Ecology ,Biodiversity and water carbon cycle
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Ecosystem
Ecology study of how plants & animals interact each other & with their surroundings
Ecosystem
Group plant , animal & other organisms interact with each other and w their environment
Examples of environment
Dessert , grassland
Habitat
Small local part of ecosystem
Examples of habitat
Grassland, woodland, local park
Community
all organisms living in particular area
Adaption
Structure or behavior helps organisms survive in habitat or within community
Producer
Green plants make food
Examples of producer
Grass , Nettles
Consumer
Organism take in food
Herbivore
Eat only plants
carnivore
Eat only animals
Omnivore
Eat both
Food chain
List organisms which each organism eaten by next on chain
Food web
Number interlinked food chains
Decomposers
feed on dead + decaying organisms bad indigestion parts of plant + animal matter in faeces .
Trophies level
Position of organism on food chain
List all consumers
primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Predator
Animal hunts + kills another animal for food EX . FOX
Prey
Animal hunted + killed for food EX. RABBIT
Adaptions
fox - forward facing eyes + sharp teeth = help find + kill prey
Rabbit - side- facing eyes + excellent hearing = help hear + run from predators
Competition
Plants - space, light, water
Animals - food, territory, mates
Interdependence
Way which plants + animals rely on each other in ecosystem.
some relationships both organisms benefit
Others only one benefit sometimes causing harm to other
Examples of interdependence
flower depend bee for pollination + bee depend on flower for nectar
Tree depend on bird to disperse seeds + bird depend tree for food + shelter
Flow of matter in ecosystem
living organisms need matter (carbon + nitrogen) carry out cell processes EX GROWTH + REPAIR
plant absorb matter from air + soil. Animals get matter by eating plants + other organisms.
Matter released into environment when organism respires, produces waste or dies Brocken down by decomposers.
Matter constantly recycled from environment into living organisms + back into environment.
Flow of energy in ecosystem
Living organisms need energy carry out cell processes EX GROWTH REPAIR
sun primary source of energy for life on earth.
Light energy from sun captured by green plants + changed to chemicals (glucose) in photosynthesis
Some glucose used by plant for cell processes + some used build plant tissue
Plant eaten by animal, animal uses energy plant tissue to carry out cell processes build more animal tissue.
Rest energy released to environment as heat or waste
Plant or animal die, decomposers release nutrients to soil + heat energy to environment
Energy not recycled in ecosystem. Enters ecosystem as light energy and leaves as heat energy.
How identify plants + animal present inhabits
Identification book or key
Set of questions help identify species of organisms
Quantitive
Records number organisms present
Qualitive
Presence or absence of organism
Estimating no. Plants
Instrument = Quadrant
Unit = 1 meter squared / 0.5 m squared
Throw pencils over shoulder into habitat area
Place quadrant on ground pencil middld
Record name each plant found inside quadrant
Repeat all previous steps fixed number time
Calculate percentage frequency
biotic factors
Living components of ecosystem plants, animals , fungi + bacteria
Abiotic
non living components
List 4 abiotic factors and equipment
Air water soil > digital thermometer
Light intensity > lux/ light meter
Wind speed > anemometer
Soil pH > pH meter
Biodiversity
Variety of living things on Earth
Sustainability
Take steps to protect + maintain ecosystem for future
Conservation
Wise management of natural resources
Importance of biodiversity
human depend other living things for food, shelter + materials
Animals (insects) important for pollinating plants .
Living things ( bacteria, fungi ) important decomposers break down matter + recycle nutrients
Plant + fungi produce important chemicals used medicine
Human rely healthy biodiverse environment for recreation + leisure
Threats to biodiversity
1. Modern food production
Pollution
Deforestation
Climate change + burning fossil fuels
Invasive species
Conservative methods used food production protect ecosystem for future
land clearing - make way growing crops destroys habitat ( forests, hedgerows)
Conservation - People not allowed remove hedgerows during nesting - breeding season for birds
Agriculture - overuse fertilizer. Fertilizer + slurry may seep into rivers , streams causing fish death
Conservation - slurry only spread dry weather
overfishing- fishing nets small mesh takes immature fish + fish will not be eaten out of water
Conservation - use nets larger mesh size
Types of pollution
Land pollution - illegal dumping
Water pollution - sewage spill into sea
Air pollution - smog cities
Conservation to pollution
recycle materials
Reduce waste
No burn fossil fuels
no dump illegal
Deforestation
Large areas forests cut down make way for buildings, destroys habitat many species of plants and animals
Conservation - replanting trees, only cutting section instead of forest
Climate change
Changing of habitat species + plants EX C.C reduction sea + land ice. Reduce hunting ground for polar bears.
conservation - reduce carbon emissions. Renewable energy . No burn fossil fuels
Invasive species
non-native species plant or animal introduced into environment. Introduced to environment by humans EX grey squirrels
Invasive compete w native species for food + space, threaten biodiversity ecosystem.
