1.5 Diagnostic Imaging of the Urinary Tract, Prostate Gland, & Uterus
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are the indications for imaging the urinary tract?
Abdominal mass
Altered urination (dysuria, pollakiuria, hematuria)
Abdominal/pelvic trauma
Abnormal renal or urinary profile
Sampiling (cystocentesis, biopsy, etc)
What are the minimum radiographic projections needed when imaging the urinary tract?
Lateral of the abdomen
Ventrodorsal of the abdomen
Free lateral projection of the urethra (caudal abdomen & perineal)
Roentgen signs
Number
Location
Size
Shape
Margination
radiopacity
Describe the normal radiographic anatomy of canine kidneys
Number: 2
Location: retroperitoneal space
- Right: cranial, renal fossa, T13
- Left: More mobile, L1-L3, more caudal
Shape: oval (bean)
Margination: smooth
Opacity: soft tissue
Size: 2.5-3.5x L2 vertebra
Describe the normal radiographic appearance of feline kidneys
Number: 2
Location: Retroperitoneal space (L1-L4, right may be more cranial)
Shape: round or oval
Margination: smooth
Opacity: soft tissue
Size: 1.9-2.6x L2 vertebra (intact cats can be up to 3x)
Describe the normal radiographic appearance of the ureters in dogs & cats
Dogs: usually not visible
Cats: potentially visible, difficult to see
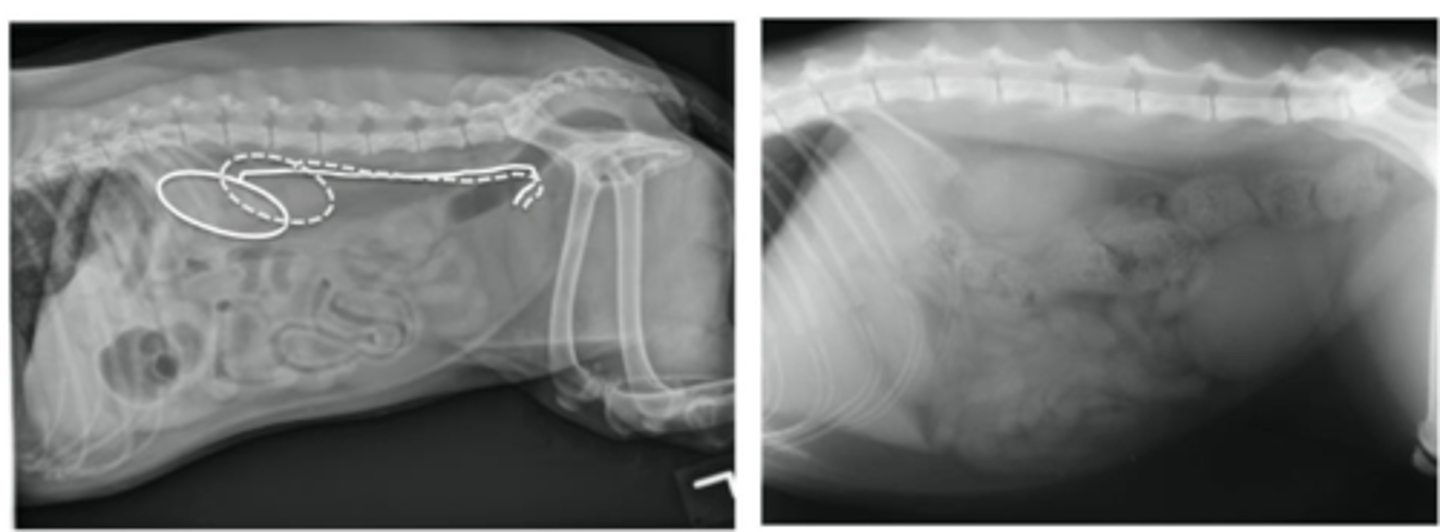
Describe the normal radiographic location of the urinary bladder
Caudoventral abdomen
Peritoneal cavity
Cranial to the pubis
Ventral to descending colon & uterine body/stump
Cranial to the prostate gland
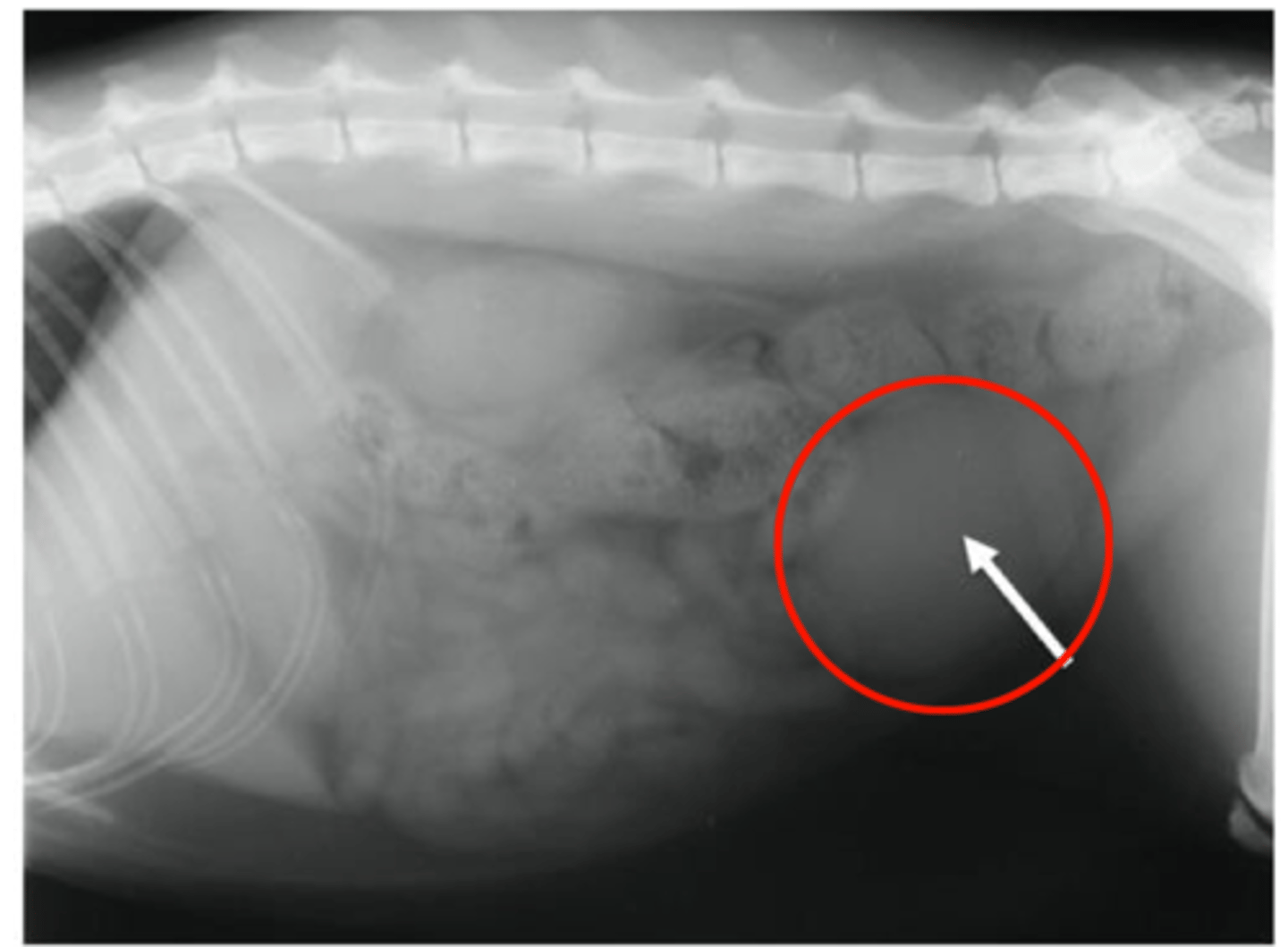
