final review (blood vessels)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
How is blood flow in capillaries regulated?
By precapillary sphincters, local chemical conditions (O₂, CO₂, pH), and sympathetic nerve fibers.
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect blood pressure?
Increases HR, SV, and vasoconstriction → ↑ BP.
How does the parasympathetic nervous system affect blood pressure?
Decreases HR and promotes vasodilation → ↓ BP.
What is the role of epinephrine/norepinephrine?
Increase HR, SV, and vasoconstriction → ↑ BP.
What is the role of angiotensin II?
Potent vasoconstrictor; stimulates aldosterone & ADH → ↑ BP.
What is the role of ADH?
Conserves water, vasoconstricts → ↑ BP.
What is the role of ANP?
Promotes water/salt loss, vasodilation → ↓ BP.
Name the three tunics of an artery.
Tunica intima, tunica media (thickest), tunica externa.
How do veins differ structurally from arteries?
Thinner tunica media, thicker tunica externa, valves in tunica intima, act as blood reservoirs.
Define hydrostatic pressure (HPc).
Blood pressure inside capillary pushing fluid out into interstitial space.
Define osmotic pressure (OPc).
Pressure from plasma proteins (albumin) pulling fluid into capillary
What happens at the arteriole end of a capillary?
HPc > OPc → fluid leaves capillary.
What happens at the venule end of a capillary?
OPc > HPc → fluid enters capillary.
Define blood flow.
Volume of blood per unit time (mL/min).
What factors contribute to peripheral resistance?
Blood viscosity, vessel length, vessel diameter
Formula for Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)?
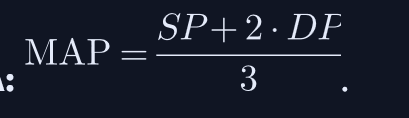
What is atherosclerosis?
Plaque buildup in arterial walls (cholesterol, fats, calcium).
How does it affect blood flow?
Increases resistance, decreases flow, can lead to arteriosclerosis, hypertension, ischemia.
What is hypovolemic shock?
Large-scale blood loss → ↓ volume.
What is vascular shock?
Normal volume, but extreme vasodilation (sepsis, anaphylaxis).
What is cardiogenic shock?
Heart fails to pump effectively.
What is the function of the hepatic portal system?
Shunts nutrient-rich blood from GI tract to liver for filtering before systemic circulation.
How does liver disease affect capillary exchange?
↓ albumin → ↓ OPc → edema.
How does protein deficiency (Kwashiorkor) affect capillary exchange?
Same as liver disease: ↓ OPc → edema.
How does pregnancy affect capillary exchange?
↑ blood volume → ↑ HPc → edema.
How does inflammation affect capillary exchange?
↑ permeability → proteins leak → ↓ OPc → edema.