Concept 9.4: During oxidative phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis
1/8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
NADH and FADH2
The two electron carriers produced during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle that account for most of the extracted energy from glucose
These donate electrons to the electron transport chain, powering ATP synthesis
Inner mitochondrial membrane
The location of the molecules of the electron transport chain in eukaryotic cells, folded into cristae for greater surface area
Mostly comprised of proteins as part of a multi-protein complex that accepts electrons
Plasma membrane
The location of the electron transport chain in prokaryotic cells
Cytochromes
Proteins with heme groups containing an iron atom
Serves as one of the carrier molecules in the electron transport chain
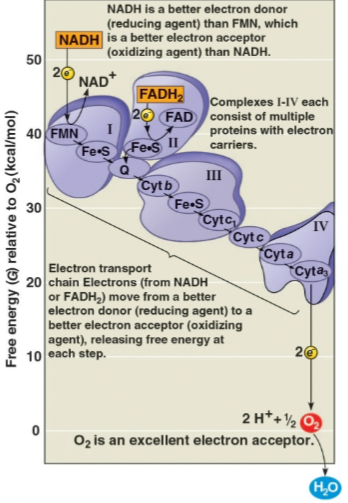
Electron transport chain
The chain of molecules that passes on electrons from NADH and FADH2 through proteins to gradually release free energy towards oxygen molecules
Serves to make energy to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space to catalyze ATP synthesis
Can also accept and release H+ to maintain the H+ gradient and couple reactions to ATP synthesis
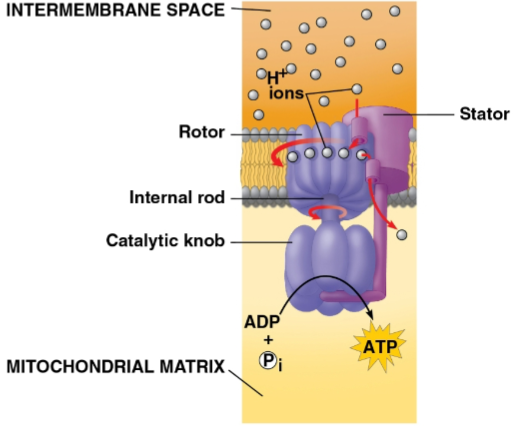
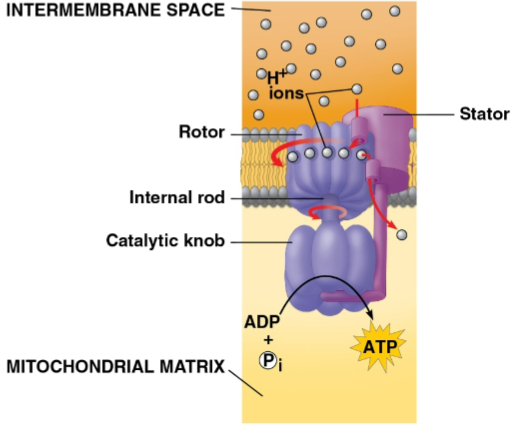
ATP synthase
The protein pump that H+ moves across after being powered by electrons to move into the intermembrane space
The movement of H+ down the concentration gradient onto this protein’s binding sites in a rotor causes a spin that catalyzes ADP phosphorylation
Chemiosmosis
The use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work
Seen in oxidative phosphorylation where H+ atoms are moved into the intermembrane space by electrons then moved into an ATP synthase rotor, catalyzing phosphorylation
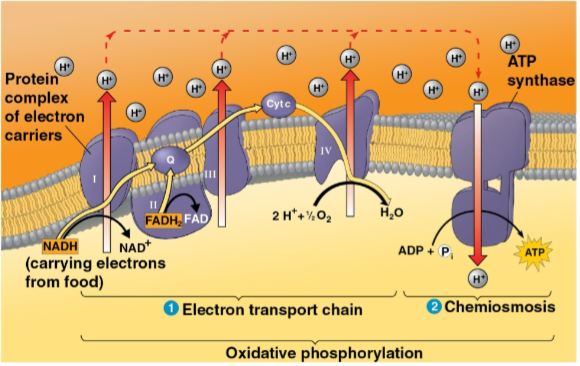
Proton-motive force
An H+ gradient with the capacity to do work
32
The approximate number of ATP molecules created as a result of cellular respiration, representing about 34% of the energy in a glucose molecule
The rest is lost as heat