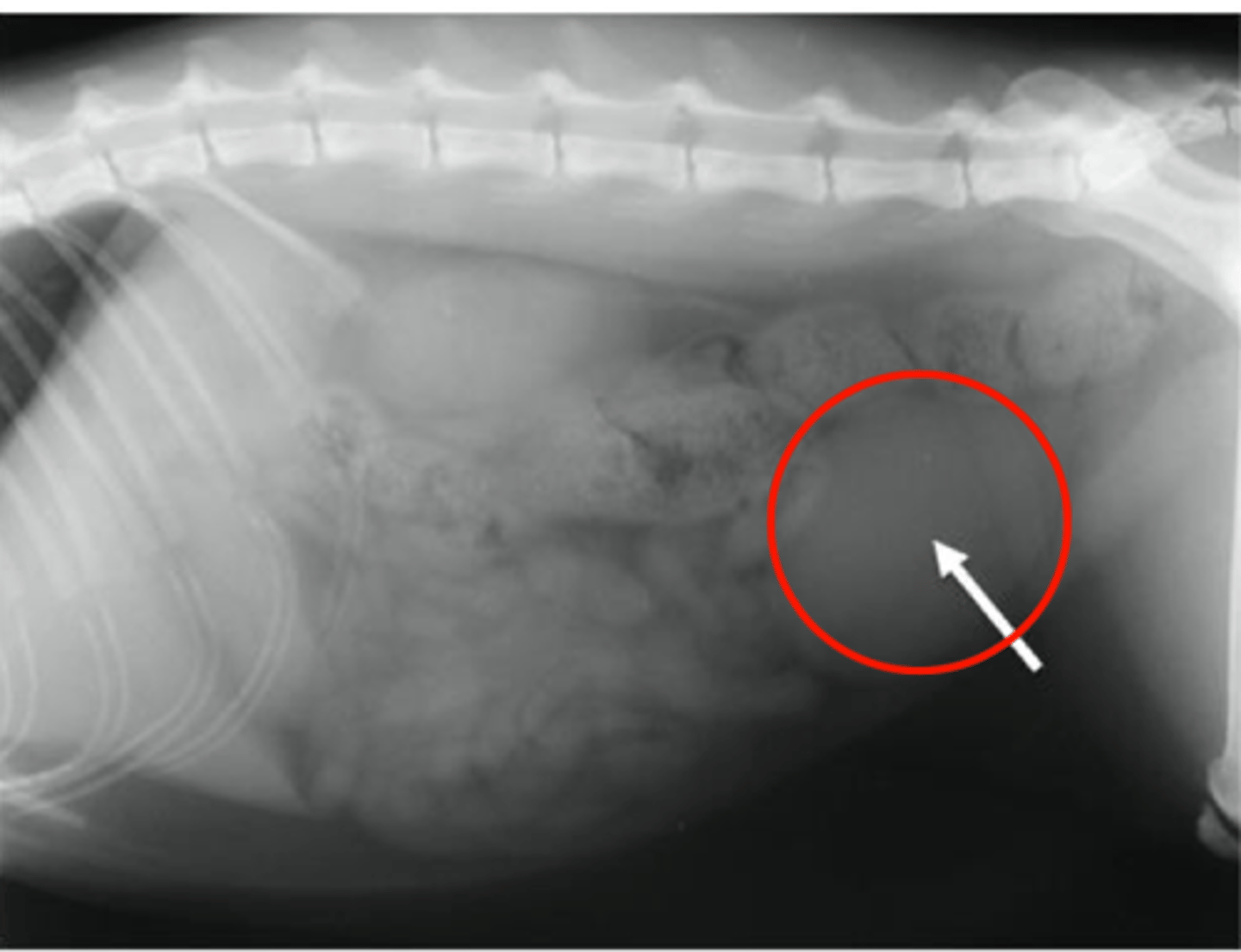
Describe the normal radiographic appearance of the urinary bladder
Size: variable (filled or empty, species differences)
Shape: oval to ellipsoid (dogs) - ellipsoid in cats
Margination: smooth
Opacity: soft tissue
Describe the normal radiographic anatomy of the canine urethra
Normally not seen
Shorter & wider in females (more obstructions in males)
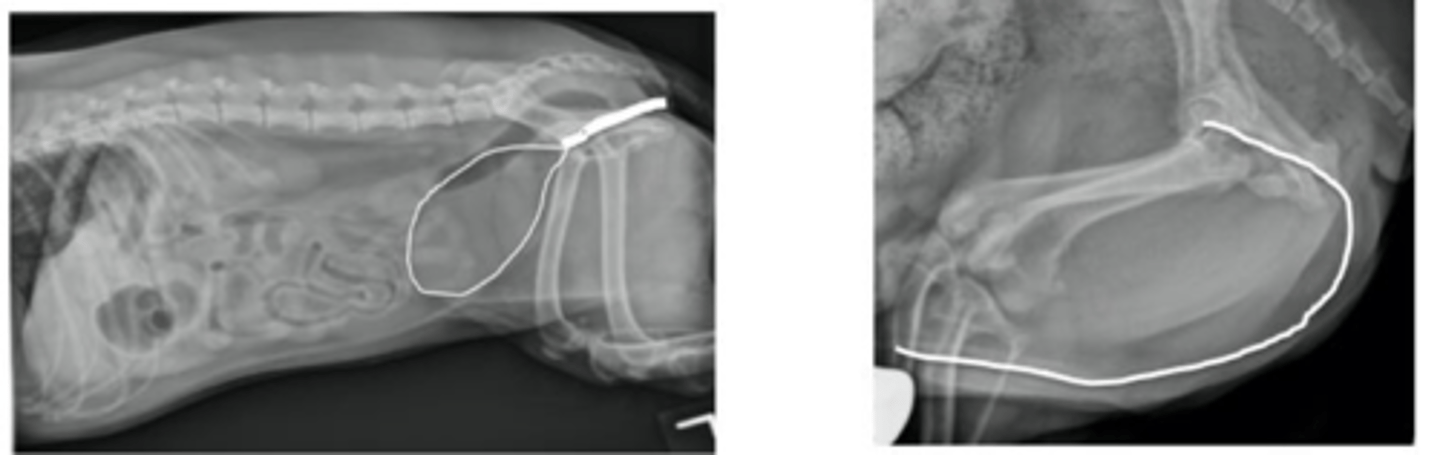
Describe the normal radiographic anatomy of the feline urethra
Normally not seen
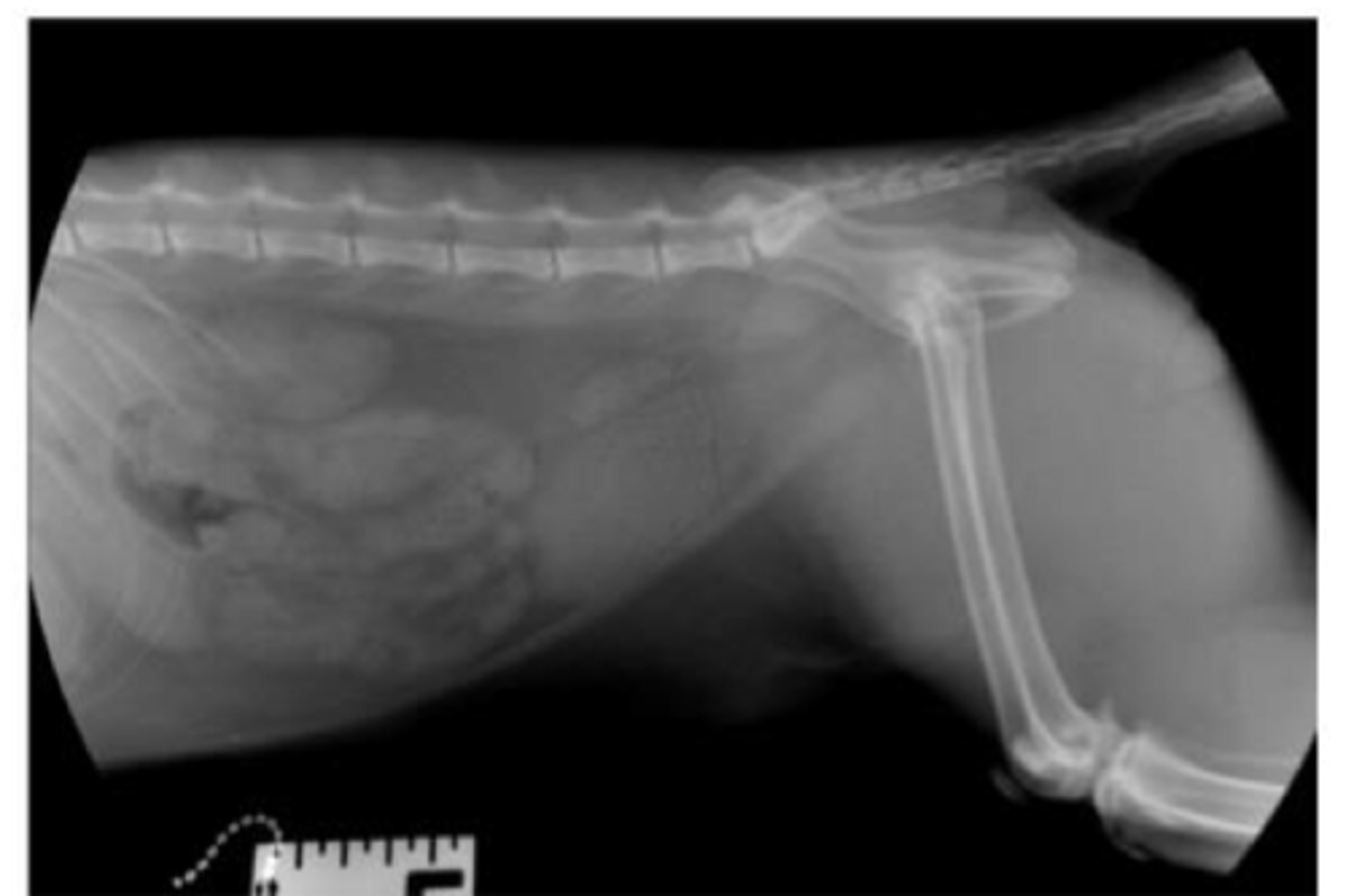
Describe the normal radiographic location of the canine prostate
Surrounds prostatic urethra
Within the pelvic canal
Ventral to the colon
Caudal to the urinary bladder
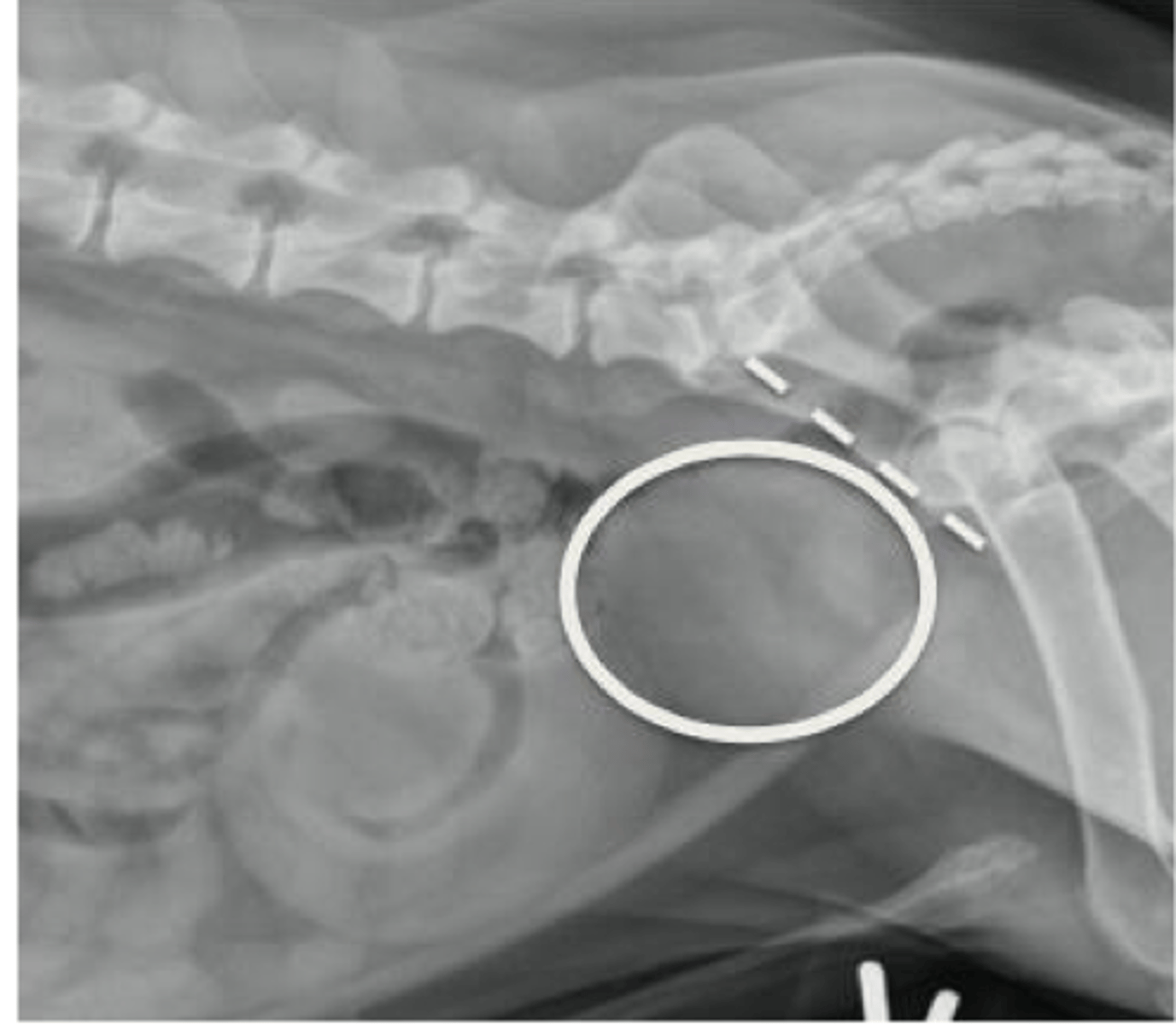
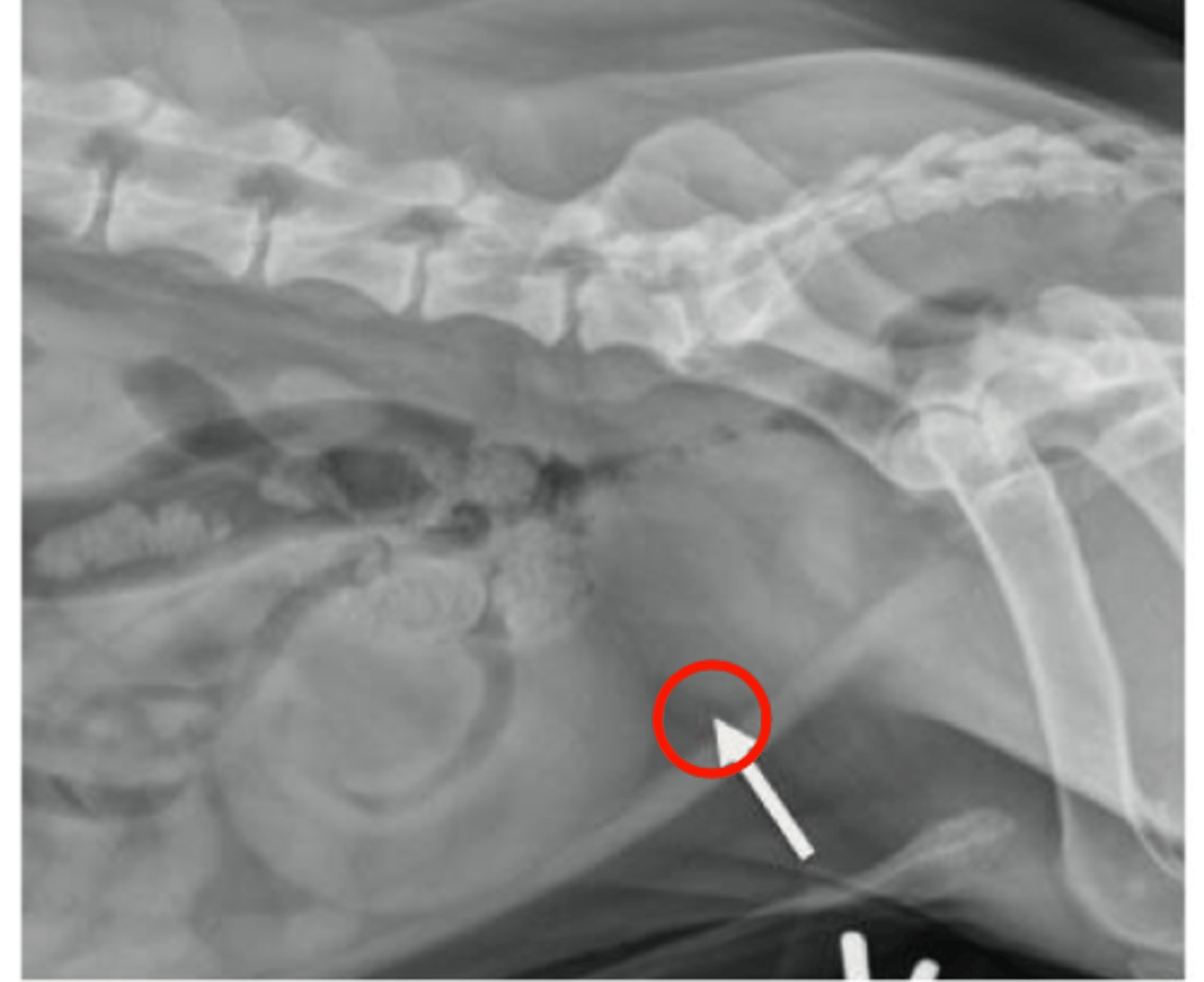
