Test 2 Principles and History of Radiation Therapy: X-Rays, Radioactivity, and Fractionation, Comprehensive Guide to Treatment Delivery Equipment in Radiation Therapy, Radiation Therapy Equipment Overview, High Energy Equipment Overview
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
What is the operating kVp range for contact therapy?
and the mm of materail for hvl
40-50 kvp
.5mm-1mm of aluminium
What is the operating kVp range for orthovoltage therapy?
and the mm of materail for hvl
200-300 kvp
1-4mm copper
What is the operating kVp range for superficial therapy?
and the mm of materail for hvl
50-150kvp
1-6mm aluminum
What is the operating kVp range for Grenz-ray therapy??
and the mm of materail for hvl
15-20 kvp
.1mm aluminium
Who discovered x-rays and when?
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen 1895.
What are the basic properties of x-rays?
X-rays are unaffected by gravity, electric fields, and magnetic fields; they travel in straight lines, are exponentially attenuated by matter, and cannot be focused.
What are the two types of electron interactions that produce x-rays?
Collision interactions (characteristic radiation) and radiative interactions (Bremsstrahlung radiation).
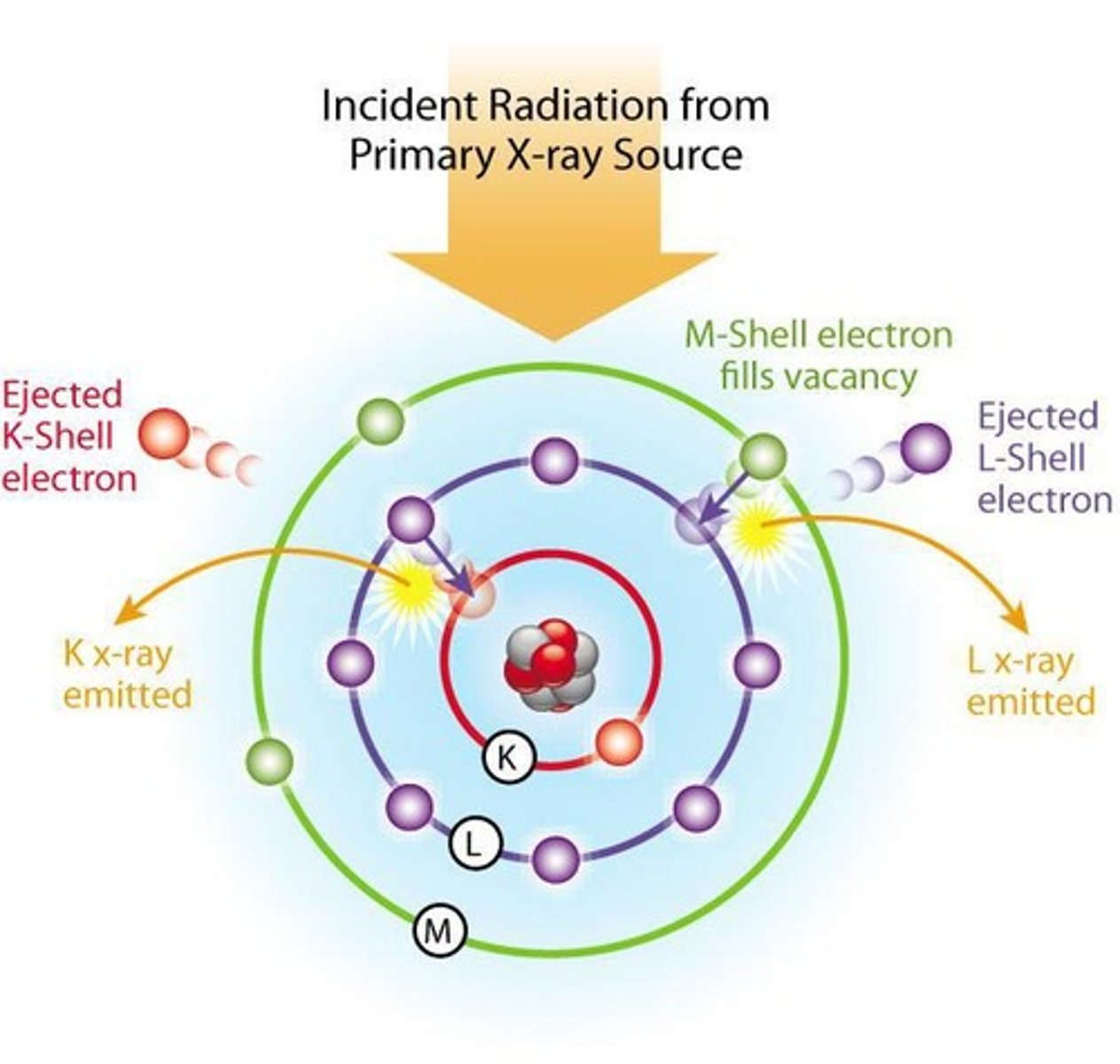
What is characteristic radiation?
