Holism vs Reductionism
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Holism
‘holos’ - means ‘all’ in Greek
the idea that human behaviour should be viewed as a whole integrated experience, not as separate parts
Reductionism
the belief that human behaviour can be explained by breaking it down into simpler component parts.
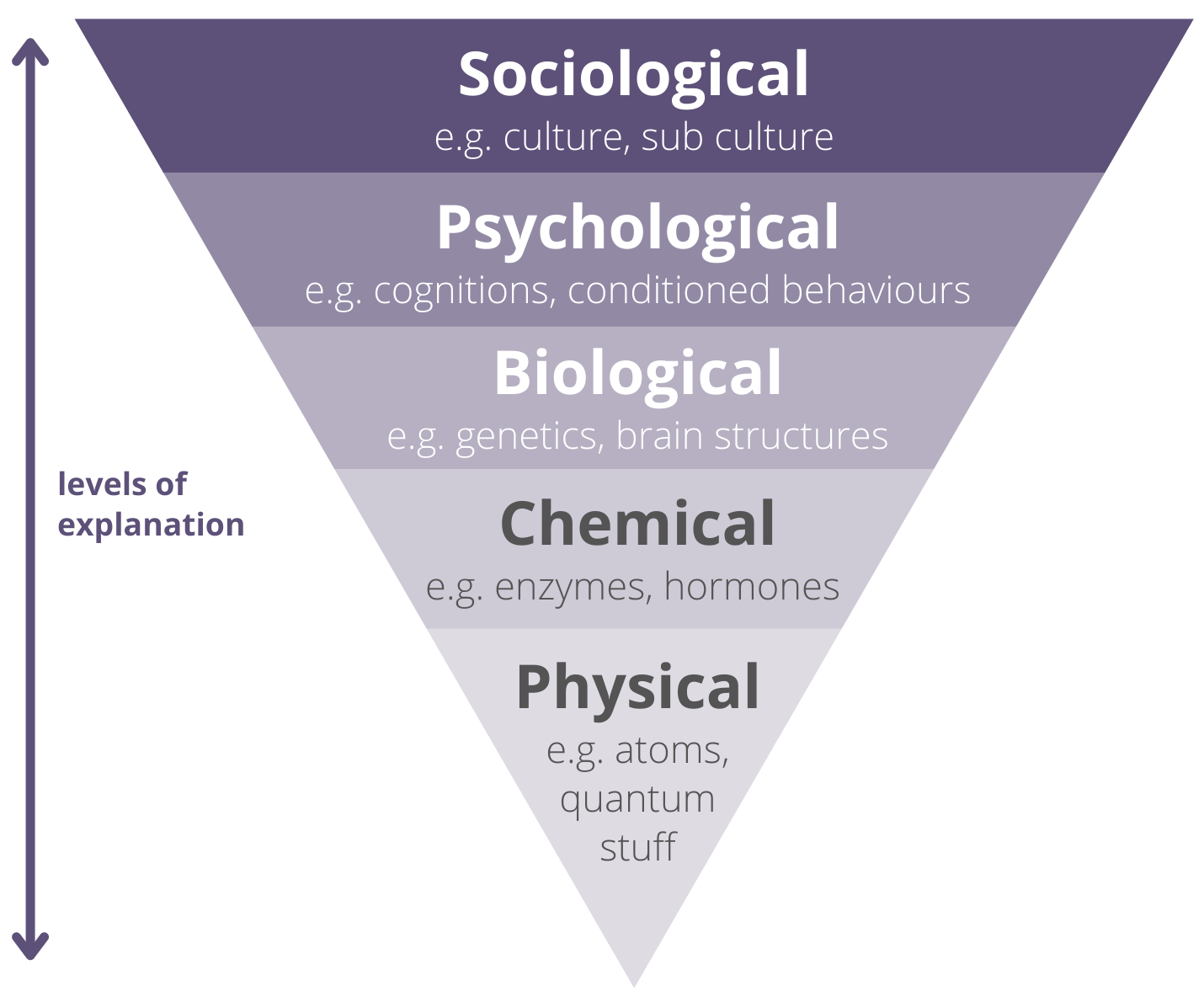
Levels of explanation using OCD as an example
different ways to explain behaviour
socio-cultural level - OCD interrupts social relationships
psychological level - the person’s experience of anxiety
physical level - movements, e.g. washing ones hands
environmental/behavioural level - learning experiences
physiological level - abnormal functioning in the frontal lobes
neurochemical level - underproduction of serotonin
increase in reductionism moving upwards

Biological reductionism
behaviour is reduced to a physical level and explained in terms of neurons, neurotransmitters, hormones, brain structure etc
Environmental reductionism
aka stimulus-response reductionism
behaviour can be reduced to the simple building blocks of stimulus response associations
Gestalt Psychology
when we perceive something in the real world, we do so as a whole rather than as a collection of bits and pieces (holistic)
Social and cultural explanations
the influence of social groups on behaviour
Psychological explanations
cognitive/behavioural/environmental
Example of social and cultural explanations in memory research
can be explained at a social and cultural level, as research suggests that cultural expectations affect what we remember and how we recall information (Bartlett, 1932 - schema theory)
Example of psychological explanations in memory research
e.g. cognitive psychologists examine certain aspects of memory. E.g., Miller (1956) examined the capacity of STM and Peterson and Peterson (1959) examined duration of STM
Example of biological explanations in memory research
e.g. Maguire et al. (2000) found an association between size of hippocampus and memory for spatial navigation
Example of biological reductionism in psychopathology research
biological approach claims OCD is caused by higher levels of dopamine and lower levels of serotonin
Example of environmental reductionism in psychopathology research
behaviourist approach claims phobias are initiated through classical conditioning and maintained through operant conditioning
Humanistic psychology
argues that humans react to stimuli as a whole, rather than a set of stimulus-response links. Uses qualitative methods to investigate all aspects of the individual, as well as the interactions between people (holism)¬a!q
Psychology as a science
STRENGTH
P: Scientists are drawn to reductionist explanations
E: E.g., most experimental psychology is based on the assumption that human behaviour can be studied effectively in relatively simple experiments, where complex behaviour is reduced to isolated variables (known as experimental reductionism)
C: This allows researchers to study the different factors that influence behaviour in a controlled manner while establishing causal relationships. Consequently, both biological and environmental reductionism are viewed as scientific approaches, whereas holism is not
Reductionism is limited
LIMITATION