Describe the normal radiographic appearance of the canine prostate
Size: <70% distance of pubis to sacrum
Shape: oval to round
Margination: smooth
Opacity: soft tissue
Mineralization indicative of neoplasia
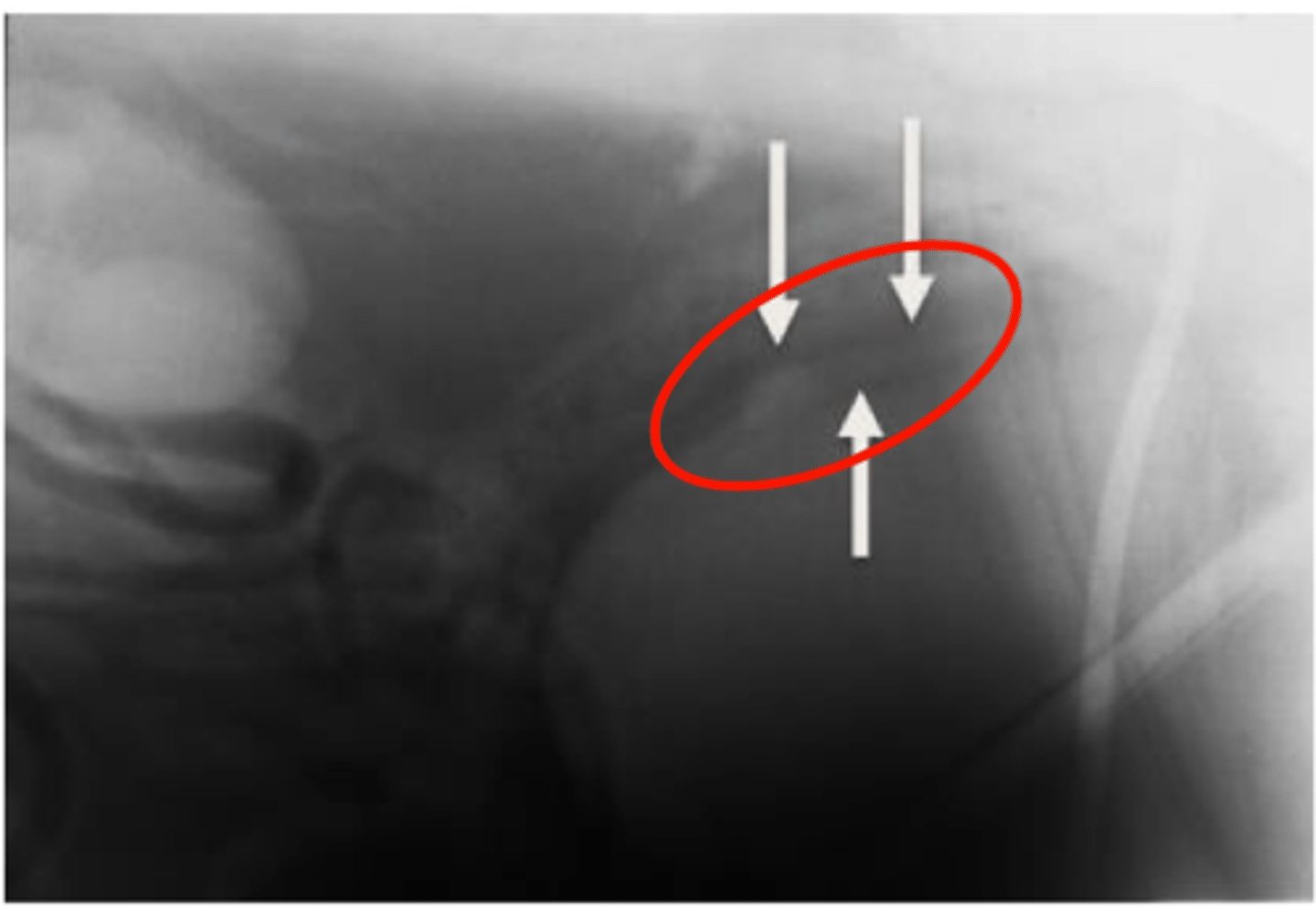
Describe the normal radiographic appearance of the feline prostate
Typically not seen
Describe the normal radiographic location of the uterus
Ventral to colon
Dorsal to urinary bladder
Describe the normal radiographic appearance of the uterus
Shape: tubular
Margination: smooth
Opacity: soft tissue
not always visible unless distended
What are the general signs/characteristics being observed on ultrasonography?
Size
Shape
Margination
Echogenicity
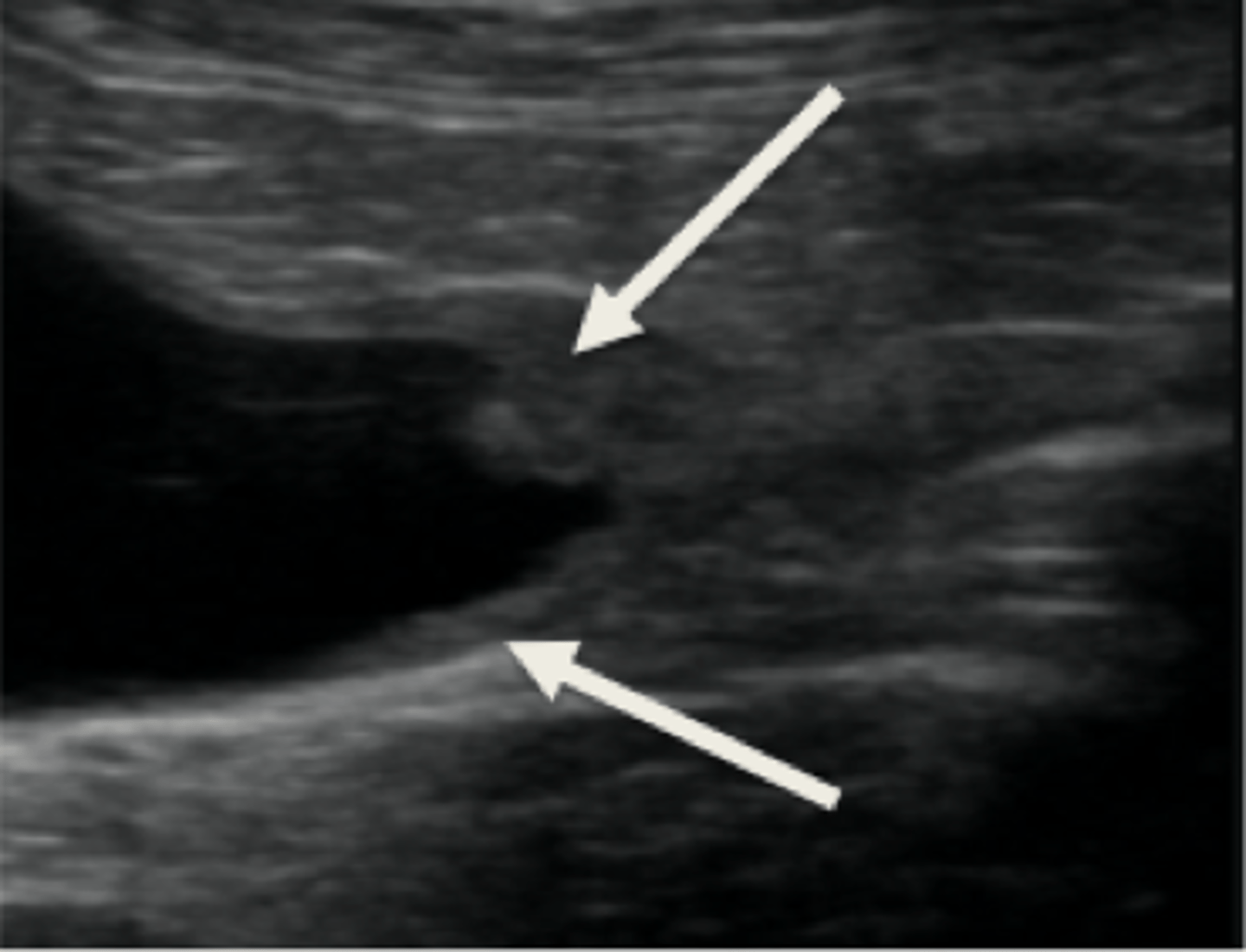
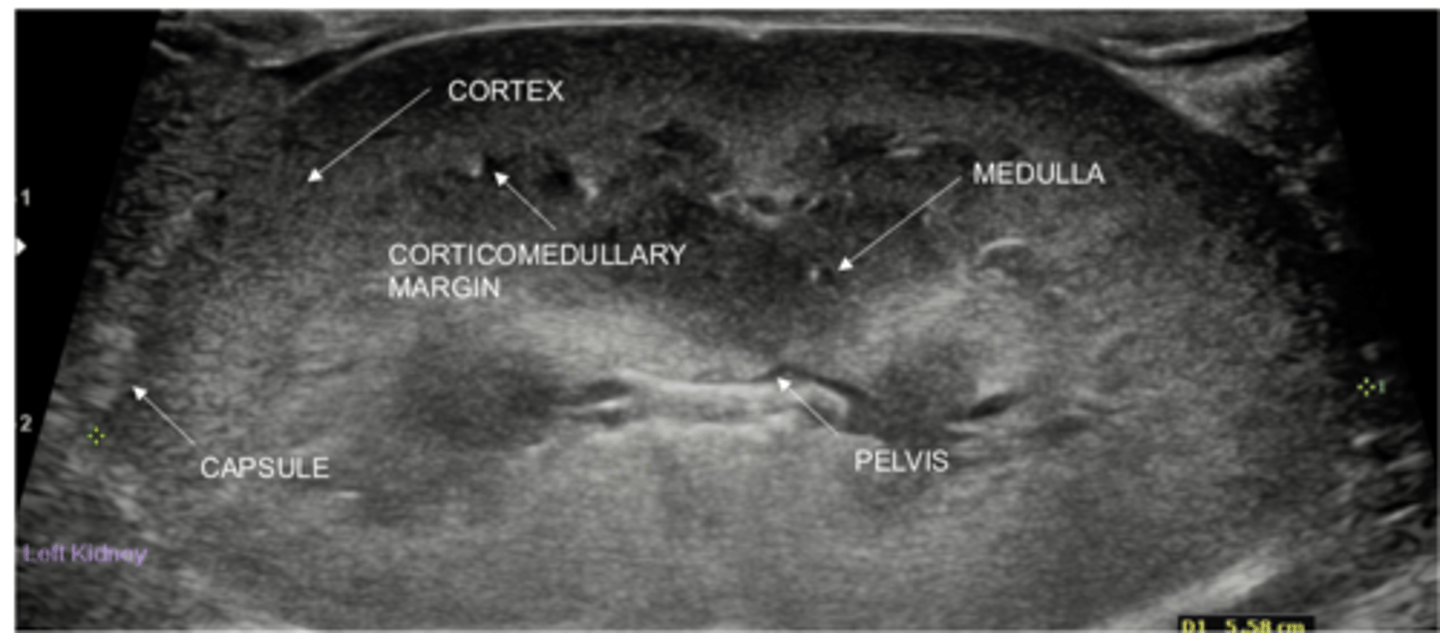