Radiation created by the direct interaction of k shell
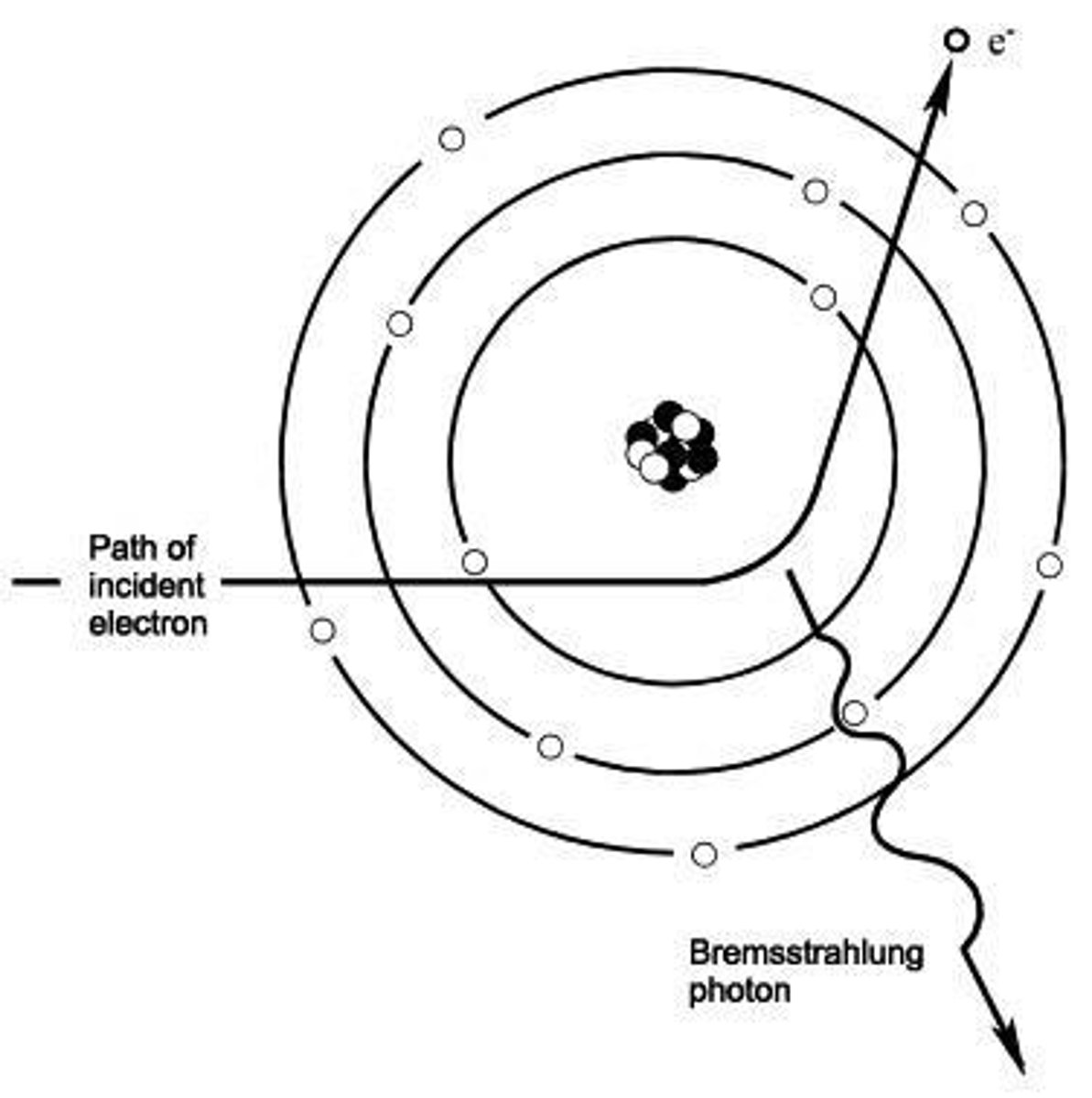
What is Bremsstrahlung radiation?
Also known as 'braking radiation', it occurs when a high-speed electron interacts with the electric field of a nucleus and is decelerated, emitting an x-ray.
What percentage of x-ray tube output is attributed to Bremsstrahlung radiation?
Approximately 75% to 80%.
Who was Henry Becquerel and what did he discover?
radioactivity in 1896.
What caused Marie Curie's death?
Aplastic anemia, likely contracted from exposure to radiation.
What was the first therapeutic use of x-rays?
Emil Grubbé treated a patient with advanced breast carcinoma
What was the significance of Claude Regaud's approach to radiation therapy?(what did he discover and wrote about)
He recognized that treatment could be more effective if delivered slowly in modest doses over several weeks, known as fractionation.
What did Henri Coutard pioneer in radiation therapy? (Used it clinically first)
The use of fractionated radiotherapy for various tumors, achieving impressive results with locally advanced laryngeal cancers.
What were the limitations of early x-ray machines?
They could not produce high energy, deeply penetrating beams, making it difficult to treat deep-seated tumors without excessive skin reactions.
What are the three fundamental aspects of accurate dosimetry in radiation therapy?
1. Accurate measurement of radium content in sources. 2. Determination of radiation output in acceptable dose units. 3. Knowledge of radiation distribution within treated tissues.
What were some early applications of radium in medicine?
Radium was used for gynecologic implants, arthritis, and gout treatments.

What was the first use of radium in the United States?
Radium was first used in 1908 for gynecologic treatments, imported from Europe.
