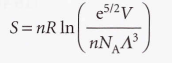Chapter 16 - Statistical Thermodynamics 1: The Concepts (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1
New cards
Adiabatic demagnetization
________- Based on that, in the absence of a magnetic field, the unpaired electrons of a paramagnetic material are orientated at random.
2
New cards
Thermal
________ wavelength- Decreases with increasing mass and temperature.
3
New cards
Population
________- The average number of molecules that occupy it.
4
New cards
Optical
________ trapping- Where atoms in the gas phase are cooled by inelastic collisions with photons from intense laser beams.
5
New cards
Sackur Tetrode
________ equation- It implies that the molar entropy of a perfect gas of high molar mass is greater than one of low molar mass under the same conditions.
6
New cards
priori probabilities
Principle of equal a(n) ________- The assumption that all possibilities for the distribution of energy are equally probable.
7
New cards
Canonical
________ ensemble- The imaginary collection of replications of the actual system with a common temperature.
8
New cards
Statistical thermodynamics
________- The link between individual molecular properties and bulk thermodynamic properties.
9
New cards
Weight of the configuration
________- The number of ways a general configuration can be achieved.
10
New cards
Canonical partition function
________ (Q)- A function of the temperature.
11
New cards
Statistical thermodynamics
The link between individual molecular properties and bulk thermodynamic properties
12
New cards
Population
The average number of molecules that occupy it
13
New cards
Principle of equal a priori probabilities
The assumption that all possibilities for the distribution of energy are equally probable
14
New cards
Weight of the configuration
The number of ways a general configuration can be achieved
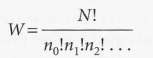
15
New cards
Stirling's approximation
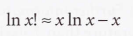
16
New cards
Boltzmann distribution
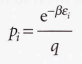
17
New cards
Molecular partition function
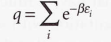
18
New cards
Common methods used to reach very low temperatures
* Optical trapping
* Adiabatic demagnetization
* Adiabatic demagnetization
19
New cards
Optical trapping
Where atoms in the gas phase are cooled by inelastic collisions with photons from intense laser beams
20
New cards
Adiabatic demagnetization
Based on that, in the absence of a magnetic field, the unpaired electrons of a paramagnetic material are orientated at random
21
New cards
Thermal wavelength
Decreases with increasing mass and temperature
22
New cards
The total energy of the system relative to the energy of the lowest state
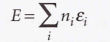
23
New cards
Boltzmann formula for the entropy

24
New cards
Canonical ensemble
The imaginary collection of replications of the actual system with a common temperature
25
New cards
Microcanonical ensemble
Where the condition of constant temperature is replaced by the requirement that all the systems should have exactly the same energy
26
New cards
Grand canonical ensemble
The volume and temperature of each system are the same, but they are open, which means that matter can be imagined as able to pass between the systems; the composition of each one may fluctuate, but the chemical potential is the same in each system
27
New cards
Canonical distribution
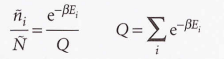
28
New cards
Canonical partition function (Q)
A function of the temperature
29
New cards
The total weight (W) of a configuration of the ensemble
The product of the average weight W of each member of the ensemble
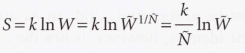
30
New cards
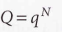
For distinguishable independent molecules
31
New cards
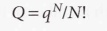
For indistinguishable independent molecules
32
New cards
Sackur-Tetrode equation
It implies that the molar entropy of a perfect gas of high molar mass is greater than one of low molar mass under the same conditions