Describe the normal appearance of a kidney on ultrasound (sagittal)
Shape: oval in dogs, more rounded in cats
Cortex: more hyperechoic
Medulla: more hypoechoic
Renal pelvis: v-shape, hypoechoic, up to 2 mm
Size: variable in dogs, 3.0-4.5 cm length in cats
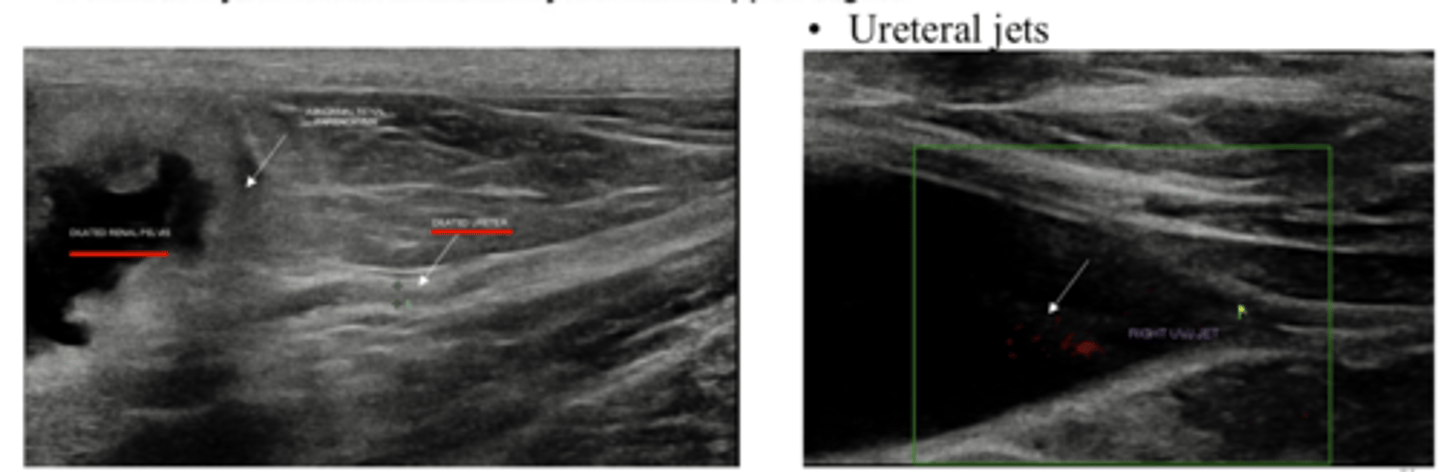
Describe the normal appearance of ureters on ultrasound
Not always visible
Ureteral jets at uterovesical junction (Doppler) shows urine movement
Need to assess if renal pelvis is distended
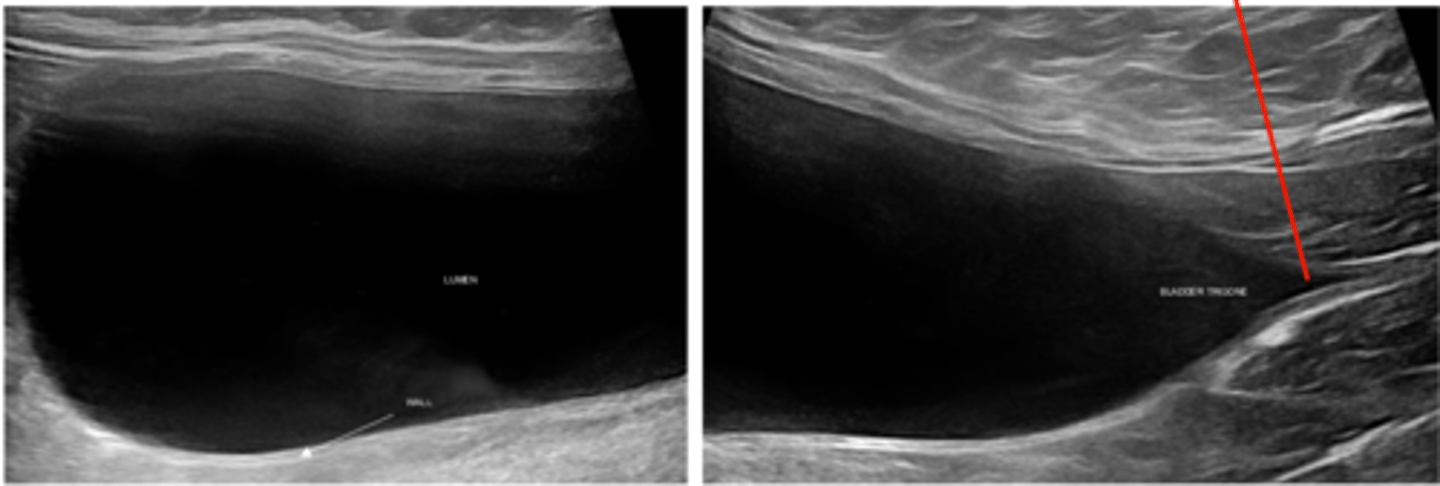
Describe the normal appearance of the urinary bladder on ultrasound
Anechoic
Wall thickness <2 mm
urethra at the edge of the bladder trigone
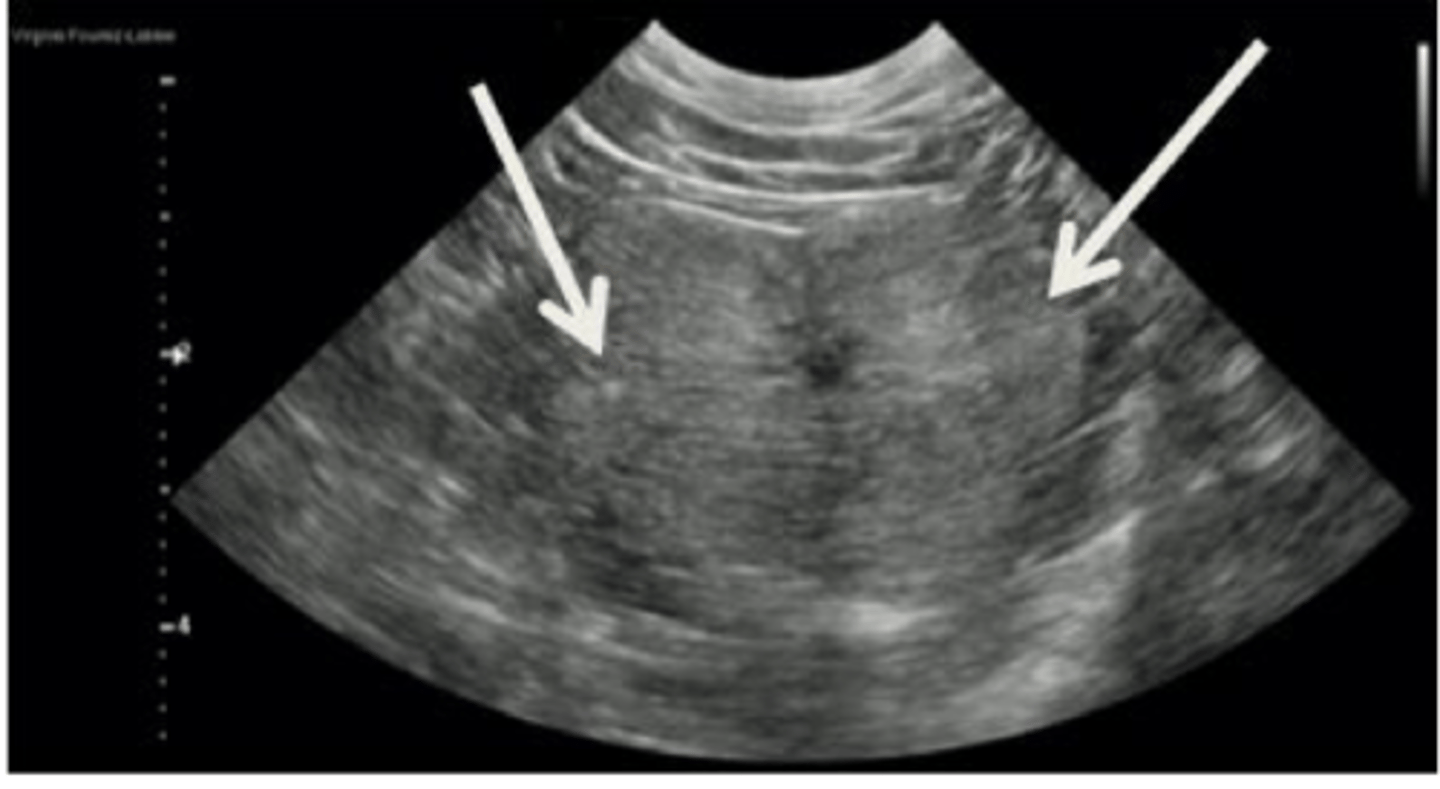
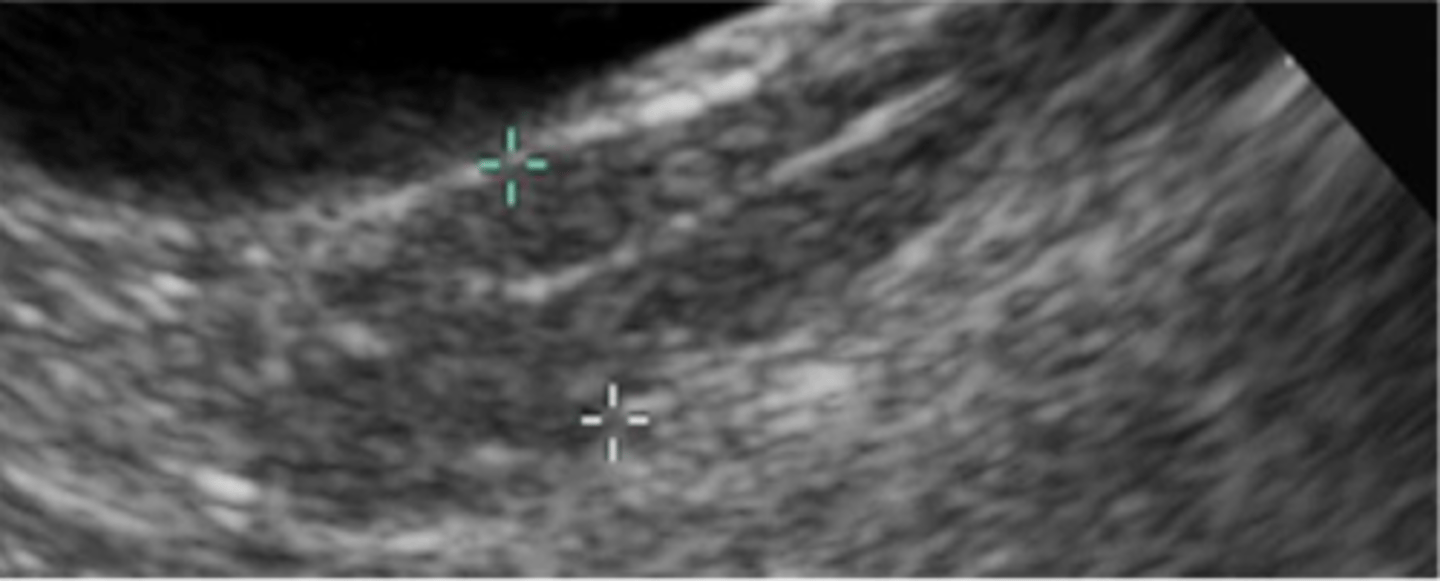
