Botany Exam 3
1/221
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Plant Toxins and the Heart | What Chili Peppers Can Teach Us about Pain | Weekly Quiz 8 | Muscles & Plant toxins | Weekly Quiz 9 | A Boosted Crop | Review Exam 3 |
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
222 Terms
Why did plants evolve toxins?
To protect from being eaten by herbivores
Family of Aconite Alkaloid
Ranunculaceae family
Family of Taxus Alkaloids
Taxaceae family
Cardiac Glycosides
Sugars that contain steroids, can be produces by some plants and toads
Sodium-Potassium Pump
A protein pump that pumps Sodium and potassium against the gradient. This uses ATP-Hydrolysis.
Action Potential
Change in voltage in the cell membrane, often in neurons
What is the difference between simple diffusion and active transport?
Simple diffusion goes along a gradient, while active hydrolyses ATP
Functions of Sodium-Potassium Pump, what gets pumped in what direction?
Pump sodium Ions outside the cell
Pump potassium inside the cell
Format of Action Potential, what is the order of operation?
Stimuli past threshold → depolarization → Action potential → repolarization → Hyperpolarization → resting state
Electrical Conduction System of the four chambered heart
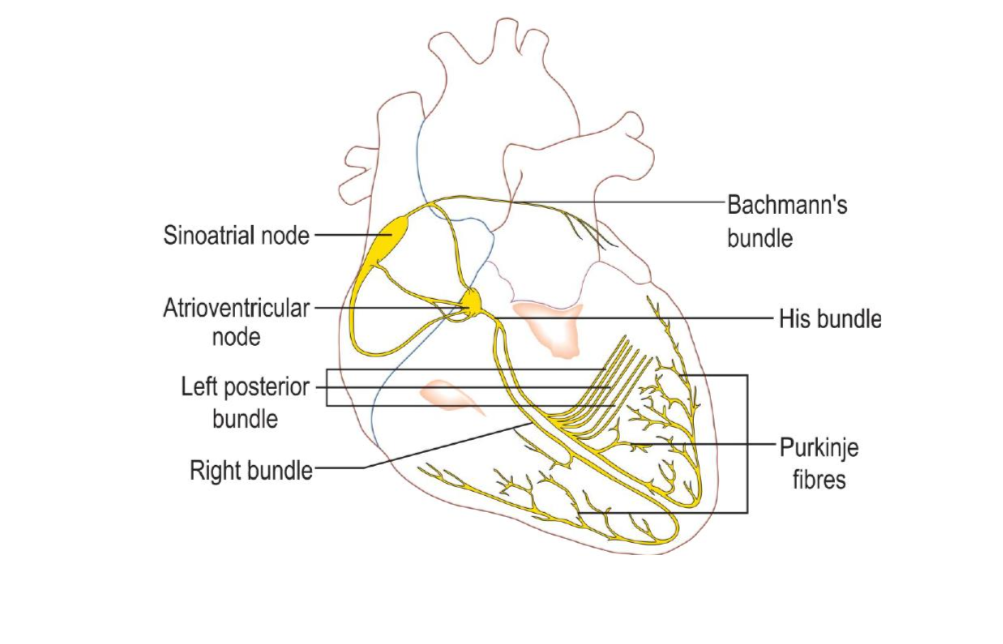
Nerves controlling the Heart
Sympathetic Nerves and Parasympathetic nerves
Functions of Sympathetic Nerves
releases norepinephrine
increases heart rate
controls contraction
receptor of norepinephrine is beta-1-adrenergic receptor
Functions of Parasympathetic Nerves
releases acetycholine on heart tisue
deceases heart rate
Receptor for acetylcholine on heart cells is muscarinic type and binding of Acetylcholine to its receptor, leading to opening of K+ channels causing hyperpolarization, therefore the effect on heart rate.
What happens during Fight or Flight?
The pituitary and adrenal glands release catecholamines, including adrenaline, noradrenaline, and cortisol. This chain of reactions results in an increased heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate
Why do tropane Alkaloids from deadly nightshades increase heart rate?
