Definitions
1/353
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
354 Terms
Factors of productions
refers to the resources that are acquired to produce goods and services.
\
(The four factor of production can be remembered using the acronym CELL)
Capital
refers to man-made resources
Entrepreneurship
Refers to the skill of organizing the three other factors of production
Land (Factors of production)
refers to natural resources e.g. agricultural land, wood, golf
Circular flow of income
a model which shows the interaction between households and firms.
Injection
reers to the additional money added to the circular flow of income
Leakage
the withdrawal of money from the circular flow of income
Free market economy
allocation of resources is determined by market forces i.e. consumers and producers.
Mixed economy
allocation of resources is determined by consumers, producers and the government.
Planned economy
Allocation of resources is determined by the government
Opportunity cost
Every choice made is associated with a cost which is known as an opportunity cost. It is the value of the next best alternative forgone when a choice is made
Free Goods
naturally abundant with unlimited supply and therefore do not incur any opportunity costs. (air, sea water, sunlight and desert sand)
Production possibility curve
a model which illustrates the different combinations of two goods or services that an economy or firm can produce.
Economic agents
economic decisions makers who interact for the purpose of production and consumption. e.g. households, firms and the government
Wages
reward for labour services
Income
collective rewards for all the factors of production. Sum of rent, interest, profit and salaries.
labour
both physical and mental human resources used in the production.
Economic goods
resources and products that are limited in supply and have economic value to society.
Free market economy
an economic system which relies on the market forces of demand and supply to allocate resources in the economy.
Marginal rate of transformation (rate of substitution)
Gradient of the PPC showing the opportunity costs between the two products in question.
Pareto efficiency
pareto efficiency is when its not possible to make one person better off without making someone else worse off.
Economic methodology
Ways in which economists study the discipline.
Real GDP
a measure of an economy's total economic output or the value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders, adjusted for inflation or deflation.
Monetary policiy
the actions and measures taken by a central bank or monetary authority to manage and control the money supply, interest rates, and credit conditions in an economy.
Fiscal policy
the use of government spending and taxation to influence the overall state of the economy. Promotes economic growth, controlling inflation, reducing unemployment, and addressing income inequality.
Stagflation
Stagflation is a macroeconomic condition characterized by both high inflation (rising prices), slow growth and high unemployment occurring simultaneously in an economy.
Austerity
austerity is a type of government policy aimed at reducing budget deficits and controlling public debt. These measures typically involve cutting government spending and/or increasing taxes to achieve fiscal discipline and stabilize the economy.
Equality
The even distribution of resources, opportunities and outcomes among individuals or groups within a society.
Economic inequality
the degree of differences between an economy's individuals in their ability to satisfy their needs and wants due to monetary constraints.
Wealth Inequality
The unequal distribution of assets, such as property, investments, and savings, among individuals in a society.
Gini coefficient
A measure of statistical dispersion representing income or wealth distribution, ranging from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (perfect inequality).
Progressive taxation
A tax system where the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases, aimed at reducing income inequality.
Lorenz curve
A graphical representation of income or wealth distribution, showing the proportion of total income earned by different segments of the population.
Poverty
The state of lacking sufficient resources to meet basic human needs and participate fully in society.
Absolute poverty
A condition where individuals lack the resources to meet basic survival needs like food, shelter, and clothing. Lives on less than 1.9 dollars per day.
Relative poverty
Poverty in a household is considered relative to income levels in other households
Households that are living with less than 50% of the median household income are considered to be in relative poverty.
Poverty line
A specific income level below which people are considered to live in absolute poverty.
Cost of living
The amount of money needed to cover basic expenses like housing, food, and transportation.
Human capital
The skills, knowledge, and abilities that individuals possess, which can increase their productivity and earning potential
political power
the ability to influence government decisions and policies
Concentration of power
When control or influence is held by a small group
Sustainable development
The ability of current generations to meet their needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
A universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all by 2030.
Social sustainability
refers to the ability of an economy to develop social processes and structures that enable its current population to live optimally and to support the ability of future populations to do the same.
Economic sustainability
refers to the optimal use of scarce resources in such a way to ensure future generations are not disadvantaged in favour of today’s generation.
Environmental sustainability
refers to the responsible use of the planet’s natural resources so that future generations are not compromised on their use of these natural resources
Single indicator
to a statistical measure of economic development that uses one particular gauge, such as literacy rates, income per capita or life expectancy.
Human development Index HDI
A composite index measuring average achievement in three basic dimensions of human development: health (life expectancy), education (mean years of schooling), and standard of living (GNI per capita).
Gender equality Index
a composite measure of development by calculating gender disparities through three dimensions, namely reproductive health, empowerment and labour market participation.
The Inequality adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI)
a composite measure of the average level of human development by accounting for inequalities in society.
Happy Planet Index
a measure of sustainable human well-being, that is, how individuals and countries are able to achieve long, happy and sustainable lives
Formula for Happy planet Index

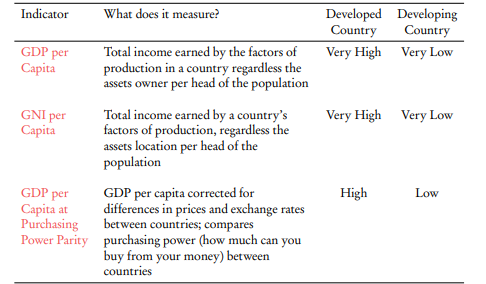
GDP/GNI per capita
(or GDP per head) is the average income in an economy, i.e. the total GDP/GNP divided by the population size.
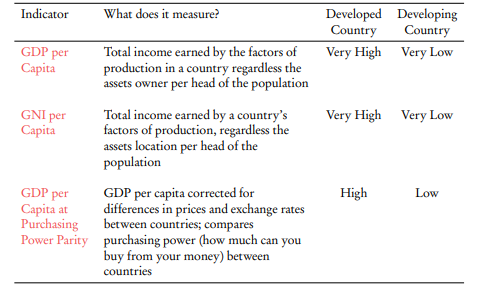
Purchasing power parity (PPP)
refers to the exchange rate that enables residents to purchase a common basket of goods and services in different countries.
Health indicators
e a category of single indicators of measuring economic development by using health-related determinants of the quality of life, such as life expectancy and the under-five mortality rate.

