PGY 206: Exam 3 Cardiovascular System
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
functions of the circulatory system
respiratory, nutritive, excretory, regulation, and protection
respiratory function of the cardiovascular system
to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
nutritive function of the cardiovascular system
to carry absorbed digestion products to the liver and to tissues
excretory function of the cardiovascular system
to carry metabolic wastes to kidneys for excretion
hormonal regulation function of the cardiovascular system
to carry hormones to target tissues to produce their effects
temperature regulation function of the cardiovascular system
to divert blood to cool or warm the body
blood clotting protection function of the cardiovascular system
to prevent blood loss when vessels are damaged
immune protection function of the cardiovascular system
includes leukocytes (WBCs) that protect against disease causing agents
components of the cardiovascular system
blood, heart, and blood vessels
components of the lymphatic system
lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes
plasma
straw-colored liquid consisting of water and dissolved solutes, mostly sodium
plasma proteins
constitute 7-9% of the plasma
albumin
produced in the liver, accounts for 60-80% of plasma proteins and maintains colloid osmotic pressure needed to pull water from interstitial fluid to capillaries, and maintains blood pressure
alpha and beta globulins
plasma proteins that transport lipids and fat soluble vitamins
gamma globulins
plasma proteins that are lymphocytes which are antibodies that function in immunity
fibrinogen
plasma protein that is an important clotting factor, converted to fibrin during the clotting process
erythrocytes