Describe the normal appearance of the prostate gland in an intact male dog on ultrasound
Bilobed with smooth contour
Homogenous echogenicity
Central urethra visible
Describe the normal appearance of the prostate gland in a neutered male dog on ultrasound
Small
Round
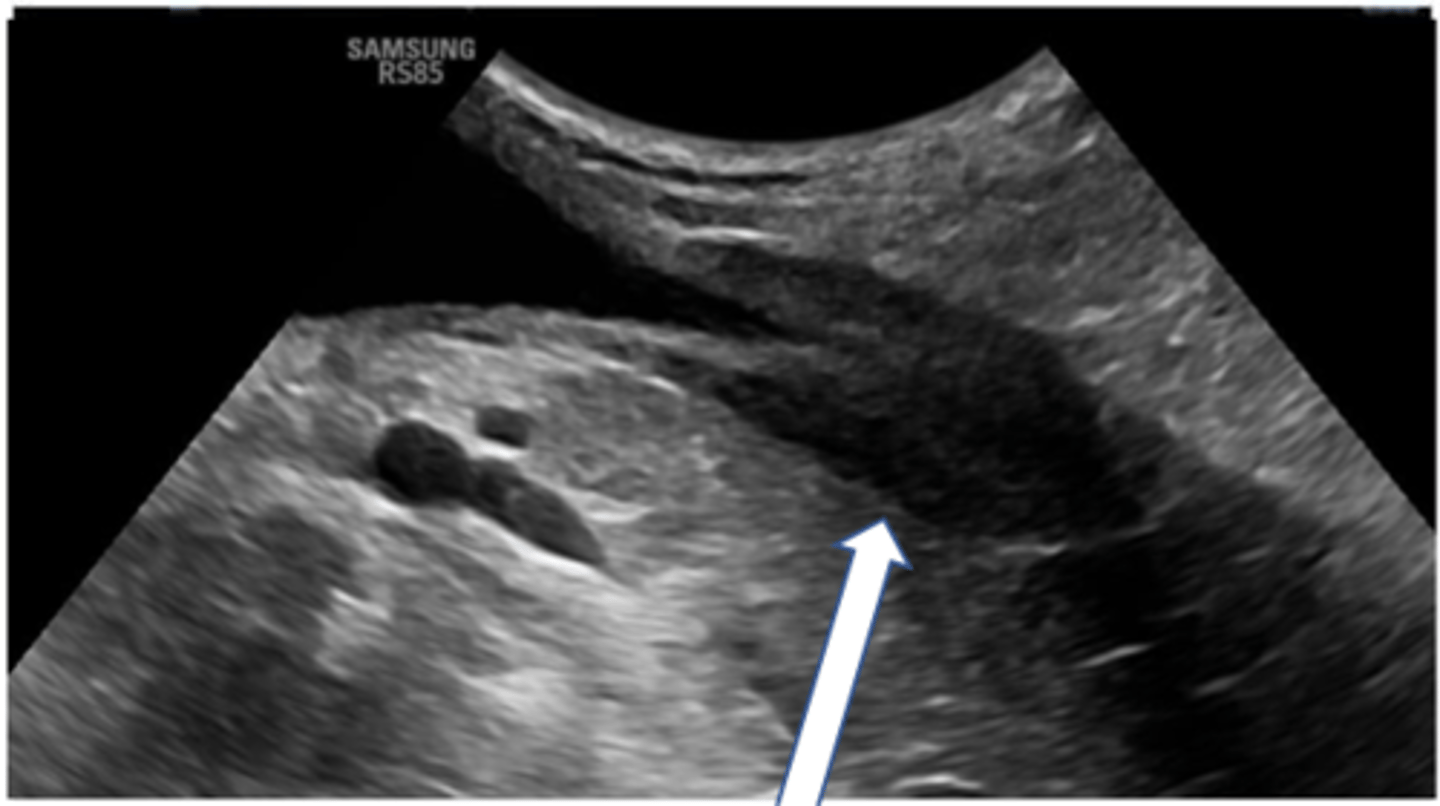
Describe the normal appearance of the uterus on ultrasound
Tubular structure dorsal to the urinary bladder
Echogenic line in the middle (collapsed lumen, mucus)
Distended if in heat or with pathology (pyometra)
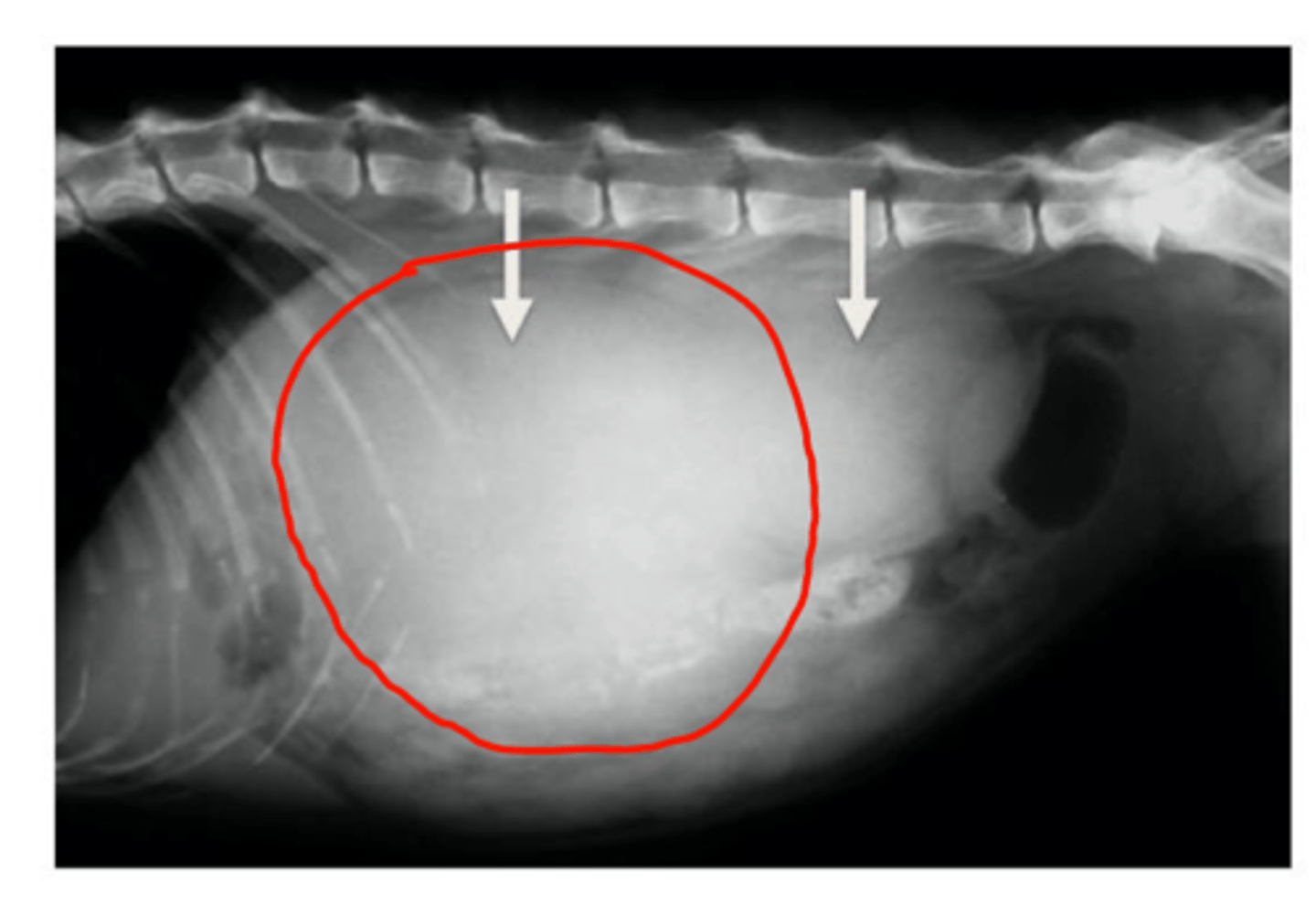
Describe the main radiographic findings in cases of nephromegaly/renomegaly
Enlarged kidney(s)
Ventral displacement of the gastrointestinal tract (mass effect)
What are some diseases that may show bilateral nephromegaly?
Lymphoma
Acute nephropathy
Hydronephrosis