EX , Japanese knotweed invasive plant species can damage buildings + soil erosion
Crayfis Cccccccccccccc
Managing invasive species
Tell public about presence of Japanese knotweed area + stop farmers cutting which lead to further spreading
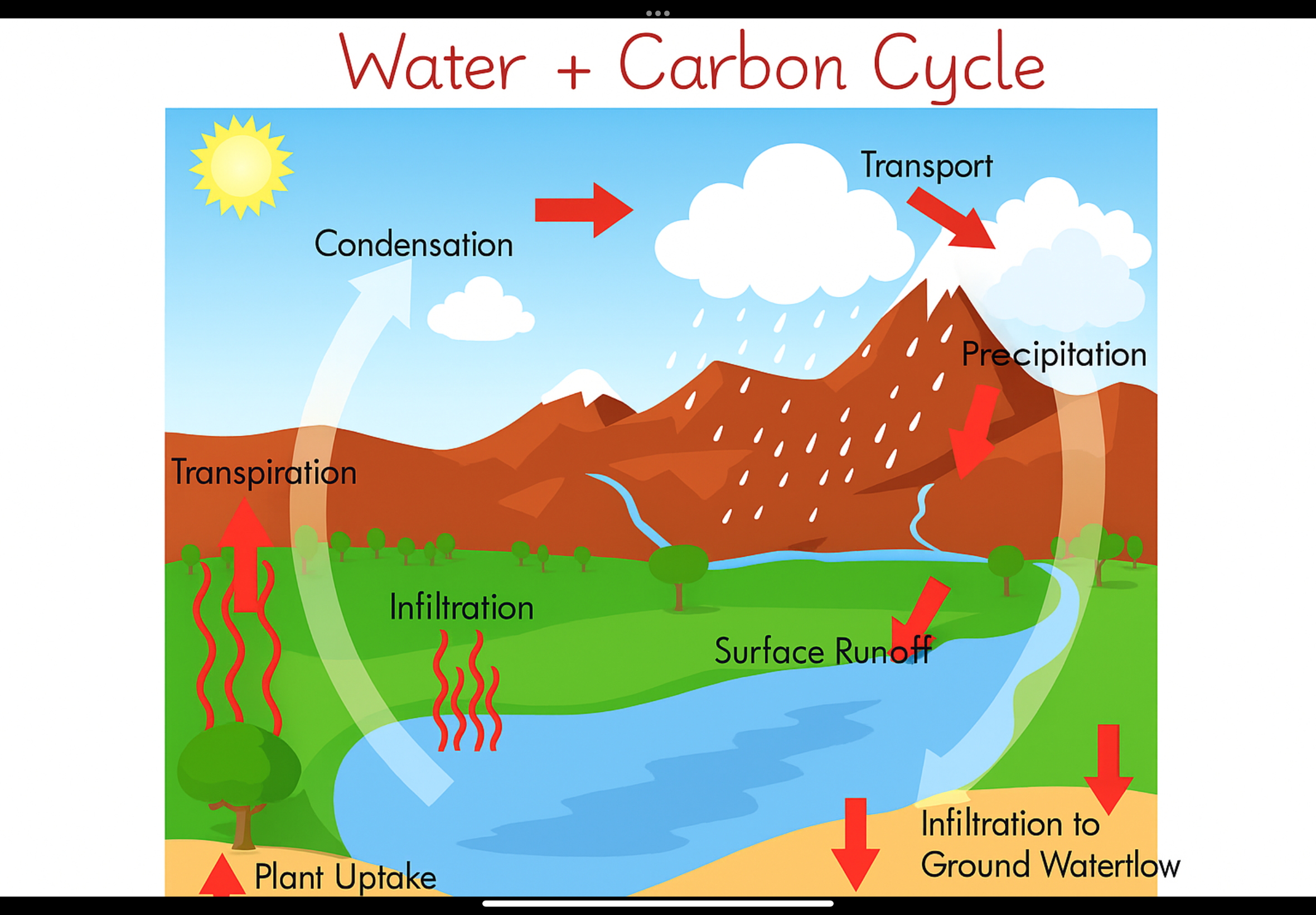
Water cycle
water is essential for life on earth. Water exists three states. Water never runs out constantly recycled in water cycle