Atropine and other tropane alkaloids prevent binding of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to its receptor and, as a result, they cause blurred vision, suppressed salivation, vasodilation, increased heart rate, and delirium
Different Aconite Alkaloids
Aconitine - Most toxic
Atisine - Nerves
Veatchinine - Milder
Symptoms of Aconitine
Arrhythmias, and effects on the heart
Symptoms of Atisine
numbness and tingling, affects the nerves
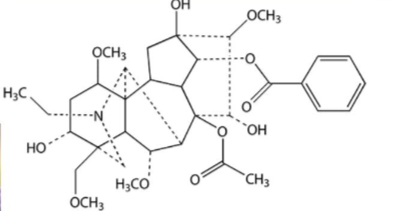
Structure of Aconitum
Species of Aconitum and their causes
350 species around the world
poison (arrow)
common causes
contamination
adulteration
Mechanisms of Aconitines
Agonist of voltage gated Na Channels, keeping them open longer and delaying repolarizations. This can cause weakness, numbness, vomiting, dizziness, arrhythmia, coma, and death.
Knowing the harms of Aconitines, what warning would you give to florists?
Wear gloves, wash hands, don’t use fatty lotions.
Family of Aconite
Rosaceae - Rose Family
Example species of Aconite
Spirea japonica (toxin from veatchine group - least toxic)
Example species of Aconitum
Monkshood

Example species of Taxus
Yew, common ornamental shrub/tree, a non flowering conifer
Common trait of Taxus Baccata L.
The seeds are toxic, not the fleshy covering
Aril
accessory covering certain seeds, found in both gymnosperms and angiosperms.
What is the difference between Juniper and Yew?
A juniper Berry is the female seed cone, but it is not a true berry. It is a cone with fleshy scales.
Order - Pinales
Family - Cupressaceae: Juniperus L.
Taxaceae: Taxus L.
What does the “L” stand for in some names
The first letter of the last name of who discovered it, for example “Linnaeus”
History of Yew Trees
Slow growing
Oldest in Europe, Wales church yard, around 5,000 years old
All parts are toxic after drying except aril
some deer can browse it
Taxine B
From Taxaceae family
In plant leaves and seeds
edible red aril
antagonist of calcium sodium channels
causes: Hypotension, cardiac arrest, and death
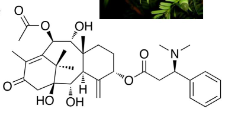
Taxol
Paclitaxel
Binds tublin, which prevents breakdown, induces apoptosis, often used with other drugs to fight cancer.
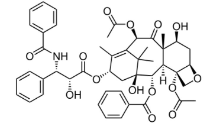
Docetaxel
demi-synthetic analogue
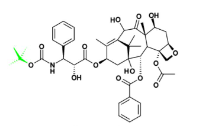
Cardiac Glycosides Flavors
Cardenolide and Bufadienolides
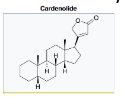
Cardenolide Structure
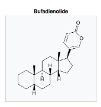
Bufadienolides Structure
Cardiac Glycosides Families
Apocynaceae
Plantaginaceae
Asparagaceae
Ranunculaceae
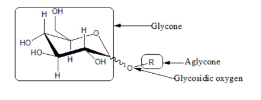
Glycosides Structures
Sugars with Hydroxyl groups + Glycosidic Bonds + Aglycone
Cardiac Glycosides effect on Sodium-Potassium pump
Pump is blocked by cardiac glycosides
cellular Na increase
Intracellular Ca causes muscle contraction (troponin
irregular, intense, can cause death
Treated with atropine
stimulates heart
Apocynaceae (Dogbane Family)
5000 spp
Most toxic to some degree
can produce cardioactive steroids and monoterpene indole alkaloids
Effects the nervous system

The Monarch Butterfly and Milkweed plant
Caterpillars the feast on the Asclepias spp, and stores the toxin as an a adult.

Digitalis lanata family and toxin
From Plantaginaceae family
creates digoxin
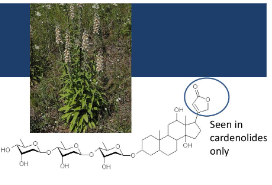
Strophanthus kombe family and toxin
From Apocynaceae family
creates g-Strophanthin (ouabain)
Arrow poison kills elephants
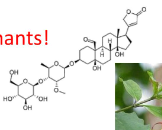
Case of Digoxin, use in medicinal practice
Used to treat patients with heart failure due to calcium forcing contractions.