red blood cells that are flattened disks with large surface area to promote diffusion of gasses, lack nuclei and mitochondria so they have a short life (replaced every 3-4 months), contains hemoglobin which contains iron, and heme helps transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues
leukocytes
white blood cells, contain nuclei and mitochondria, granular (help detoxify foreign substances) and agranular (produce antibodies)
platelets
fragments of megakaryocytes, lack nuclei, important for blood clotting by releasing seratonin to vasoconstrict and reduce blood flow to that area
intrinsic blood clotting pathway
exposes subendothelial tissue (collagen) to the blood, exposure to collagen activates plasma protein factors to form fibrin
extrinsic blood clotting pathway
damaged tissue releases through thromboplastin (tissue factor NOT part of the blood) which initiates a short cut to formation of fibrin
blood clotting features
extensive cascade of clotting factor mostly produced by the liver, and common to both pathways is the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin by thrombin
pulmonary circulation
path of blood from the right ventricle through the lungs and back to the heart
systemic circulation
path of oxygen-rich blood pumped to all organ systems to supply nutrients
cardiac muscle
striations, muscle fibers, intercalated disks, contains nucleus (similar to skeletal muscle but contains intercalated disks)
cardiac muscle cells
made up of sarcomeres which contain actin and myosin, contracts via sliding-filament mechanism, these are activated by calcium transients, joined by gap junctions (electrical synapses), APs occur spontaneously, cells behave as one unit
myocardial action potential
