P2.4 - Approach to Arthritis Degenerative Disorders
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Degenerative
ID type of arthritis
Inflammatory
ID type of arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Inflammation of the bone and joint
Rheumatoid arthritis with secondary osteoarthritis (aka inflammatory arthritis with secondary degeneration)
The radiographic features here are consistent with which process?
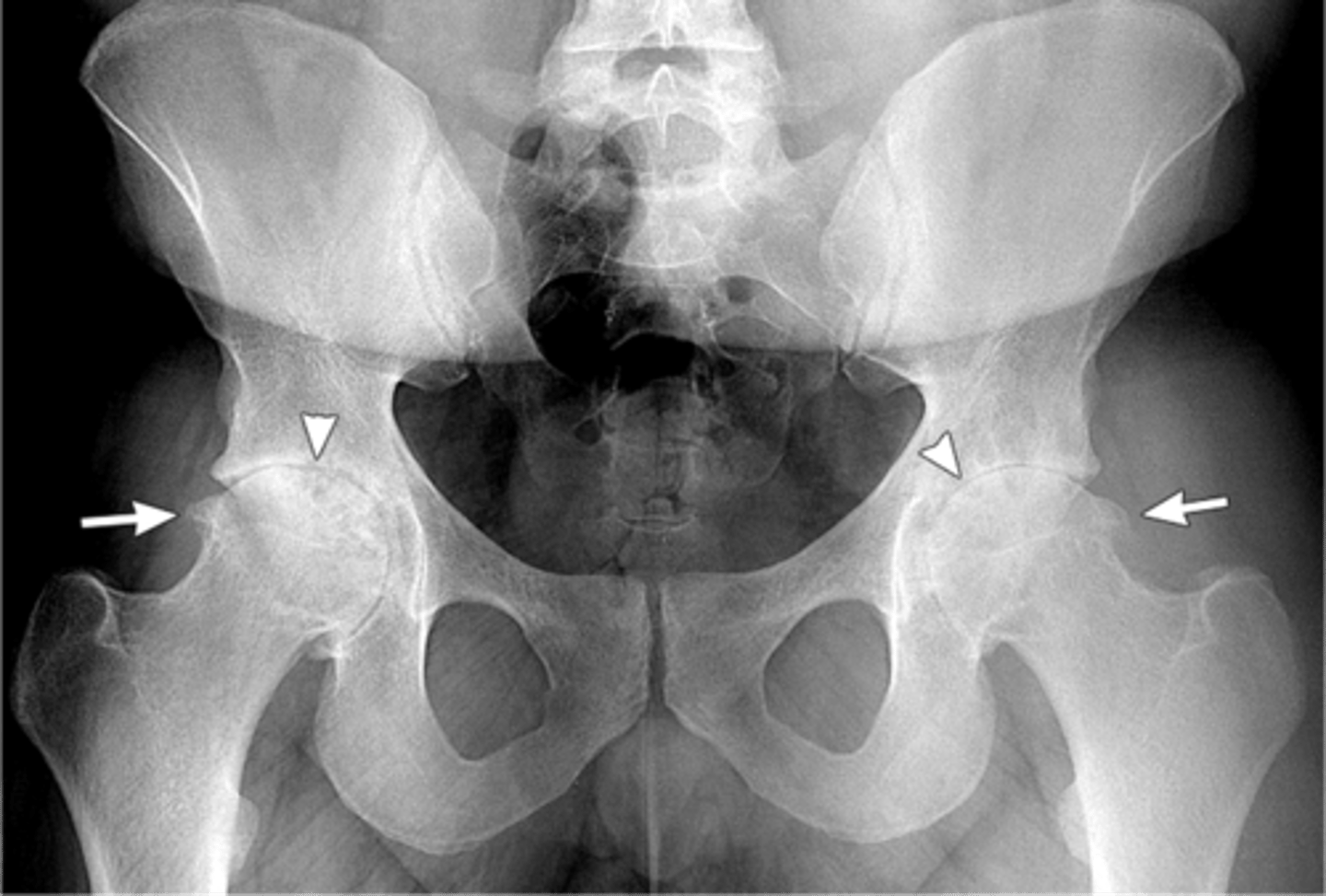
Arthritis
_____ is the foremost crippler in the USA
Articular disease
- Costs >$14 billion annually (CDC - 128 billion for AORC)
- Affects 1/7 people
X-ray
_____ evaluation is usually the first and most extensively used method of evaluation for articular disease
Fibrous
_____ joints:
- Cranial sutures
- Syndesmoses (tibia-fibula, radius-ulna)
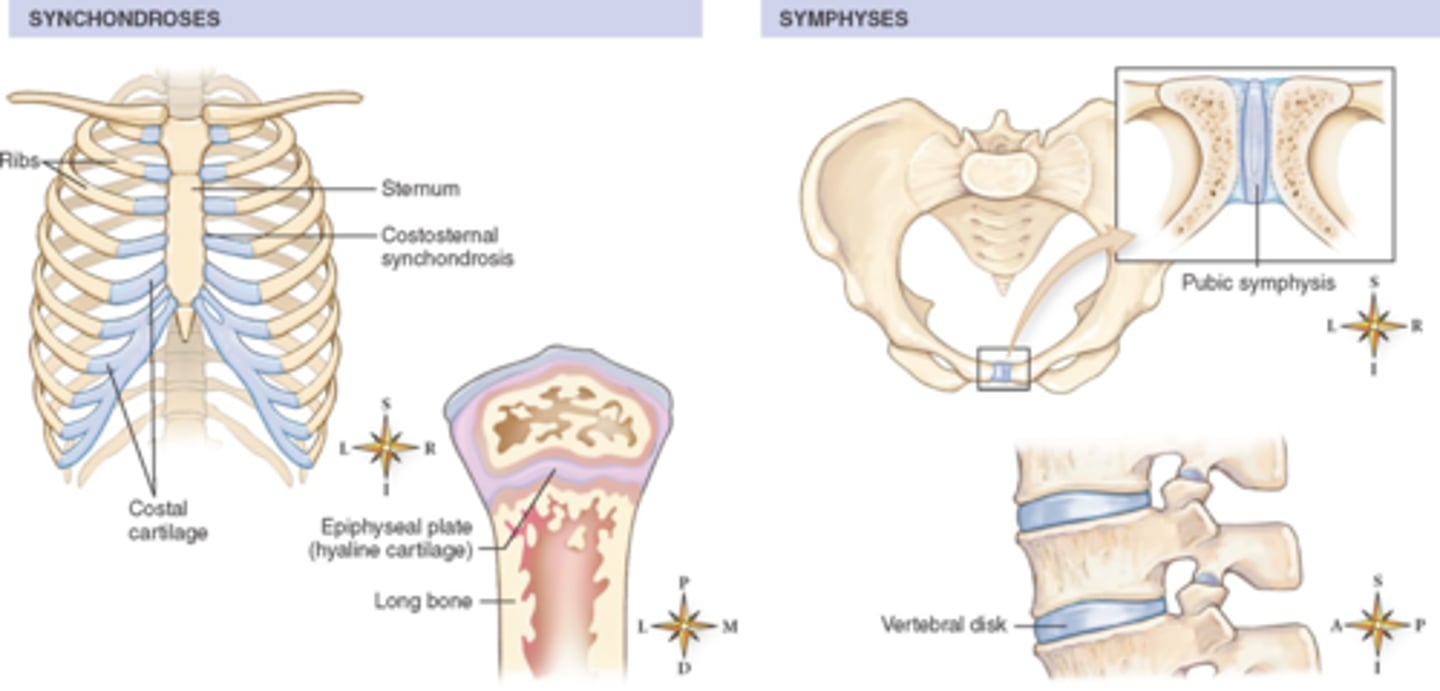
Cartilaginous
_____ joints:
- Symphysis pubis
- Intervertebral discs
- Manubriosternal joint

Synovial
_____ joints:
- Facet joints
- SI joints
- Hips
- Knees
- Shoulders
- Fingers
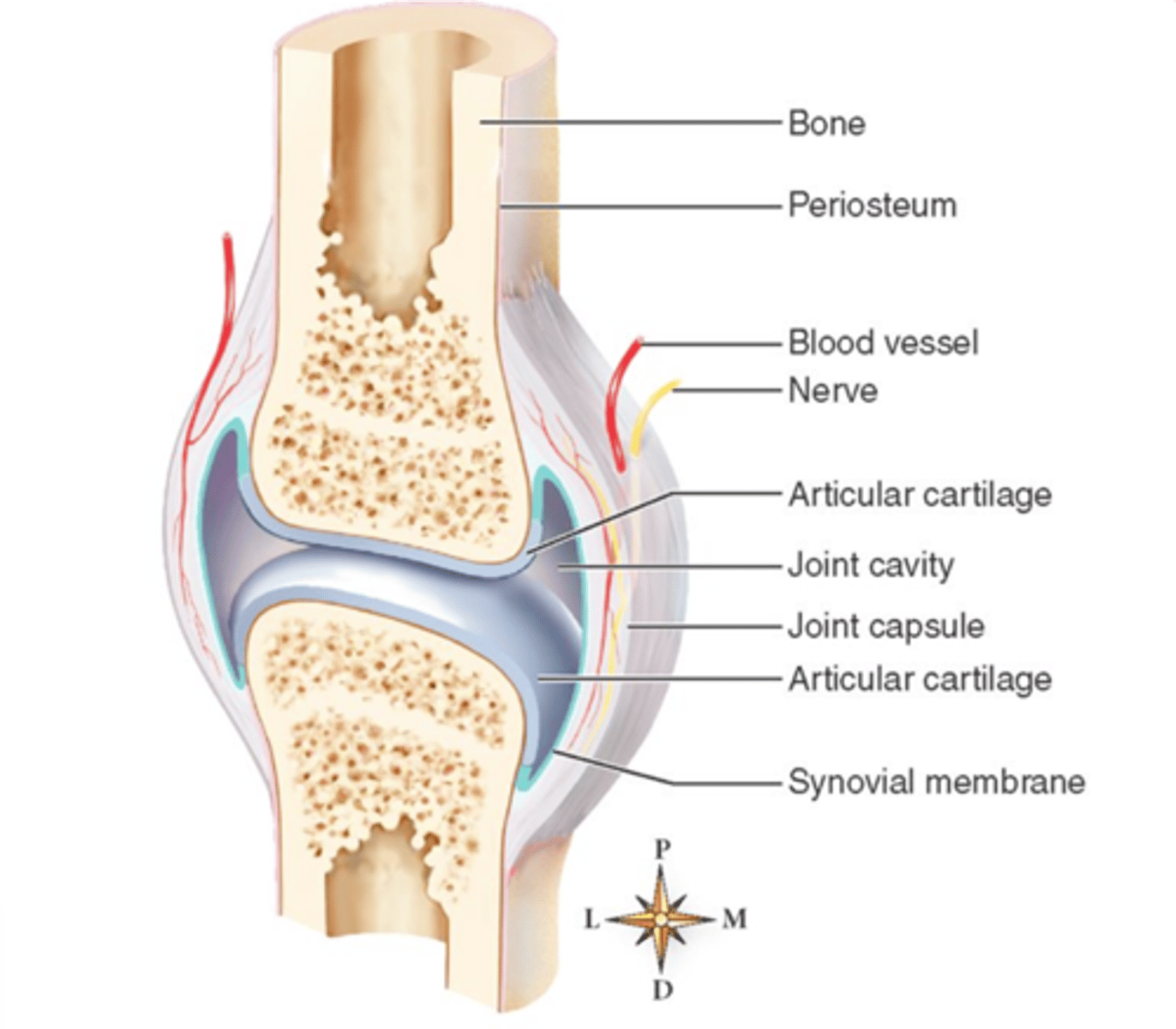
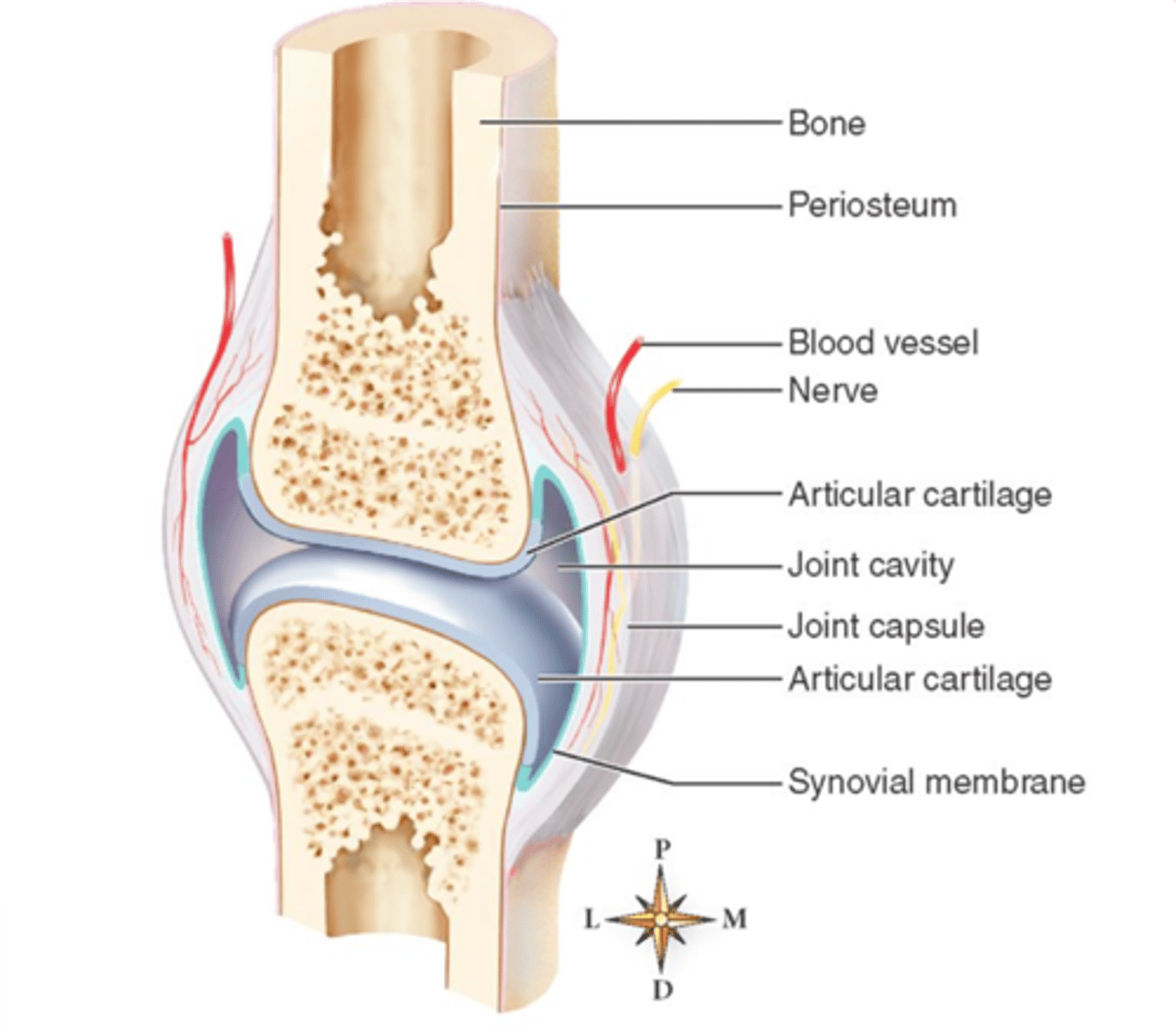
Intracapsular
With synovial joints, there is no periosteum found around the _____ cortices
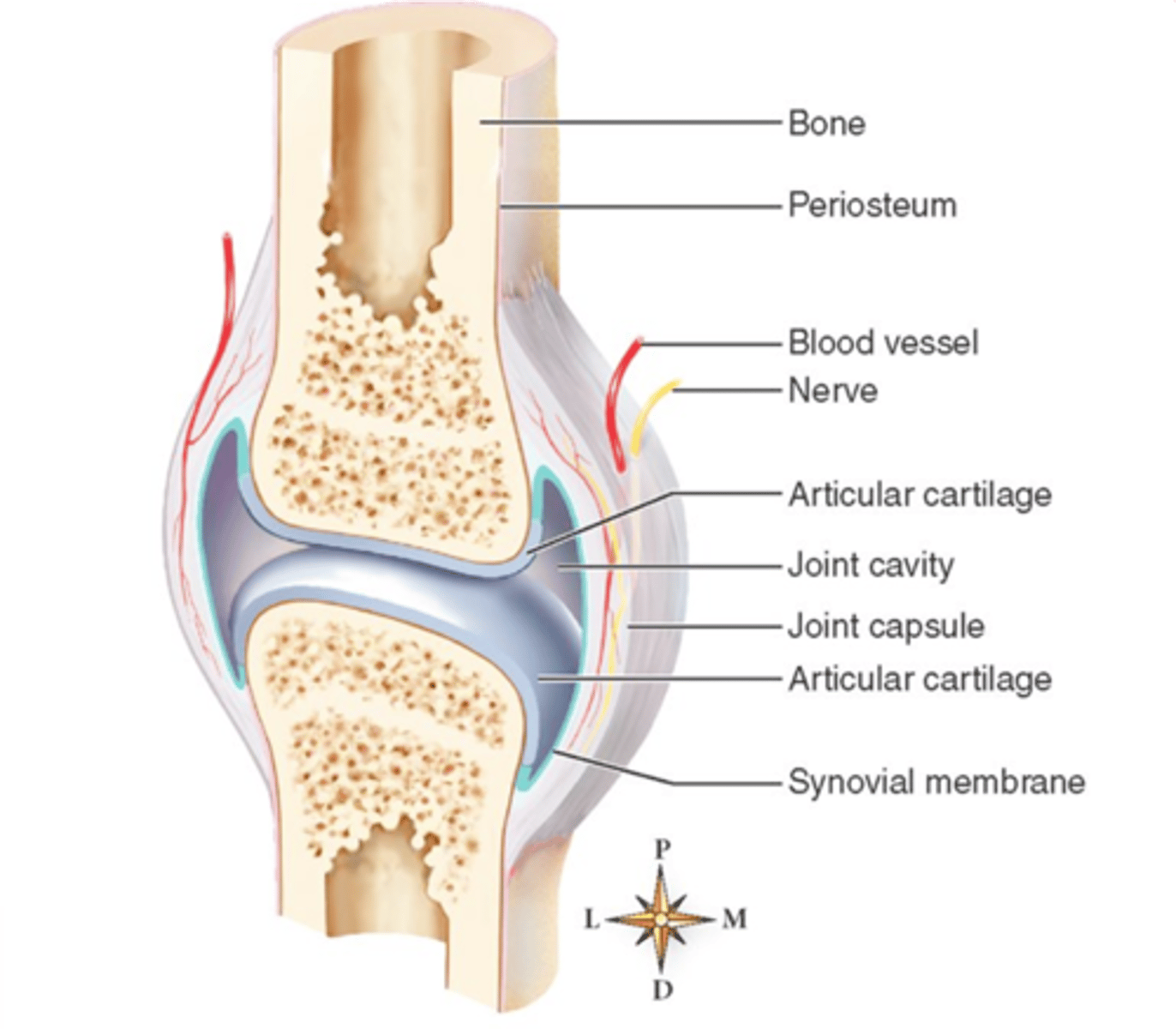
Periosteal response
Because there is no periosteum found in the intracapsular cortices of synovial joints, there is a lack of _____ in this area
Uniform
_____ loss of joint space (inflammatory)
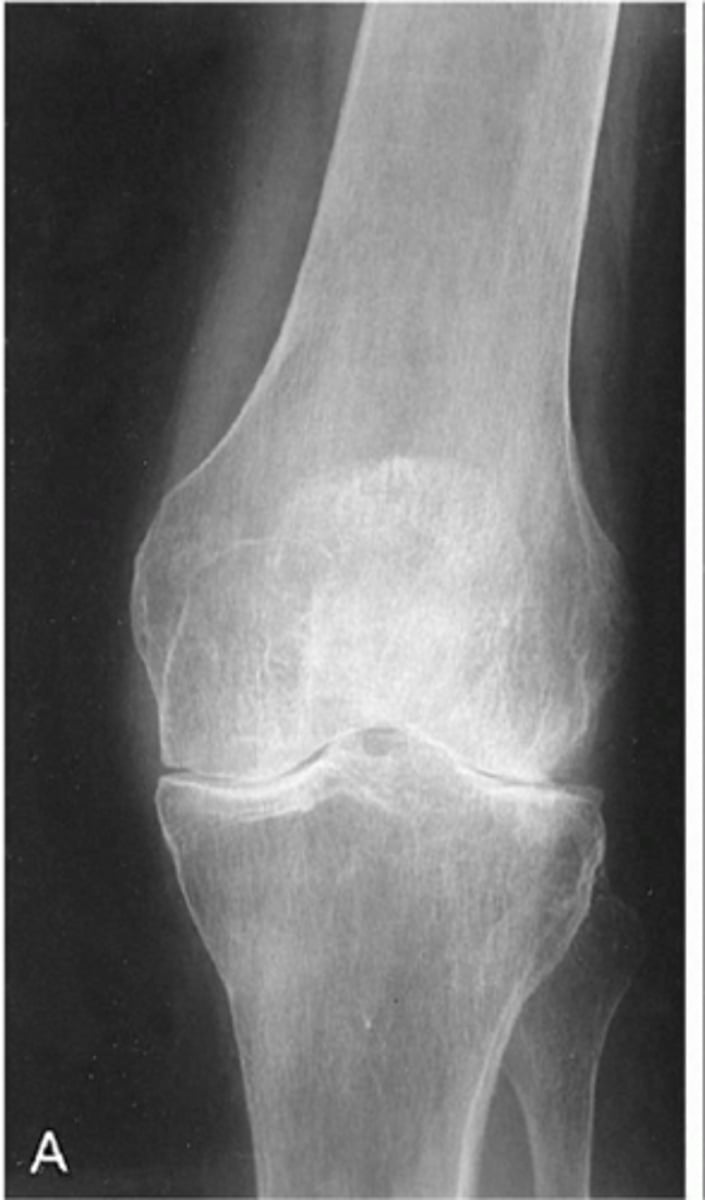
Non-uniform
_____ loss of joint space (degenerative)