What is the 'erythema dose' in radiation therapy?
The radiation dose necessary to cause redness of the skin, used to estimate the proper length of treatment.
What did Pierre Curie contribute to the field of radiation therapy?
He applied radium to his arm and documented the phases of moist epidermitis, providing radium to physicians for patient testing.
What was the significance of the first basal cell epithelioma cure in 1899?
It marked the beginning of using ionizing radiation for the treatment of cancer.
What was the role of filtration and distance from the source in radiation therapy?
These factors were recognized as important in minimizing skin burns and optimizing treatment effectiveness.
What is the primary use of kilovoltage units in radiation therapy?
To treat skin and superficial lesions.
What are the three types of kilovoltage machines mentioned?
Grenz-ray therapy machine, superficial treatment machine, and orthovoltage machine.
What led to the decreased use of kilovolt machines in radiation therapy?
The increased popularity of cobalt-60 units.
What is the half-life of cobalt-60?
5.26 years.
How do linear accelerators work?
They use high frequency electromagnetic waves to accelerate charged particles such as electrons to high energies via a linear tube.
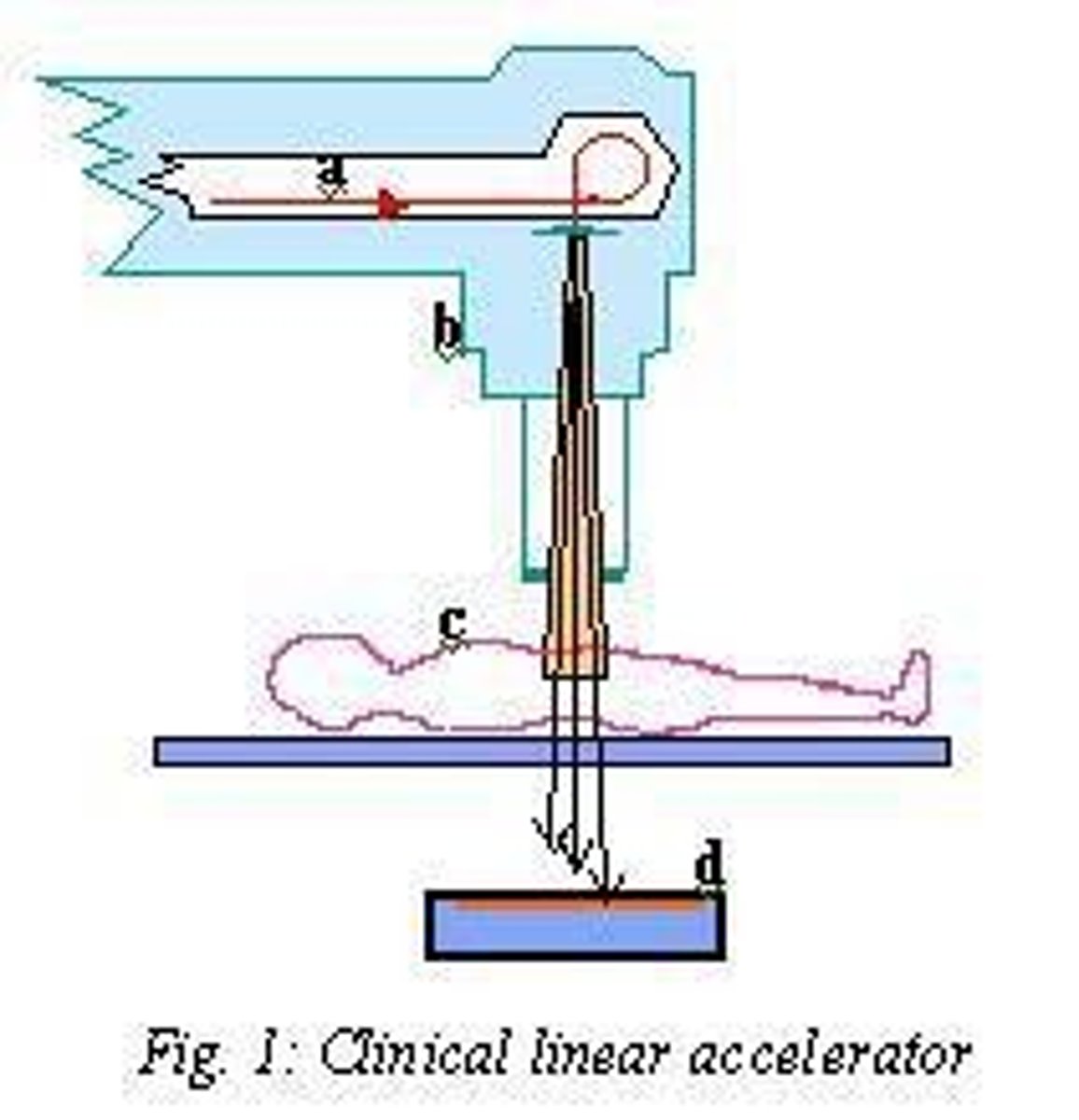
What is the minimum voltage generated by megavoltage therapy units?
1 MV.
What are the advantages of megavoltage units over kilovoltage units?
They can reach deep-seated malignancies and spare skin and normal tissues.
What happens to skin sparing as beam energy increases?