the depolarization comes from the gap junction, then rapid upshoot occurs (voltage-gated Na+ channels open causing inward diffusion of Na+), plateau phase (membrane potential stayed depolarized but voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open causing inward flow of Ca2+), rapid repolarization (voltage-gated K+ channels open slowly causing rapid outward diffusion of K+ to repolarize cells)
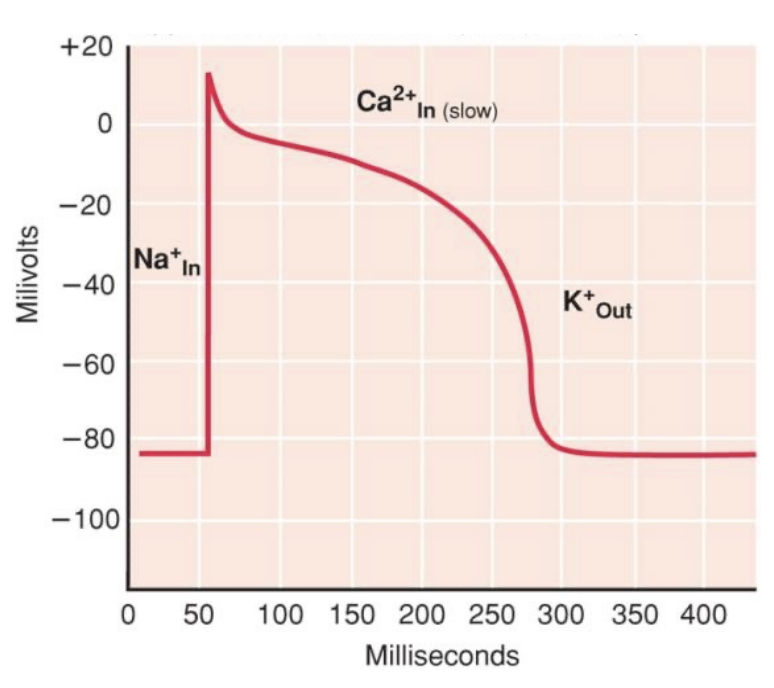
excitation-contraction coupling in the heart muscle
APs of myocardial cells stimulates opening of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in sarcolemma, Ca2+ diffuses into cell stimulating the opening of Ca2+ release channels in sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) by a Ca2+ induced Ca2+ release mechanism, Ca2+ binds to troponin and stimulates contraction
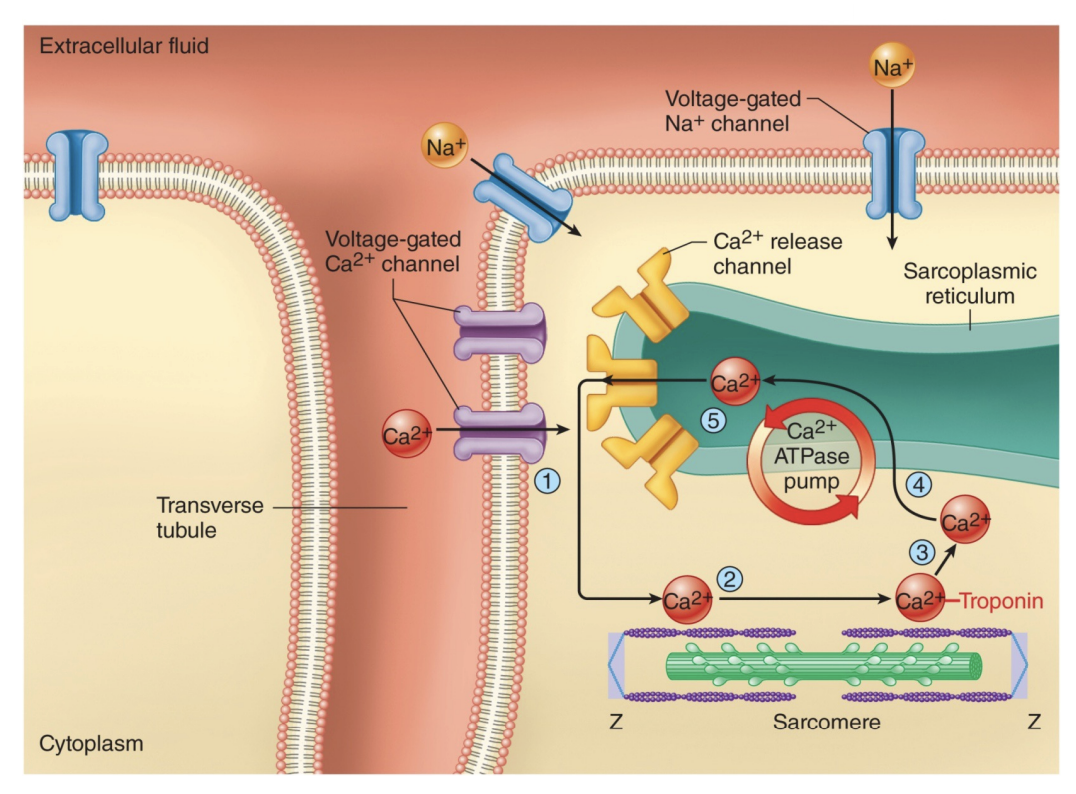
characteristics of myocardial APs
refractory periods last almost as long as contraction does, voltage-gated Na+ must “reset” at repolarized potentials before they can open again, not tetanus (due to long refractory period allowing heart muscle to relax)
heart pumping sequence
Cardiac depolarization begins in SA node in the right atria, this depolarization spreads to other (left) atria, and then it passes to the ventricle septum to the bottom of the heart and along the walls of the ventricle, then atria contract and push blood in to the ventricle, ventricles contract and push blood up and out large arteries
electrocardiogram (ECG)
measures the electrical activity of the heart per unit time, does not measure flow of blood
P wave of ECG
atrial depolarization
QRS complex of ECG
ventricular depolarization, atrial repolarization
T wave of ECG
ventricular repolarization
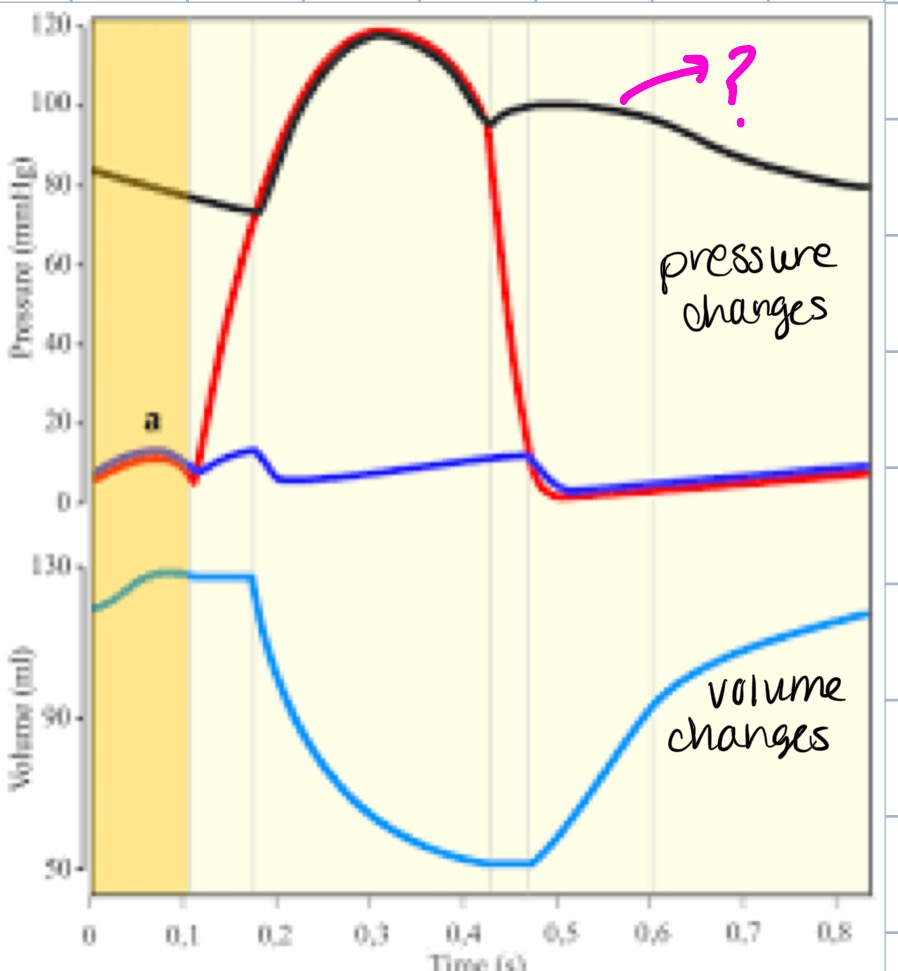
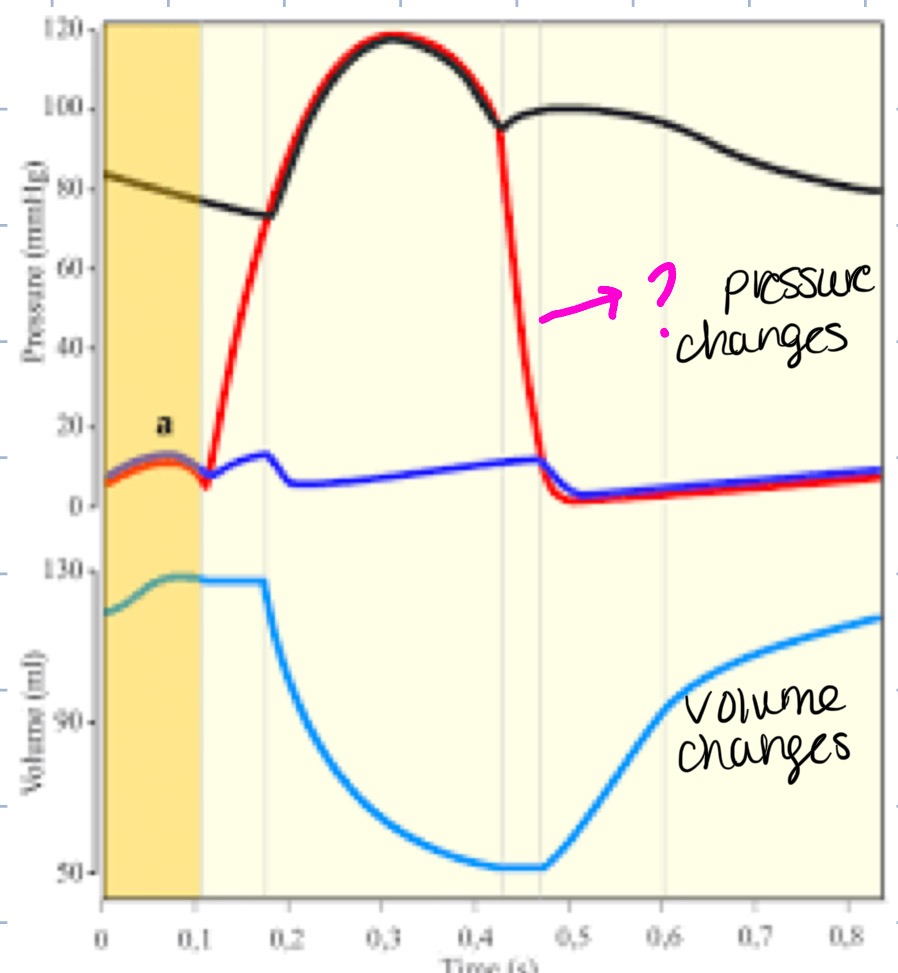
cardiac cycle
refers to the repeating pattern of contraction and relaxation of the heart
systole
phase of contraction
diastole
phase of relaxation