Education indicators
a category of single indicators of measuring economic development by using education related determinants of the quality of life, such as literacy rates and the mean years of schooling.

Energy Indicators
a category of single indicators of measuring economic development by using factors that create affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all citizens.
Environmental indicators
a category of single indicators of measuring economic development by using environmental issues that influence or determine the quality of life, such as global warming and climate change.
Desertification
land degradation caused by natural processes or human-induced activities that result in fertile land becoming desert; that is, the over-exploitation of soil and land through human activity.
Poverty trap
A self-reinforcing mechanism that causes poverty to persist across generations, making it extremely difficult for individuals or communities to escape without external intervention.
Economic barriers
Structural challenges that prevent countries from achieving sustainable economic growth and development.
Primary sector
The sector of the economy that produces primary commodities, which are goods arising from the factor of production land.
informal economy
Part of the economy that lies outside the formal economy, involving unregistered and legally unregulated economic activities.
Capital flight
The large-scale and rapid movement of financial assets or capital from a country to foreign markets, often due to economic instability or political uncertainty.
Political barriers
Obstacles to economic growth and development that arise from government structures, policies, and power dynamics, rather than economic factors.
Social barriers
Obstacles to economic growth and development that stem from societal norms, cultural practices, and social structures.
Institutional framework
The formal and informal rules, systems, and organizations that govern economic, political, and social interactions in a country.
Diversification
The process of expanding the range of products, services, or markets to reduce risk and enhance economic stability.
helps countries avoid over-reliance on a single commodity or sector, reducing vulnerability to price fluctuations and external shocks.
Foreign Aid
Financial or technical assistance provided by one country or organization to another, typically for development or humanitarian purposes.
Balance of payments
A systematic record of all economic transactions between residents of a country and the rest of the world over a specific period.
Usually one year and t includes the country’s trade in goods and services with other countries
Credit items
payments received from consumers, firms and institutions or governments located outside of the economy.
Debit items
payments made to consumers, firms and institutions or governments located outside of the economy.
Surplus of an account
Exists when the total value of credit items exceeds the total value of debit items, over a given
Deficit on an account
exists when the total value of debit items exceeds the total value of credit items, over a given period of time.
Current account
a record of all trade flows (exports and imports of goods and services), income flows and income transfers between countries by individuals, firms and governments.
Balance of trade
the difference between a country’s total export earnings and its total import expenditure on both goods and services, that is, the value of (X – M).
Current transfers
The inflows and outflows of money that are not made in exchange for trade or any corresponding output of goods or services.
Current account balance
the sum total of all items listed in the current account. The balance can be in deficit (when M > X), in surplus (X > M) or zero (X = M).
Current account deficit
Occurs when the sum of money flowing out of a country’s current account exceeds the money flowing into the current account, per time period.
A current account surplus
occurs when the sum of money flowing into a country’s current account exceeds the money flowing out of its current account, per time period.
Capital transfers
the different forms of capital inflows and outflows of a country, such as debt aid, debt forgiveness and the flow of money by emigrants and immigrants
Transactions in non-produced, non-financial assets
refer to the rights to natural resources and intellectual property rights. The income stream from these intangible assets for the country are recorded in its financial account.
financial account
a record of the transactions that relate to the change in ownership of assets, that is, cross-border investments. These include foreign direct investment, portfolio investment, reserve assets and official borrowing.
Current account formula
= financial account + capital account + net errors & omission
Exchange rate
The price of one currency expressed in terms of another currency.
Foreign exchange market
Where currencies are bought and sold
Floating exchange rate
A system where the value of currency in terms of another is determined by the market forces of supply and demand without government intervention.
Appriciation
An increase in the value of a currency relative to another currency due to the forces of demand and supply
Depreciation
A decrease in the value of a currency relative to another currency due to the forces of demand and supply
Remittance
money transfers from people working abroad to their home country.
Speculation
The act of buying or selling assets with the hope of making a profit from future price changes.
Fixed exchange rate
a system where a country's currency value is tied to another currency or a basket of currencies. This means that the exchange rate remains constant and does not fluctuate with market forces.
Devaluation
when the price of a currency operating in a fixed exchange rate system is officially and deliberately decreased.
Revaluation
when the price of a currency operating in a fixed exchange rate system is officially and deliberately increased.
Managed exchange rate
A system where exchange rates are primarily determined by market forces but are occasionally adjusted by central banks to maintain stability within a target range.
Pegging currency
A system where a country's currency value is fixed to another currency or a basket of currencies, maintained through active central bank intervention.
Overvalued currency
A situation where a currency's exchange rate is higher than its market equilibrium level, making exports more expensive and imports cheaper.
Undervalued currency
A situation where a currency's exchange rate is lower than its market equilibrium level, making exports more expensive and imports cheaper.
Economic Integration
The process of increasing cooperation and coordination between countries through the reduction of trade barriers and alignment of economic policies.
Preferential Trade Agreement
a trade treaty between two or more countries, giving special or favourable terms and conditions of trade to member countries