Veterinary Immunology: Viral Recognition, Immune Responses, and Evasion Strategies
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Viruses are __, their existence is threatened by the immune system or death of their host
obligate intracellular organisms
What tends to happen when a virus first encounters its host species or infects the wrong species?
The diseases may tend to be lethal.
What are examples of infections where virus-host adaptation is poor, resulting in acute and severe diseases?
Rabies, feline panleukopenia, canine parvovirus-2, Newcastle disease (virulent form).
What are examples of infections that may be severe but have low mortality and can be persistent?
Foot-and-mouth disease, influenza.
What are examples of infections that can result in persistent infection where the immune system cannot eliminate them?
Lentivirus infections, equine infectious anemia, Maedi-visna of sheep, AIDS in humans.
What is the role of interferons in viral resistance?
Interferons are released from virus-infected cells and stimulate the production of proteins that have antiviral activity.
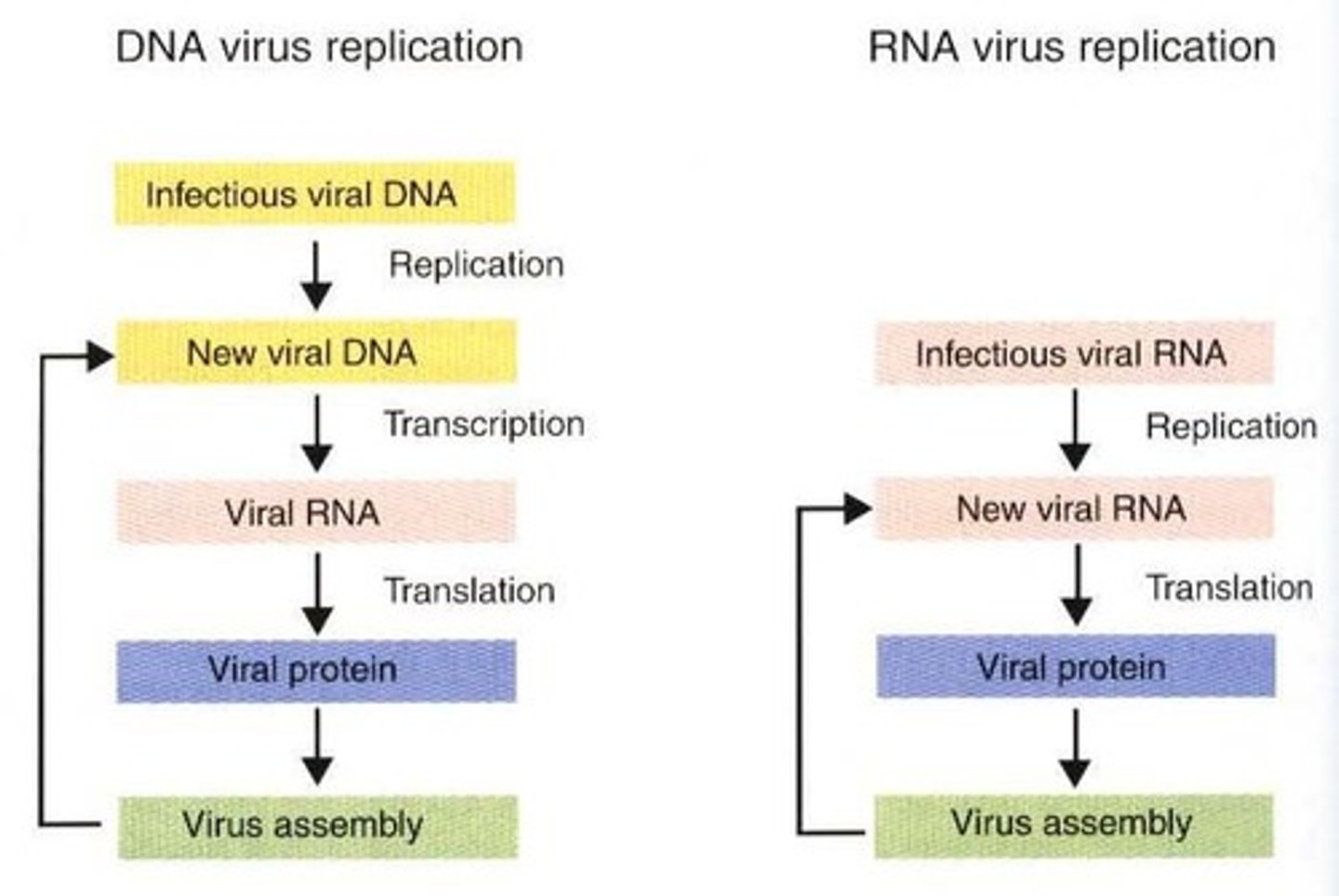
What are the steps in viral replication?
1. Attachment to a surface receptor on a susceptible host cell. 2. Entry into the cell. 3. Uncoating of viral nucleic acid. 4. Replication of viral nucleic acid and synthesis of virus-encoded proteins. 5. Assembly of newly-formed virus particles and release from host cell.
What are the main functions of antibodies in the immune response to viruses?
1. Blocking the adsorption of virions to target cells. 2. Stimulating phagocytosis of viruses. 3. Triggering complement-mediated virolysis. 4. Causing viral clumping.
Which immunoglobulins are significant in neutralizing viruses?
IgG and IgM in serum, and IgA in secretions.
What is the major destructive mechanism of T cell-mediated immunity?
Cytotoxic T cells recognize peptide-MHC complexes and kill infected cells.
What is antigenic variation and how do viruses use it to evade the immune response?
Antigenic variation involves changes in viral surface proteins, allowing viruses to evade detection by the immune system.
What is antigenic drift in influenza viruses?
Gradual changes in the structure of hemagglutinins and neuraminidase due to mutation and selection.
What is antigenic shift in influenza viruses?
A sudden, major genetic change resulting in a new strain, often due to recombination between two strains.
How do some viruses inhibit the effectiveness of antiviral interferons?
By blocking the signaling pathways that interferons use to exert their antiviral effects.
What is the relationship between stress and viral diseases?
Stress can lead to increased steroid production, which may be immunosuppressive and contribute to the development of viral diseases.
What is the role of nitric oxide synthase in the immune response to viruses?
It prevents virus growth in interferon-activated macrophages.
How do antibodies kill infected cells?
Through complement-mediated cytolysis or antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
What is the significance of immunological memory to viruses?
Antibodies against viruses may persist for many years in the absence of the virus, providing long-term immunity.
What are the roles of leukocytes and NK cells in the immune response to viral infections?
They contribute to the innate immune response and help control viral infections.
What is the importance of MHC class I molecules in viral infections?
They present endogenous antigens on the surface of infected cells, allowing recognition by cytotoxic T cells.
What is the effect of viral infections on apoptosis in host cells?
Cells invaded by viruses may undergo premature apoptosis.
What is the role of antigen-stimulated T cells in the production of interferons?
They are a major source of IFN-γ.
What is the significance of the duration of immunological memory to viruses?
It is highly variable, with some antibodies persisting for many years.
How do some viruses interact with bacteria to overcome the immune system?
For example, Mannheimia hemolytica can interact with bovine herpesvirus-1 to evade immune responses.