end-diastolic volume (EDV)
total volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole
stroke volume (SV)
amount of blood ejected from the ventricles during systole, also calculated by EDV-ESV
end-systolic volume (ESV)
amount of blood left in ventricles at the end of systole
lub
first sound produced by the closing of the AV valves during isovolumetric contraction
dub
second sound produced by the closing of the semilunar valves when pressure in ventricles falls below the pressure in the arteries
atrial systole
step 1 of cardiac cycle, atrial contraction occurs and pushes 10-30% more blood into the ventricle
isovolumetric contraction
step 2 of cardiac cycle, contraction of the ventricle causes ventricular pressure to rise above atrial pressure, AV valves close, then ventricular pressure is less than aortic pressure, semilunar valves are closed, volume of blood in ventricle is EDV
ejection
step 3 of cardiac cycle, contraction of the ventricle causes ventricular pressure to rise aortic pressure (approx. 80 mmHg), semilunar valves open, then ventricular pressure is greater than atrial pressure, AV valves are closed and the volume of blood ejected is SV
isovolumetric relaxation
step 4 of cardiac cycle, ventricular pressure drops below aortic pressure and back pressure causes semilunar valves to close, AV valves are still closed, volume of blood in the ventricle is ESV
rapid filling of ventricles
step 5 of cardiac cycle, ventricular pressure decreases below atrial pressure, AV valves open, rapid ventricular filling occurs
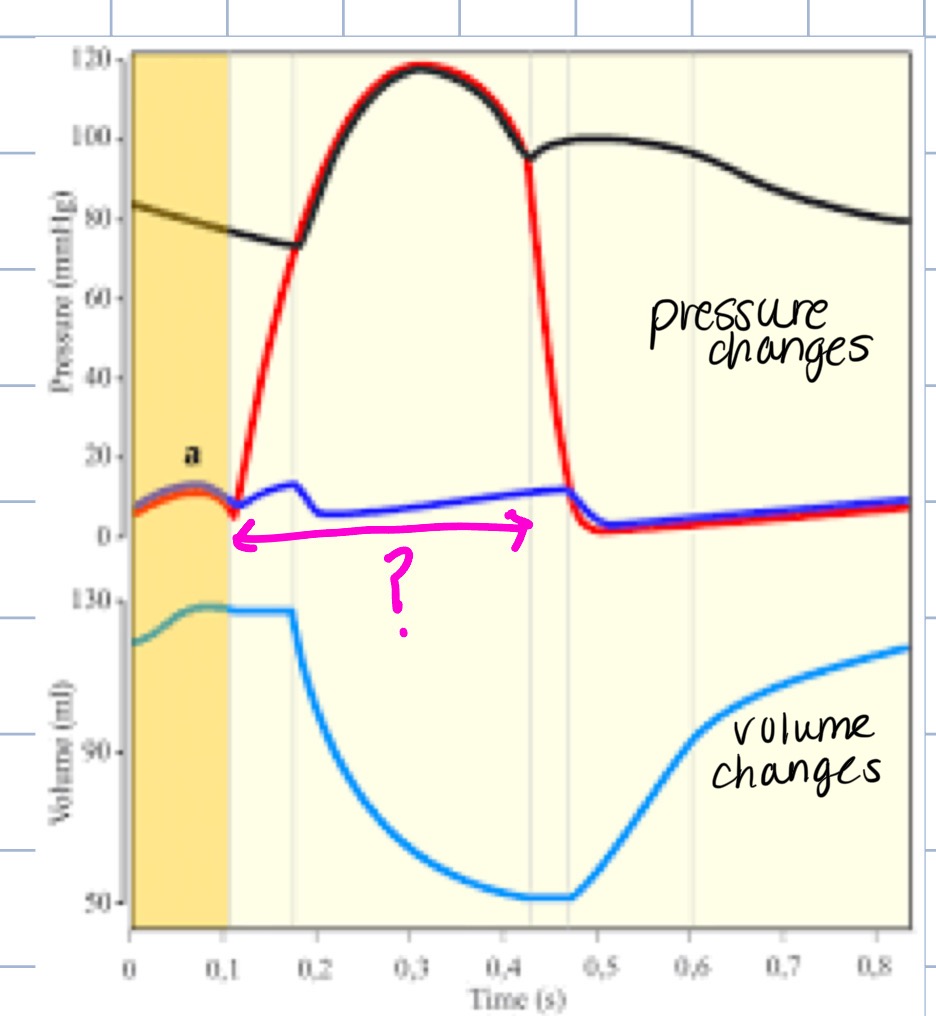
what phase of the cardiac cycle does this represent
systole
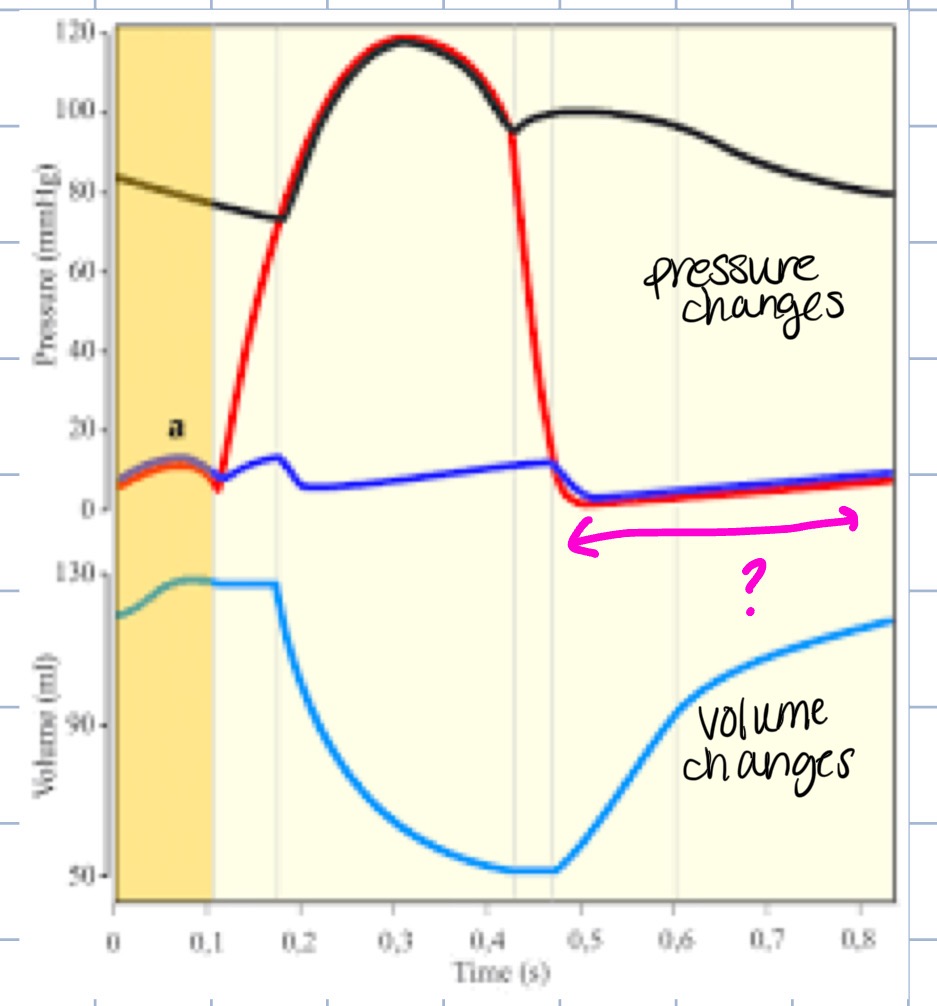
what phase of the cardiac cycle does this represent
diastole
what part of the heart does this represent
artery
what part of the heart does this represent
