Deep Sea Test
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
SCUBA - Self Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus
method of swimming underwater with an air tank, allowing humans to breathe underwater and stay down longer than free diving
ROV - Remotely Operated Vehicle
underwater robots that are operated by people on a boat
AUV - Autonomous Underwater Vehicle
Underwater robots that are not tethered to the surface
can be programmed to follow specific instructions
equipped with sonar
HOV - Human Occupied Vehicle
Vessel used to take humans to depths they cannot reach by any other means
carry mechanical arms, sampling gear, camera, lights
ADS - Atmospheric Diving Suit
one-man diving suit that keeps the diver at the same pressure as surface pressure
useful for situations that require a human perspective or skills to survey or repair underwater equipment deeper than SCUBA would allow
pressure
increases as depth increases
collapse lungs, store oxygen in muscles, high myoglobin concentration
adaptations that allow seals and sperm whales to dive deep in the ocean
myoglobin
oxygen-carrying proteins contained in the blood
swim bladder
used by fish to control bouyancy
can be inflated/deflated to adjust bouyancy
doesn’t collapse at depth b/c gas inside is at the same pressure as the water outside
symptoms of bringing deep sea animals to the surface
cell membranes burst & fluids leak out
nerve functions fail
swim bladder swells & often sticks out of mouth
absorbed in the ocean
red & violet wavelengths of light
reflected by the ocean
blue & green wavelengths of light
camouflage
the reason many sea animals are red
euphotic zone
“good light”
high sunlight & oxygen
low pressure
warmest temperature
contains 90% of all life while making up only 1% of the ocean
disphotic zone
“difficult light”
not enough light for photosynthesis, low light
low oxygen
increased pressure
cold temperature
low diversity of life
aphotic zone
“no light”
little oxygen
extreme pressure
near freezing temperature
low diversity of life
crust
top layer of the earth that is broken into pieces
liquid magma
tectonic plates move because the crust sits on ______ ______ outer core
convergent boundary
divergent boundary

transform boundary

convergent colliding boundary
plates move towards each other and form mountains
convergent subducting boundary
plates move towards and one goes under, forming a trench
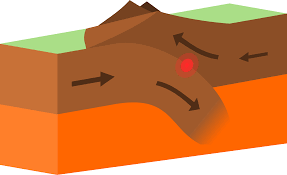
divergent boundary
plates move away from each other and form a rift, which turns into an oceanic ridge when underwater
transform boundary
plates slide past each other and form fault lines
how mid-ocean ridges are formed
cracks made by the divergence of plates are filled by rising magma, creating ridges
seamounts
underwater mountains formed by volcanic activity, also referred to as guyots
Mariana Trench
deepest underwater trench in the world at 7 miles deep
hydrothermal vents
underwater features located at divergent rifts that release very hot water full of nutrients
reason water from hydrothermal vents does not boil
the extreme pressure of the ocean, as well as the low temperatures at that depth, increase the boiling point of water
chimney
forms from dissolved metals when the hot water of the vents and cold water of the ocean interact
chemosynthesis
the process of converting chemicals into sugars
chemoautotrophs
form the base of the food web near hydrothermal vents, gaining their energy from the released chemicals
enlarged and sensitive eyes
an adaptation that uses what little light is available to help animals see
upward pointing eyes
light & food are above the animals, so they use this adaptation to see
transparency
an adaptation used to camouflage
photophores on ventral side
an adaptation that allows animals to camouflage by blending in with the light above them
large teeth and stretchable jaws
an adaptation that allows deep sea animals to eat whatever food they come across
low metabolism
an adaptation used by deep sea animals due to the scarcity of food in their habitat
stretchable stomach
an adaptation used by deep sea animals that allows them to fit large amounts of food in their stomach
photophores
the structure that allows organisms to bioluminesce
two ways an organism can bioluminesce
bioluminescent bacteria or photophores
functions of bioluminescence
headlights, lures, mating, communication, evading predators