Higher energy (MV) results in more skin sparing.
What is the energy range of Grenz-ray therapy?
15- 20 kVp.
What are Grenz-rays also known as?
Bucky rays, named after Gustav Bucky.
What is the inherent filtration of a Grenz-ray tube?
0.1 mm of aluminum.
What is the operating kVp range for contact therapy?
and the mm of materail for hvl
40 to 50 kVp.
.5mm-1mm of aluminium
What is the typical kVp range for superficial treatments?
and the material needed for hvl
50 to 150 kVp.
1-6mm aluminum
What is the purpose of aluminum filters in superficial treatments?
To harden the beam.
What is the kVp range for orthovoltage therapy?
material and thicknes for hvl
200- 300 kVp.
1-4mm of copper
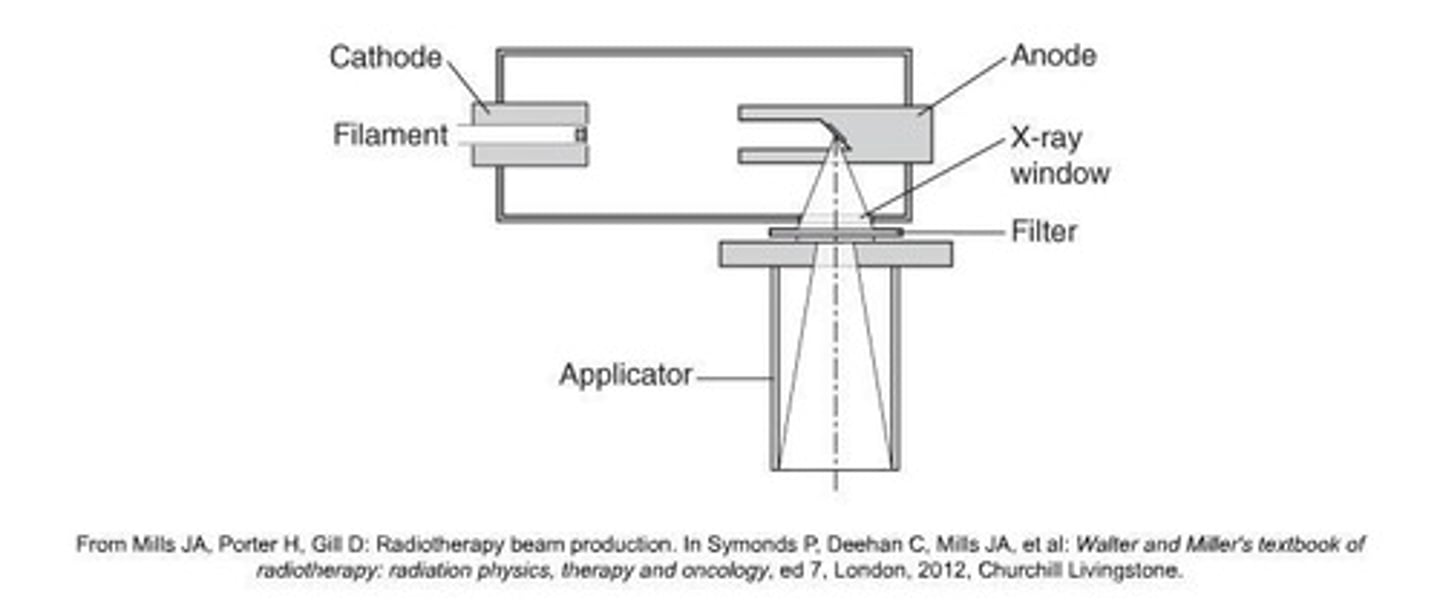
What is another name for orthovoltage therapy?
Deep therapy.
What is the typical operating range for most orthovoltage equipment?
200 to 300 kVp and 10 to 20 mA.
What types of cancers are primarily treated with orthovoltage therapy?
Skin, mouth, and cervical cancers.
What is the limitation of orthovoltage machines for treating lesions?
They experience limitations in treating lesions deeper than 2 to 3 cm.
What is the SSD (Source to Skin Distance) for most orthovoltage treatments?
50 cm.
What is the significance of cobalt-60 units in radiation therapy?
Cobalt-60 units have a half-life of 5.26 years and led to the decreased use of kilovoltage machines.
What is the function of a linear accelerator in radiation therapy?
It uses high frequency electromagnetic waves to accelerate charged particles like electrons to high energies.