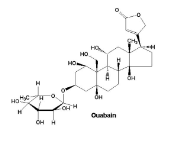
Strophanthus spp. (Toxin and its effects)
ouabain
increase cardiac output (not heart rate)
increase contraction strength
less absorbed by GI tract, rapidly eliminating
Digoxin (Medicinal use)
used in systolic heart failure (weak left ventricle)
increase contraction strength
reduces hospitalizations
Nerium oleander, family and toxin
From Apocynaceae family
Contains Oleandrin
Entire plant is toxic, dry and wet
Ranunculaceae, toxin present and example species.
Similar cardenolide type cardiac glycosides present in some general of buttercup
Adonis (Pheasant’s eye)

Asparagaceae Family, example and toxin
Example: Convallaria majalis (lily of the valley)
Creates convallotoxin, a cardiac glycoside

Functions of Aril
The fleshy red coverings found in yew trees, it lacks cardiotoxic alkaloid, taxine B, which targets Sodium calcium Channels.
convallotoxin - structure
Khat
Catha edulis (Celastraceae)
Chewed where alcohols is banned, acts as a stimulate
Common education about plants
do not eat random plants
don’t drink random nectar
learn about plants you bring home
keep plants away from kids and pets
don’t burn random plants
don’t cook with random plants
don’t use fatty hand lotions
Alcohol from Juniperus
Gin, only alcohol from Cucurbitaceae
How would you introduce Dr. D Julius to a cell and molecular/biomedical sciences class?
Dr. David Julius, known for his work on pain sensation, identified the TRPV1 receptor activated by capsaicin, significantly advancing our understanding of pain perception. His research also extends to studying diverse sensory systems, such as infrared sensing in snakes and electroreception in aquatic animals.
What is the main theme of work of Dr. David Julius?
The main theme of Dr. David Julius's work is the understanding of pain sensation and the molecular mechanisms underlying sensory perception.
Which stimuli that can impact/trigger the TRPV1 receptor in the peripheral nervous system?
Heat
Capsaicin (found in chili peppers)
Inflammatory chemicals, contributing to heightened sensitivity during injury.
What it a TRP receptor?
TRP receptors are cellular ion channels involved in sensory processes, including temperature and taste perception, contributing to physiological regulation and sensation.
What are the different types of TRP receptors and what are their stimuli?
TRPV (Vanilloid) receptors:
Stimuli: Heat, capsaicin, protons, endovanilloids
TRPM (Melastatin) receptors:
Stimuli: Temperature, voltage, osmolarity, taste molecules
TRPC (Canonical) receptors:
Stimuli: Phospholipase C-dependent pathways, including G-protein-coupled receptors
TRPA (Ankyrin) receptors:
Stimuli: Cold temperatures, environmental irritants, reactive oxygen and nitrogen species
Where in humans are the different types of TRP receptors found?
TRPV (Vanilloid) receptors:
Found in sensory nerve endings, the skin, and the bladder
TRPM (Melastatin) receptors:
Located in the brain, the kidneys, and the heart
TRPC (Canonical) receptors:
Found in smooth muscle cells, the brain, and the kidneys
TRPA (Ankyrin) receptors:
Present in sensory neurons, the respiratory system, and the gastrointestinal tract
How do different TRP receptors function?
TRPV (Vanilloid) receptors:
Respond to temperature changes, as well as specific chemical stimuli, such as capsaicin and protons.
TRPM (Melastatin) receptors:
Regulate calcium and magnesium ion flow, responding to temperature, osmolarity changes, and various taste molecules.
TRPC (Canonical) receptors:
Operate as non-selective cation channels, mediating calcium influx and contributing to various intracellular signaling pathways.
TRPA (Ankyrin) receptors:
Participate in detecting environmental irritants, cold temperatures, and reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, leading to the sensation of pain and inflammation.
What is the Wasabi receptor?
The "Wasabi receptor" refers to the TRPA1 receptor, which is activated by compounds found in wasabi, as well as by environmental irritants, cold temperatures, and reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
What plant family has roots that impacts the wasabi receptor (TRPA1)?
Brassicaceae family, such as wasabi, horseradish, and mustard
How did the wasabi receptor (TRPA1) gain notoriety?
gained attention due to its involvement in sensing environmental irritants, cold temperatures, and reactive substances, contributing to the sensation of pain and inflammation
What roles do the TRP receptors play in human behavior?
TRP receptors play essential roles in mediating sensations such as temperature, taste, and pain perception, thereby influencing human behavior through the interpretation of external environmental stimuli and the regulation of physiological responses
What groups of people may have issues with the functions of TRP receptors?