left ventricle
types of blood vessels
arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins
tunica externa
outer layer of connective tissue of arteries and veins
tunica media
middle layer of smooth muscle of arteries and veins
tunica interna
innermost simple endothelial cell layer of arteries and veins
elastic arteries
numerous layers of elastin fibers between smooth muscle, they expand when the pressure of the blood rises acting as a recoil system when ventricles relax
muscular arteries
are less elastic and have a thicker layer of smooth muscle, diameter changes as BP rises and falls
arterioles
contain highest % of smooth muscle, greatest pressure drop and greatest resistance to flow
capillaries
smallest blood vessels, only 1 endothelial cell thick, these provide direct access to cells permitting the exchange of nutrients and wastes
continuous exchange in capillaries
adjacent endothelial cells tightly joined together, contain intercellular channels that permit passage of molecules (not proteins) between capillary blood and tissue fluid, found in muscles, lungs and adipose tissue
fenestrated exchange of capillaries
wide intercellular pores, provides greater permeability, found in kidneys, endocrine glands, and intestines
discontinuous (sinusoidal) exhange of capillaries
large, leaky capillaries found in liver, spleen and bone marrow
capillary hydrostatic pressure
blood pressure exerted against the inner capillary wall, promotes movement of fluid into tissues (filtration)
colloid osmotic pressure
blood pressure exerted by plasma proteins, promotes reabsorption into circulatory system (capillaries)
net blood pressure
hydrostatic pressure (Pcap) - colloid osmotic pressure (π)
venules
formed when capillaries unite
veins
contain little smooth muscle or elastin, capacitance vessels (blood reservoirs), contain 1-way valves that ensure blood flow to the heart