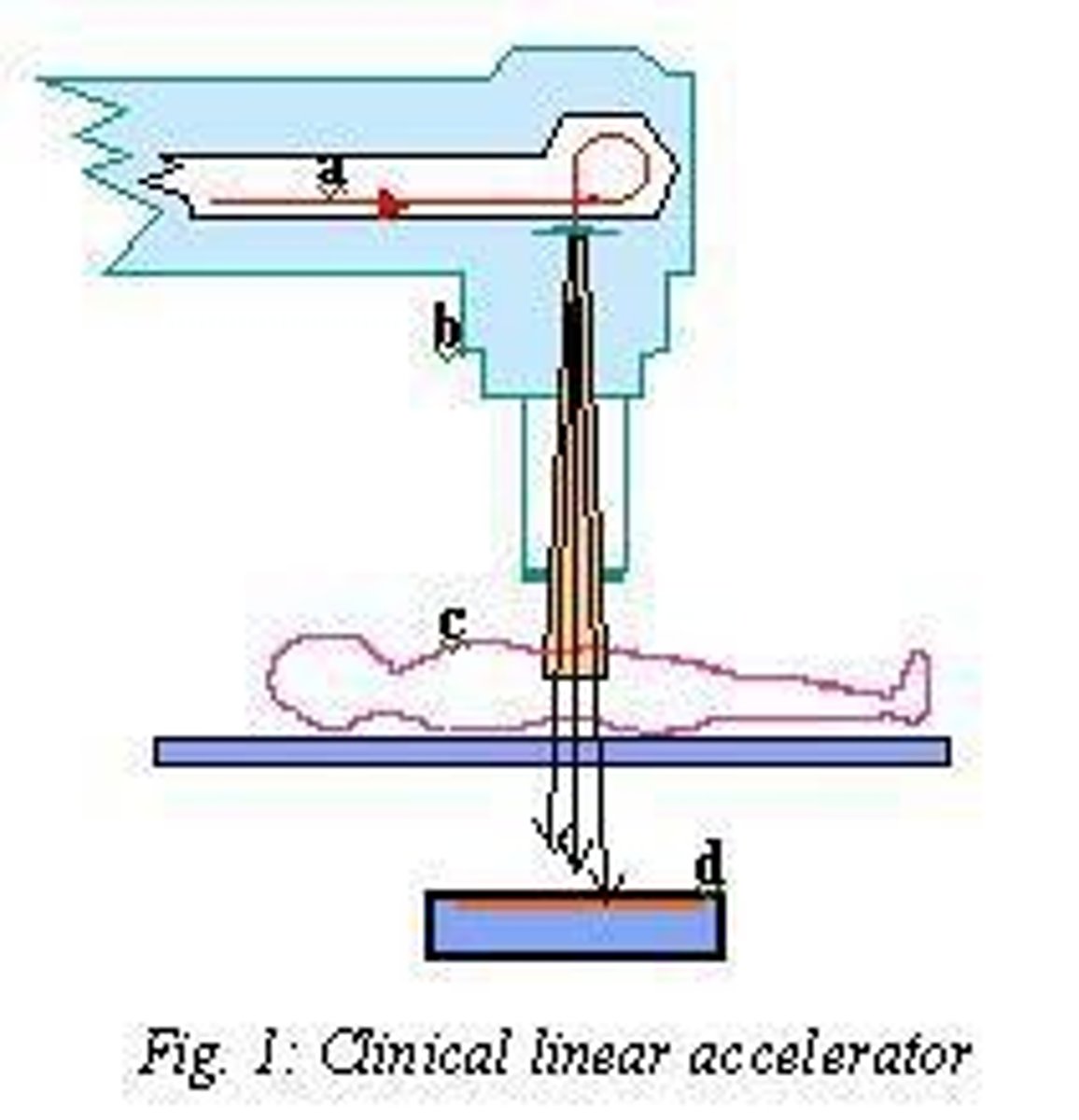
What are megavoltage therapy units capable of generating?
Beams of 1 MV and higher.
What is the advantage of megavoltage units over kilovoltage units?
They can reach deep-seated malignancies and spare skin and normal tissues.
How does beam energy relate to skin sparing in radiation therapy?
Higher beam energy (MV) results in more skin sparing; for example, 10 MV energy penetrates farther than 6 MV energy.
What was the primary limitation of kVp machines used before 1950?
They could not penetrate deep tissues.
What is a distinct disadvantage of orthovoltage machines compared to megavoltage machines?
Orthovoltage machines have increased scatter dose to tissues outside the treatment area, leading to decreased skin sparing.
What is the useful depth dose range for Grenz-ray therapy?
0.5 micrometers.
What types of conditions can Grenz-rays effectively treat?
Inflammatory disorders, Bowen's disease, mycosis fungoides, and herpes simplex.
What is the operational kVp range for contact therapy?
40 to 50 kVp
.5-1mm aluminum
What is the maximum depth for tumors treated with contact therapy?
Tumors not deeper than 1 to 2 mm.
What is the purpose of aluminum filters in contact therapy?
To absorb soft rays and reduce scatter.
What is the typical kVp range for superficial treatments?
50 to 150 kVp.
1-6mm of aluminium
What is the SSD (Source to Skin Distance) for superficial treatments?
15 to 20 cm.
What is the typical operating range for most orthovoltage equipment?
200 to 300 kvp
1-4mm of copper
What types of cancers are primarily treated with orthovoltage therapy?
Skin, mouth, and cervical cancers.
What is the limitation of orthovoltage therapy in treating lesions?
It has limitations in treating lesions deeper than 2 to 3 cm.
What is the filtering material used in orthovoltage therapy?
Copper, typically 1 to 4 mm thick.
What is the disadvantage of using orthovoltage machines for deep lesions?
Inability to use isocentric techniques.
What is the purpose of lead cutouts in superficial treatments?
To tailor fit the treatment area.
What is the inherent filtration of the Grenz-ray tube made of beryllium?
0.1 mm of aluminum.
What is the Van de Graff Generator and when was it invented?