What are some diseases that may show unilateral nephromegaly?
Hydronephrosis
Peri-renal pseudocyst
What are some diseases that may show bilateral nephromegaly with irregular margins?
Polycystic kidney disease
Neoplasia
What are some diseases that may show unilateral nephromegaly with irregular margins?
Mass lesion (cyst, neoplasia, abscess)
Nephrolithiasis
Presence of renal calculi (stones)
Main radiographic finding is increased opacity
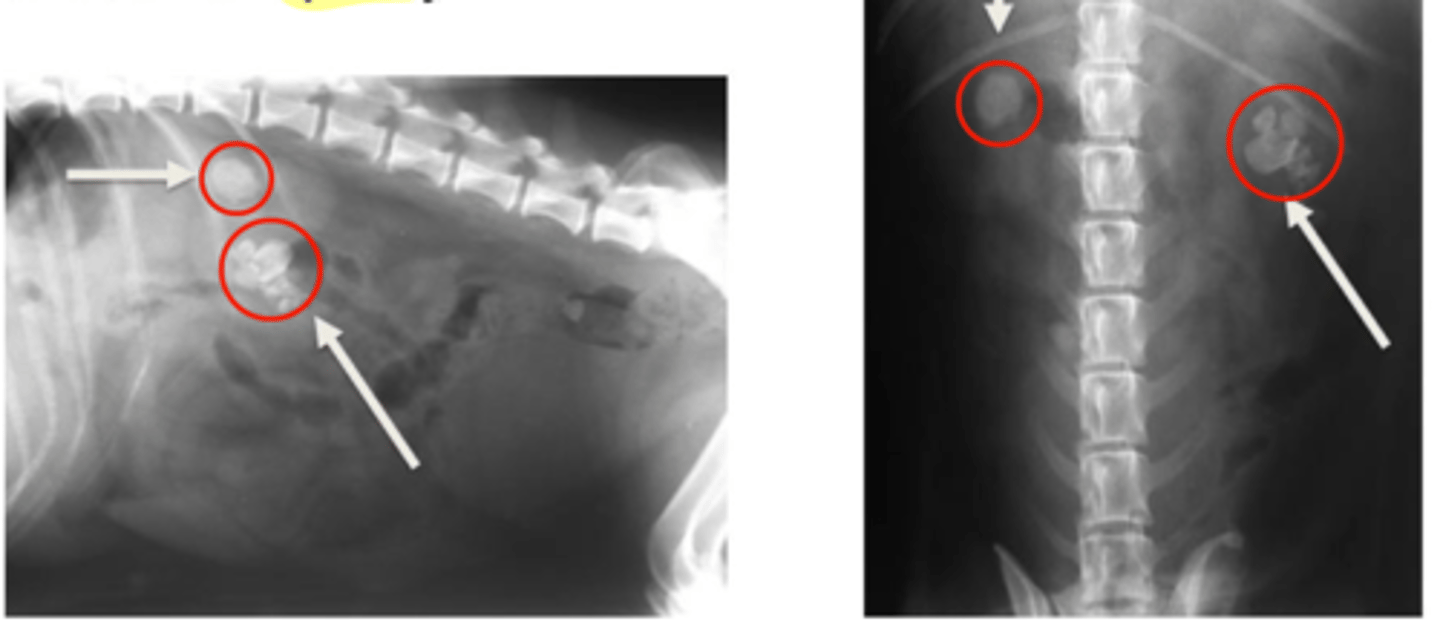
What is a common radiographic abnormality of the urinary bladder diagnosed on radiography?
Calulus/calculi/urolithiasis
Radiopaque: Struvite or calcium oxalate
Non-radiopaque: Urate or cysteine
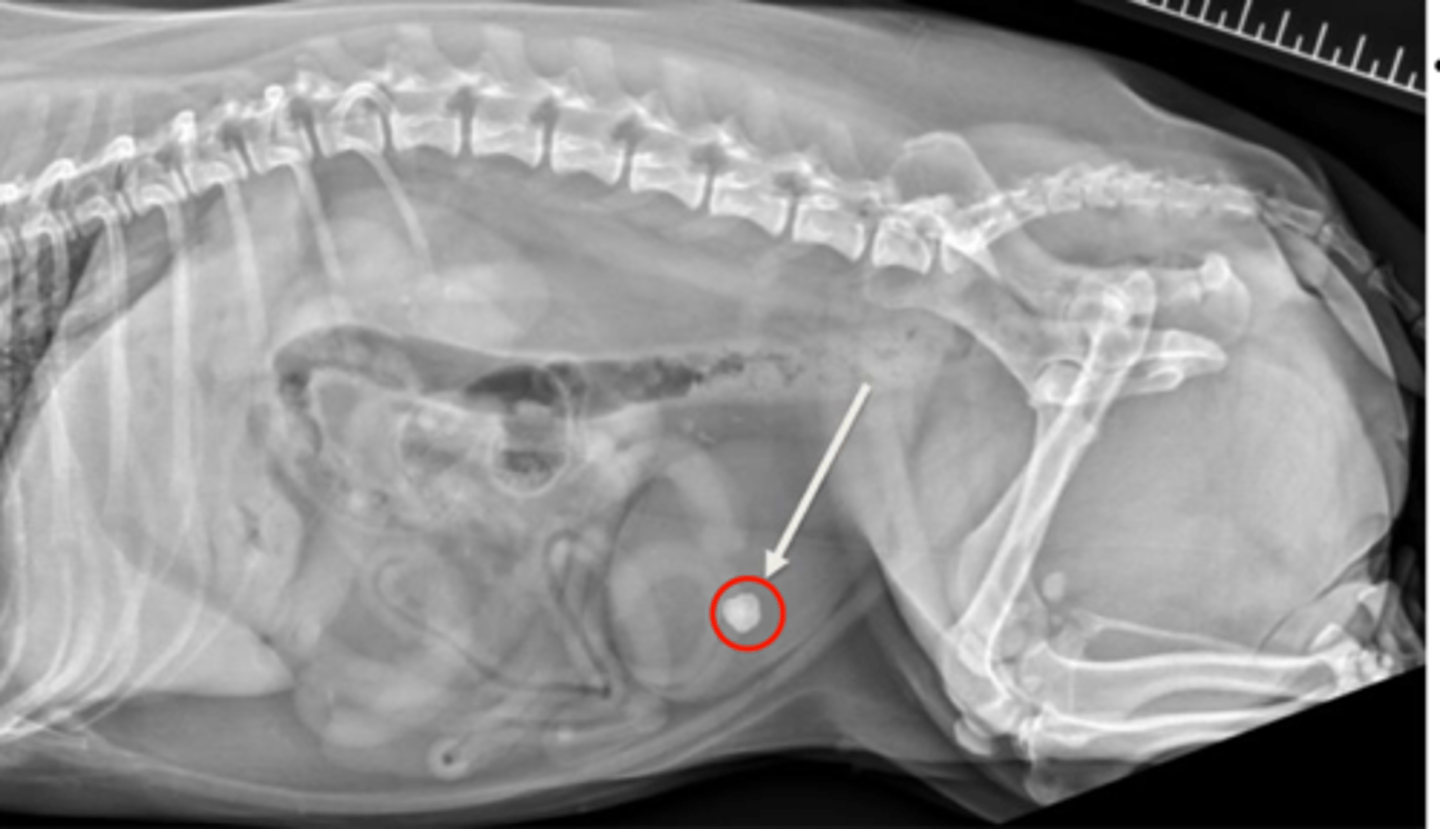
What are some causes/predispositions for development of urate calculi?