- Soft tissue swelling
- Uniform loss of joint space
- Bone erosions
- Juxta-articular osteoporosis
- Occasional periostitis (adjacent metaphysis)
State the radiographic features of inflammatory arthritis
- Pannus
- Bare area
Erosive changes from _____ formation affecting the _____
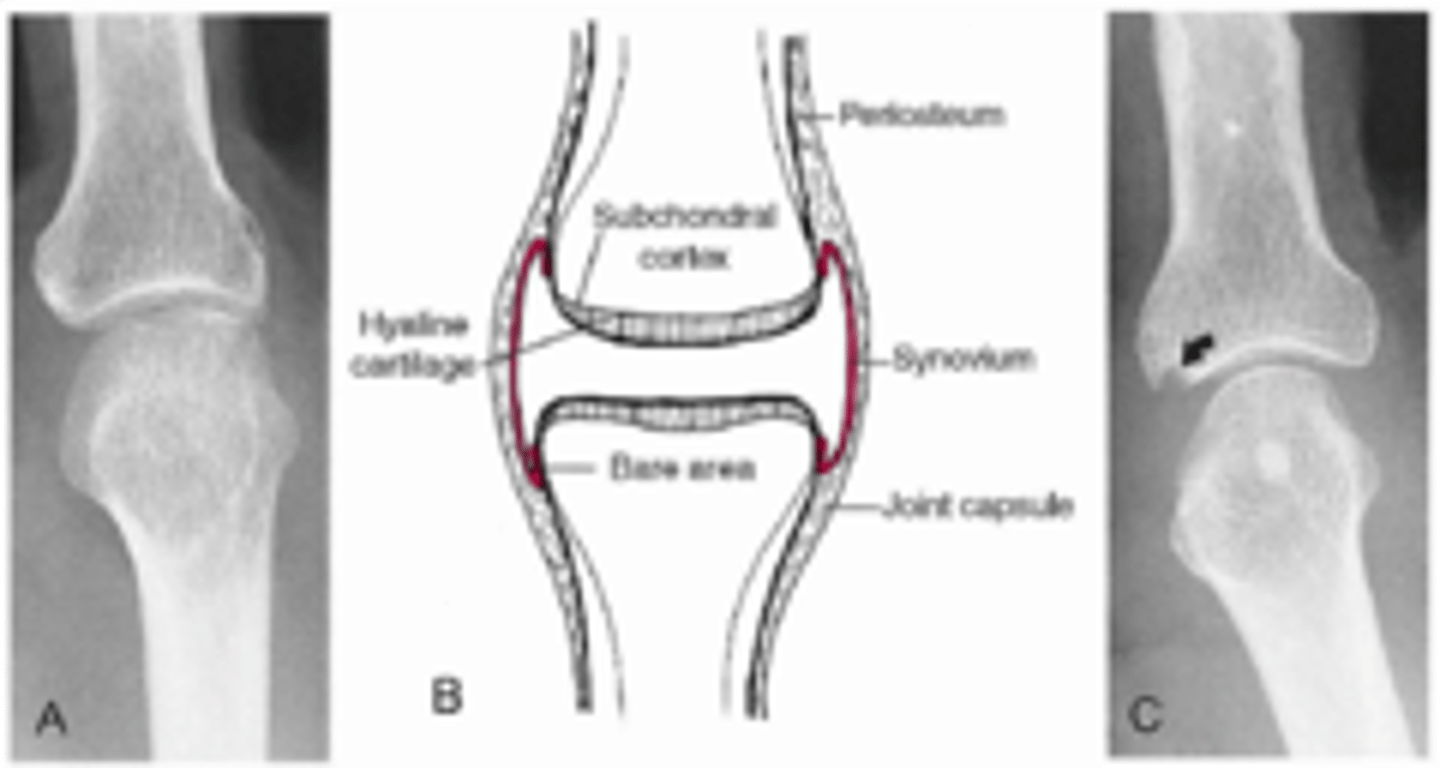
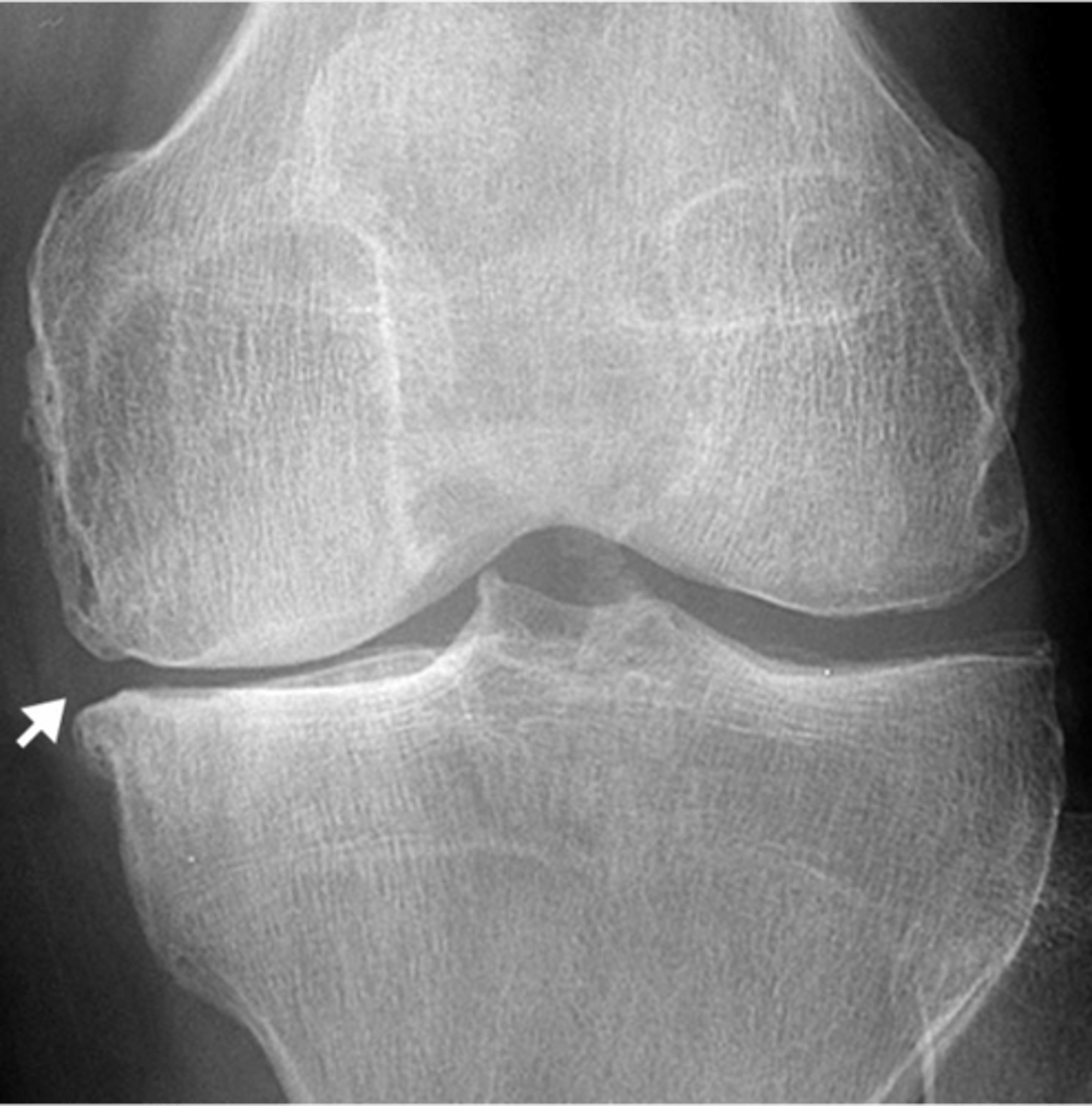
Metabolic joint disease
Relative preservation of joint space with well-marginated erosions away from the joint
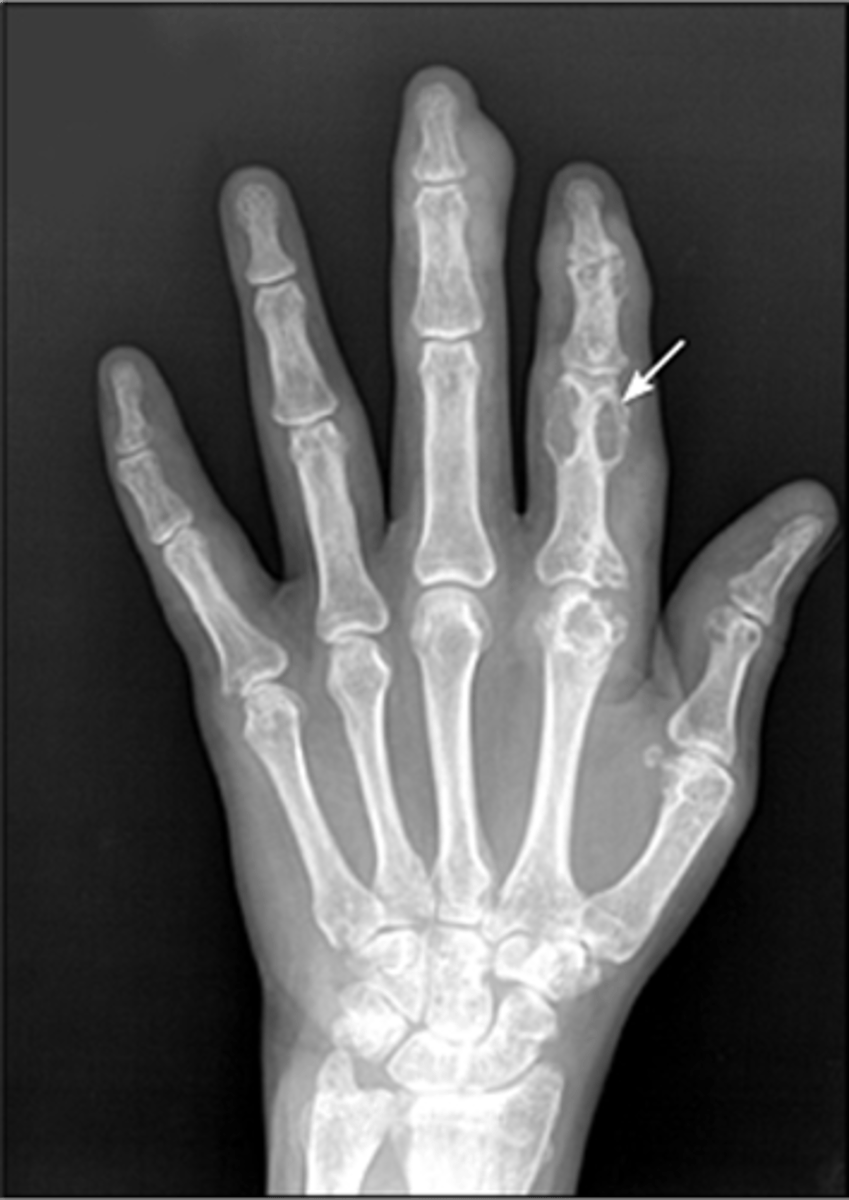
Degenerative joint disease (DJD)
_____ is the most common articular affliction
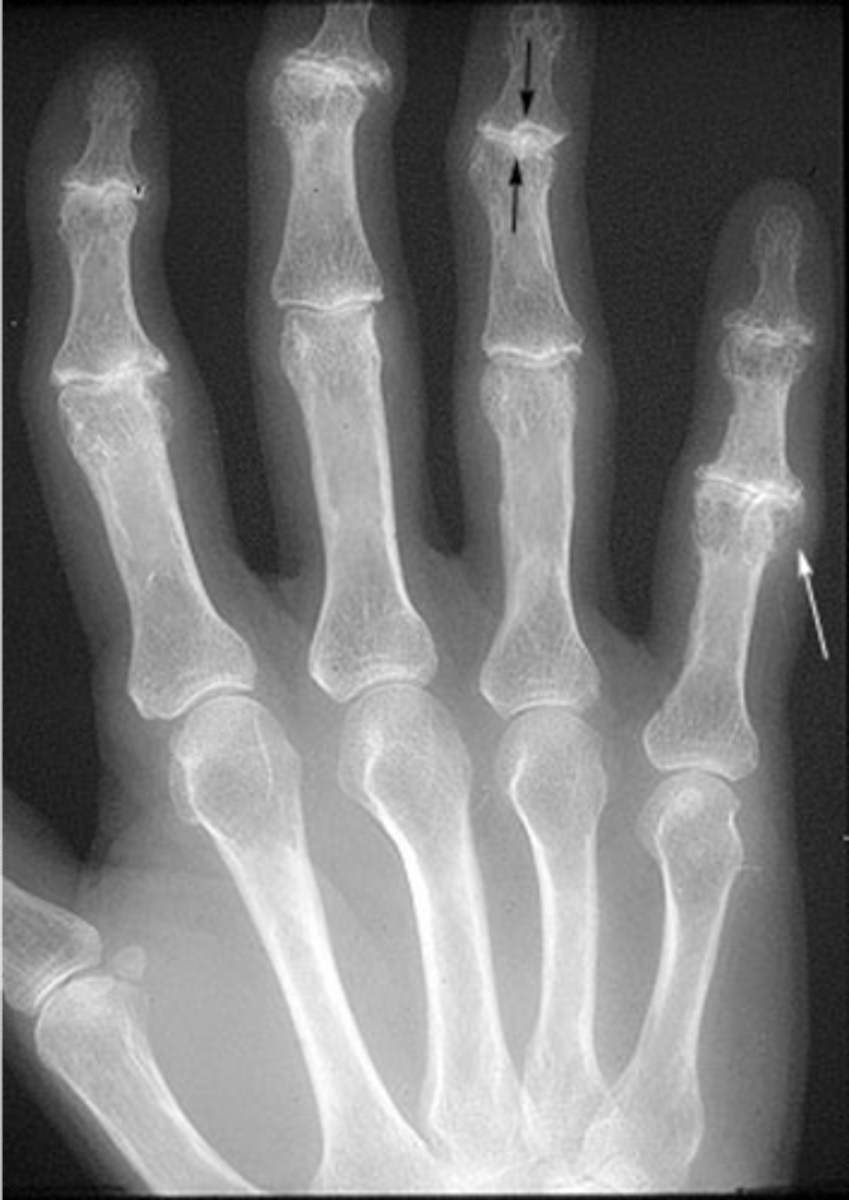
Progressive, non-inflammatory
Degenerative joint disease is a _____ disease
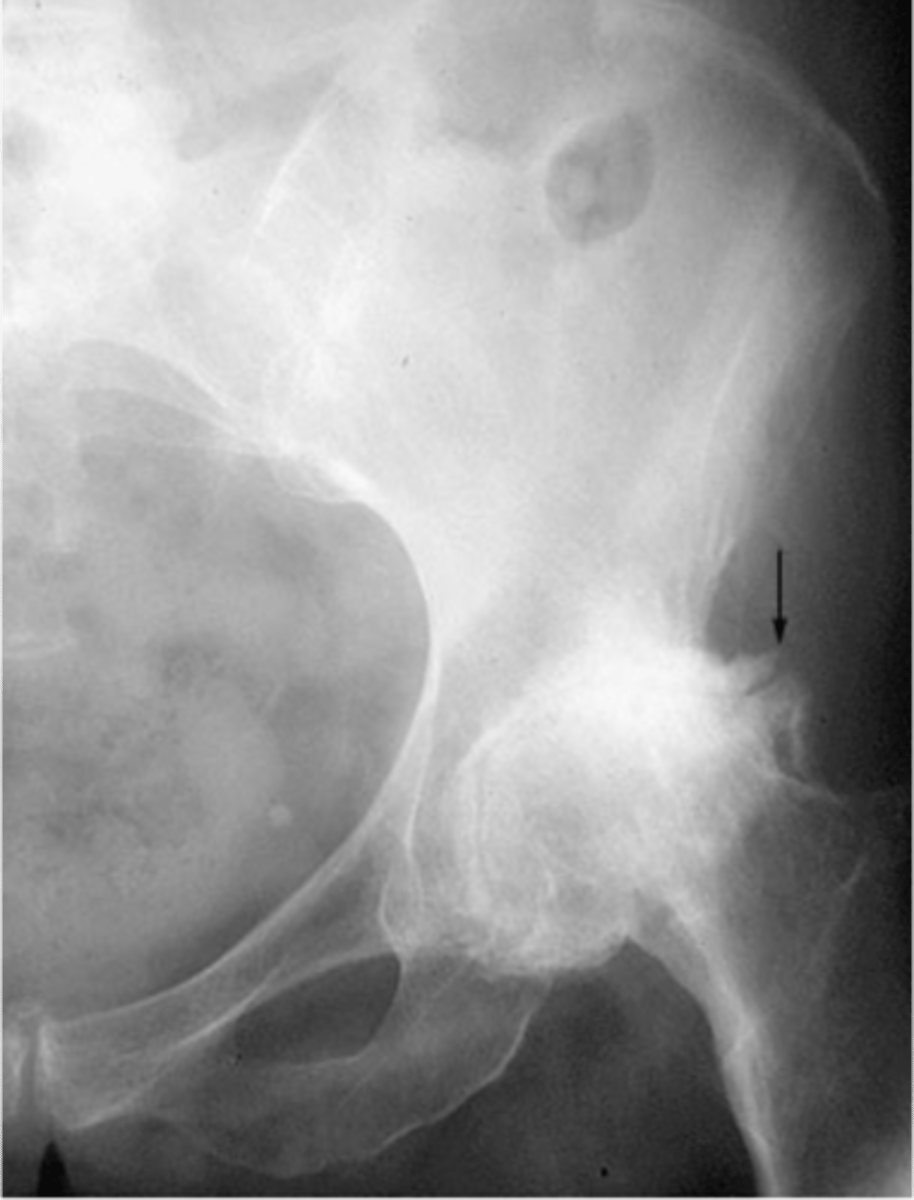
Primary
_____ osteoarthritis:
- No known or proven factors
Secondary
_____ osteoarthritis:
- Known precipitating factors:
• Trauma
• Congenital anomalies
• Crystal deposition disease
Poor
A _____ correlation exists among the extent of radiologic changes and clinical signs and symptoms of degenerative joint disease
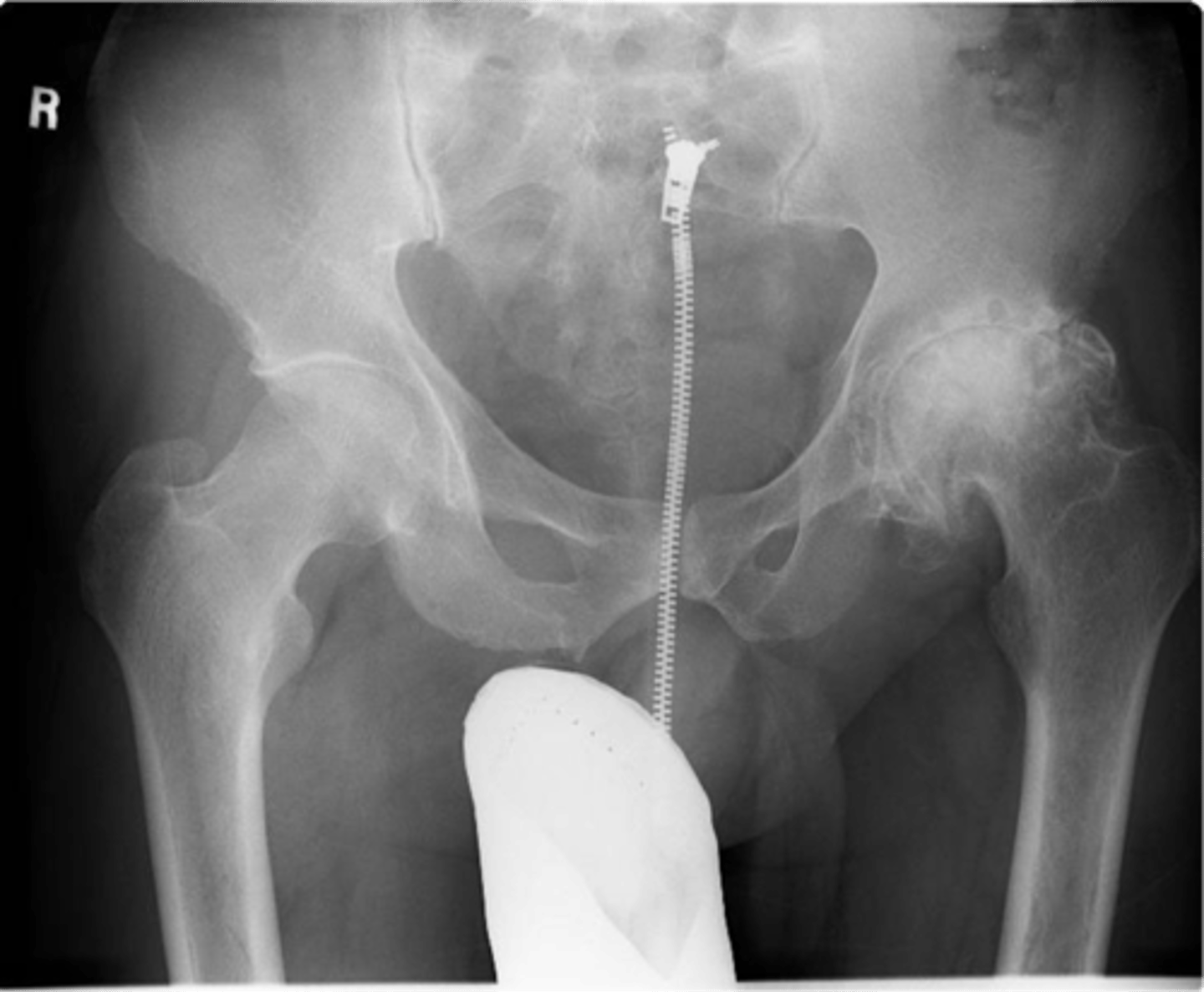
- Weight-bearing joints of the spine, hips, and knees
- AC joint
- First MTP
- First metacarpal-trapezium