Individuals with conditions such as diabetes or leprosy, which can lead to reduced sensation in extremities
Where are opioid receptors?
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral sensory neurons
What are 3 effects opioid receptors can have on humans?
Pain relief
Euphoria or feelings of well-being
Respiratory depression
Characterize what is meant by “on-target side effects”
"On-target side effects" refer to unintended physiological effects that occur due to the specific interaction of a drug with its intended target
What exciting sensory field is considered a frontier of new research?
Infrared sensing, particularly in snakes, is an exciting sensory field considered a frontier of new research endeavors
Why could infrared sensing contribute to our understanding of pain?
Studying infrared sensing could enhance our comprehension of pain as it shares neural pathways with other sensory processes
What long range outcome does research on infrared sensing and pain receptors hope to address?
Research on infrared sensing and pain receptors aims to advance pain management strategies and develop innovative non-opioid pain treatments
Wasabi was mentioned in the reading. What is the plant family previously discussed in class?
Brassicaceae
What are the TRPV1 receptors mainly located?
Peripheral Nervous System
What inspired Dr. Julius’ interest in pain?
Supermarket Visit
Use of Peyote
curiosity of the function of neurotransmitters
folk medicine and use of natural products
Hansen’s disease patients and some individuals with complications from diabetes lack the ability to perceive pain.
True
Capsaicin is a/an _____ that binds to the TRPV1 receptor
agonist
You feel the hot chili pepper on your lips when the primary afferent sensory neuron and nociceptors send a signals to a second neuron in the spinal cord eventualy gets taken to the brain centers where you sense something noxious and painful. This particular receptor also binds to ___ and ___ agents.
Heat, inflammatory
Digoxin has been used as a drug for systolic failure because it
increases cardiac output
Taxaceae (visual examples)

In the “Unearthed” podcast Lakhvinder Cheema was murdered on 27 January 2009 in Southall, west london, by his former lover, Lakhvir Kaur Singh through the use of poison derived from the ____ plant, which contain the highly toxic alkaloid ____.