Portosystemic shunt
French Bulldog
Dalmatian
What are some abnormal findings on ultrasonography that would indicate urinary bladder calculi?
Abnormal echogenicity (normal urine is anechoic)
hyperechoic shadow interface
Thickened bladder wall
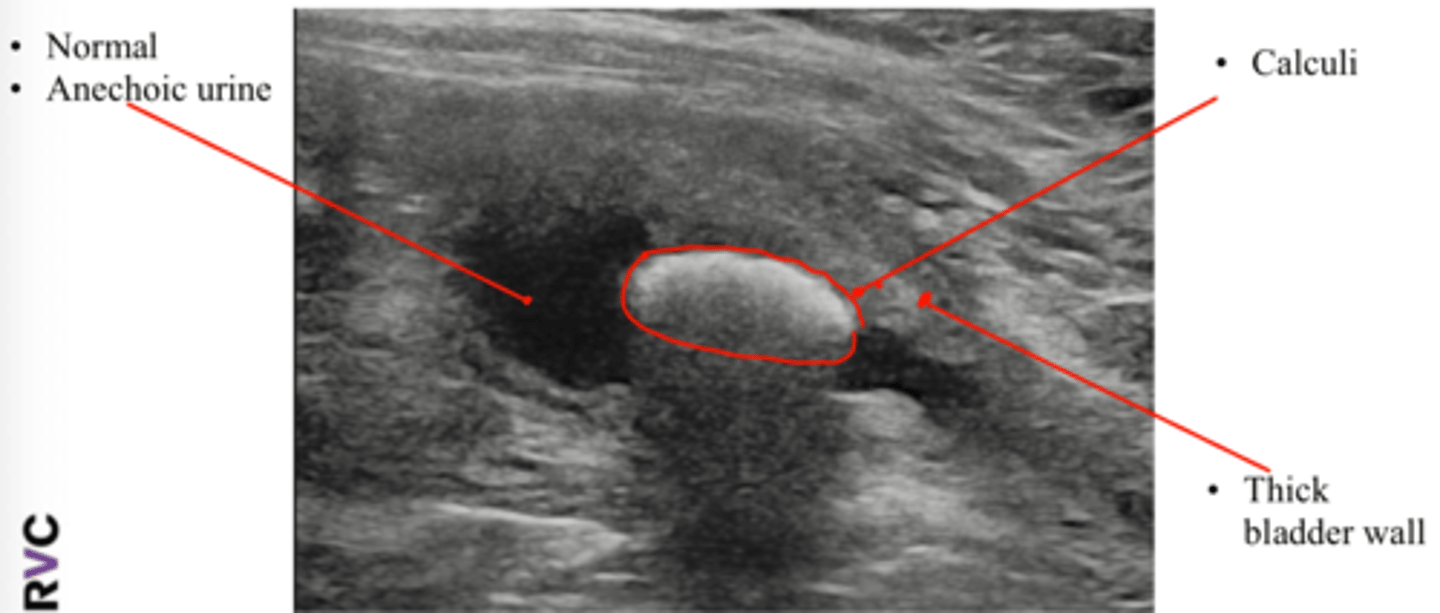
What are some characteristics of blood clots in the urinary bladder on ultrasound?
Heterogenous echogenicity (changes with probe movement)
Mobile
No shadowing
No blood flow on doppler
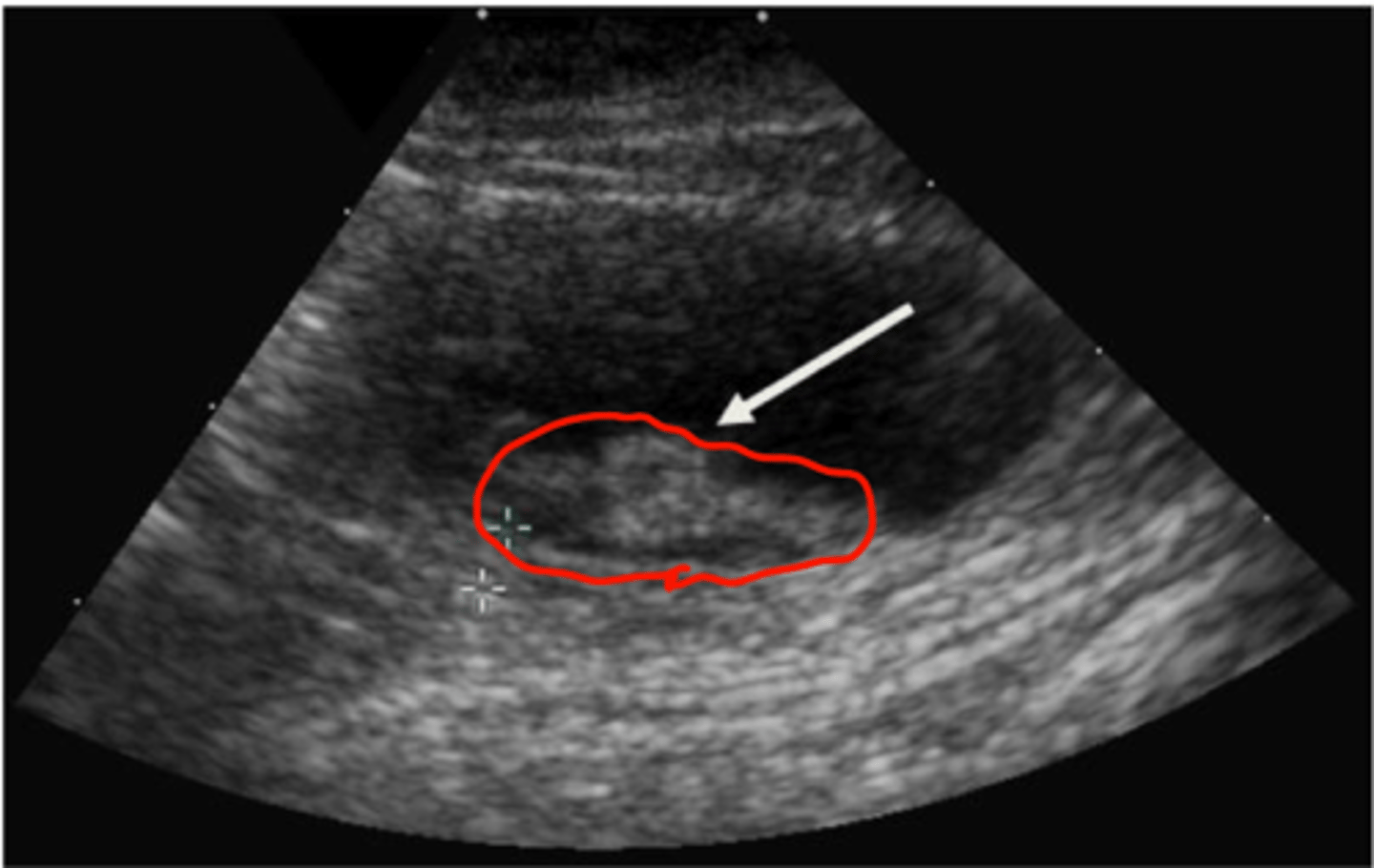
What are some characteristics of bladder neoplasia on ultrasound?
Heterogenous mass
Often located at trigone/prostate/urethra in dogs
May be at trigone or other bladder regions in cats
Important to check medial iliac lymph nodes
Check ventral aspect of lumbar vertebra on radiograph for metastasis to bone
transitional cell carcinoma is most common