- Distal interphalangeal joint (DIP) of the hands
- Any joint may be affected if conditions are right
State the common locations affected by degenerative joint disease
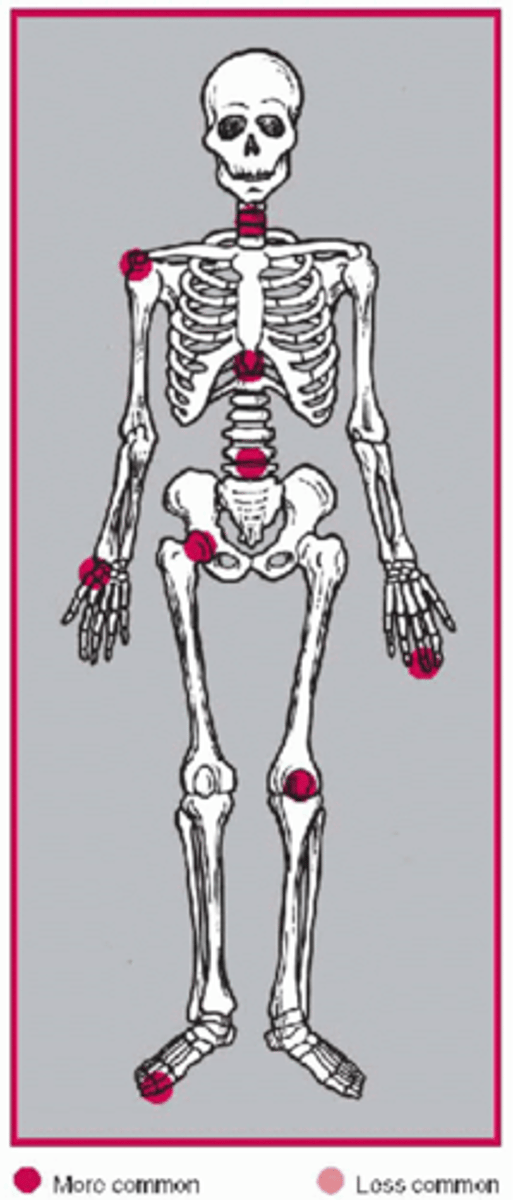
- M>F
- >45 y.o.
State the clinical features of degenerative joint disease
- Insidious onset of intermittent achy pain, stiffness, and swelling
- Stiffness typically occurs with rest, particularly in the morning
• Gradually disappearing with activity (<30 mins)
Explain the symptomatology of degenerative joint disease
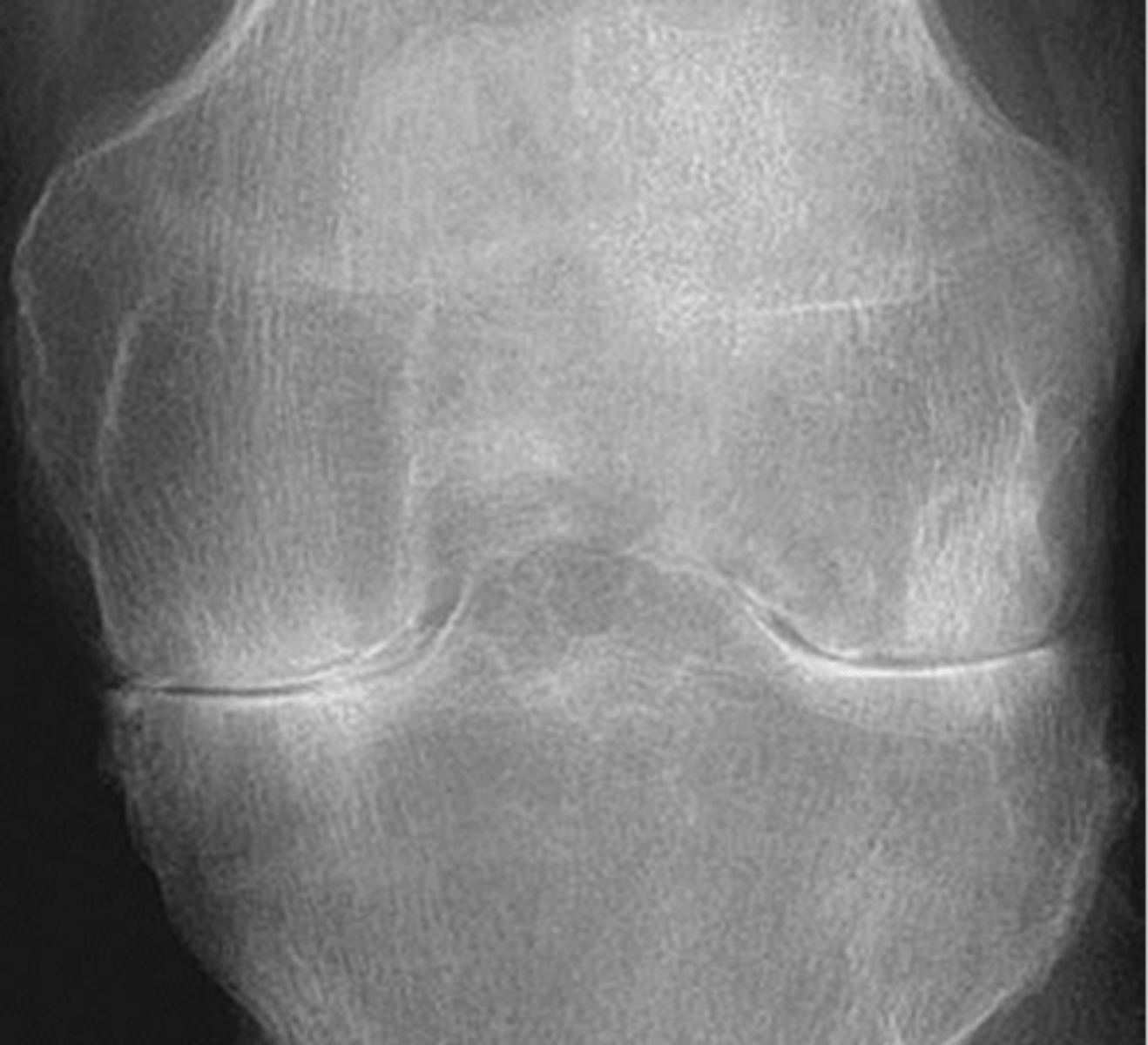
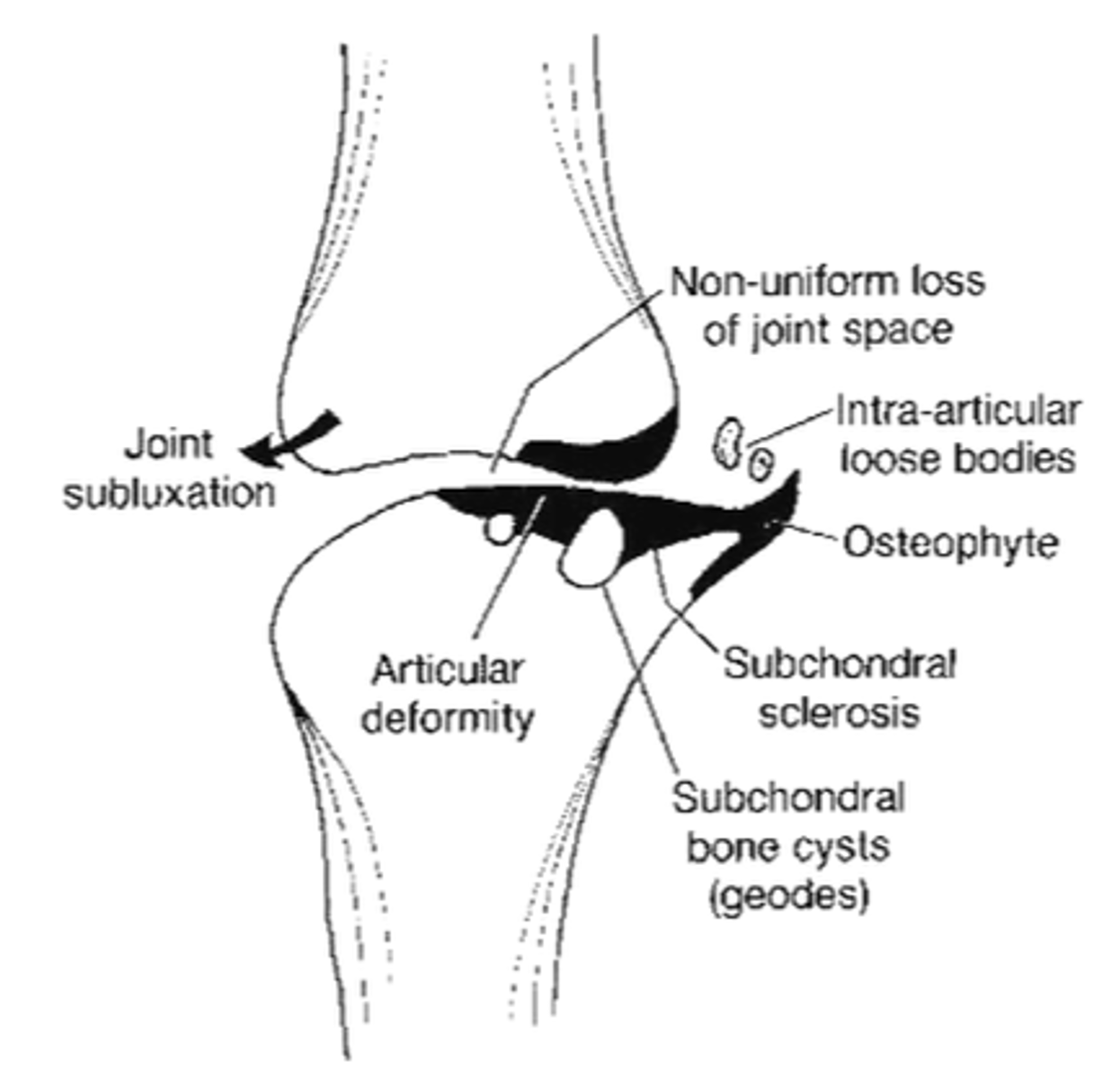
- Osteophytes
- Non-uniform joint space loss
- Subchondral sclerosis
- Subchondral cysts
- Subluxation
- Unilateral or bilateral
State the radiographic findings of osteoarthrosis
Asymmetric
_____ distribution of osteoarthritis
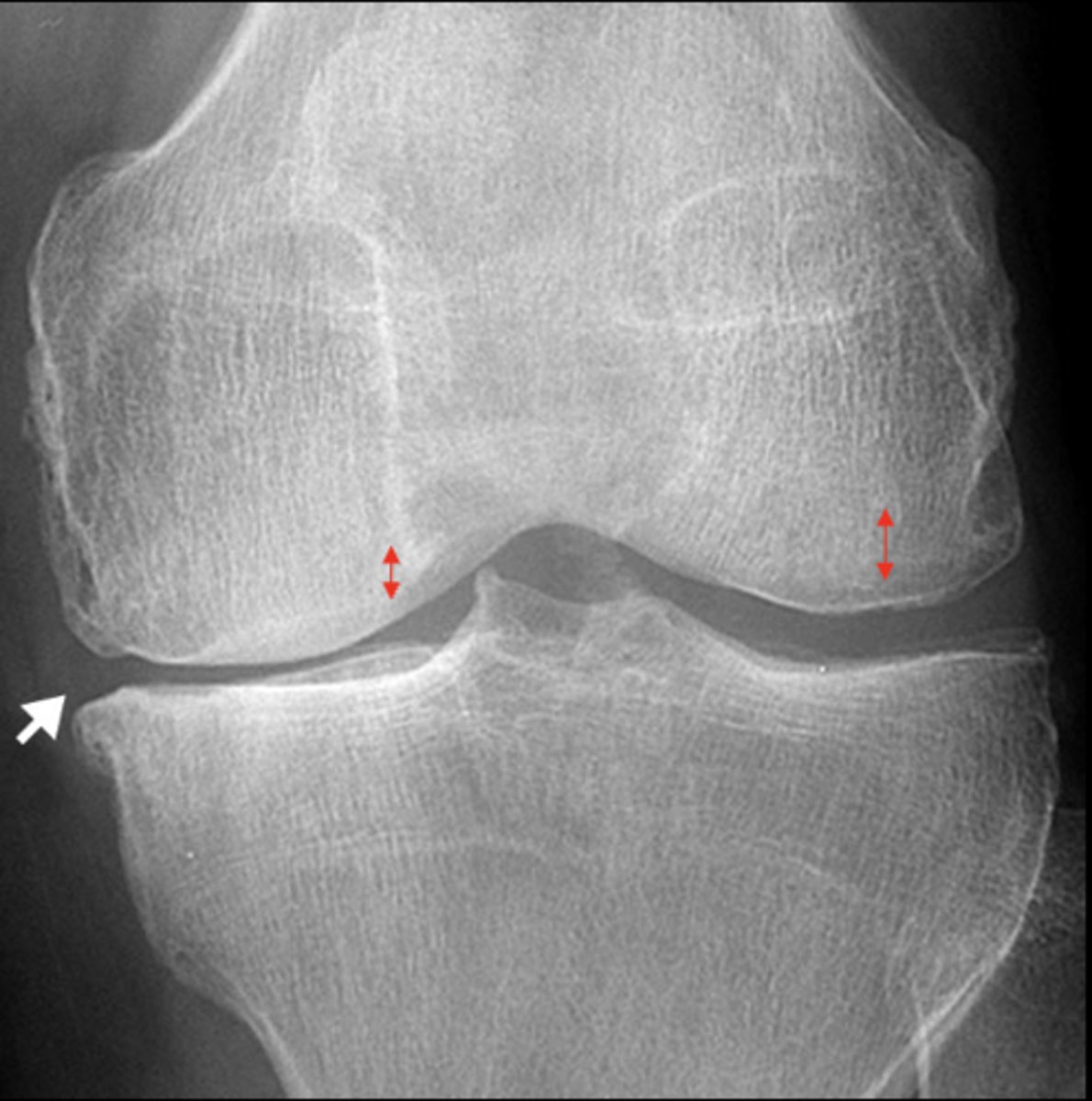
Non-uniform
Degenerative _____ loss of joint space
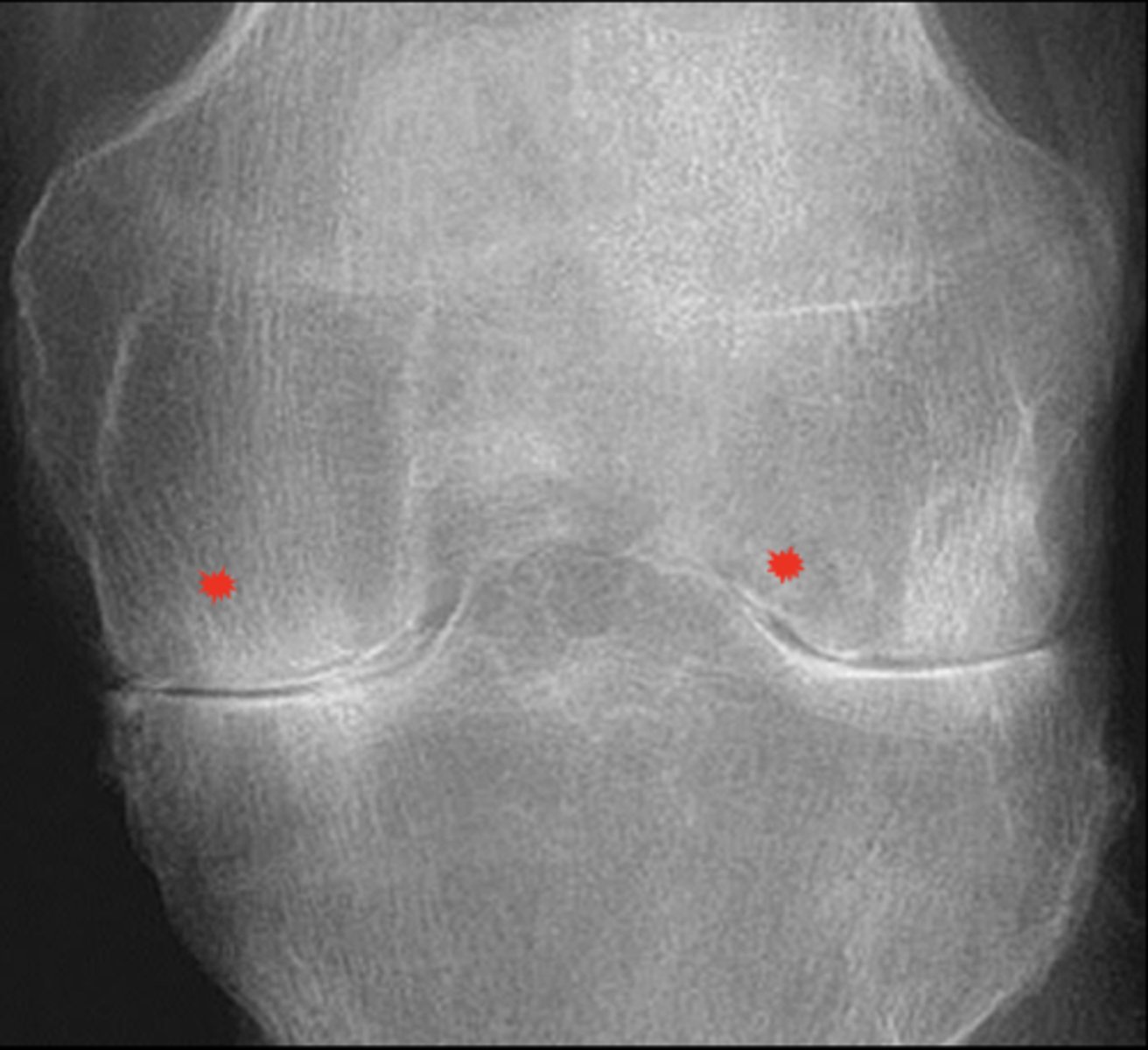
Uniform
Inflammatory _____ loss of joint space
Osteophytes
Bone spurs
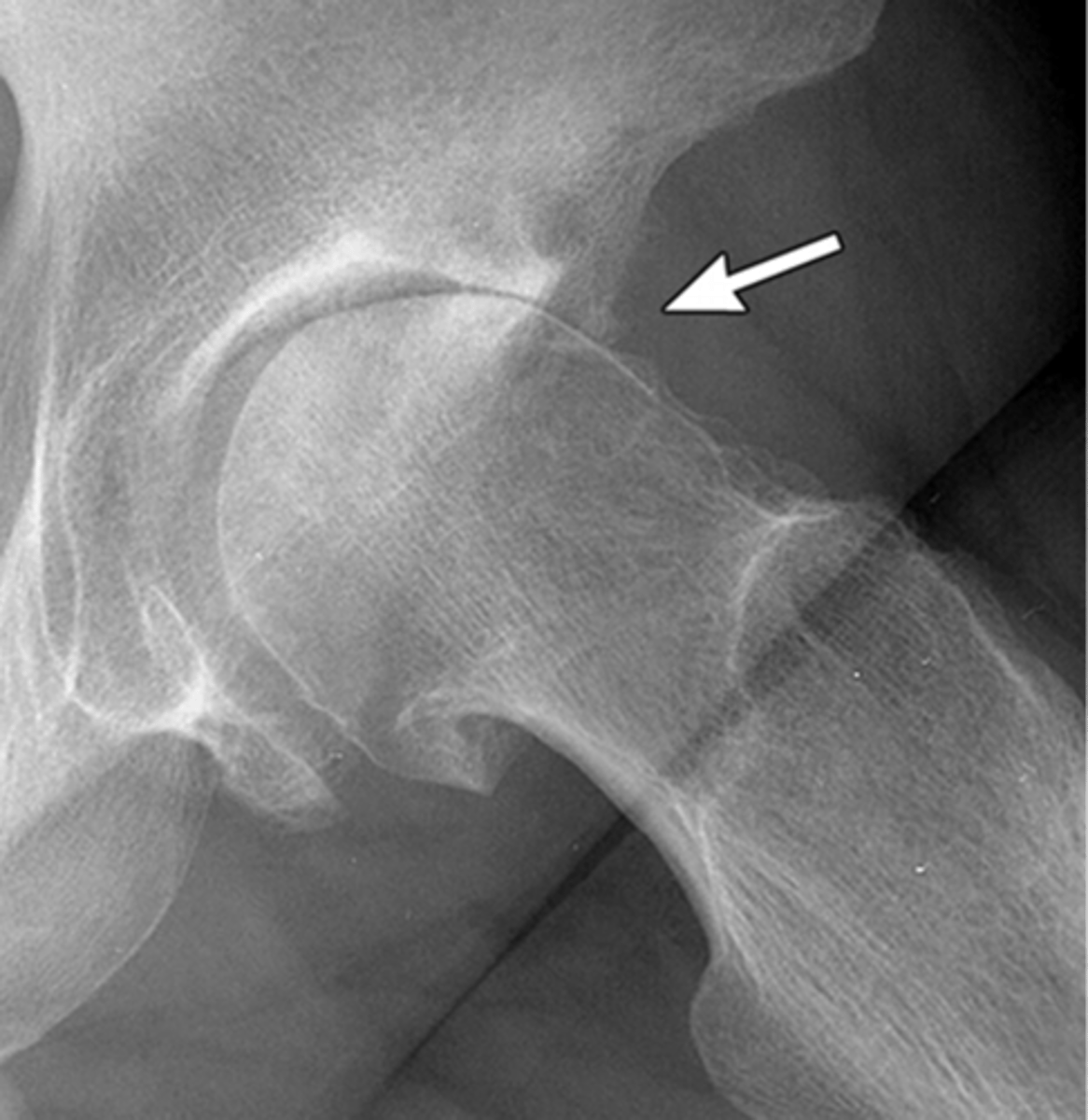
Subchondral sclerosis
Increased density of bone just deep to articular surface
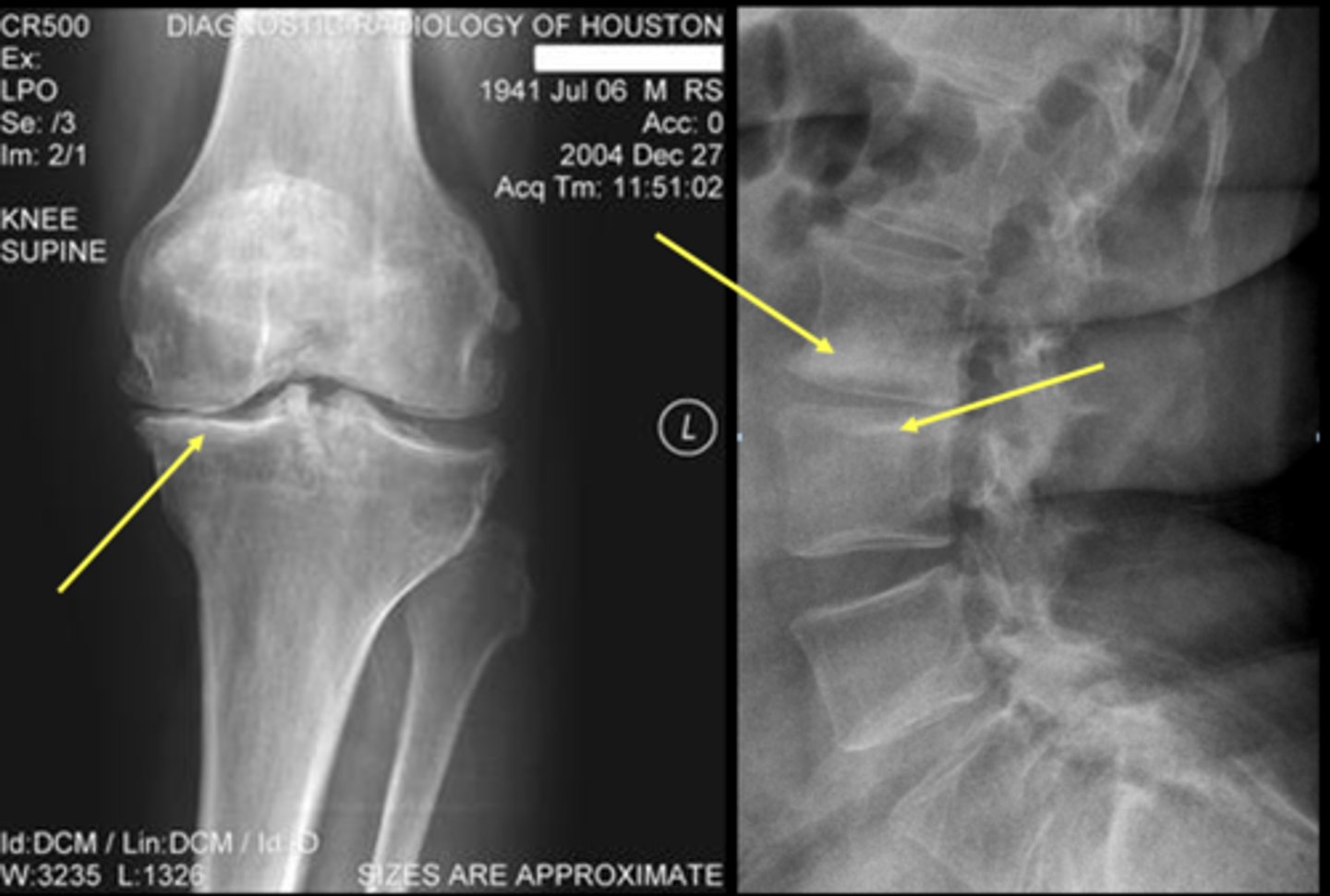
Subchondral cysts
Fluid-filled sacs in subchondral bone