P: Some psychologists argue that biological reductionism can lead to errors of understanding because it ignores the complexity of human behaviour
E: E.g., to treat conditions like ADHD with drugs in the belief that the condition consists of nothing more than neurochemical imbalances is to mistake the symptoms of the phenomenon for its true cause. Ritalin may reduce these symptoms, but the conditions which gave rise to the ADHD have not been addressed
C: Furthermore, since success rates of drug therapies are highly variable, the purely biological understanding seems inadequate and therefore explanations which consider multiple factors are more suitable
Approaches linked to reductionism
Biological - biological reductionism
behaviour is broken down into biological processes
Behaviourist - environmental reductionism
behaviour is broken down into simple stimulus-response associations
Social learning theory - partially reductionist
shares elements of both behaviourist and cognitive approach
Cognitive - experimental reductionism
behaviour is investigated in terms of isolated variables (e.g. STM capacity)
Psychodynamic
behaviour is reduced to innate drives
Approaches linked to holism
Psychodynamic
takes multiple aspects of human behaviour into account
Humanist
focuses on understanding all aspects of human experience and interaction
Holistic group insight
STRENGTH
P: An advantage of holism is that often, there are aspects of social behaviour that only emerge within a group context and cannot be understood at the level of the individual group members
E: For instance, the effects of conformity to social roles and the de-individuation of the prisoners and guards in the Stanford Prison Experiment could not be understood by studying the participants as individuals. It was the interaction between people and the behaviour of the group that was important
C: This shows that holistic/same level explanations provide a more complete and global understanding of behaviour than reductionist approaches
Effective combined approach
STRENGTH
P: Another alternative to reductionism, which is subtly different to holism, is the interactionist stance
E: Whereas holism is more concerned with higher level explanations of behaviour, such as the behaviour of individuals within a group,, interactionism considers how different levels of explanation may combine and interact. An example of this approach is the diathesis-stress model which has been used to explain the onset of mental disorders such as schizophrenia, depression and OCD. Such disorders are seen to come about as the result of a predisposition which is triggered by some stressor
C: This model has led to amore multidisciplinary and holistic approach to treatment - combining drugs and family therapy, for instance - and is associated with lower relapse rates
Difficulties with drug therapies
LIMITATION
P: Drug therapies are fraught with difficulties
E: Their success rates are variable and they treat the symptoms not the causes, and thus may not have lasting effects
C: Therefore, reducing mental illness to the biological level (i.e. biological reductionism) ignores the context and function of such behaviour. Psychological explanations take more account of these and have produced many successful therapies
Hierarchy of sciences
most reductionist at the bottom