Processes removing carbon from atmosphere
Photosynthesis (biological)
Dissolves in ocean
Processes releasing carbon to atmosphere
respiration
decay + decomposition dead matter + waste by microorganisms
Combustion (burning fossil fuels)
Released from ocean by motion of waves
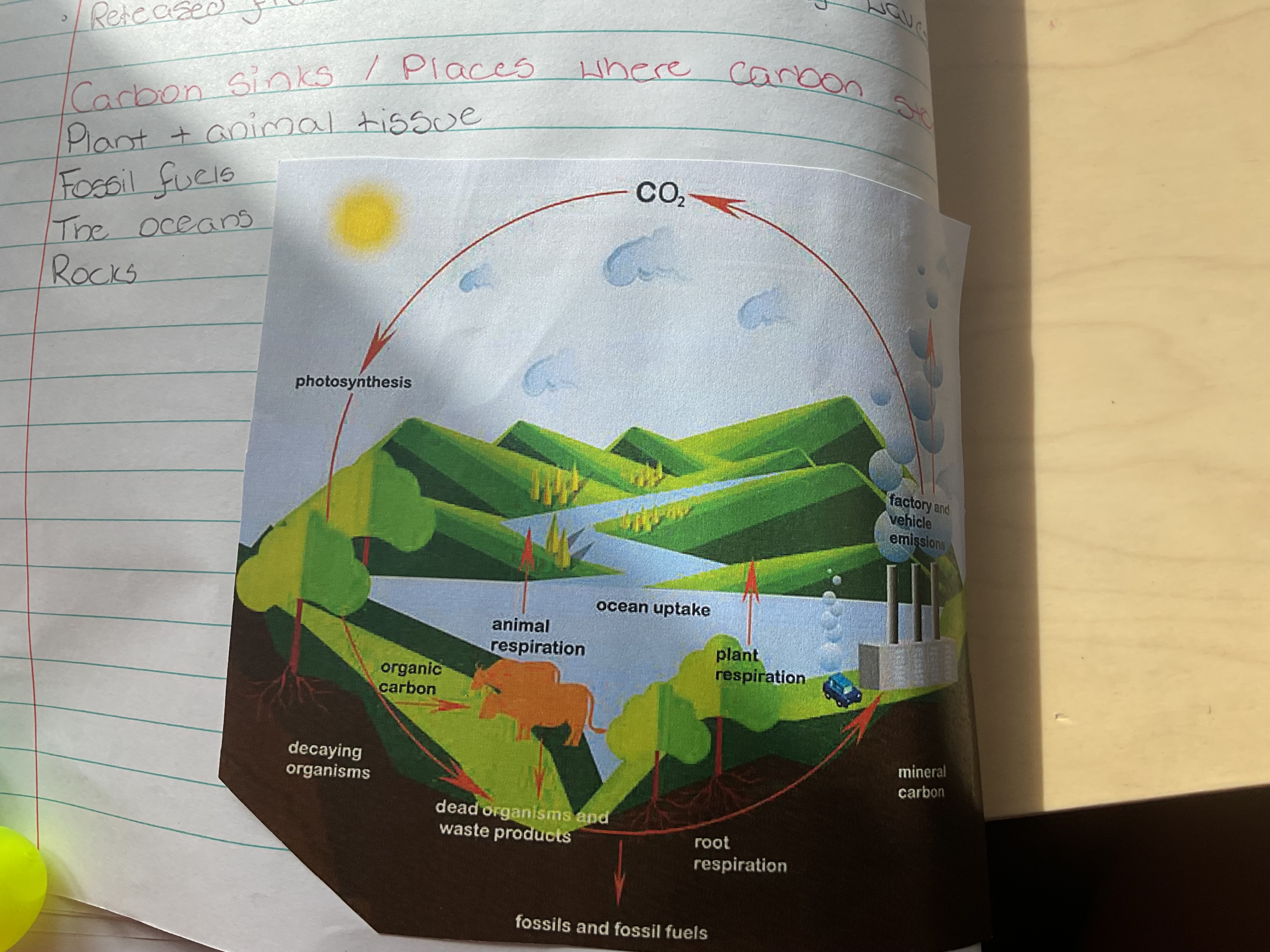
Where is carbon stored
Plant + animal tissue
Fossil fuels
The oceans
Rocks
F