Interventions for Cognitive and Perceptual Deficits
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
Cognition
Mental actions of knowing, thinking, learning, judging, and processing information
6 Areas of Cognition
1. Memory
2. Orientation
3. Perseveration
4. Executive functions
5. Attention
6. Alertness
Perception
Interpretation or reasoning of stimuli
True or False: If a client has an impairment in one area of cognition then their overall cognition will be impaired.
True
What are cognitive-perceptual impairments an important predictor of?
Recovery outcomes and prognosis
3 Treatment Approaches for Cognitive-Perceptual Impairments
1. Functional approach
2. Adaptation of the environment
3. Remedial approach
Functional Approach
Use of repetitive practice during functional activities; compensatory; skills may not generalize to other activities
What type of clients would benefit from use of the functional approach for cognitive-perceptual impairments?
Clients with poor learning potential and awareness
Adaptation of the Environment
changing aspects of the of the task or environment when compensation is not possible; used with clients who have poor learning potential
Remedial Approach
Restoration of a function or skill; used acute stages, short-term benefits in later stages
3 Questions to Consider When Selecting a Treatment Approach
1. Does the patient have the potential to learn?
2. Is the patient aware of errors during task performance?
3. (If yes) Does the patient have the potential to seek solutions?
2 Types of Assessments
1. Paper tests
2. Performance-based tests
Paper Tests
- Contrived, not the real world
- Non-functional
- Low ecological validity
Example of Paper Test
Trail making task
Performance based tests
Will provide client with some tangible information about self
Are neurobehavioral deficits better assessed with paper or performance-based tests?
Performance-based test
Which type of assessment is preferred; paper or performance-based tests?
Performance-based test (preferred)
Assessment Considerations
- Environment (e.g. quiet room, free of distractions)
- Rapport with the client to optimize performance & motivate client
Low-Level Cognitive Skills
Memory
Initiation of activity
Arousal
Simple command following (1-2 step commands)
Orientation
Attention
Recognition
(MIA SOAR)
High-Level Cognitive Skills
Planning
Insight
Multi-step command following (e.g. brush teeth)
Mental flexibility
Problem solving
New learning (e.g. new setting)
Abstraction (abstract thinking)
Generalization of new learning
Safety/judgement (e.g. awareness)
(PIMP NAGS)
Arnadottir OT-ADL Neurobehavioral Evaluation (A-ONE)
Lowenstein OT Cognitive Assessment (LOTCA)
Multiple Errands Test (MET)
Executive Function Performance Test (EFPT)
Kettle Test
What are these assessments used for?
cognitive assessments
Arnadottir OT-ADL Neurobehavioral Evaluation (A-ONE Assessment)
Occupation-based tool to assess impact of neurological impairment on activities of daily living
Is the A-ONE assessment an example of a paper or performance-based test?
Performance based-test
What is the A-ONE assessment used to indicate?
Level of assistance needed
What 3 factors does the A-ONE assessment consider?
1. Sensory stimuli
2. Central nervous system processes
3. Behavior responses in analysis of neurobehavior
What does the A-ONE assessment require before administration?
Training (5-day course)
Lowenstein Occupational Therapy Cognitive Assessment (LOTCA)
Assessment of orientation, awareness, thinking, operations, visual perception, spatial perception, praxis, visuomotor organization, and perception
Is the LOTCA assessment an example of a paper or performance-based test?
Paper test
Is the LOTCA assessment standardized or non-standardized?
Standardized
What population is the LOTCA assessment used with?
Stroke
Dementia
Traumatic brain injury
Central nervous system dysfunction
Intellectual disability
18-69 year-olds
Multiple Errands Test (MET)
Assesses executive function through the use of real-world tasks using specific parameters
Is the MET assessment an example of a paper or performance-based test?
Performance-based test (met)
What 4 tasks are typically observed during the MET assessment?
1. Picking up an envelope
2. Using a telephone
3. Posting a letter
4. Writing down items
What are 2 appropriate settings for the MET assessment to be administered in?
1. Hospital
2. Community
How is the MET assessment completed?
By measuring the number of rule breaks or omission; free
Executive Function Performance Test (EFPT)
Determines which executive functions are impaired, an individual's capacity for functioning independently, and amount of assistance needed to complete tasks
Is the EFPT assessment an example of a paper or performance-based test?
Performance-based test (EFPT)
What 4 tasks are typically observed during the EFPT assessment?
1. Simple cooking
2. Telephone use
3. Medication management
4. Bill payment
How is the client graded in the EFPT assessment?
On the amount of cueing needed to perform tasks
True or False: The EFPT assessment is occupation-based.
True
Does the EFPT assessment focus on low or high-level cognitive skills?
High-level cognitive skills
What is the EFPT assessment used to make recommendations about?