The Van de Graff Generator is the first electrostatic accelerator, invented in 1937, that produces static electricity at high voltage and low continuous current.
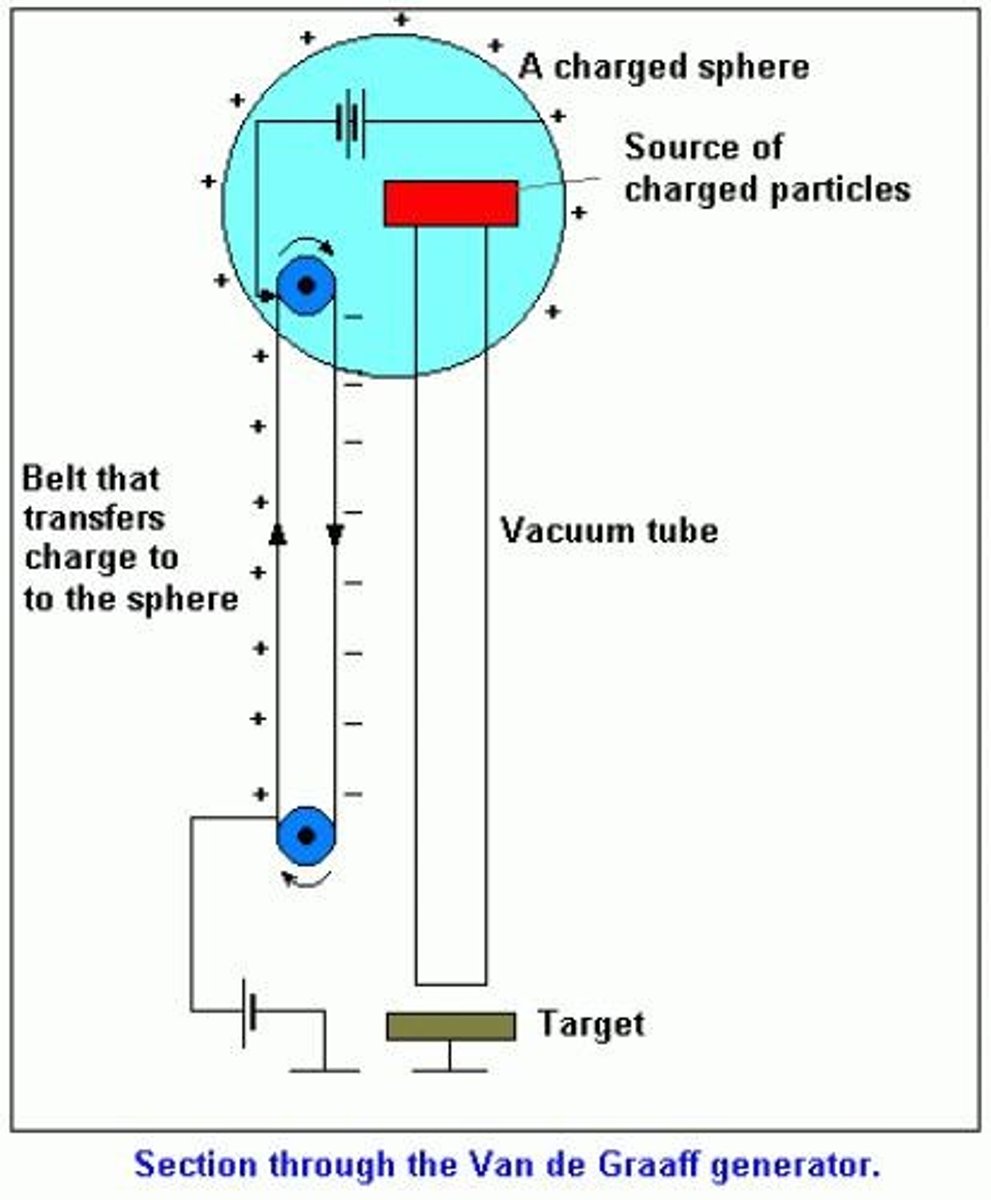
What are the dimensions of the Van de Graff Generator?
It is 3 feet in diameter and 5 feet high.
What is the operating dose rate of the Van de Graff Generator at a source-to-skin distance (SSD) of 100 cm?
It operates at 200 cGy/min.
What is one of the main uses of the Van de Graff Generator?
It is useful for treating seminomas, whole brain, or mantle fields.
What is the main principle behind the Betatron?
The Betatron accelerates electrons in a changing magnetic field, allowing them to move in a circular orbit.
When was the first Betatron developed and what energy could it produce?
The first Betatron was developed in 1941 and could produce x-rays with energies of 2 MV.
What are the energy ranges for electrons produced by Betatrons?
Betatrons can produce electron energies ranging from 6 MeV to 40 MeV.
What are some disadvantages of Betatrons compared to modern machines?
Betatrons have lower x-ray dose rates and field size capabilities compared to medical linacs and modern cobalt machines.