arrythmia
abnormal heart rhythyms
bradycardia
heart rate slower than 60 beats per minute
tachycardia
heart rate faster than 100 beats per minute
flutter
extremely rapid rates of excitation and contraction of atria or ventricles, can lead to fibrillation
fibrillation
contractions of different groups of myocardial cells at different times, makes coordination of pumping impossible, ventricular fibrillation is life-threatening (atrial is not)
atrial fibrillation
most common type of irregular heartbeat (no P wave on ECG), occurs when abnormal firing of electrical impulses cause atria to quiver/fibrillate, treated by cardioversion, ablation, blood thinners, anti-arrhythmic medications
murmurs
produced as blood regurgitates through valve flaps due to damaged or defective valves, can be caused by: damaged valves from antibodies made in response to infection or congenital defects, mitral (bicuspid) valve becomes thickened and calcified, damage to papillary muscles, or valves do not close properly
septal defects
typically congenital, holes form in the septum between the left and right sides of heart, may occur in interatrial or interventricular septum, causes blood to pass from left to right during contraction
atherosclerosis
most common form of ateriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), happens in 50% of US population, plaque builds up in small arterioles increasing resistance to blood flow, occurs from hypertension, smoking, high cholesterol, and diabetes which damage endothelial cell wall
process of atherosclerosis
monocytes become macrophages and engulf lipids to transform into foam cells, smooth muscle cells synthesize connective tissue proteins where smooth muscle cells migrate to tunica interna and proliferate forming fibrous plaques.
