fulfillment and self - actualization
How does self develops (Carl Rogers)
Through interaction with important people and awareness of one’s own characteristics
Weakness of the looking glass self (Charles Cooley)
May develop negative self image if perceived unfavorably and development of wrong self identity because of different perceptions
Central to achieving is the
development of self concept
Components of self concept (Carl rogers)
Real and Ideal self
Real self
awareness of what one is and what one can do
Ideal self
perception of what one should be or what one aspires to be
Normal
closer to the ideal and real self, more fulfilled and happy
Neurotic
Far from the real self often results to unsatisfaction and unhappiness
Erik Erikson (1902 - 1994)
Developmental psychologist and psychoanalyst
Famous for coining the phrase identity crisis and formulated the eight major stages of development each posing a unique developmental task
Erik Erikson
Brahman (Hinduism)
Have a knowledge of true reality. Realization will dissolve individual identity.
Atman (soul/spirit)
true knowledge of self
Human suffering is the result of
failure to realize distinction between true (permanent) and non true self (impermanent)
Law of karma
Actions good or bad will eventually extend to the incarnation of the soul
Incarnation
Atman will be continuously reincarnated until nirvana is reached
Nirvana
non birth
Founder of buddhism
Siddharta Gautama
Budh
Awake
Buddhism
“Every person has the seed of enlightenment,
hence, the potential to be a Buddha. But the seed should be nurtured.”
Nirvana ideally is achieved by
meditating
Noble Truths
Life is suffering, Suffering is caused by attachment of desires, Suffering can be eliminated, Practicing eightfold path eliminates suffering
Right view
know the truth
right intention
free your mind of evil
right speech
say nothing that hurts others
right action
work good the good of others
right livelihood
respect life
right effort
resist evil
right concentration
practice meditation
right mindfulness
control your thoughts
“Man” is just a title for the summation of
(matter, sensation, perception, mental constructs, and consciousness)
Confucian doctrines are found in
Analects
Golden rule
“Do not do to others what you would not want others do to you.”
Cardinal relationships
Between Ruler and Minster, Between Father and Son, / Between Husband and Wife, Between Brothers, Between Friends
Chinese counterculture
Rejects the confucian thoughts
Taoism/ Daoism
Self if an extension of the cosmos, not of social relations
Yin and Yang
There should be harmony and unity among opposing elements
Tao
foundation of all that exists
The perfect man has no sense of self
The selfless person leads to a balanced life, in harmony with both nature and society.