Intra-articular loose bodies
ID radiographic feature of osteoarthrosis

Articular deformity
Due to repetitive stress and trabecular remodeling, fracture, or collapse

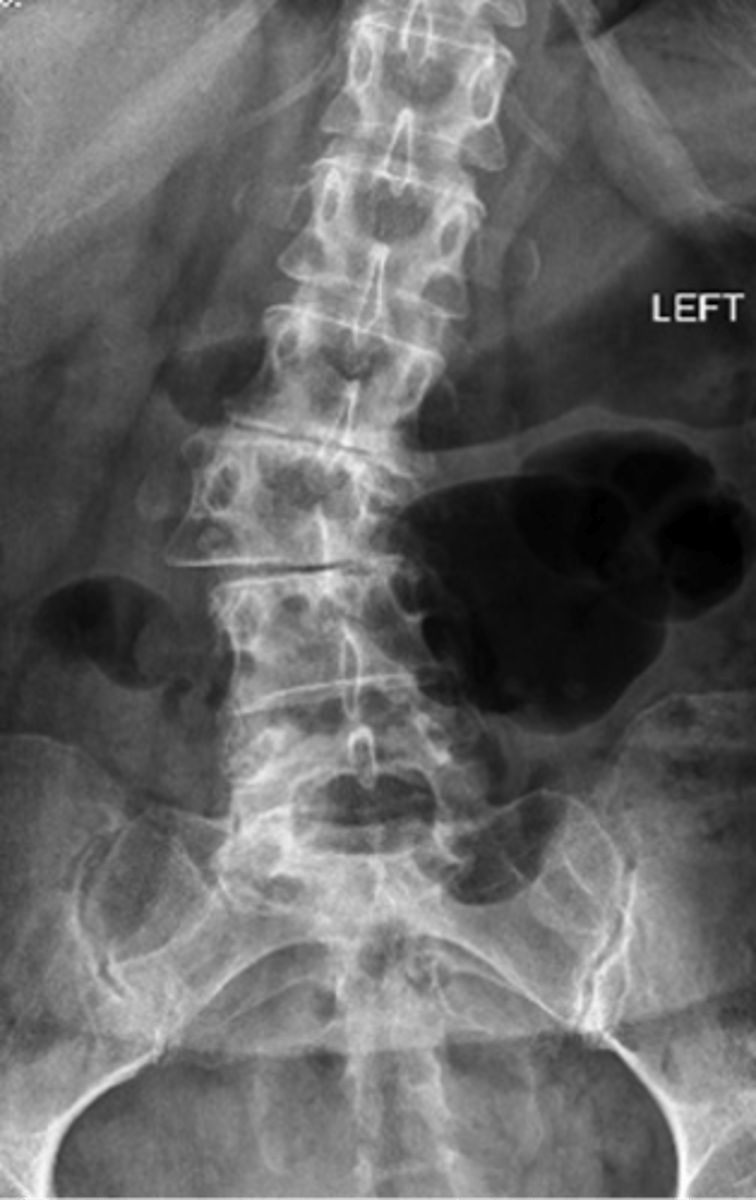
Lateral listhesis
ID type of joint alignment change
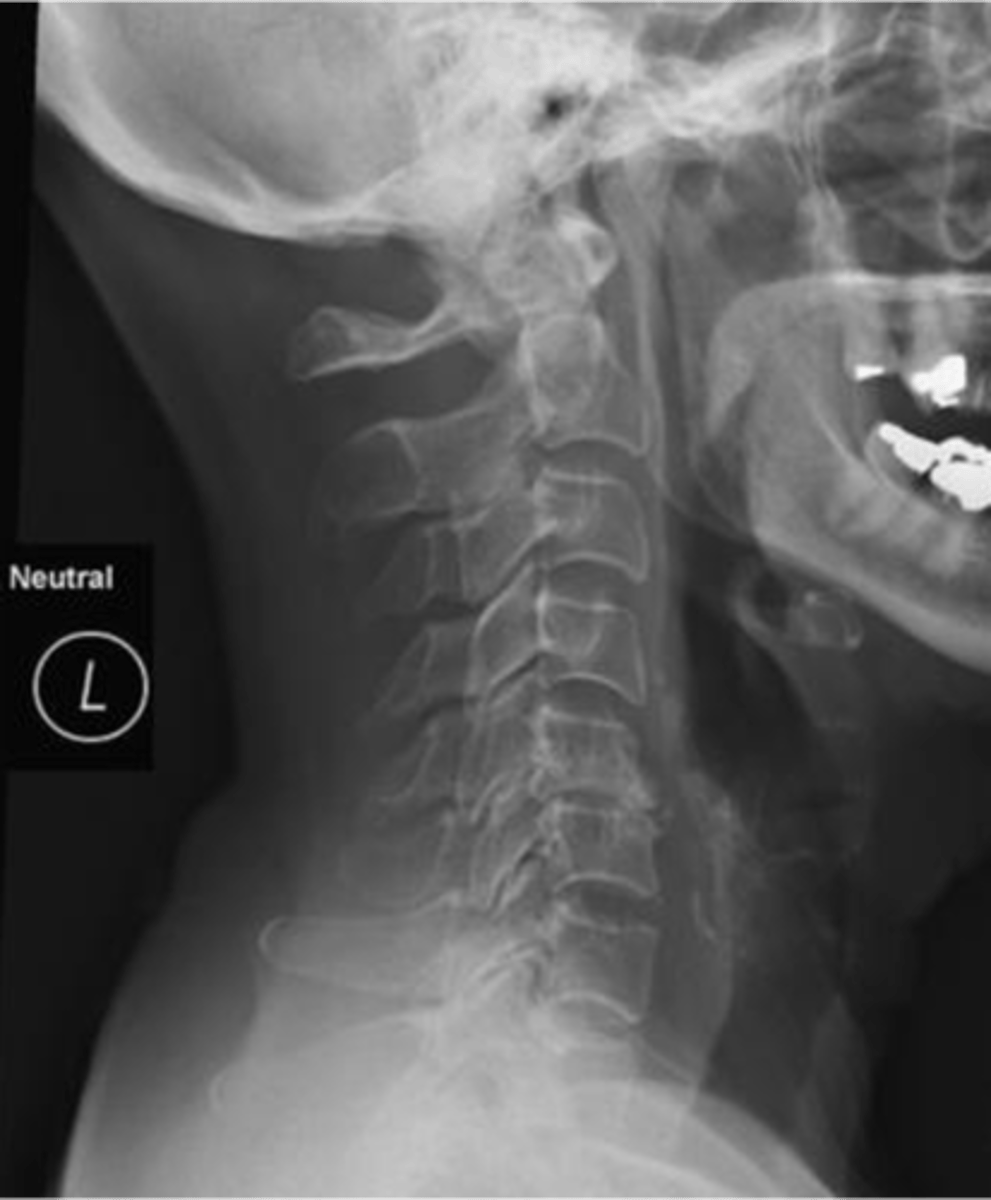
Retrolisthesis
ID type of joint alignment change
- C5-C7
- T2-T5, T10-T12
- L4-S1
- Discovertebral
- Uncovertebral
- Apophyseal
- Costovertebral
State the target sites of degenerative spine disease
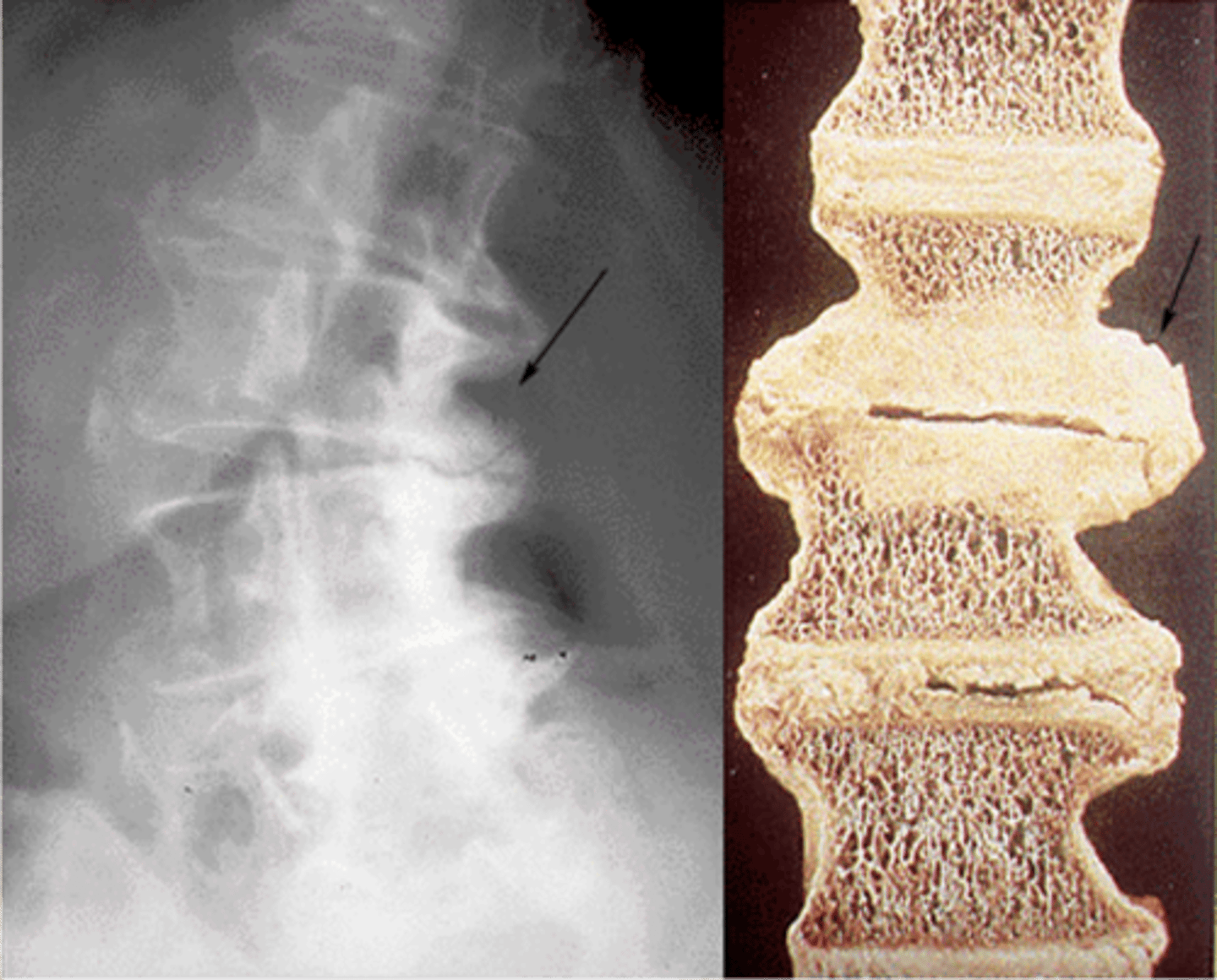
- Loss of disc height
- Osteophytosis
- Endplate sclerosis
- Vacuum cleft
State the radiographic features of degeneration of the intervertebral disc
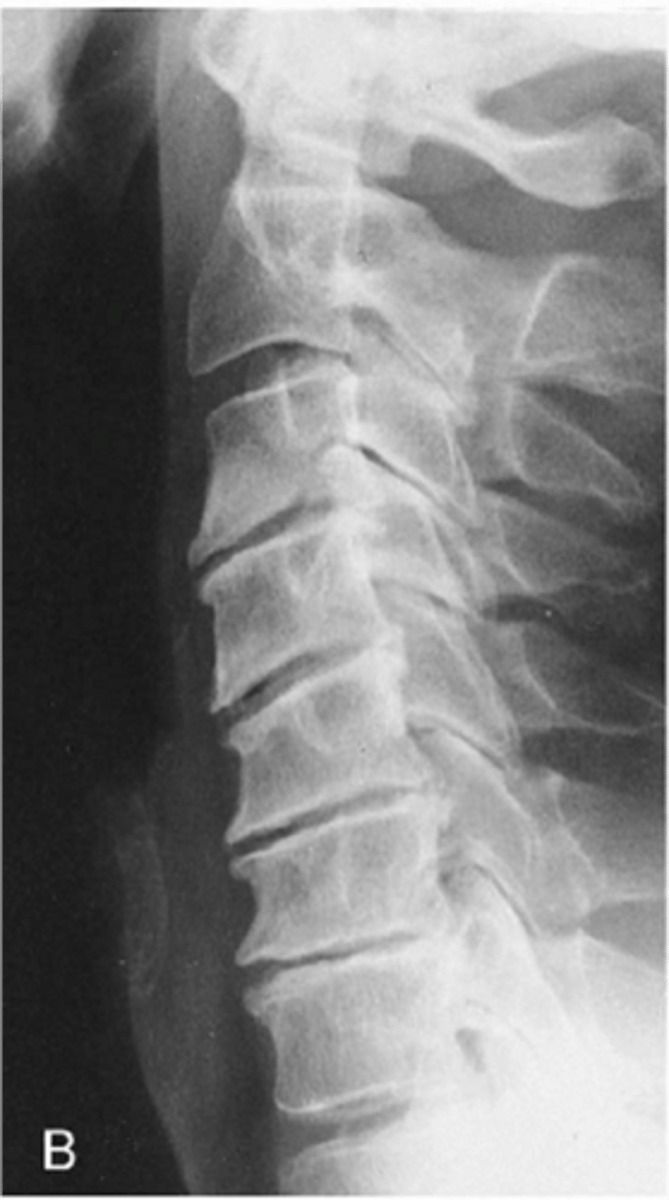
Lower cervical spine
Degeneration of intervertebral discs is usually worse in the _____
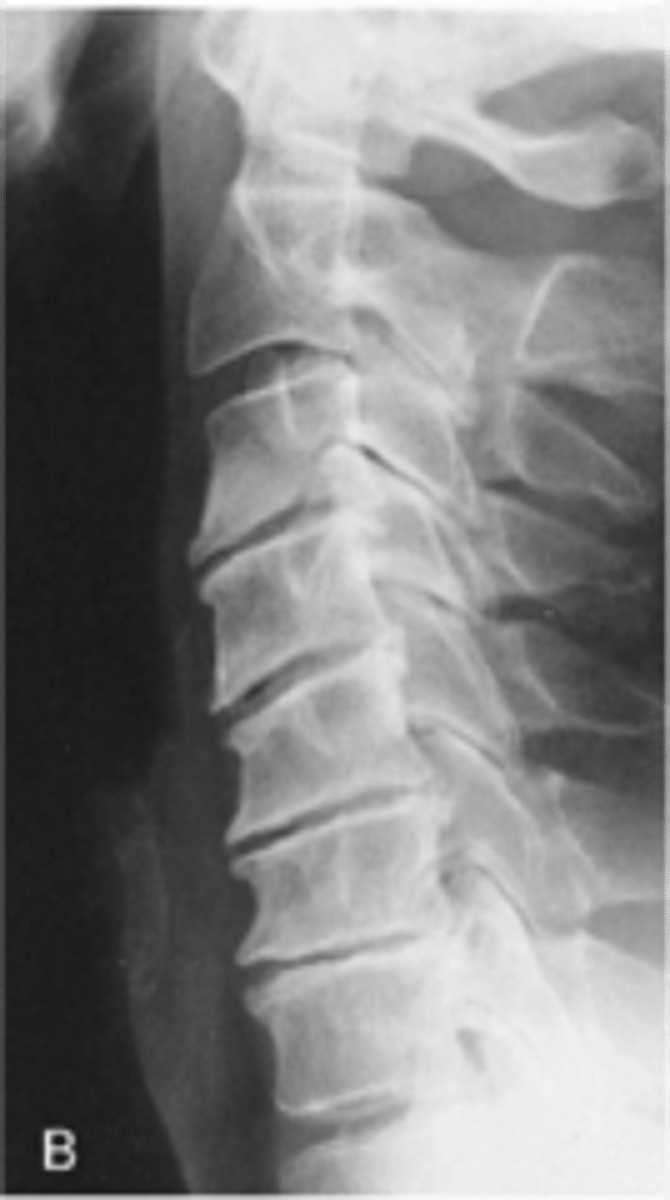
Facet joint osteoarthrosis
ID type of degenerative spine disease

Facet hypertrophy
- Enlargement of facet joints
- May be the result of the body responding to degenerative disease
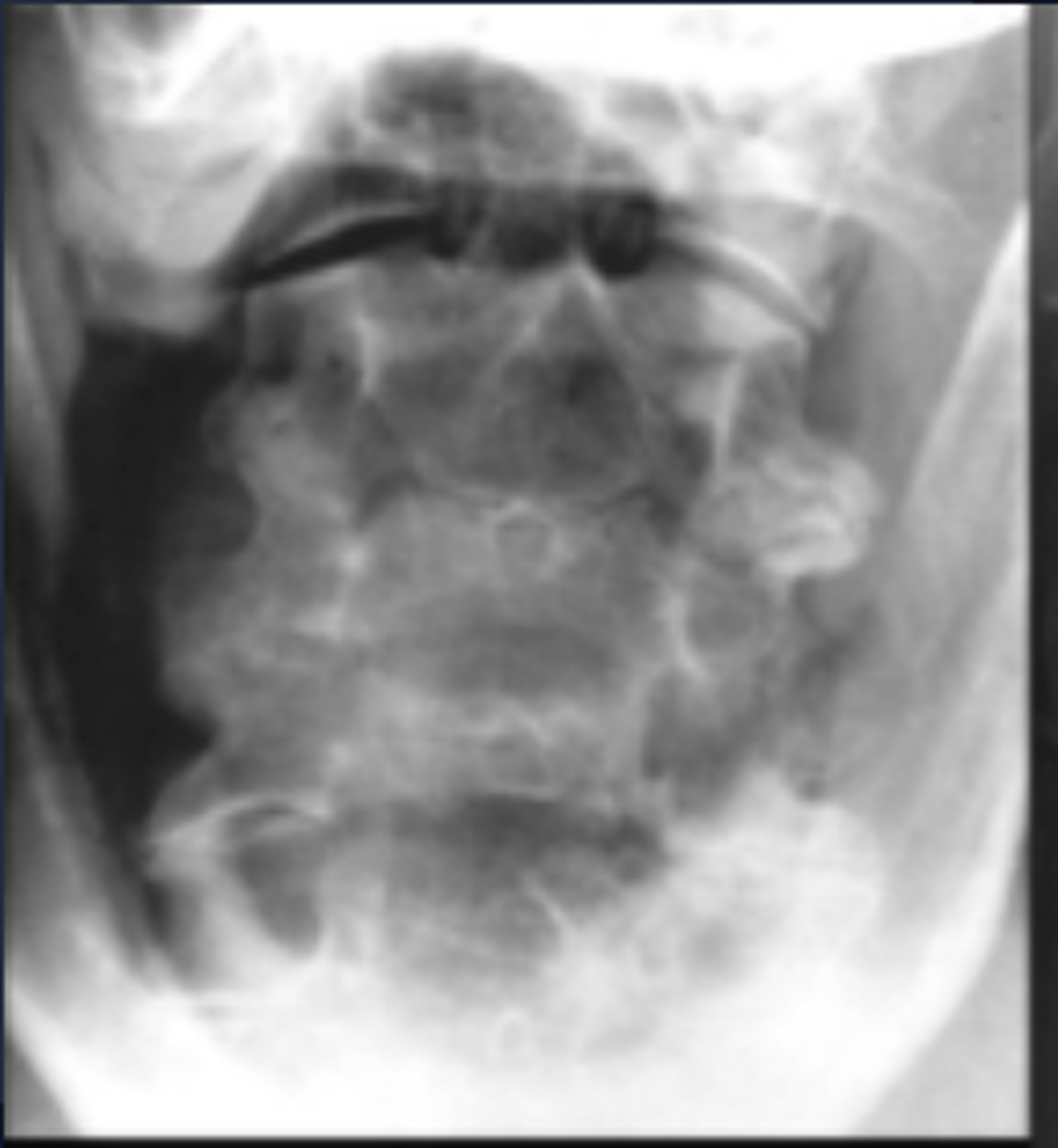
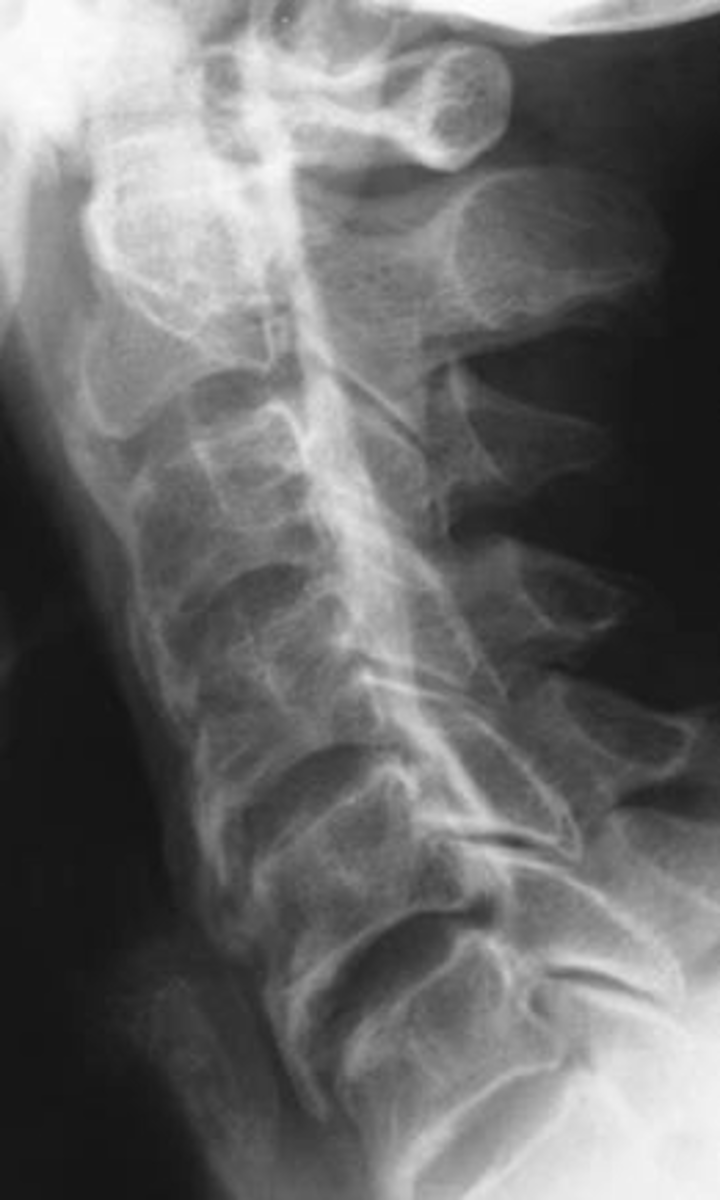
Uncovertebral osteoarthrosis
ID type of degenerative spine disease

C5-C6
Which levels are you expecting uncinate hypertrophy to be on the AP lower cervical?
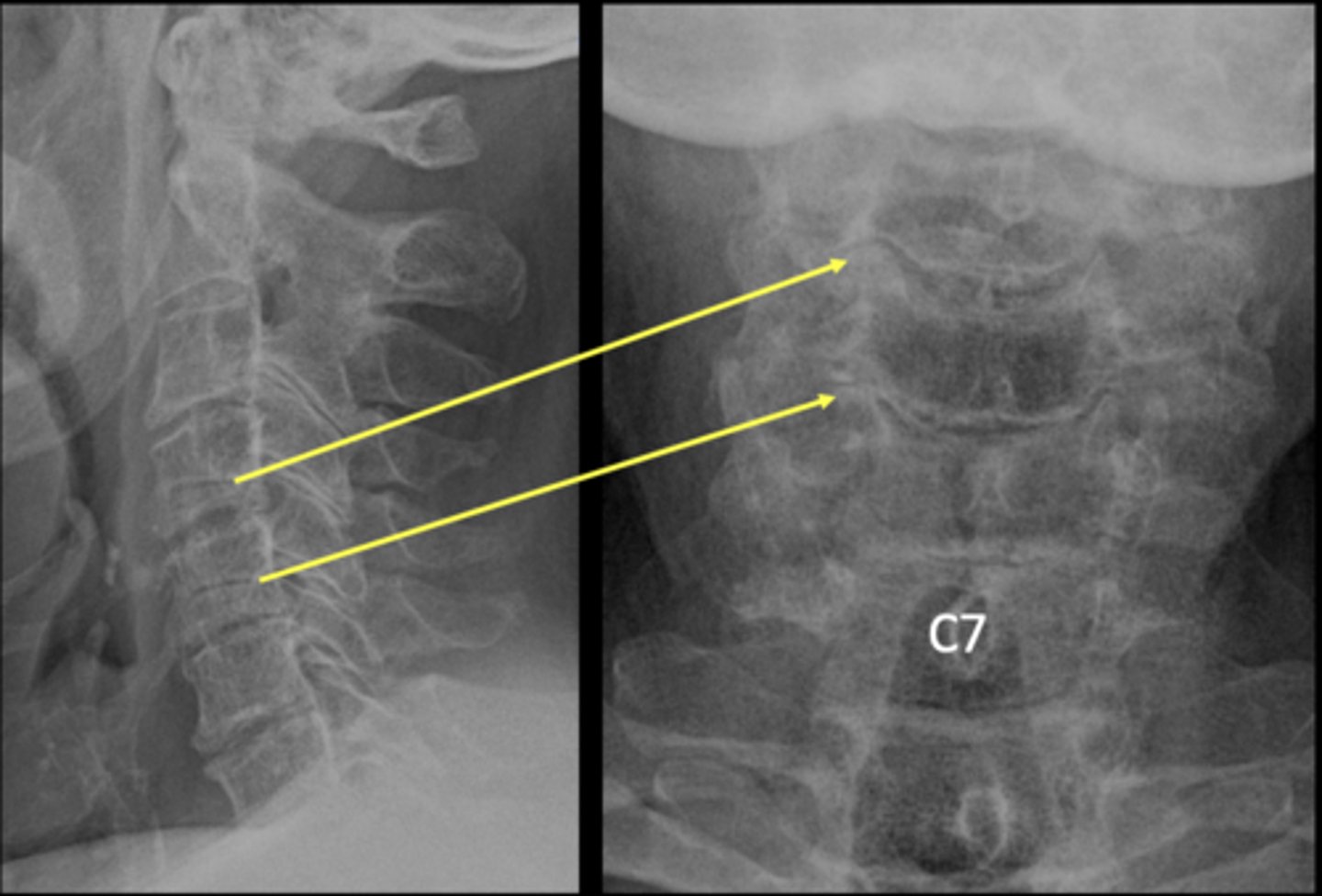
Cervical spondylosis: foraminal encroachment
ID type of degenerative spine disease