Aconitum , Pseudaconitine
Strophanthus kombe produces the toxin ouabain, its extract known as kombe has famously been used as an arrow poison to kill which of the following animal?
elephant
Which of the following are used in traditional chinese medicine?
Spirea japonica
Angelica sinensis
You made a fire and threw in the plants that sprouted on the path near your country house. As soon as the fire flared up, you recognized one of the plants as Nerium oleander. Should you be concerned and what could you do?
Yes, and you should immediately extinguish the fire only if safely possible or immediately seek help to do so
What medication is used to eliminate the toxin effects of cardiac glycosides?
atropine, a propane alkaloid
Which of the following plant families produces the secondary metabolite digoxin, a compound that is used to treat systolic heart failure.
Plantaginaceae
Docetaxel is a semi-synthetic version of the toxin paclitaxel and is used as a cancer treatment. Which of the following is it's correct mechanism of action?
Binds to surface receptors and triggers apoptosis
Three types of muscles
Skeletal
voluntary control
Smooth muscle
autonomic nervous system
GI tract
blood vessels
airways
eye
uterus
bladder
Cardiac
Heart, autonomous activity but also influenced by nervous system
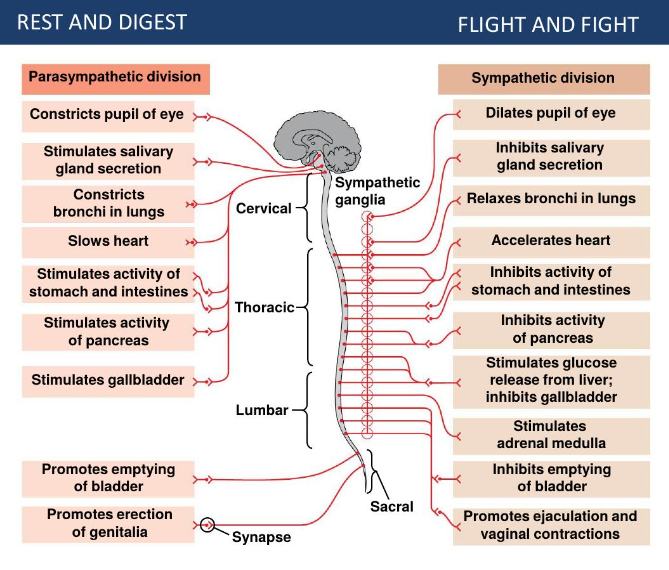
Autonomic Nervous System, divisions and their functions
Parasympathetic division
rest and digest
muscarinic
releases acetylcholine
Sympathetic division
flight and fight
nicotinic
Two types of ACh (Acetylchloine) receptors
Nicotinic
Muscarinic
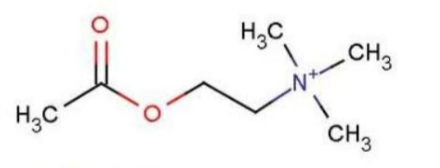
ACh (Acetylcholine) Structure
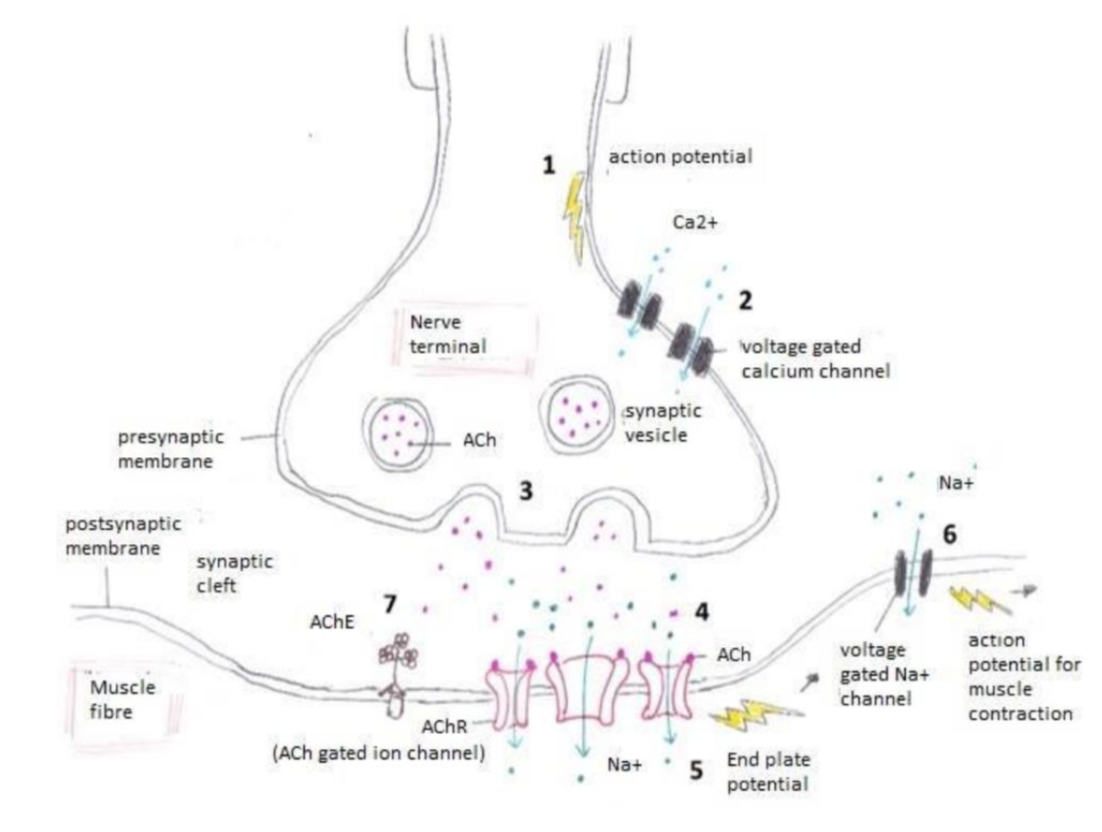
Neuromuscular junction, order of operations
Action potential depolarizes the nerve terminal
Voltage gated Ca2+ channels allow Ca+2 influx
Ca2+ evoked vesicle exocytosis of ACh
ACh activates AChRs
Cation influx through AChRs depolarizes muscle fibers forming EPP
Voltage gated Na+ channels generate action potential
AChE degrades ACh to terminate the signal
Neuromuscular junctions | diagram
What nerve and chemical targets smooth muscles?
Nervous systems and hormones
Paralyzing Curares are from which families
Menispermacea
Logoniaceae
Fabacea
Piperidine Alkadloids families
Solanaceae
Apiaceae
Quinolizidine family
Fabaceae
Example of Menispermaceae
Chondrodendron tomentosum
