Structure and Bonding
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Elements of unsaturation
[(2*#C + 2 + #N - #H - #X(F, Cl, Br, I)] \ 2
Double bonds = 1
Ring = 1
Triple bond = 2
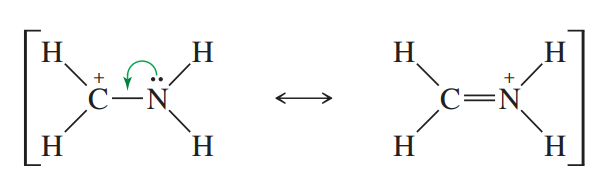
Resonance structures
The movement of electrons between three or more p-orbitals. Will always exist when there is a lone pair adjacent to an atom with a p-orbital (double bond)
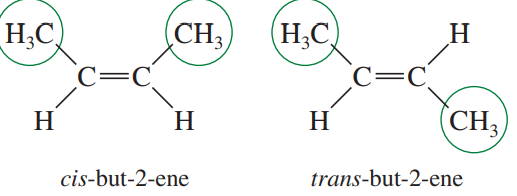
Stereoisomers/Configurational isomers
Isomers that have the same molecular formula and connectivity, but differ in the three-dimensional spatial arrangement of their atoms
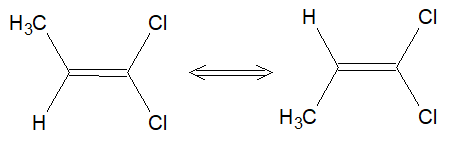
Conformational isomers
An isomer that can be interconverted by rotating around a single sigma bond
Constitutional isomers
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different atom connectivity. The atoms are bonded together in a different order
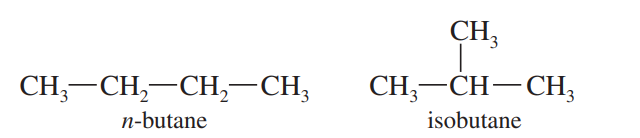
Determining the major resonance contributor
Resonance form with the most full octets
Resonance form with most # of bonds (not counting to H)
Least amount of charge separation
What atom is charge on (e.g. negative charge on most electronegative atom)