Cervical spondylotic myelopathy and radiculopathy
ID type of degenerative spine disease
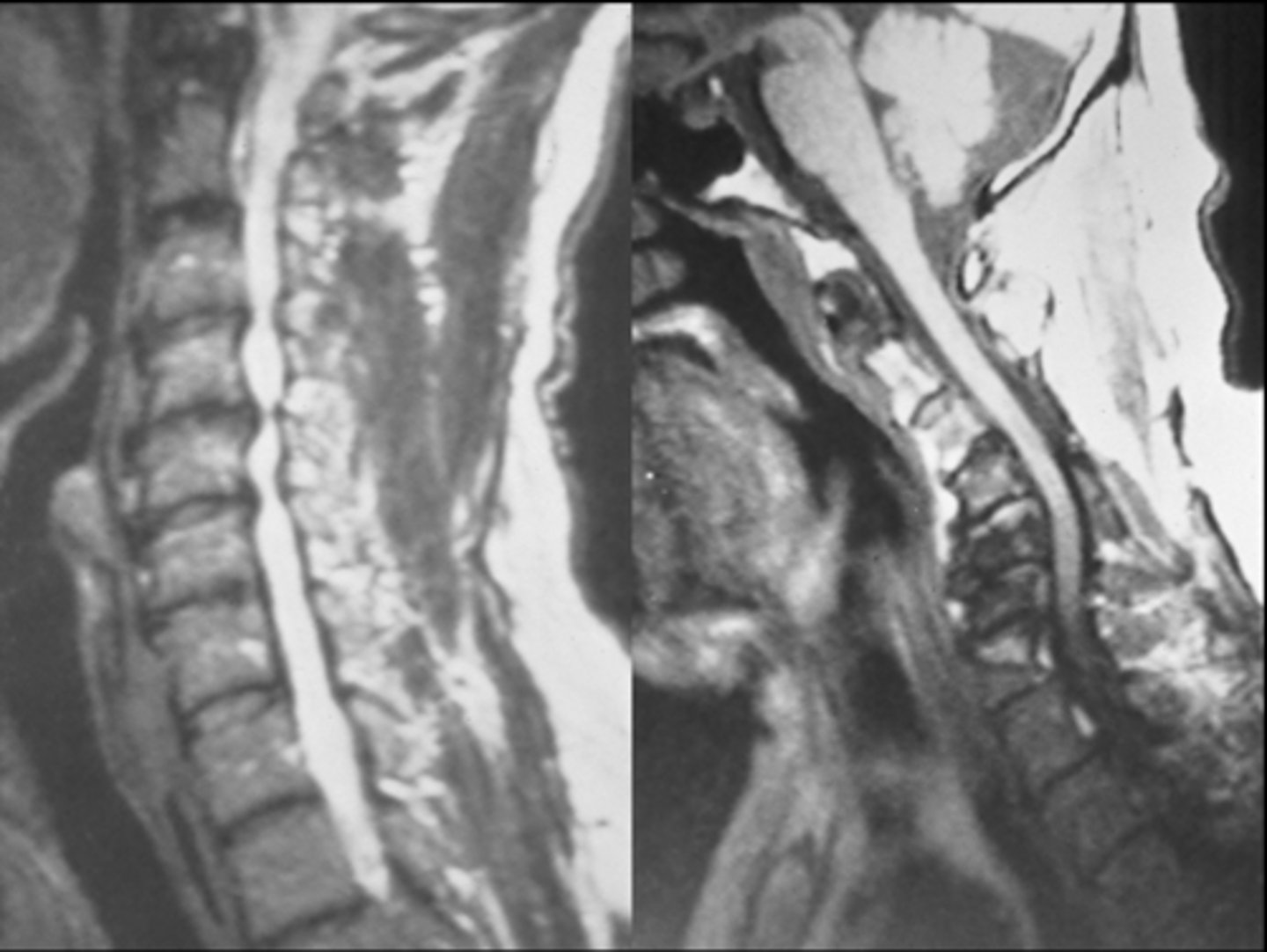
Intercalary bone
Calcification within the annular fibers
- A sign of degenerative disc disease
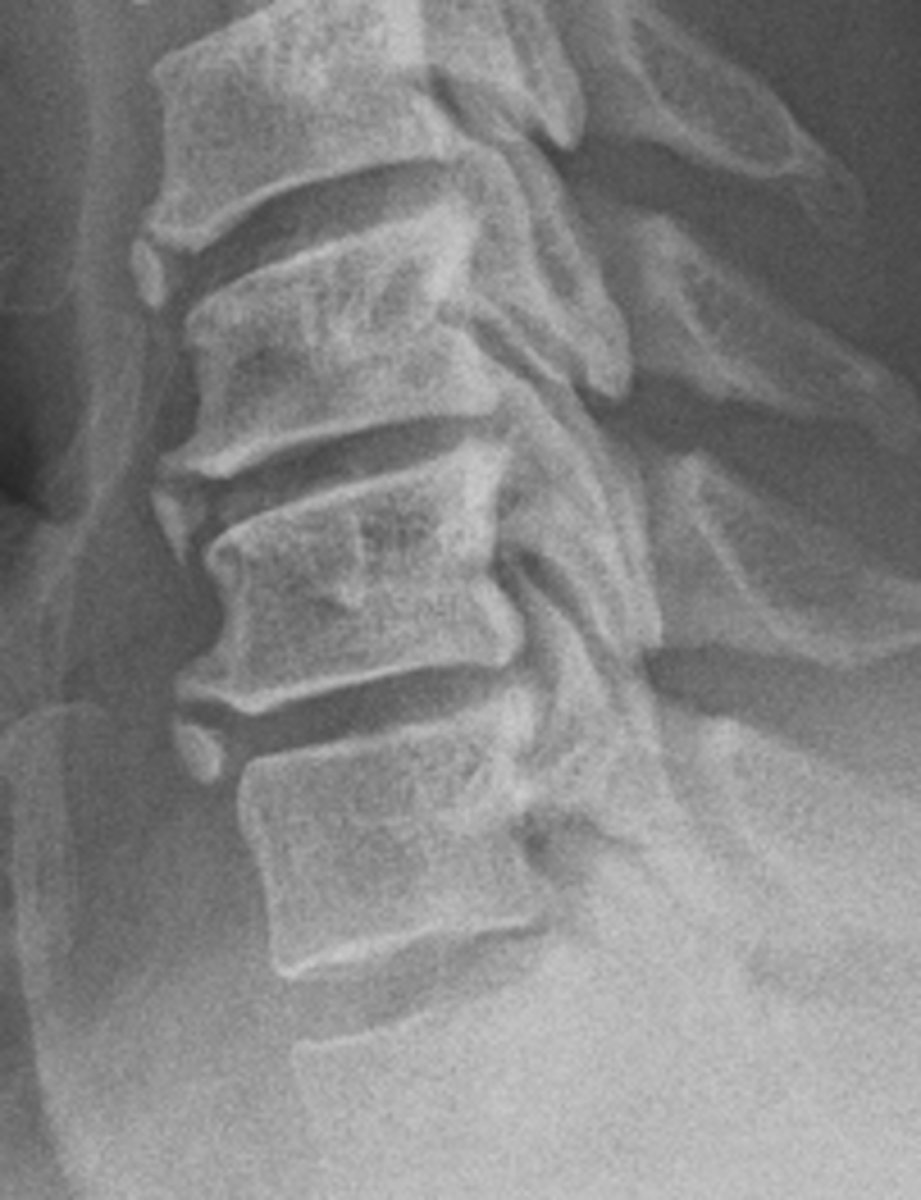
Limbus bone
- Not an intercalary ossicle
- Notice the parent site

Atlantoaxial osteoarthrosis
ID type of degenerative spine disease
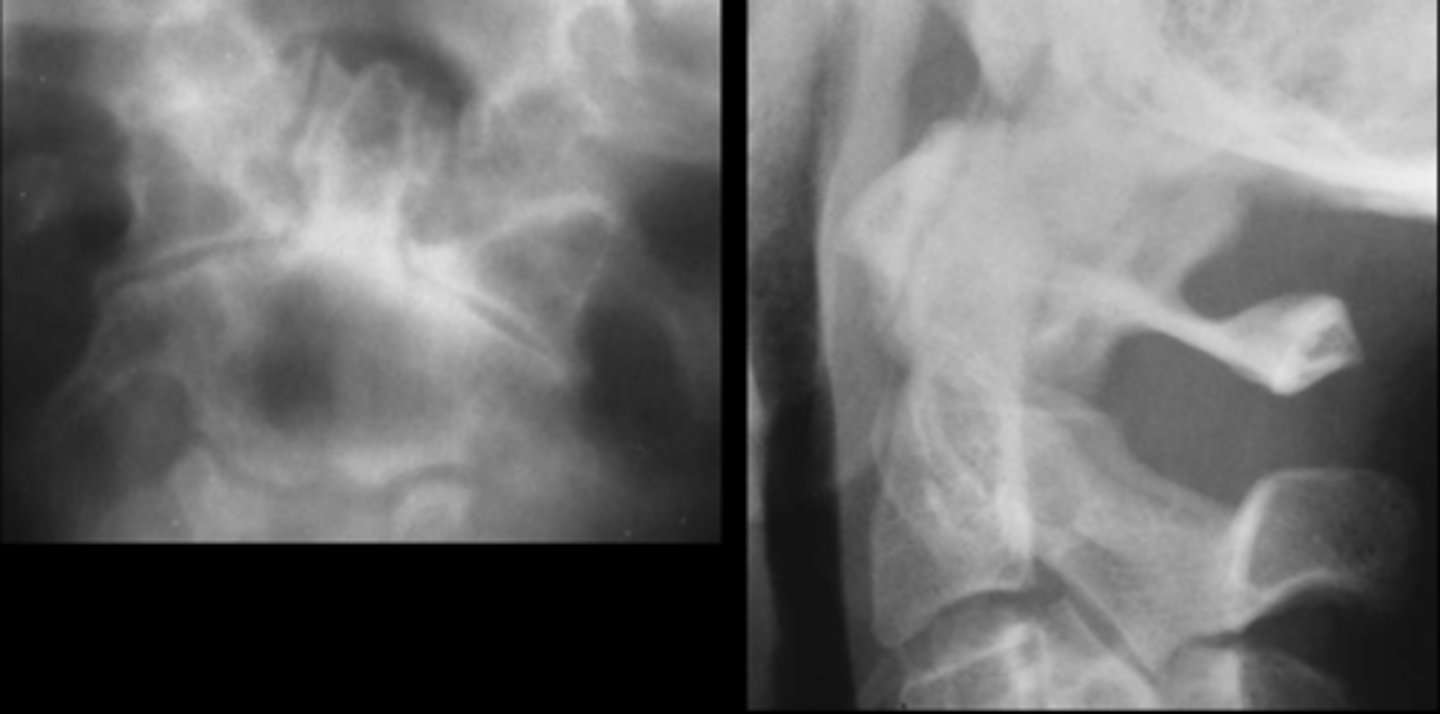
- Osteophytes
- Sclerosis
- Subluxation
State the radiographic features of apophyseal joints in degenerative cervical spine disease
- Osteophytes
- Foraminal encroachment
State the radiographic features of uncovertebral joints in degenerative cervical spine disease
- Decreased height
- Osteophytes
- Vacuum
- Canal stenosis
- Ligament calcification
State the radiographic features of discovertebral joints in degenerative cervical spine disease
Spondylosis and senile kyphosis
ID type of degenerative spine disease in the thoracic spine

Costovertebral arthrosis
ID type of degenerative spine disease in the thoracic spine
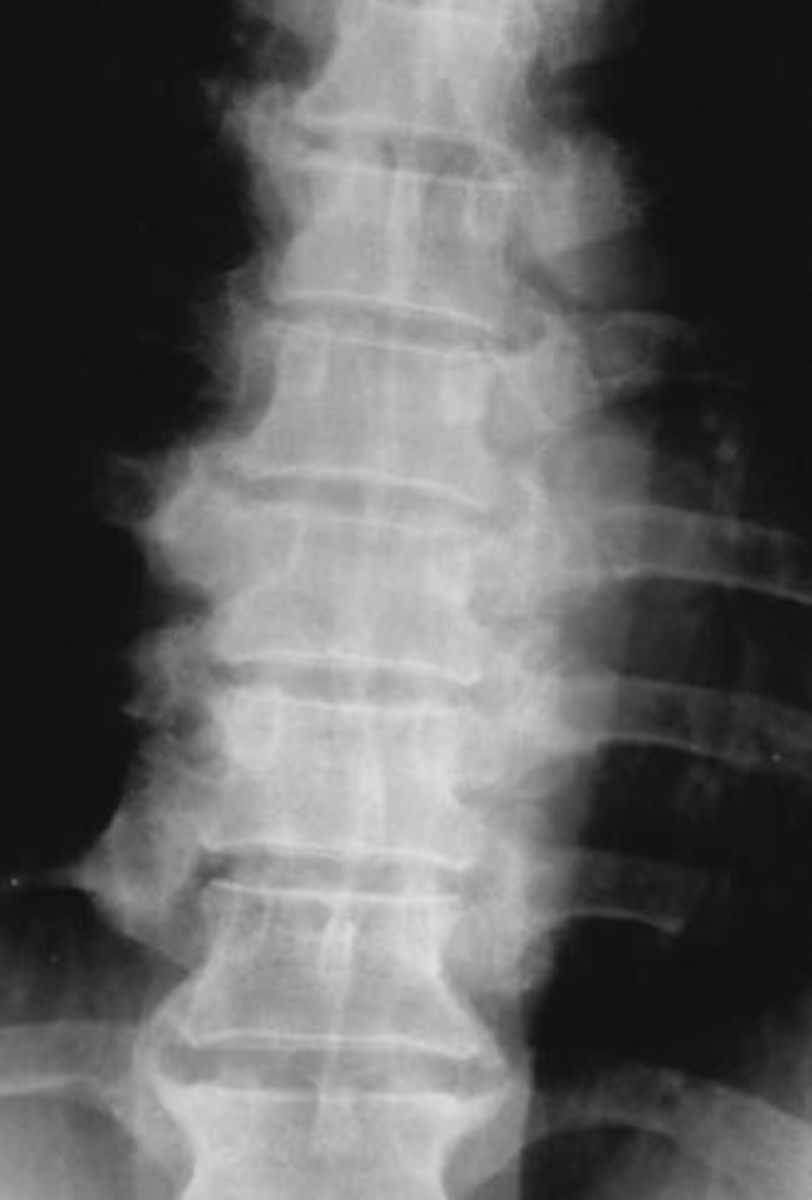
- Osteophytes
- Sclerosis
- Subluxation
State the radiographic features of apophyseal joints in degenerative thoracic spine disease
- Osteophytes
• Unilateral
• Right side
State the radiographic features of costovertebral joints in degenerative thoracic spine disease
- Decreased height
- Osteophytes
- Vacuum
- Kyphosis
State the radiographic features of discovertebral joints in degenerative thoracic spine disease
Facet joint osteoarthrosis
ID type of degenerative spine disease in the lumbar spine
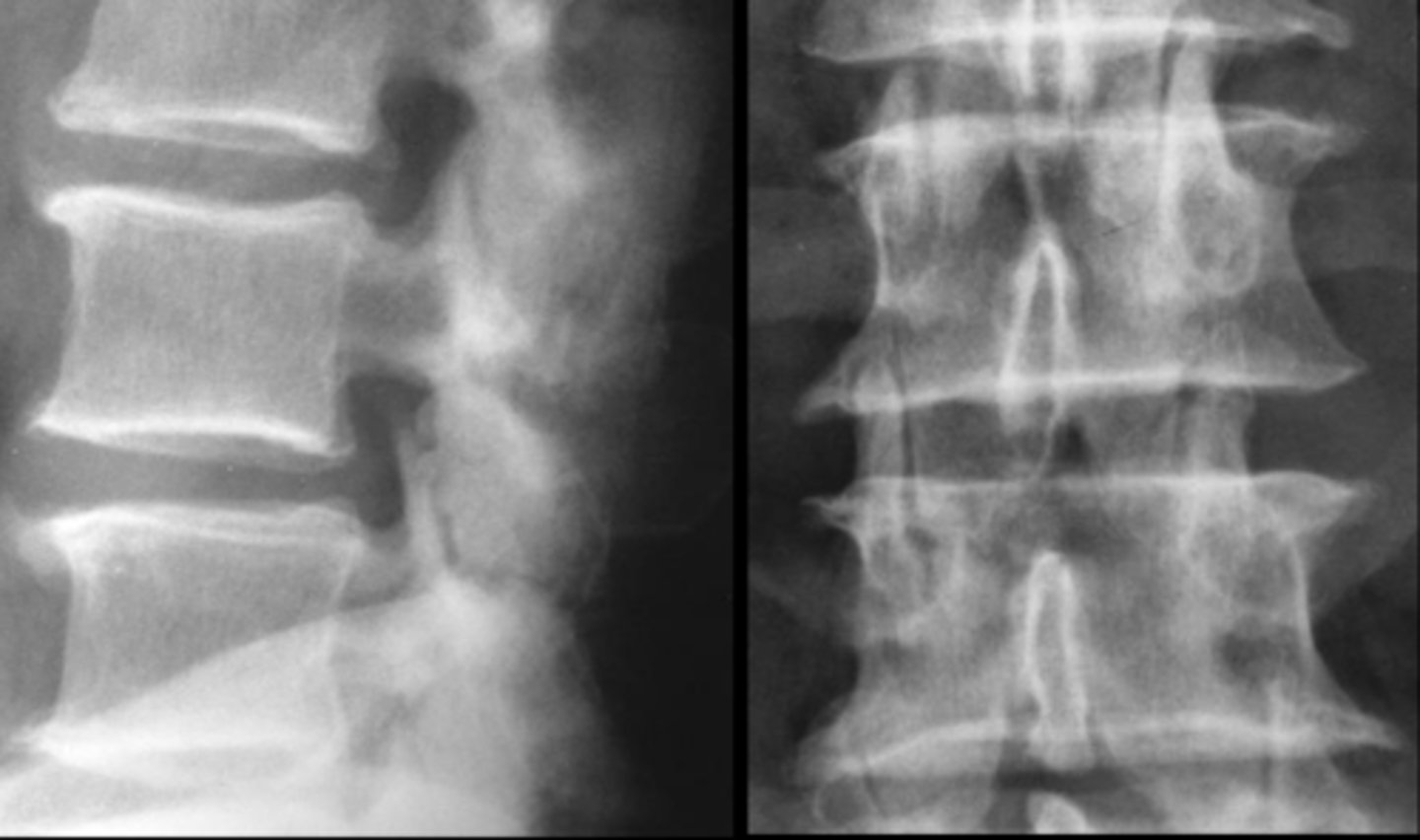
- L4-L5 and L5-S1 MC sites
- L4-L5 disc normally tallest
- Osteophytes
- Sclerosis
- Narrowing
- Vacuum phenomenon
State the radiographic features of degenerative lumbar disc disease
Degenerative disc disease
ID type of degenerative spine disease in the lumbar spine
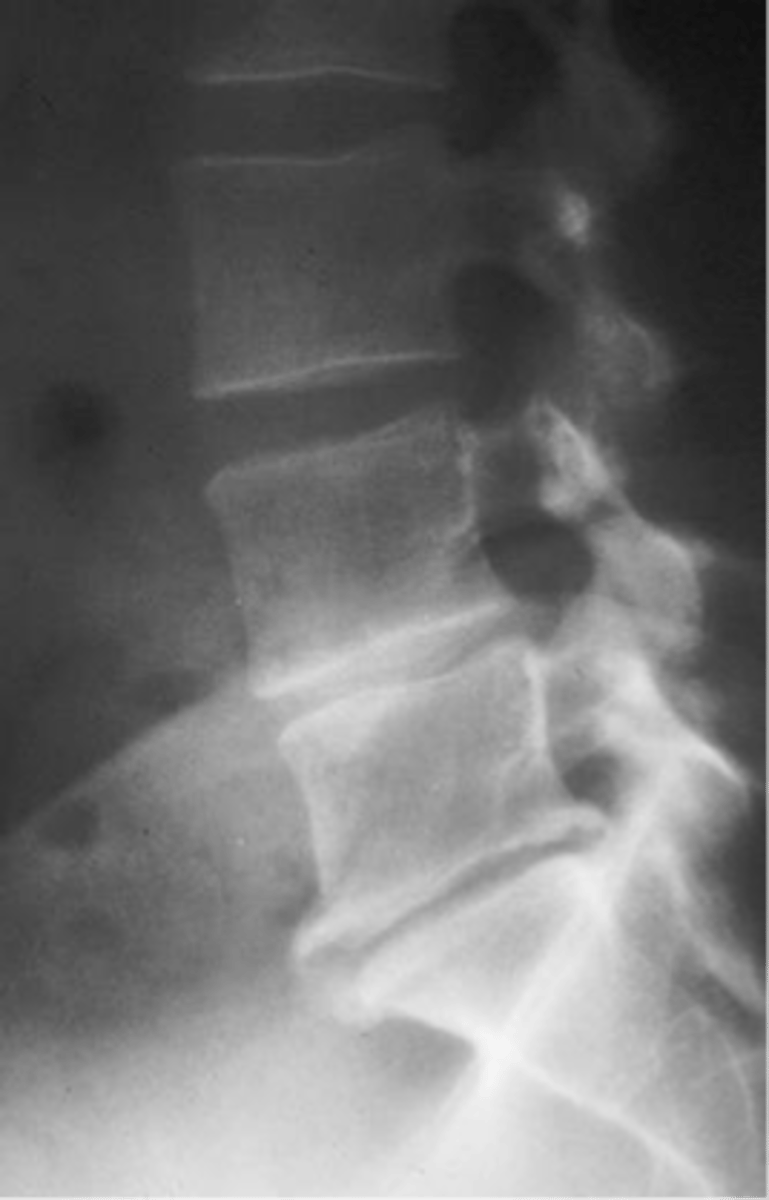
Vacuum phenomena
ID feature of degenerative lumbar spine disease

- Osteophytes
- Sclerosis
- Subluxation
- Decreased space
- Instability: degenerative spondylolisthesis
State the radiographic features of apophyseal joints in degenerative lumbar spine disease
- Decreased height
- Osteophytes
- Vacuum
- Body sclerosis
- Stenosis
- Subluxation
State the radiographic features of discovertebral joints in degenerative lumbar spine disease
- Stenosis
- Instability
- Degenerative spondylolisthesis
- Degenerative scoliosis
- Baastrup's disease
- Vertebral body sclerosis
State the complications of lumbar spine degenerative disease
Spinal stenosis
ID complication of degenerative lumbar spine disease
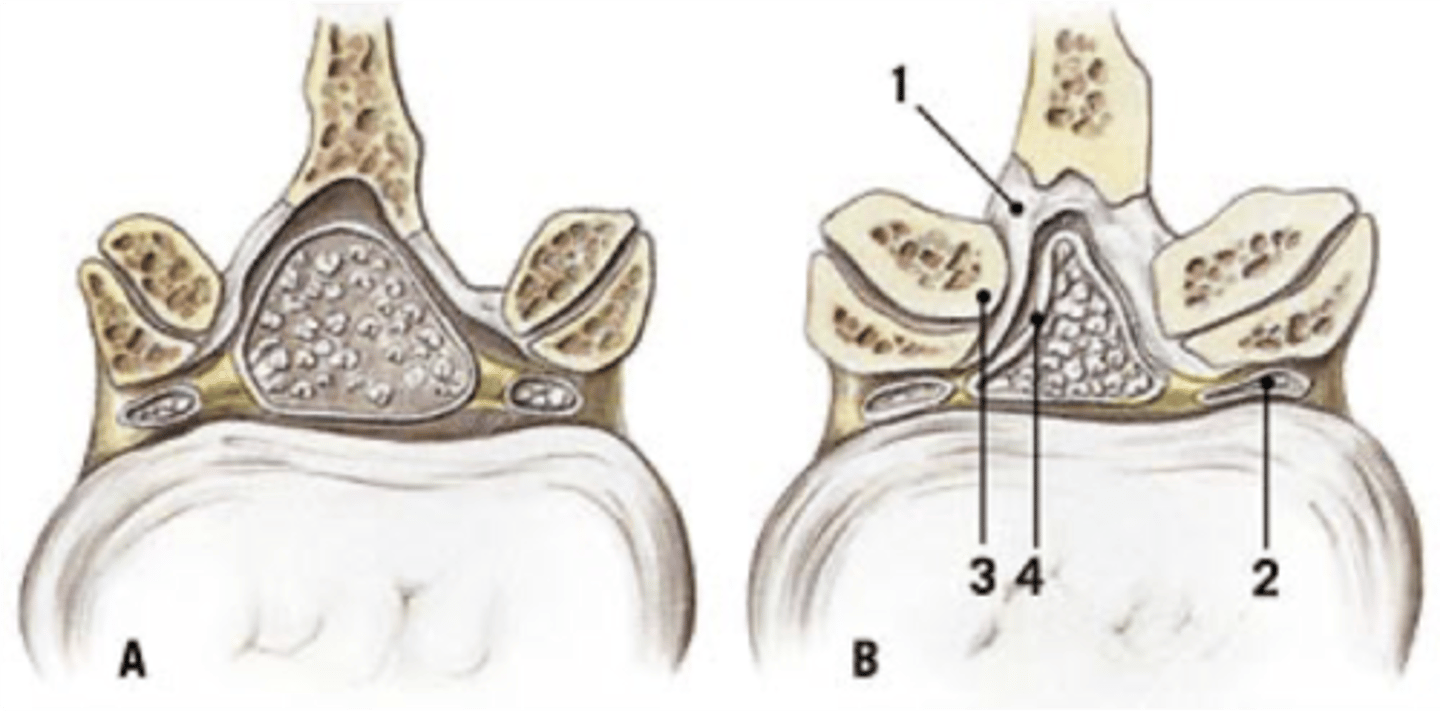
Degenerative spondylolisthesis
ID complication of degenerative lumbar spine disease