Next level of care
Kettle Test
Performance based tool used to screen for cognitive functional performance through the use of a Kettle
What 5 areas of cognition are assessed in the Kettle Test (LAWCE)?
1. Attention
2. Working memory
3. Cognition
4. Executive functioning
5. Life participation
2 Treatment Considerations
1. Environment
2. Generalization
How can environmental influences affect a client in treatment?
Affects how the client performs an activity
Example of Environmental Influence on Treatment
Cluttered environment can cause disorientation and confusion while an organized environment can reduce distractions and increase attention
What should the occupational therapist analyze prior to treatment?
Activity
Client's strengths and weaknesses
Why should the occupational therapist analyze the activity and the client's strengths and weaknesses?
Provide optimal environment
Generalization
Ability to perform skill or activity in multiple contexts
What are the 2 ways in which a client should practice a skill to increase generalization?
1. Across multiple tasks/contexts (e.g. sit-to-stand)
2. Across multiple environments (e.g. transfers)
What is the purpose of the continuum for transfer of learning?
to promote generalization
Near transfer
1-2 components of the task are changed from the original practiced task
Intermediate transfer
3-6 components are changed from the original practiced task
Far transfer
tasks are conceptually similar but share only one similarity
Very far transfer
tasks are very different
3 Intervention Considerations
1. Activity processing
2. Behavior modification
3. Group therapy
What does the therapist discuss with the client in activity processing?
Purpose of activity
What does the therapist emphasize in the rehabilitation process of activity processing?
Purpose of activity
What does activity processing allow the therapist to assess?
Awareness
What does activity processing allow the client to do?
Engage in treatment
What does activity processing enhance?
Metacognition
Behavior Modification
Use of prompting, shaping, and contingent reinforcement
What can behavior modification improve a clients independence in?
Daily activities
Group Therapy
Clients receive feedback from their peers
What can clients learn from group therapy?
Other's mistakes
What can clients practice in group therapy?
Monitoring their own behavior
What is the most common intervention consideration used for clients with cognitive-perceptual impairments; activity processing, behavior modification, and group therapy?
Group therapy
3 Levels of Awareness for Clients to Efficiently and Effectively Participate
1. Anticipatory (recognize how problem affects performance)
2. Emergent (recognize problem during a task)
3. Intellectual (recognize they have a problem)
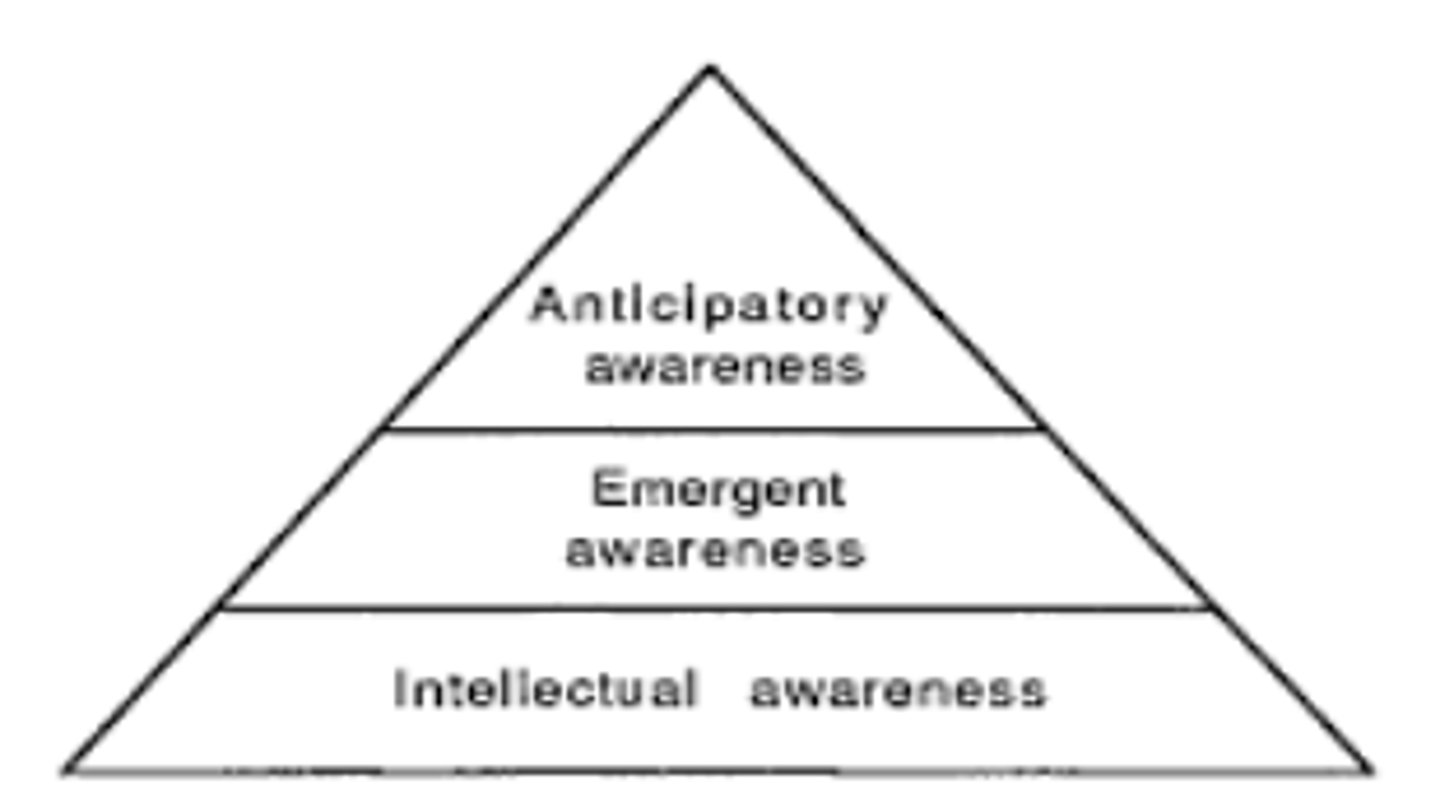
What is the foundational level of awareness for clients to efficiently and effectively participate; intellectual, emergent, or anticipatory?