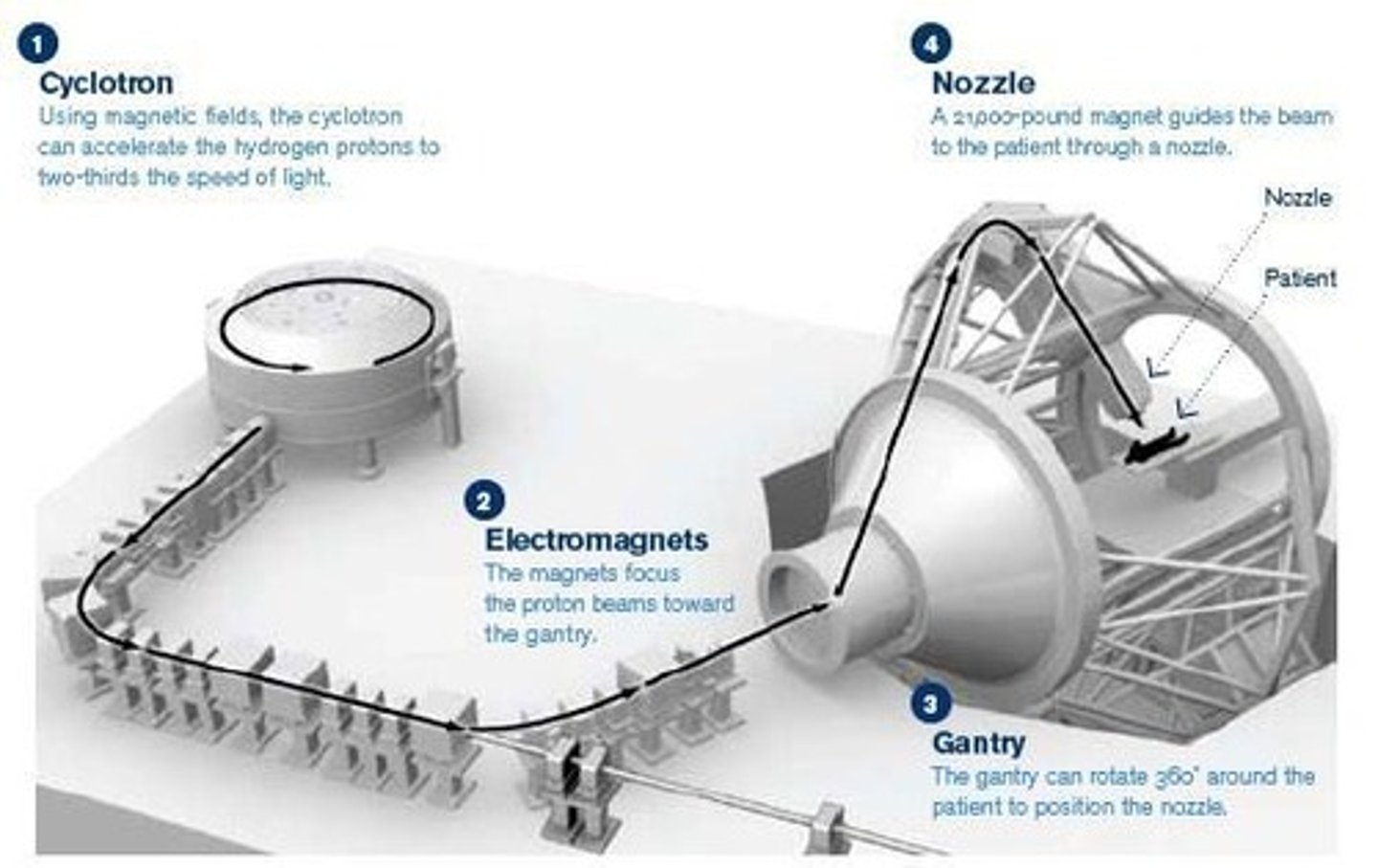
What is the Cyclotron primarily used for?
The Cyclotron is a charged particle accelerator used mainly for nuclear research and generating proton and neutron beams.