Degenerative scoliosis
ID complication of degenerative lumbar spine disease
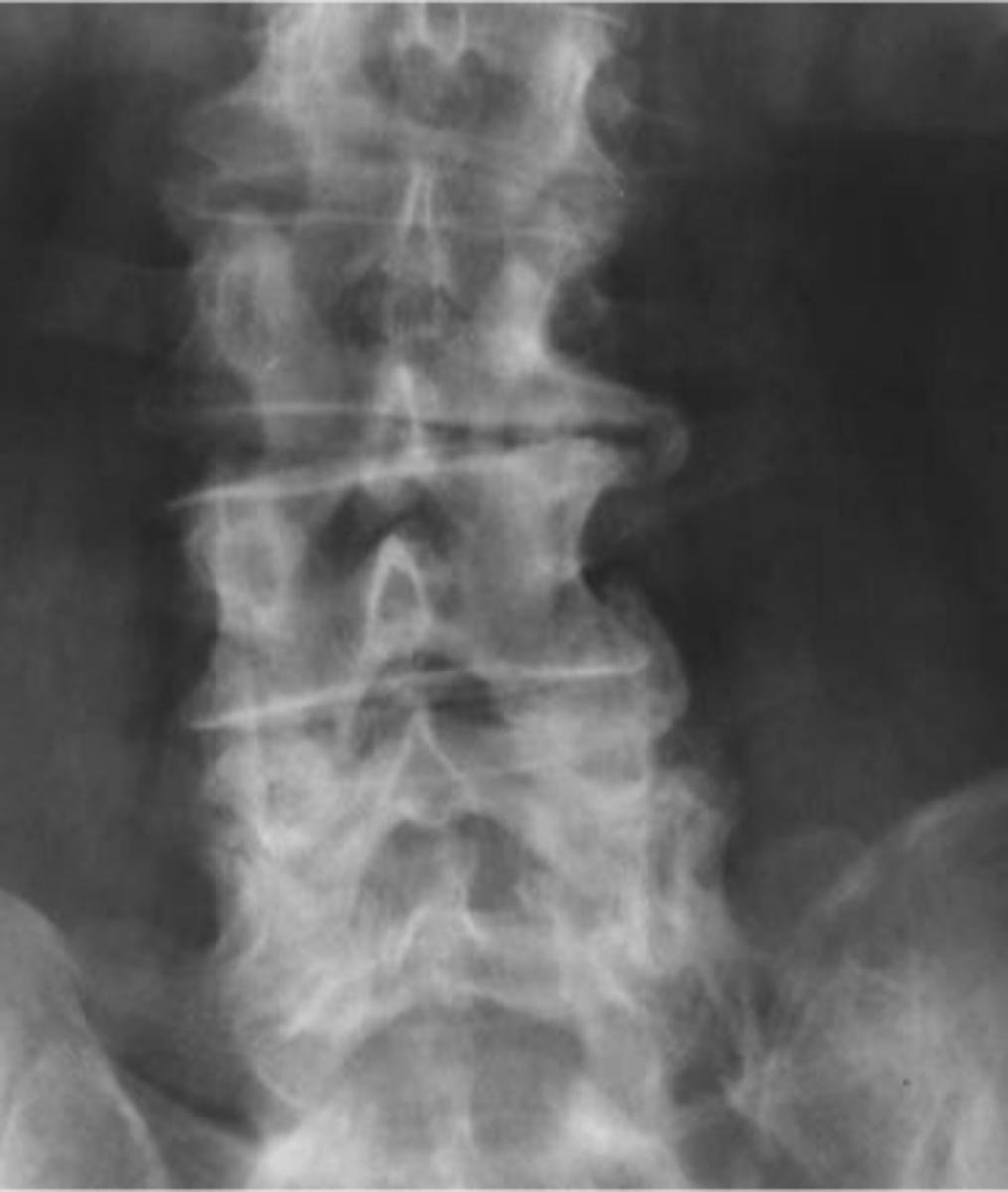
Baastrup's disease
ID complication of degenerative lumbar spine disease
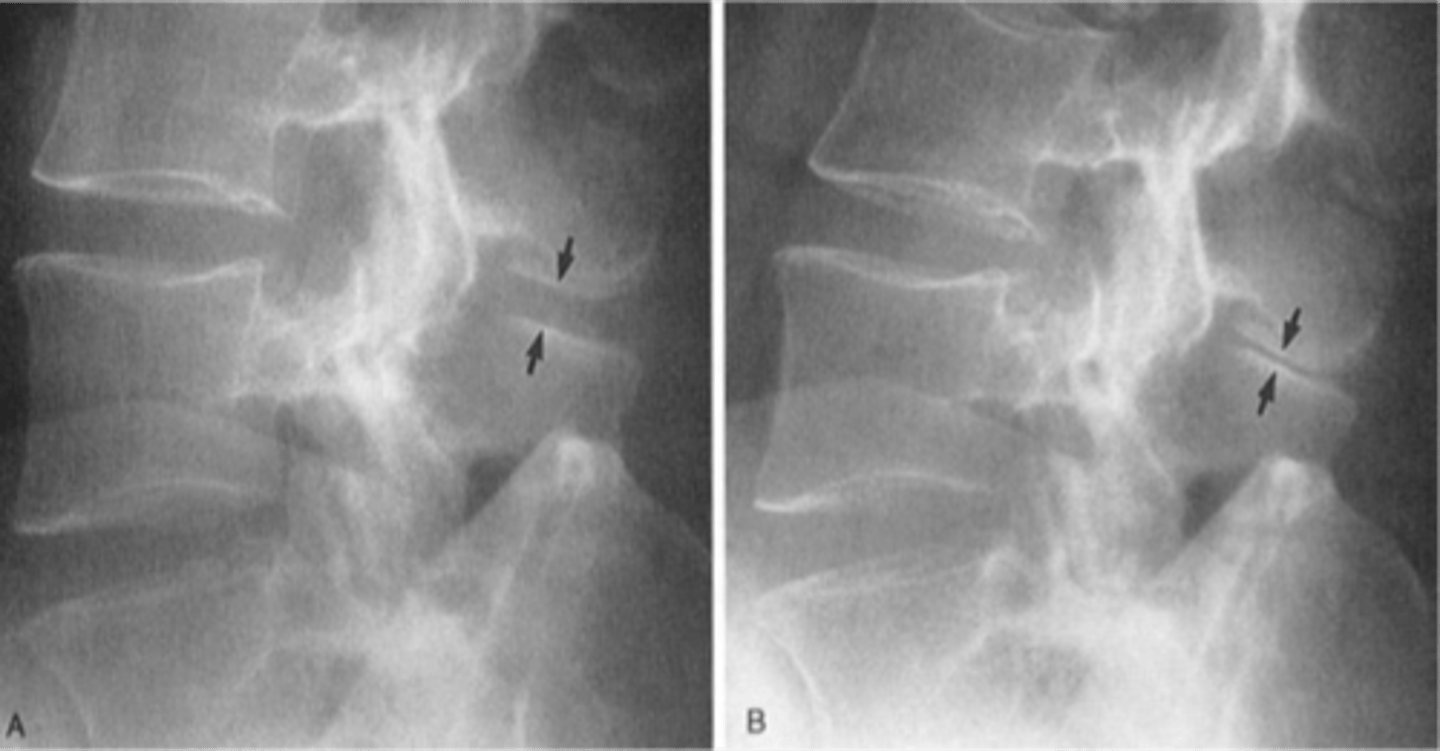
Kissing spine syndrome
Another term for Baastrup's disease
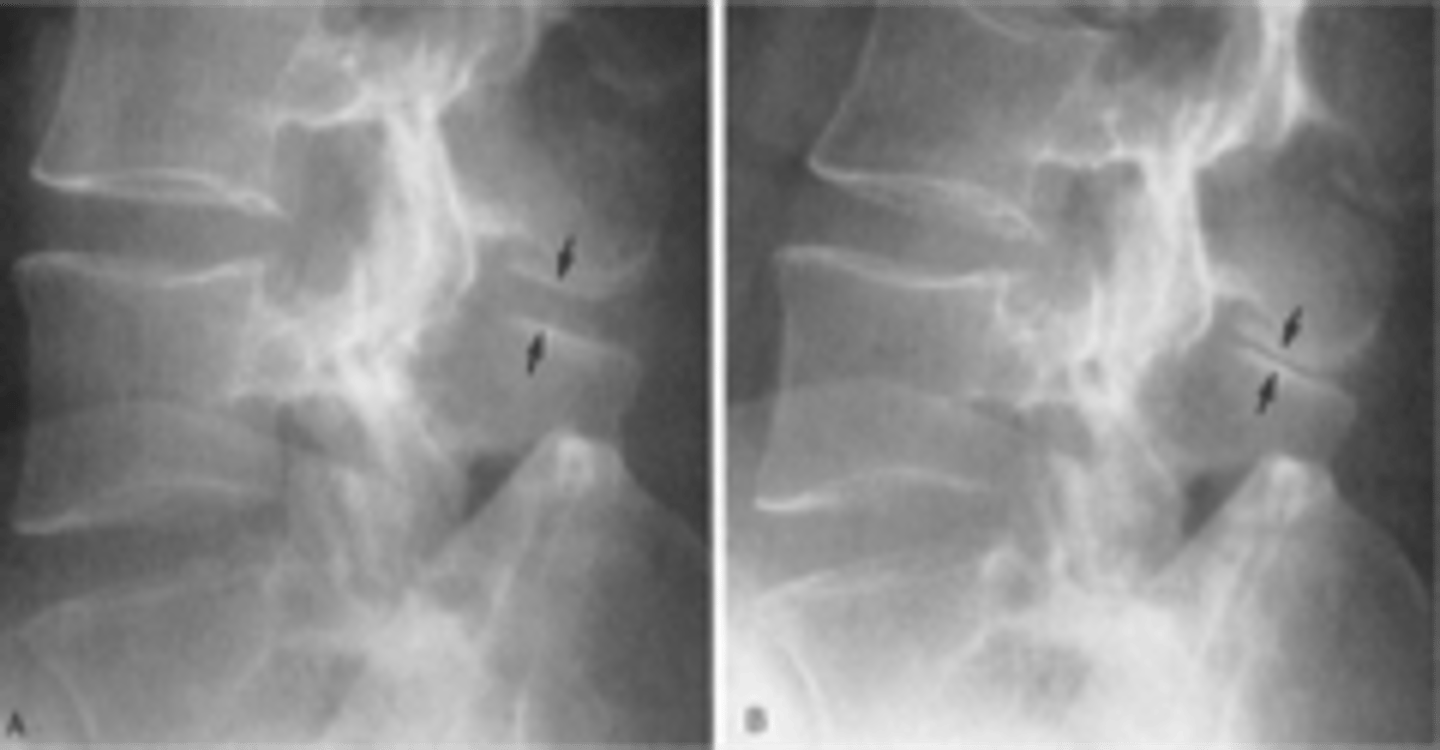
Extension
_____ is more painful for patients with Baastrup's disease
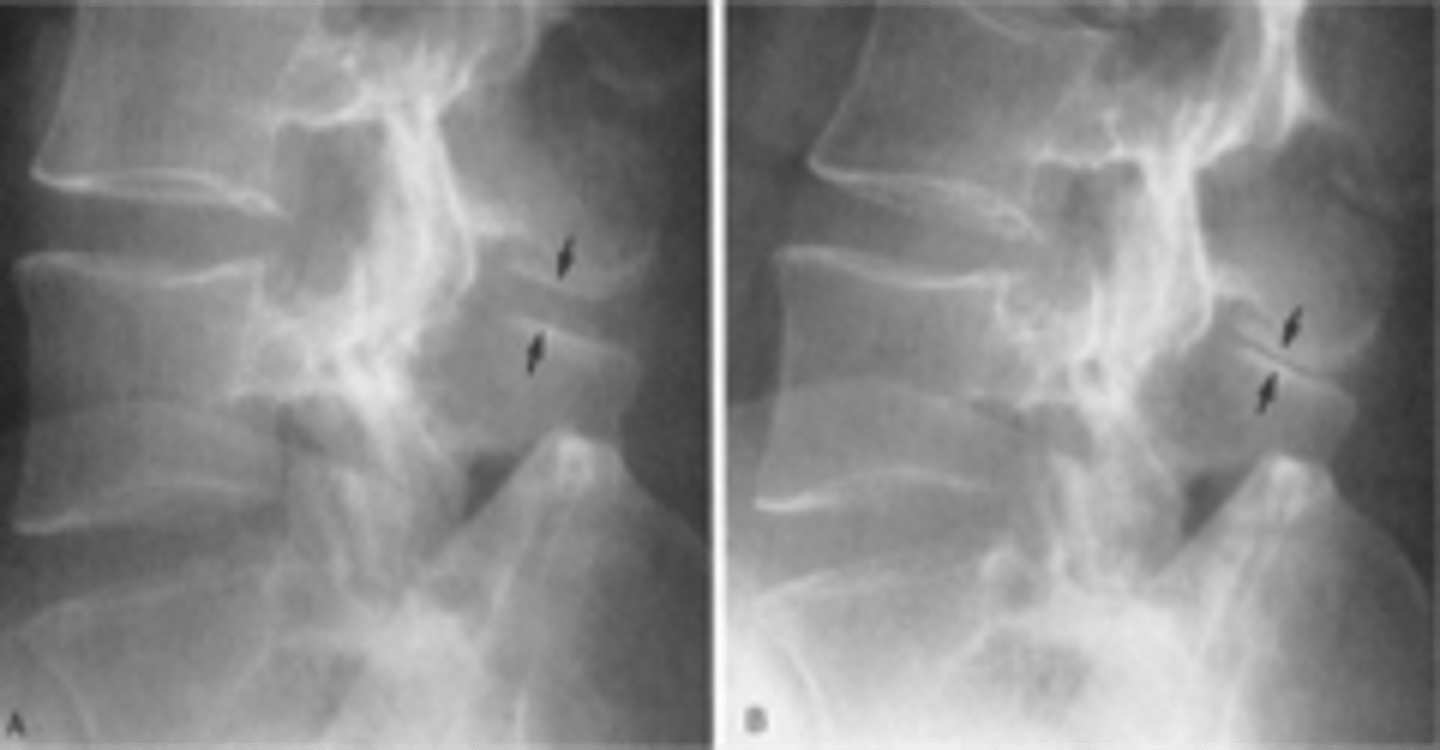
Degenerative sclerosis
ID complication of degenerative lumbar spine disease
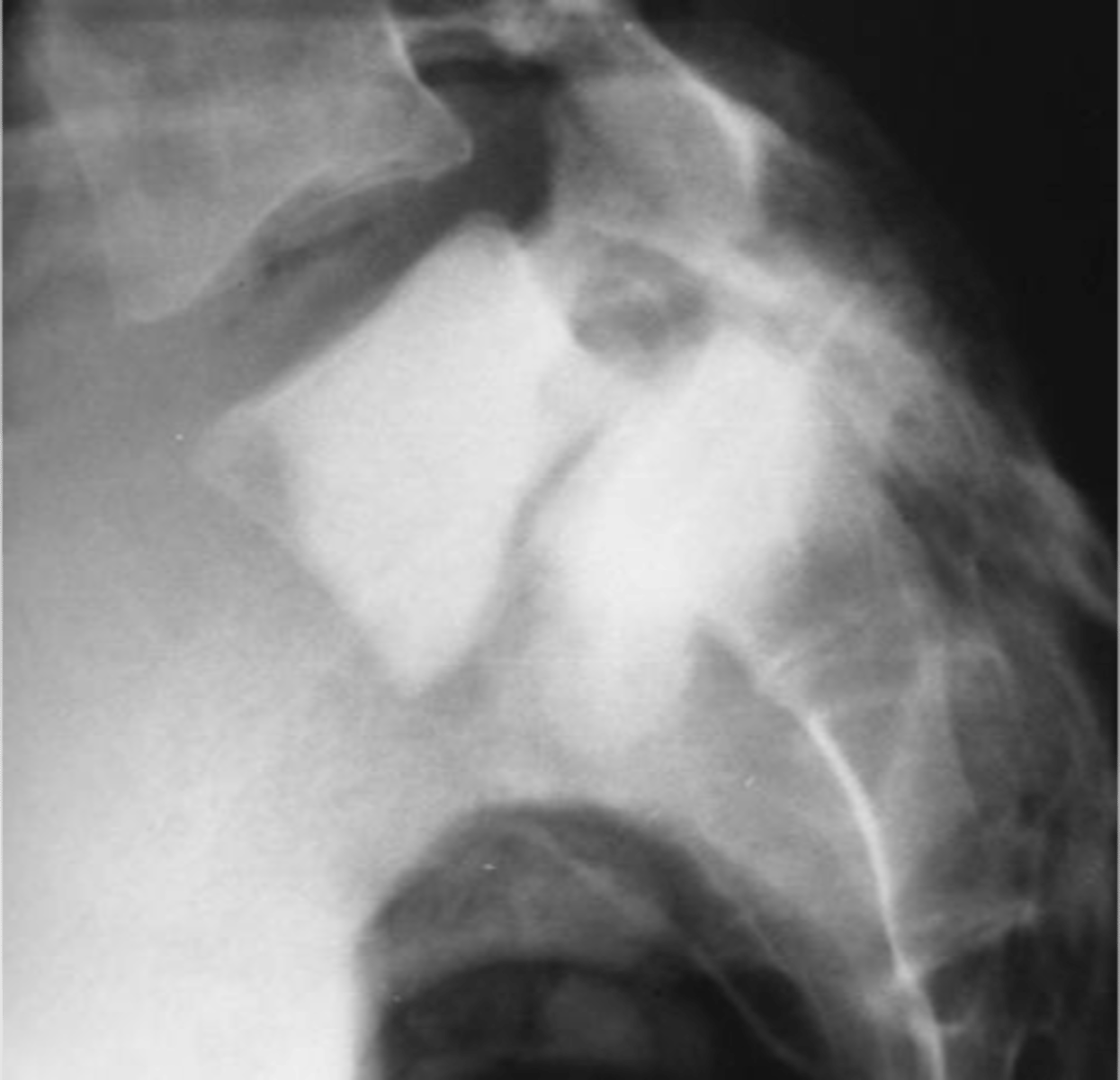
SI joint degeneration
ID complication of degenerative lumbar spine disease
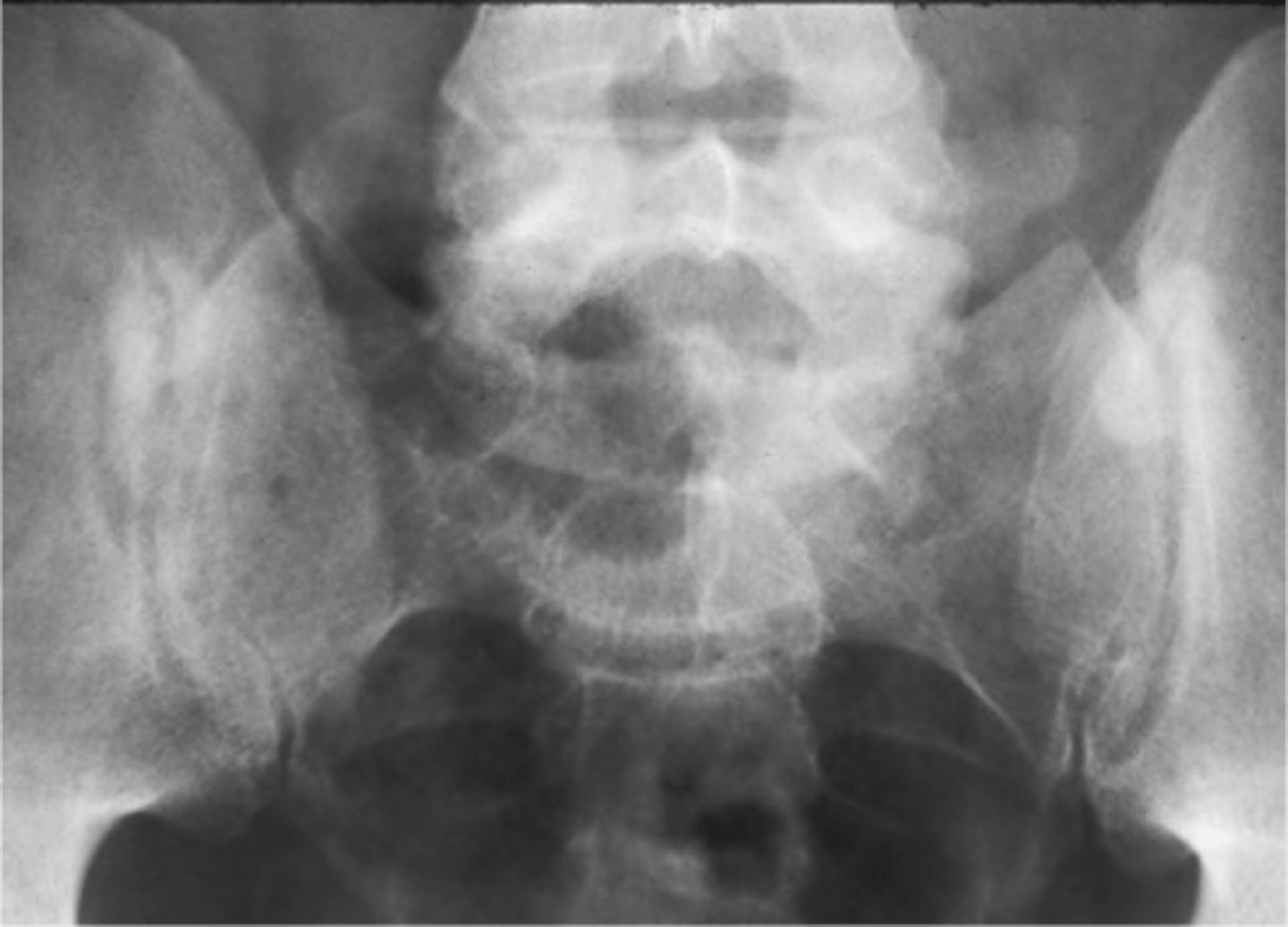
Superior
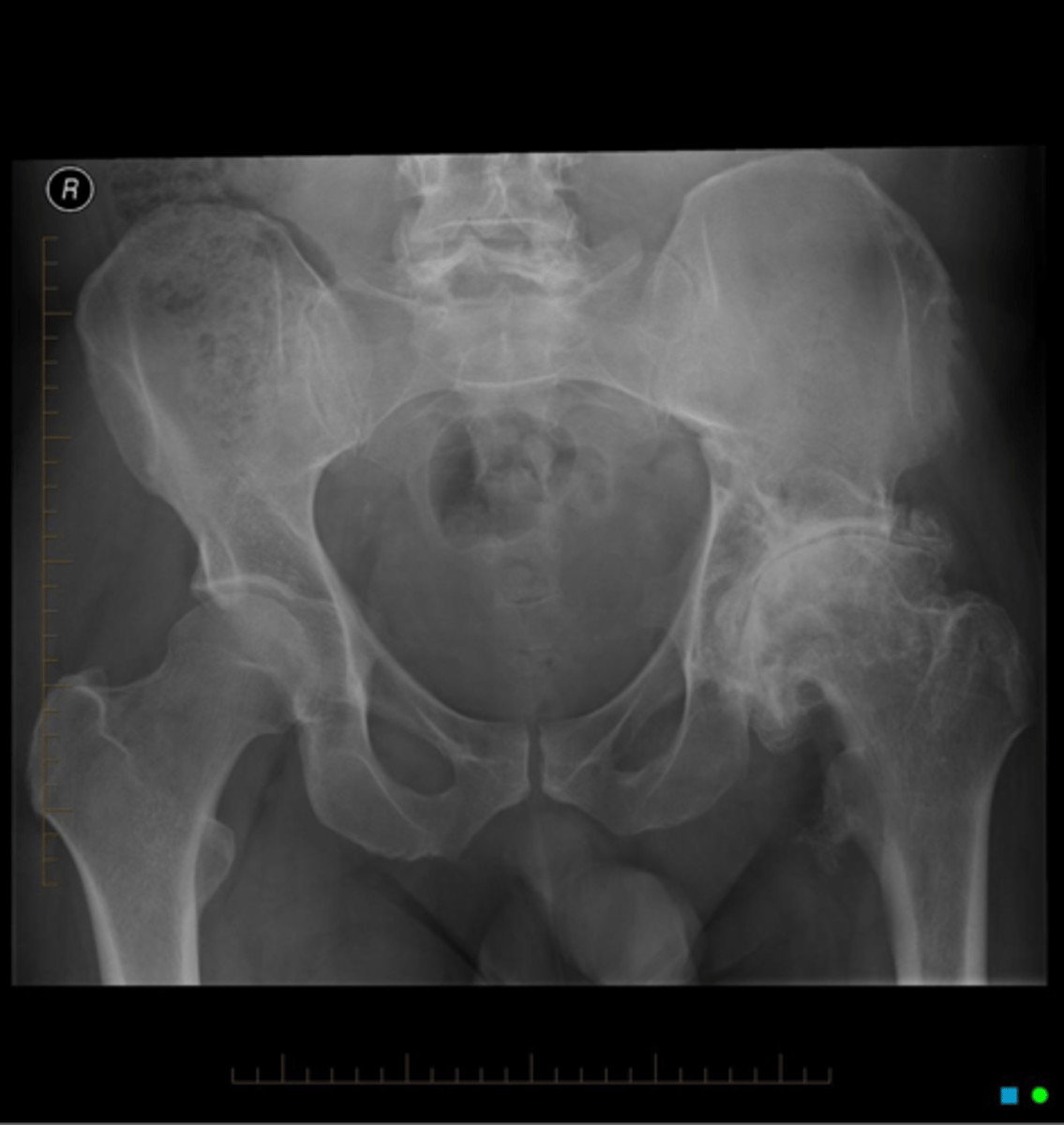
With osteoarthrosis of the hip joint, the _____ joint space is most commonly involved
- Superior migration of femoral head
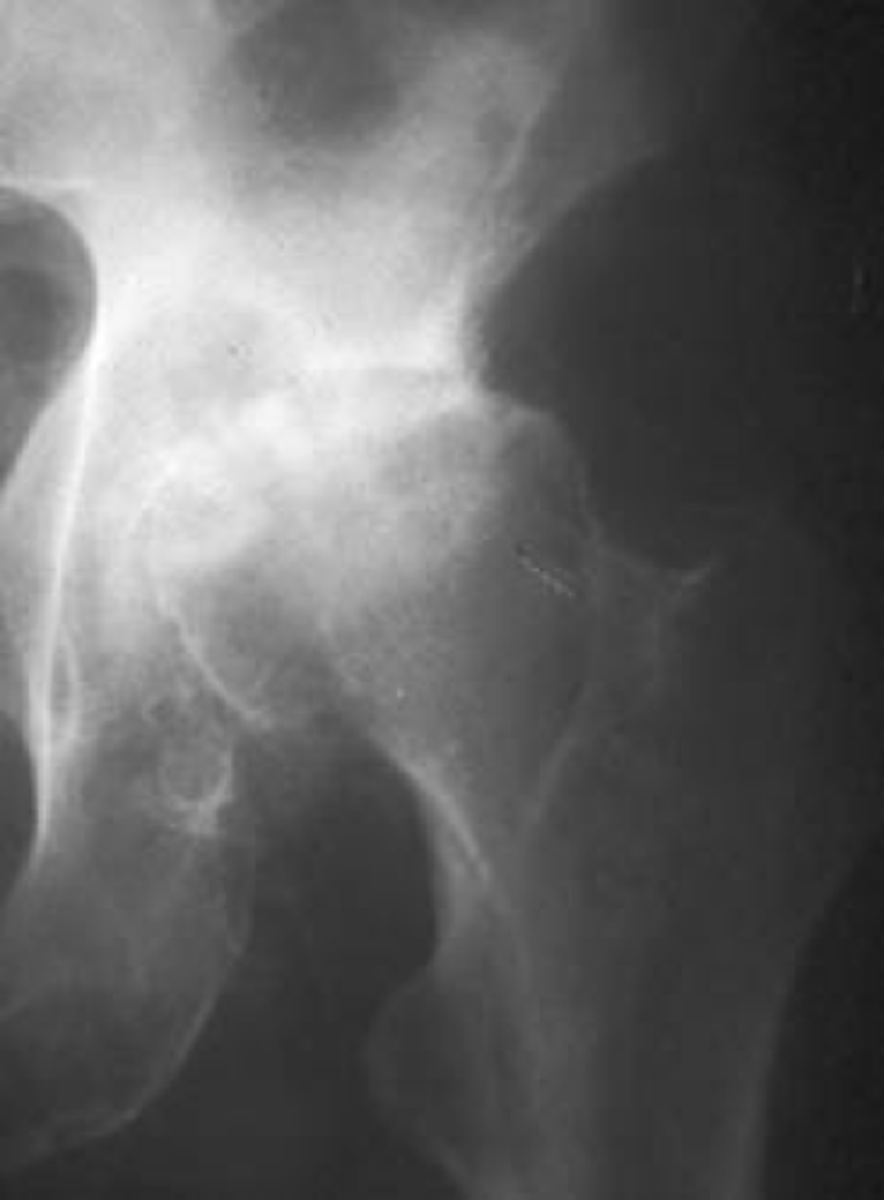
"Collar"
What is the term for the circumferential osteophytes in osteoarthrosis of the hip joint?