lipoproteins
carry lipids in the blood
Low-Density Lipoproteins (LDLs)
produced in the liver, carry cholesterol to the arteries, high in peopel who eat a diet rich in saturated fats
High-Density Lipoproteins (HDLs)
carry cholesterol away from the arterial wall, protect against atherosclerosis, low in sedentary people, can be increased by drugs like statins fibrates, or niacin
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft surgery
treats blocked heart arteries by creating new passages for blood to flow to your heart muscle. It works by taking arteries or veins from other parts of your body (grafts) and using them to reroute blood around the clogged artery
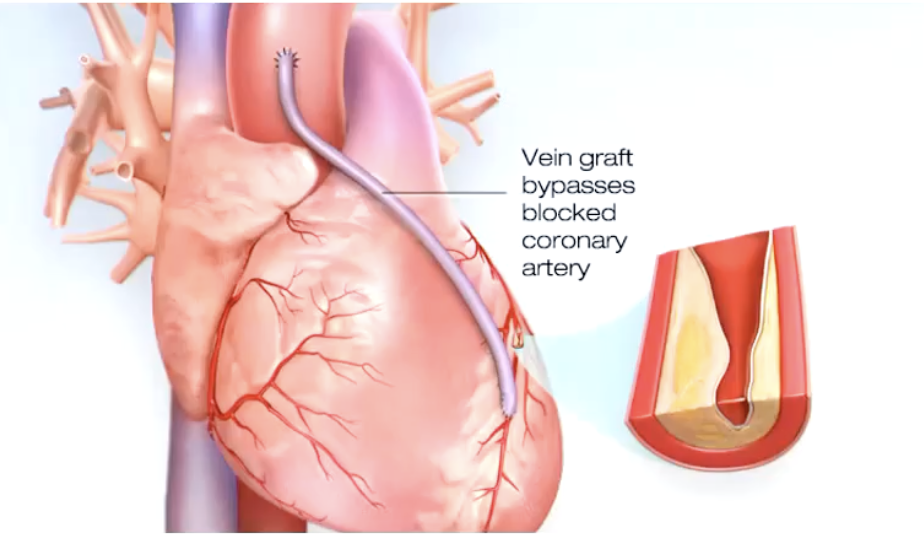
Ischemia
oxygen supply to tissue is deficient, most common cause is atherosclerosis of coronary arteries
angina pectories
substernal pain
myocardial infarction
changes in ST segment of ECG, can be tested by increased blood levels of creatine phosphokinase (CPK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and troponins (T and I).
ischemic heart disease or MI symptoms
chest discomfort, pain and discomfort in other areas (one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach, shortness of breath, other signs may be breaking out in a cold sweat, nausea, or lightheadedness. More common in women
ischemic heart disease or MI symptoms more common in women
pain and discomfort in back, neck, or jaw, shortness of breath, and nausea
hypertension (HTN)
(130/80 mm Hg) blood pressure in excess of normal range for age and gender
primary/essential hypertension
result of a complex or poorly understood process (most common)
secondary hypertension
result of a known disease process
dangers of hypertension
patients are asymptomatic until damage occurs, increases workload of the heart, congestive heart failure, damaged cerebreal blood vessels (can cause stroke)
treatments of hypertension
modification of lifestyle (stop smoking and alcohol intake, weight reduction, reduced Na+ intake, more K+ intake), medications (diuretics, beta blockers, calcium antagonists, ACE inhibitors, Angiotensin II-receptor antagonists)
heart failure
cardiac output is insufficient to maintain blood flow required by body (to meet metabolic demand), increased venous volume and pressure
causes of heart failure
myocardial infarction, congenital defects, hypertension, aortic (semilunar) value stenosis, disturbances in electrolyte concentrations (K+ and Ca2+)
treatment for heart failure
vasodilators and diuretics
mean arteriole pressure (MAP)
represents the average arterial pressure during the cardiac cycle (closer to diastolic pressure as the period of diastole is longer than systole), depends on how much blood is being pumped by the heart (cardiac output) and diameter of the arterioles
equation for mean arterial pressure
mean arterial pressure = cardiac output x total peripheral resistance
auscultation (art of listening)
indirect method of correlating blood pressure and arterial sounds
laminar flow
normal blood flow, blood in the central axial stream moves faster than blood flowing closer to the artery wall, smooth and silent
turbulent flow
vibrations produced in the artery when cuff pressure is greater than diastolic pressure and lower than systolic pressure
measurement of MAP
blood pressure cuff is inflated above systolic pressure, occluding the artery. As cuff pressure is lowered, the blood will flow only when systolic pressure is above cuff pressure, producing the sounds of Korotkoff. Korotkoff sounds will be heard until cuff pressure equals diastolic pressure, causing the sounds to disappear