Intellectual awareness
Interventions for Awareness
- Anticipatory compensation (e.g grocery shopping in am vs pm)
- Recognition compensation
- Situational compensation (e.g. use tape recording for memory)
- External compensation (e.g. alarms)
- Use meaningful activities (apply treatment in a meaningful way)
- Goal focused
Use prompts or cues (e.g. "how do you know this is correct?")
What level of awareness does recognition compensation require; intellectual, emergent, or anticipatory?
Emergent
What type of problem does an inability to distinguish foreground from background indicate?
Figure ground discrimination
Interventions for Figure Ground Discrimination
- Teach awareness of deficit
- Teach organization skills (e.g. simplify environment (declutter)
- Slow down to identify all details of object or stimuli before
- Use contrasts between foreground objects and background
- Task practice
Examples of Task Practice for Figure Ground Discrimination
- Sorting objects (e.g. coins)
- Routine of returning objects to their place
- Maintaining a simple environment
What should clinicians assess before implementing interventions for figure ground discrimination?
Environment
What type of problem does difficulty finding one's way in the environment indicate?
Topographical disorientation
Interventions for Topographical Disorientation
- Mazes simple to complex
- Colored dots to mark the route client has to take
- Practice directional instructions (e.g. turn right at elevator)
- Practice taking the route with a map (occasional glances)
- Draw the path (home setting)
What is the last step to practicing taking a route with a map for topographical disorientation?
Removal of map
When should clinicians take away cues for topographical disorientation?
With mastery
How should clinicians remove cues for topographical disorientation?
Gradually
What type of problem does an inability to detect stimuli indicate?
Agnosia
Does agnosia occur as a result of a defect in one sensory or motor modality?
Sensory
3 Types of Agnosia
1. Finger agnosia
2. Somatoagnosia (body scheme)
3. Tactile agnosia
True or False: There is no specific remediation for agnosia.
True (Agnosia)
Interventions for Agnosia
- Increase awareness
- Compensate by using alternate intact senses
Apraxia
Dysfunction of purposeful movement due to difficulty conceiving and planning the movement
What 3 impairments does apraxia not result from?
1. Motor
2. Sensory
3. Comprehension
Ideational Praxis
Impairment in using everyday objects and tools for their intended purpose
Example of Ideational Praxis
Using comb as toothbrush or putting socks over shoes
What do clients with ideational praxis make significant errors in?
Sequencing common multitask activities
What 2 conditions does ideational praxis rarely occur without?
1. Aphasia
2. Dementia
What does ideational praxis occur as a result of damage to?
1. Prefrontal and premotor cortex in either hemisphere
2. Left inferior parietal lobe
3. Corpus callosum
How are clients with ideational praxis evaluated?
By giving the client everyday objects and asking them to use them
Ideomotor Praxis
Inability to 'motor plan' the task even though the client understands what they wish to do
How can a clients movements with ideomotor praxis be described?
Clumsy and awkward
Example of Ideomotor Praxis
Does not know how to put on shirt but understands how it fits
How are clients with ideomotor praxis evaluated?
By requesting the client to ‘show you how they would’ or ‘pantomime’ an action without the affordances of the actual objects (e.g. “pretend to comb your hair”)
2 Interventions for Apraxia
1. Strategy training
2. Errorless completion and training of details
Strategy Training
Teaching a variety of compensatory strategies to combat impairment and improve activity performance