Hip replacement surgery
What is the treatment for osteoarthrosis of the hip joint?

Medial
With osteoarthrosis of the knee joint, the _____ tibiofemoral joint is more commonly affected
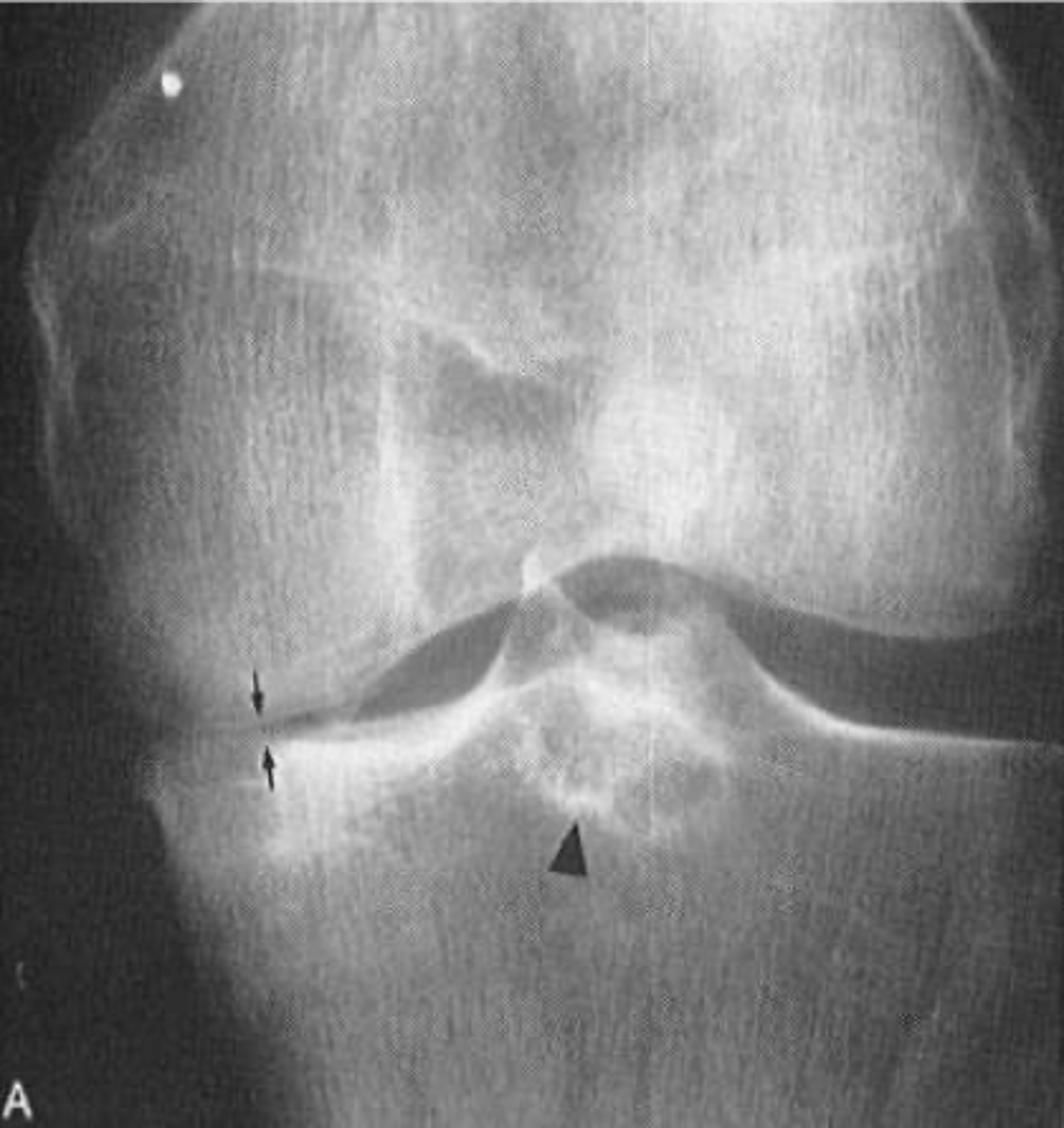
Tibial spines
With osteoarthrosis of the knee joint, osteophytes are seen on the _____

- Subchondral cysts
- Sclerosis
- Genu varum
State the other radiographic features of osteoarthrosis of the knee joint
- AP weight-bearing view
- Tunnel view
What views do we need to see osteoarthrosis of the knee joint?
Patellar tooth sign (enthesophyte)
ID radiographic feature of osteoarthrosis of the knee joint
Trauma
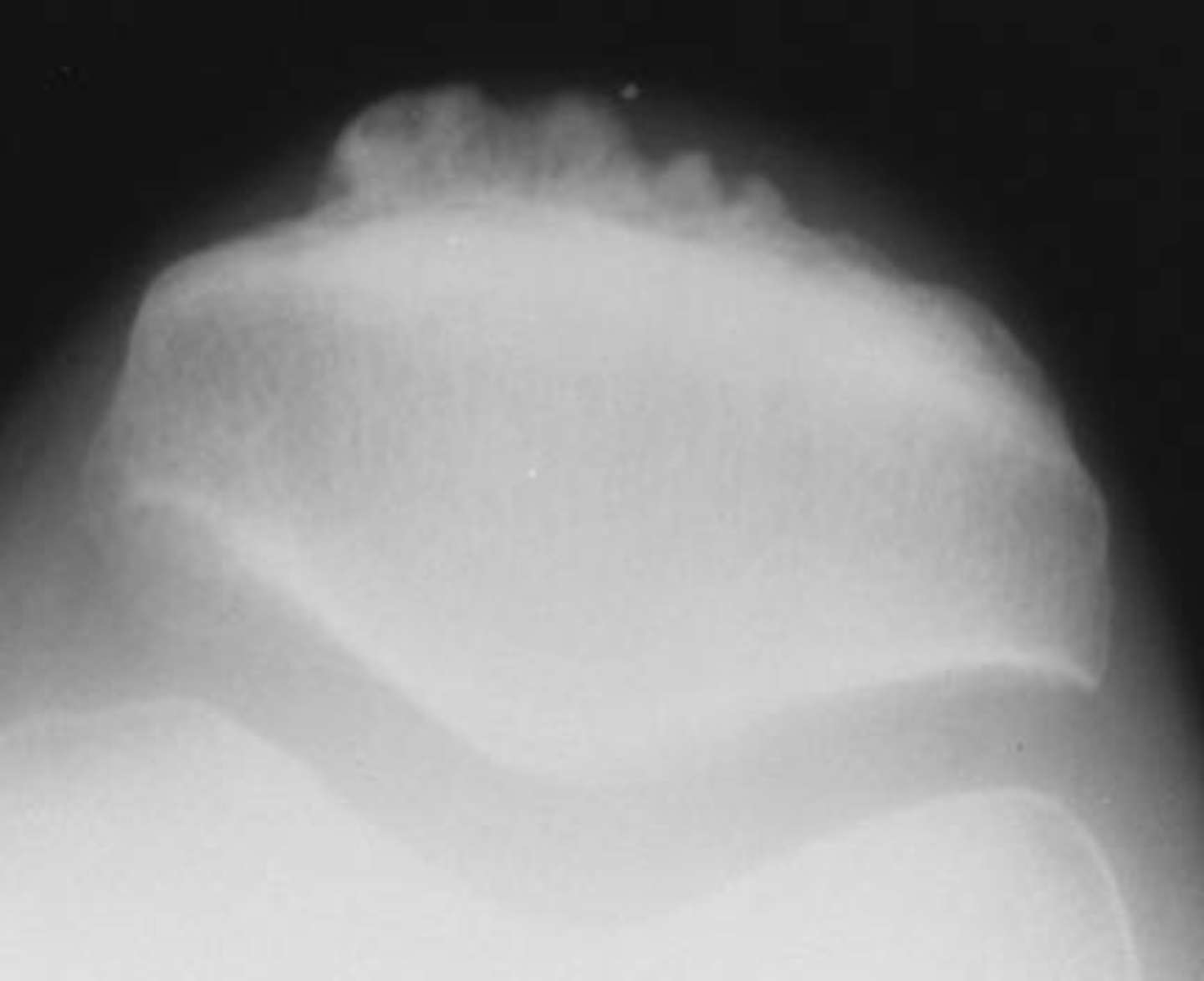
Osteoarthosis of the ankle is rare except after _____

Enthesophyte
With osteoarthrosis of the ankle, an _____ can be seen in the calcaneus
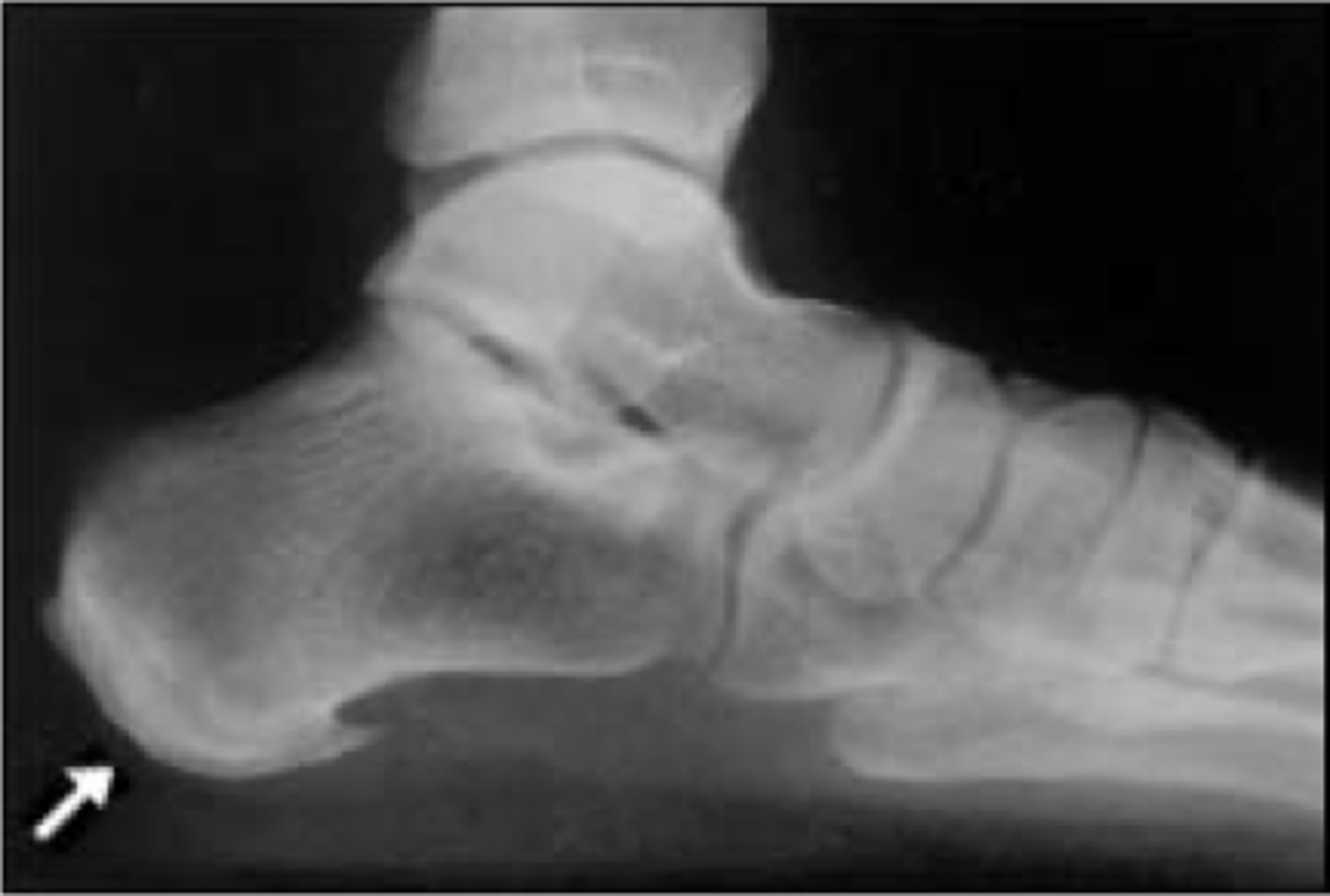
- 1st MTP
- Bunion
• Hallux valgus
State the clinical features of osteoarthrosis of the foot
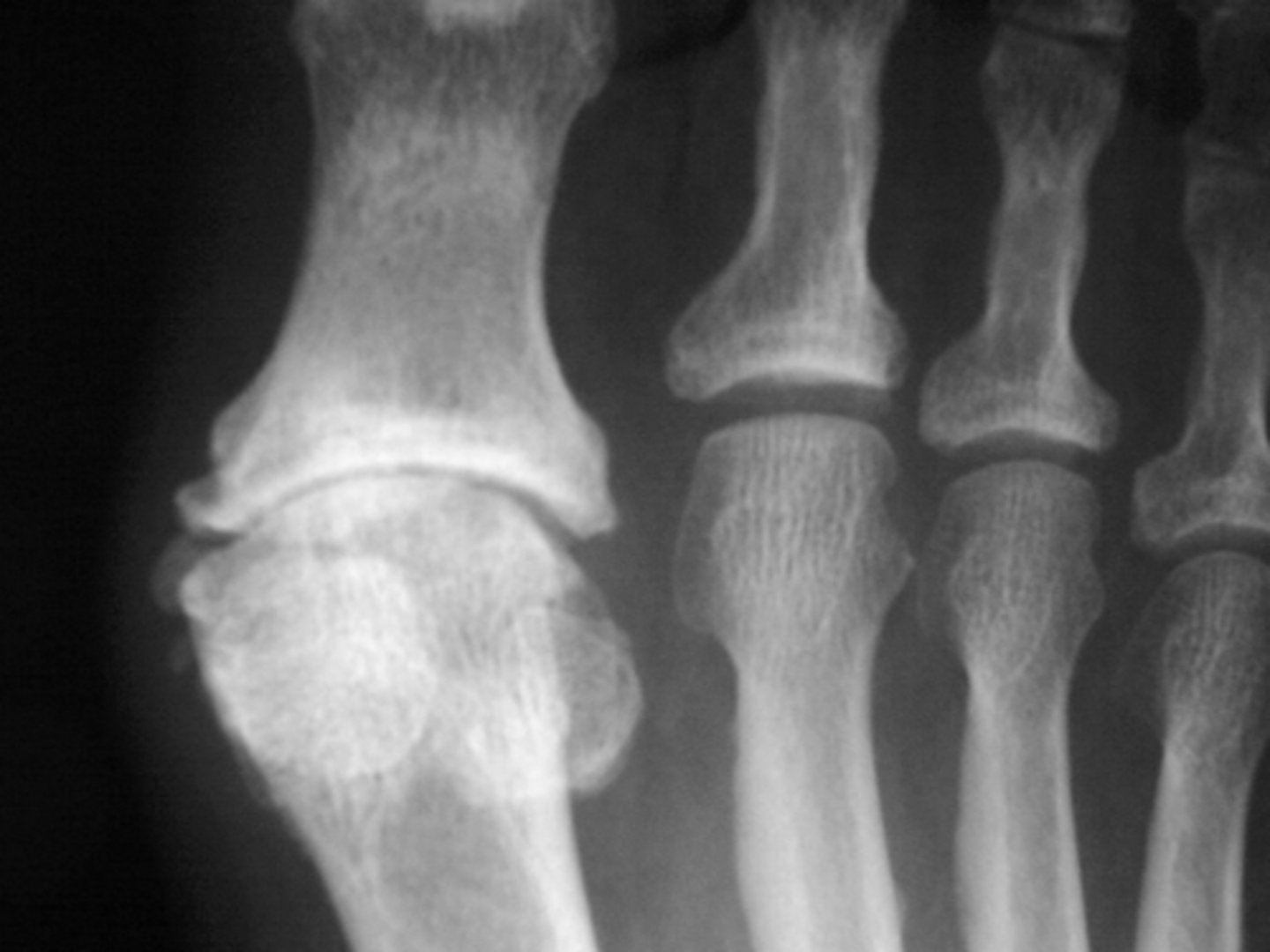
Uncommon
Osteoarthrosis of the shoulder is _____
- AC joint (MC)
- Glenohumeral joint
• Rare
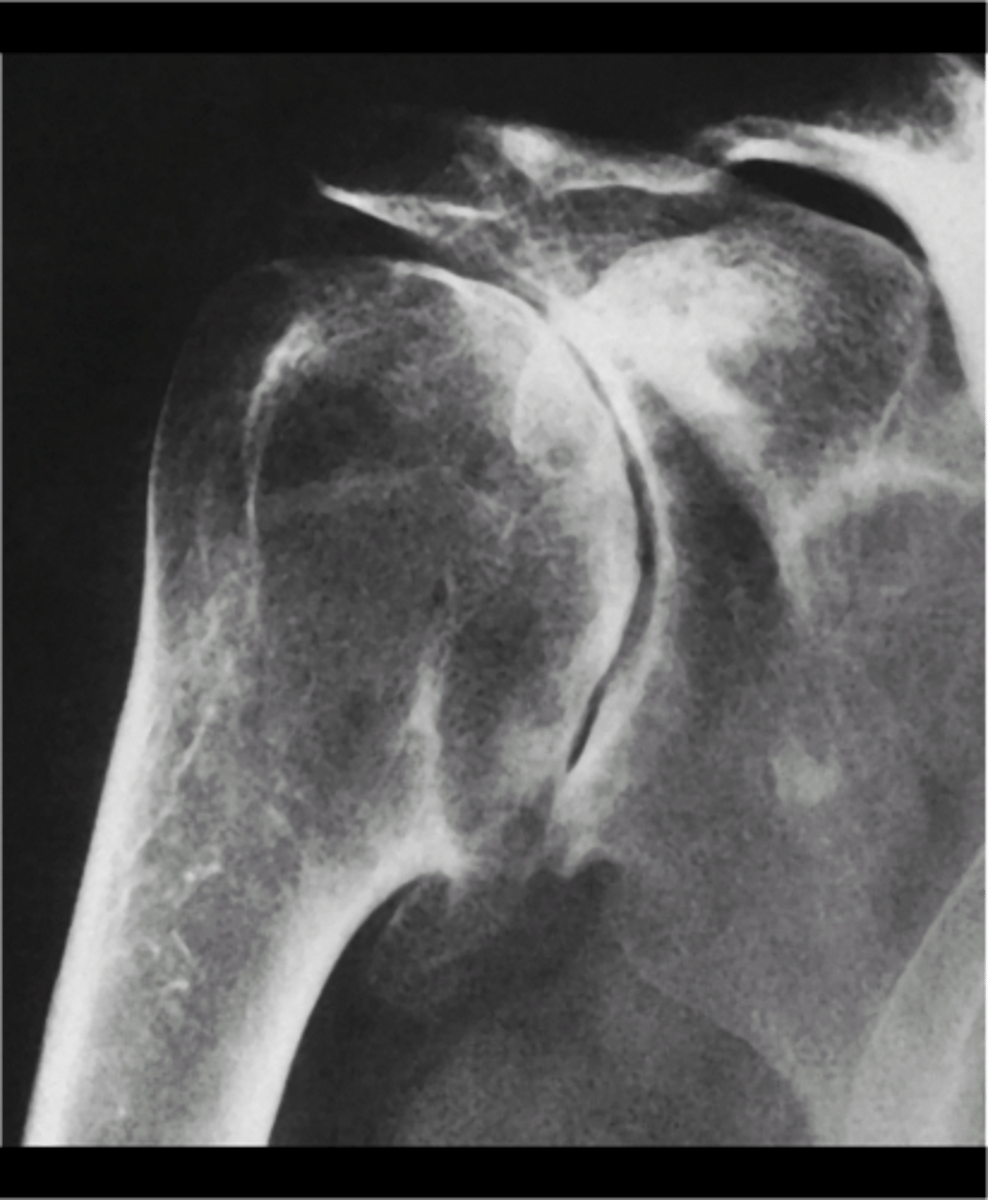
- Trauma
- Occupational or activity-based stressors
- Altered biomechanics (rotator cuff tendinopathy)
What is osteoarthrosis of the shoulder secondary to?