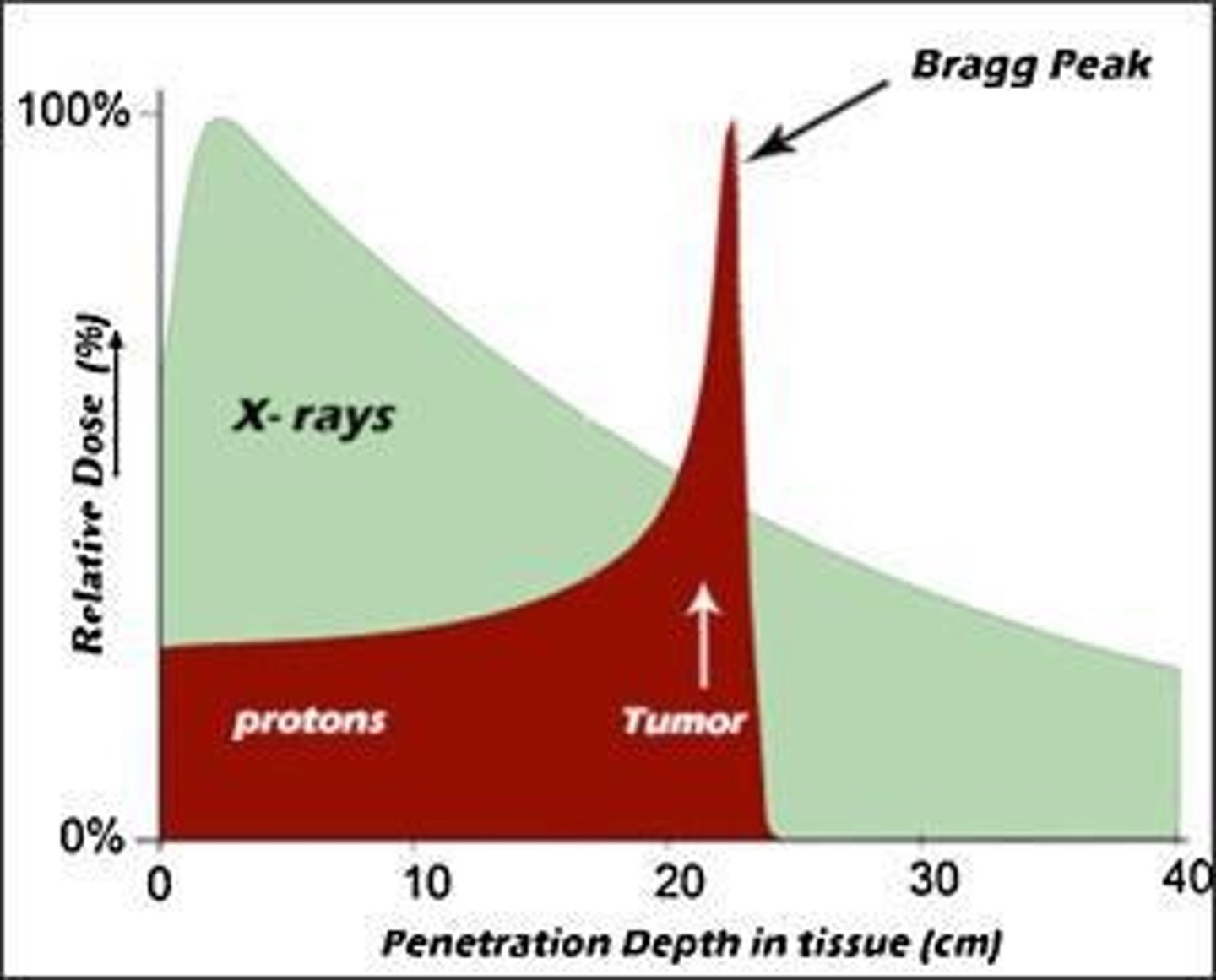
What is the Bragg Peak Effect in radiation therapy?
The Bragg Peak Effect refers to the phenomenon where protons deposit most of their energy at a specific depth, allowing for precise targeting of tumors.
What is the Grenz-ray Therapy machine and its energy range?
The Grenz-ray Therapy machine uses low energy x-rays below 20 kVp, also known as Bucky rays.
What is a significant disadvantage of kVp machines compared to megavoltage machines?
kVp machines have increased scatter dose to tissues outside the treatment area, leading to decreased skin sparing.
What type of cancers are typically treated with Betatrons?
Betatrons are used to treat gynecologic, bladder, and prostate cancers.
What is the typical treatment time for Betatron therapy?
Treatment times usually average 3 to 5 minutes at a dose rate of 200 cGy/min.
What is the main advantage of megavoltage therapy units over kilovoltage units?
Megavoltage therapy units can reach deep-seated malignancies and spare skin and normal tissues.
What are the limitations of Orthovoltage machines in treating lesions?
Orthovoltage machines experience limitations in treating lesions deeper than 2 to 3 cm.
What is the purpose of using aluminum filters in contact therapy?
Aluminum filters are used to absorb soft rays and reduce scatter in contact therapy.
What is the typical SSD for superficial treatments using x-rays?
Superficial treatments usually provide a source-to-skin distance (SSD) of 15 to 20 cm.
What types of tumors are treated with superficial x-ray therapy?
Superficial x-ray therapy is used for skin cancer and tumors no deeper than 0.5 cm.
What is the inherent filtration of the Grenz-ray tube?
The Grenz-ray tube has an inherent filtration of 0.1 mm of aluminum.
What is the significance of the term 'depth dose' in radiation therapy?
Depth dose refers to the amount of radiation exposure at various depths within the tissue.
What is the typical treatment distance for contact therapy?
Contact therapy applicators can provide a distance of 2 cm or less from the skin.
What types of lesions are treated with contact therapy?
Contact therapy is historically used to treat superficial skin lesions, including hemangiomas.
Filters do what
Harden the beam
Cobalt 60 is what type of particle
Gamma
Cyclotron makes what
Protons
Whats the metallic disk that helps make protons in the cyclotron
Dee's or D's
When did roentengen discover X-rays
1895
When was radiactvitbty discovered and by who
Becqueral in 1896
Basic properties of xray
Unaffected by gravity (they have no mass)
* Unaffected by electric fields
* Unaffected by magnetic fields
* Travel in straight lines
* Exponentially (decrease or increase in the rate
of change) attenuated by matter
* Cannot be focused
Produce two electron interactions:
1. Collision Interactions
Characteristic radiation production
2. Radiative Interactions
Bremsstrahlung radiation
Photoelectric is more
Diagnostic
Most common interaction in rad therapy
Compton
Bremmstralung
Electrón get close to the nucleus and is ejected out
Characteristic
Electrón interact with the K shell
What % of interactions r bremmstarlung
75%