- Calcified cartilaginous fragments (joint mice) frequently seen
- Triceps enthesophyte may accompany it
State the radiographic features of osteoarthrosis of the elbow

- Trauma
- Occupational or activity-based stressors
What is osteoarthrosis of the elbow secondary to?
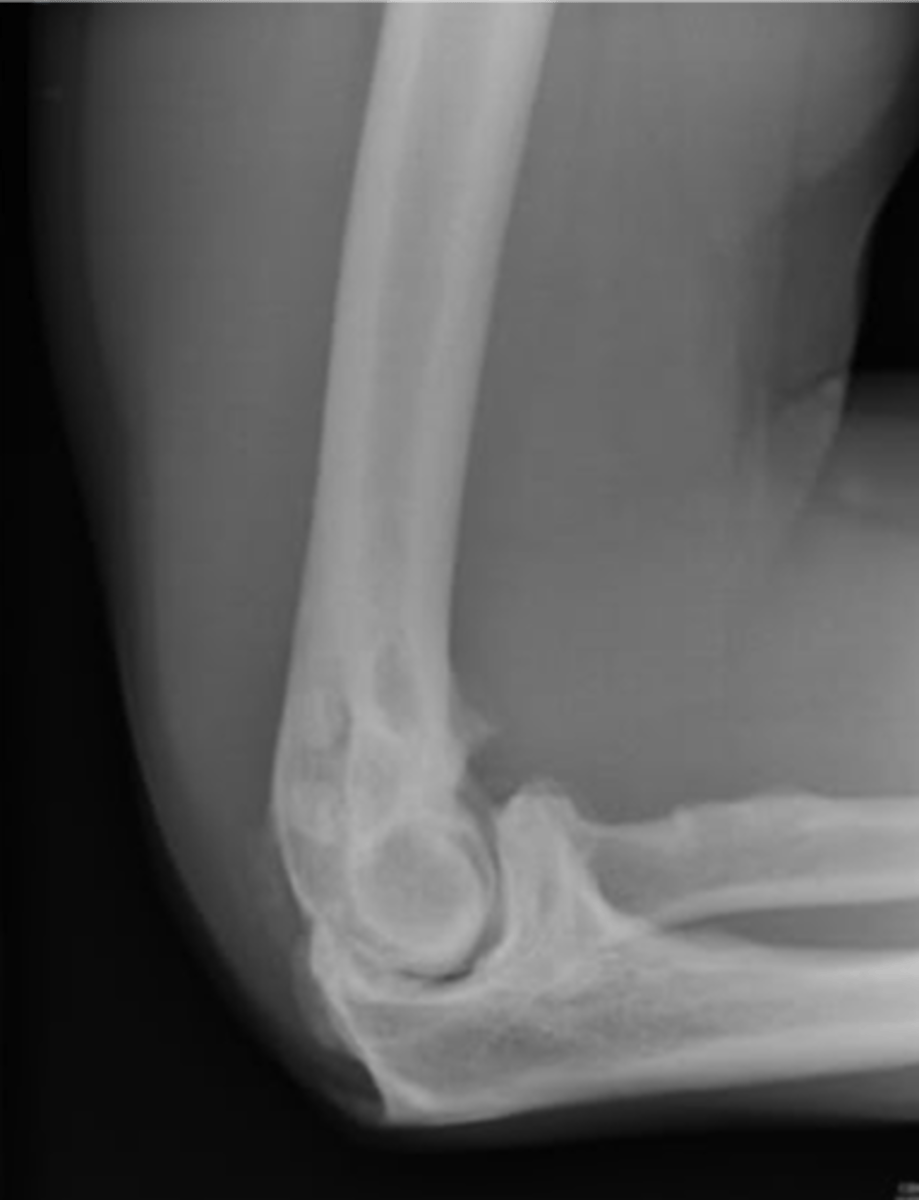
1st metacarpal-trapezium joint
State the common location of osteoarthrosis of the wrist
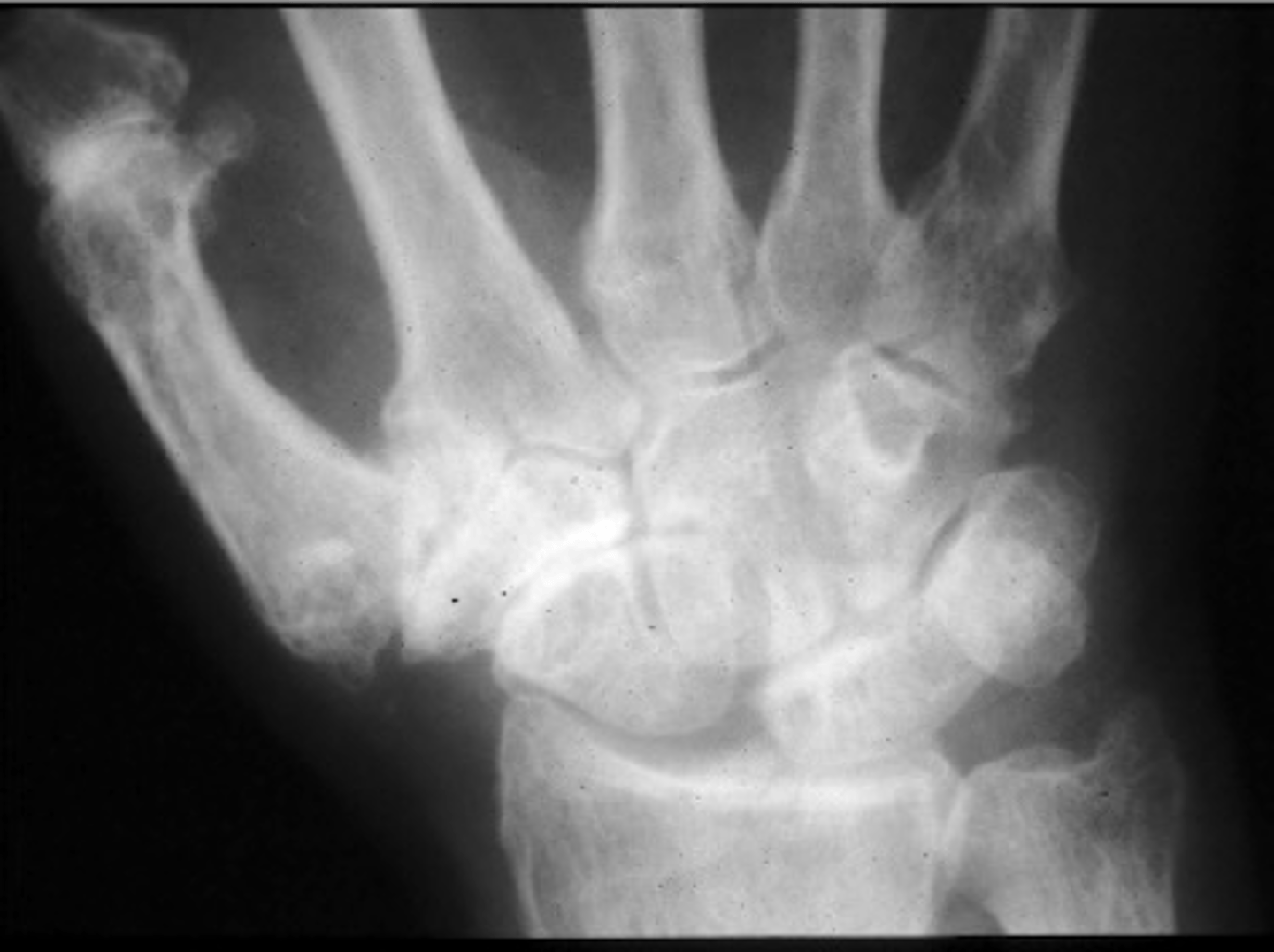
Trauma
What is osteoarthrosis of the wrist secondary to?

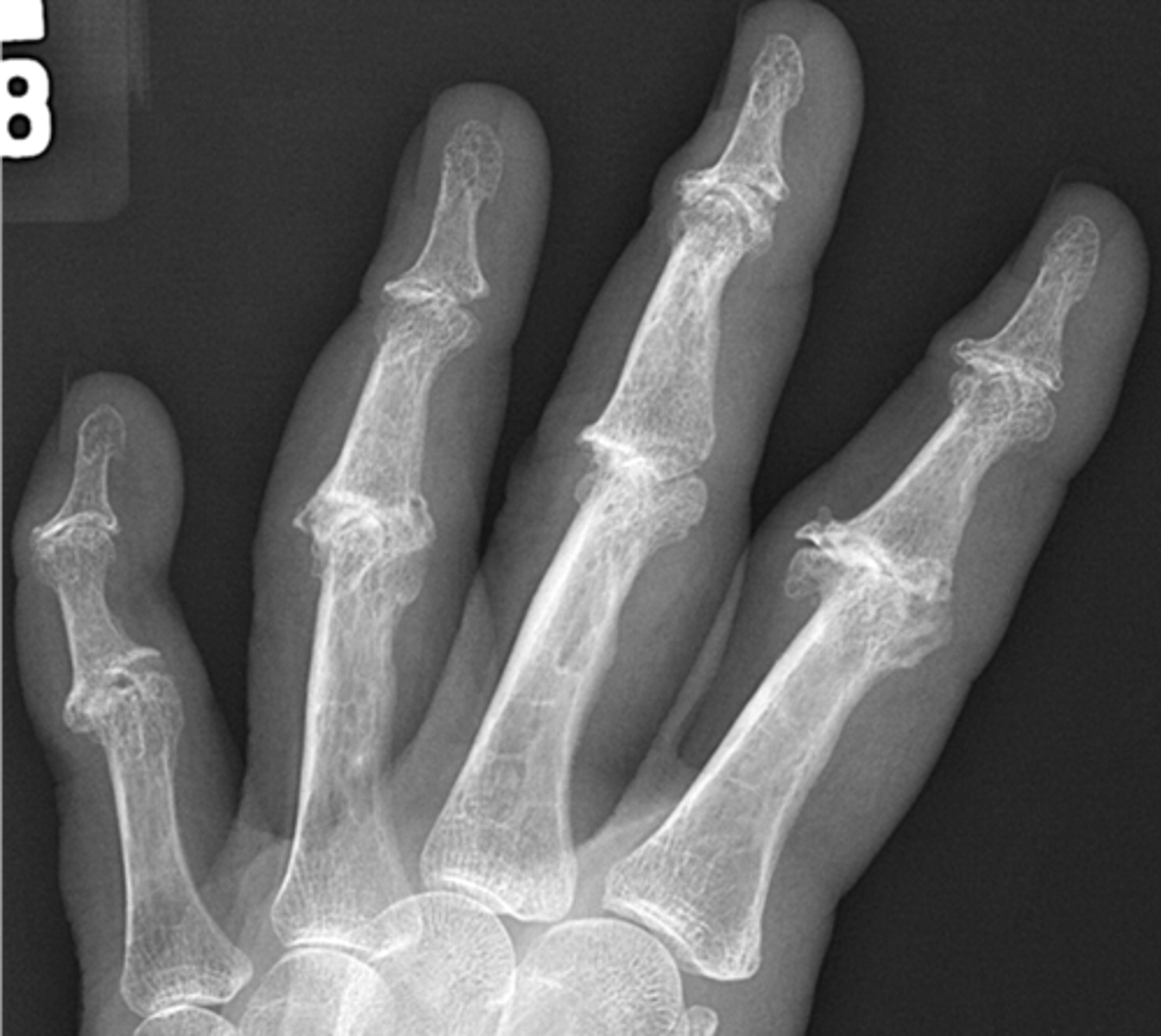
Heberden's nodes
With osteoarthrosis of the hand, what radiographic feature is present in the distal interphalangeal joints?

Bouchard's nodes
With osteoarthrosis of the hand, what radiographic feature is present in the proximal interphalangeal joints?
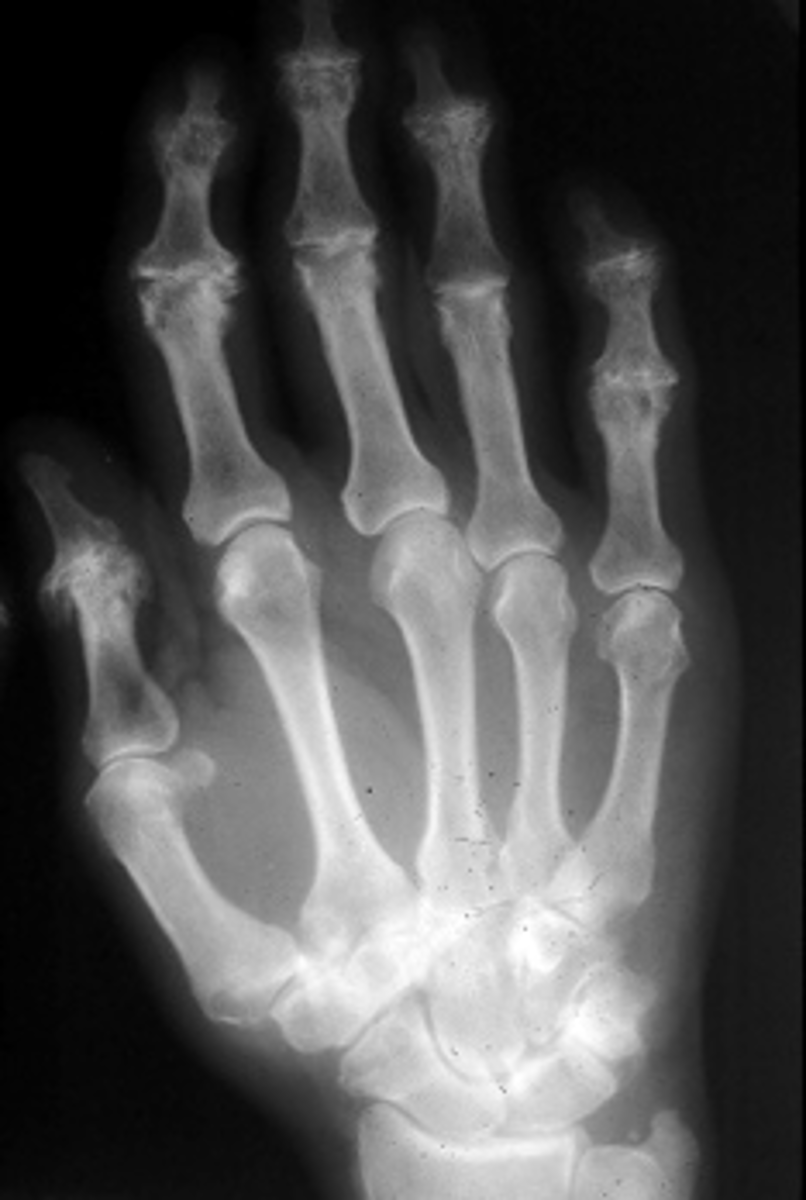
- Middle-aged females
- Inflammatory variant of osteoarthritis
- Symmetric
- DIPs and PIPs
- Normal labs
- Pain, edema, redness
- Residual deformities
- Chronic progressive changes
State the clinical features of erosive osteoarthritis

- Osteophytosis
- Subchondral sclerosis
- Loss of joint space
State the degenerative joint disease-like changes seen with erosive osteoarthritis
- Erosions (including central area)
- Periostitis
- Ankylosis
State the inflammatory-like changes seen with erosive osteoarthritis
Gull wing deformity
ID radiographic feature of erosive osteoarthritis

- Ligamentous calcification and ossification
- Most prominent in the spine, involving the anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL)
State the radiographic features of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)
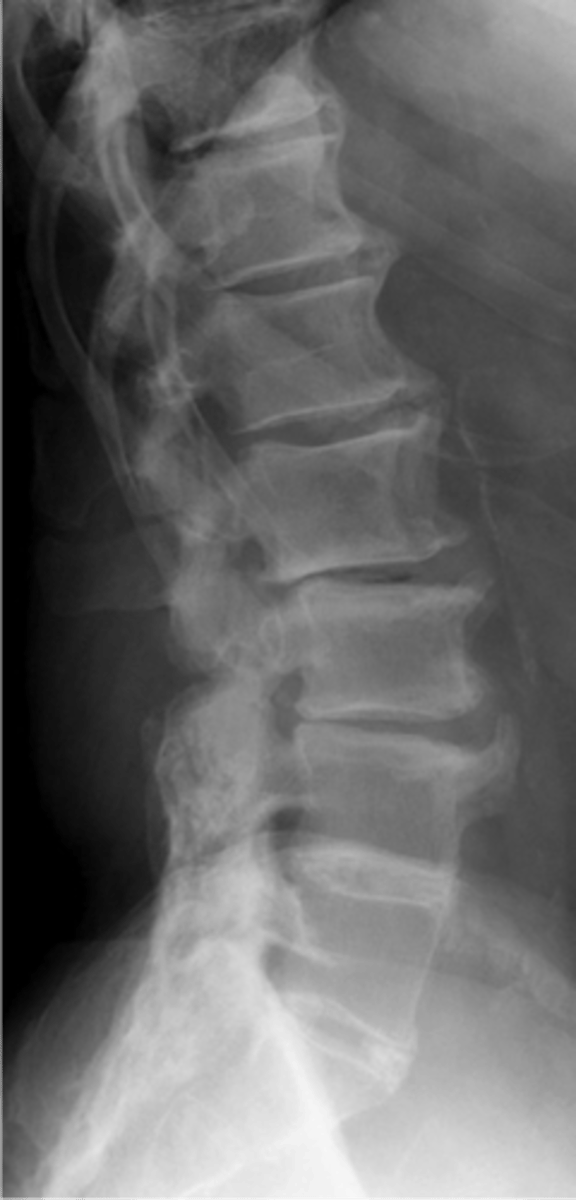
- 25% of men over 50 y.o.
- 15% of women over 50 y.o.
State the epidemiology of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)

- Mild low back pain and stiffness
- Dysphagia
- Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
- 20% have diabetes mellitus
State the clinical features of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)

- T7-T11 MC
- Cervical
- Thoracic
- Lumbar
- Extraspinal enthesophytes
- Ligament ossification
State the target sites of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)
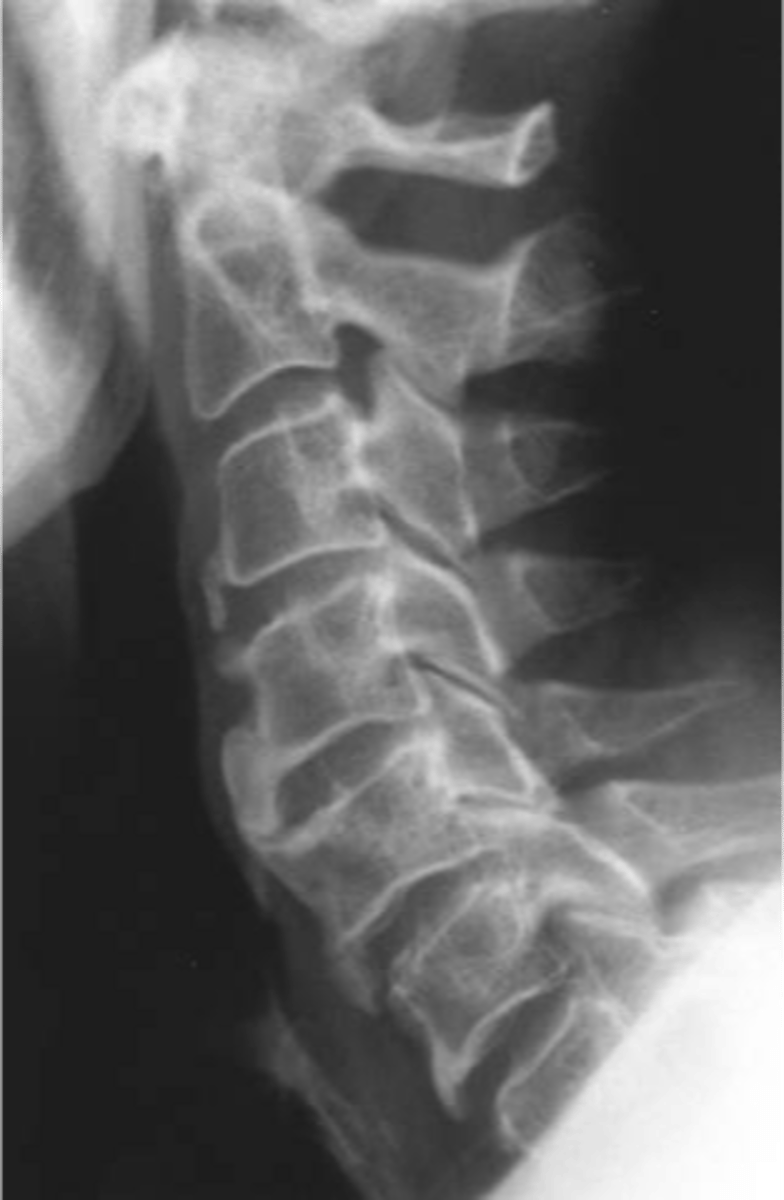
- Flowing hyperostosis
- Preservation of disc spaces
- 4 contiguous segments
- Absence of facet ankylosis
- No sacroiliac involvement
State the criteria for diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)
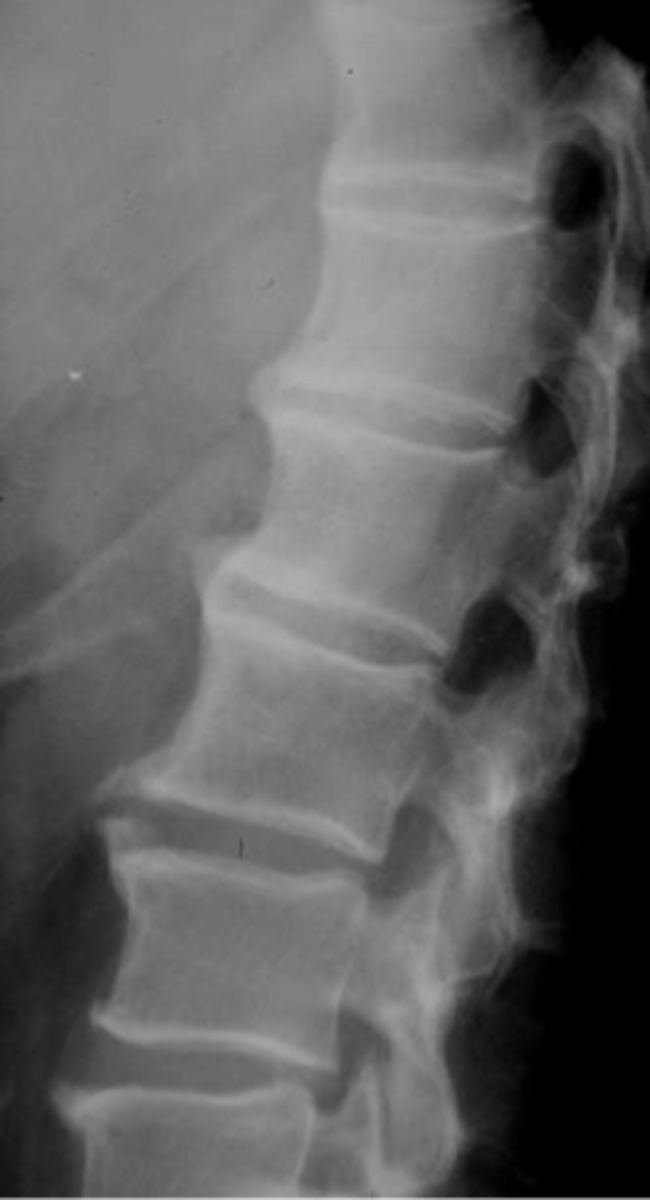
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL)
ID complication of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)