alcohol
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are hydrocarbons?
-Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrocarbon atoms
What characteristics does carbon have?
-Covalence of four (has four valence electrons, so can covalently bond with four atoms/compounds to have a full outer shell)
-Can be bonded to eachother to form straight chains, branched chains and rings
-Can form single, double or triple bonds with other carbon atoms or non metal atoms
How to name hydrocarbons
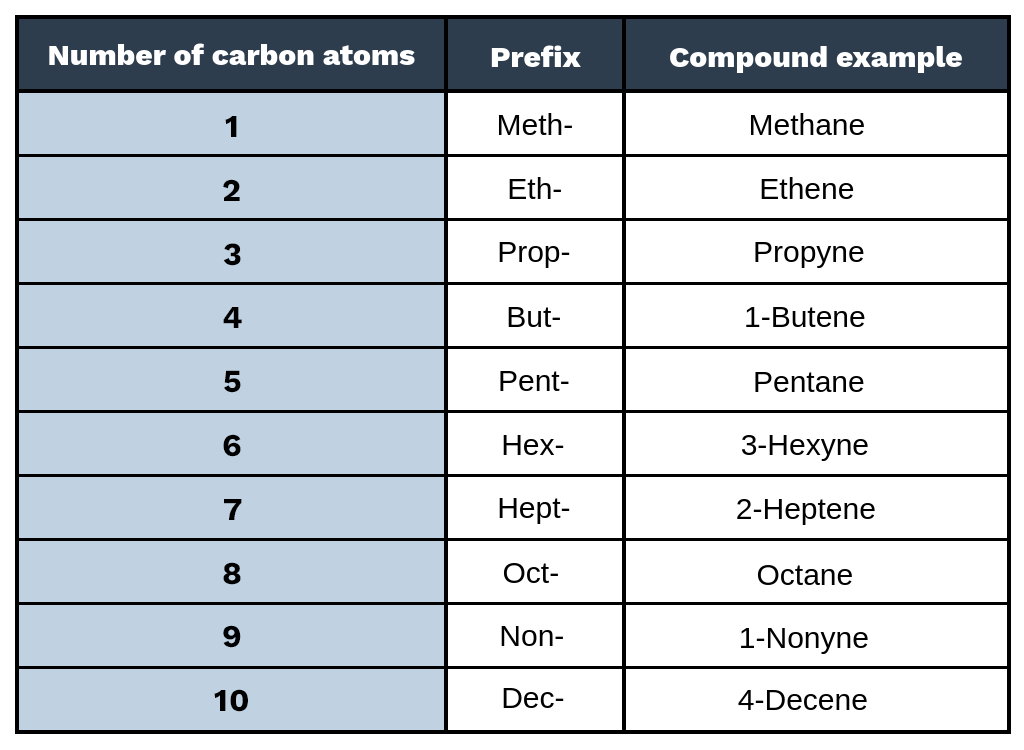
Count how many carbons are in longest carbon chain & assign this to the corresponding prefix
Identify what branches are present and label them according to their position on the carbon chain; lowest of two values
Add number position and name of branch then add ane, ayne, ene or ol to the end depending on the type of thing
What are the prefixes?
What are the alkyl branches?
Methyl: -CH3
Ethyl: -CH2CH3
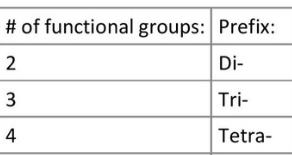
What are the prefixes for when a compound has 2 or more of the same branch?
(number of functional groups means number of branches—same thing)
*If a molecule has multiple different branches of different types they are named in alphabetical order (Ethyl before Methyl)
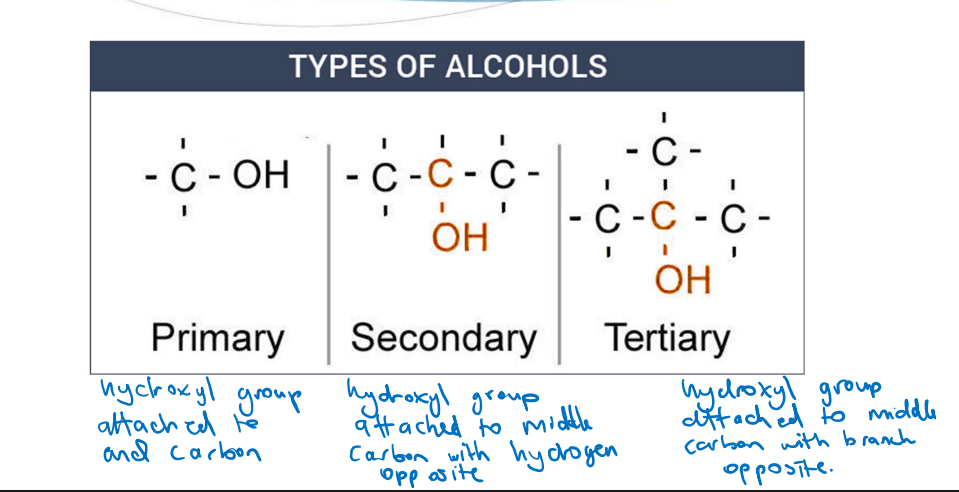
What are alcohols?
A class of organic compounds that contain at least one hydroxyl (-OH) functional group
Types of Alcohols
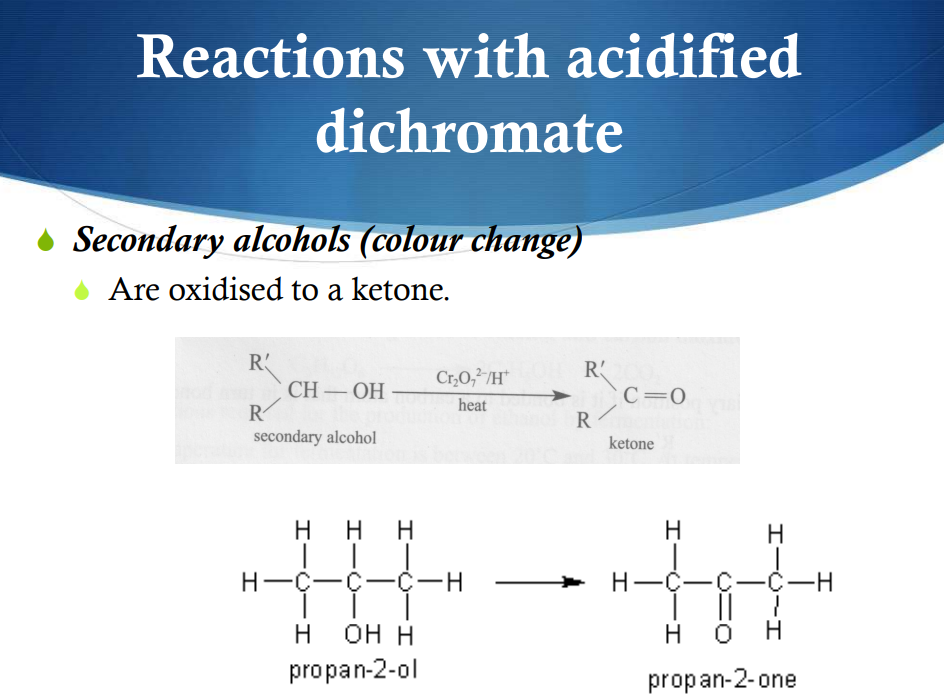
What is oxidation of alcohols?

Reactions with acidific dichromate—Primary
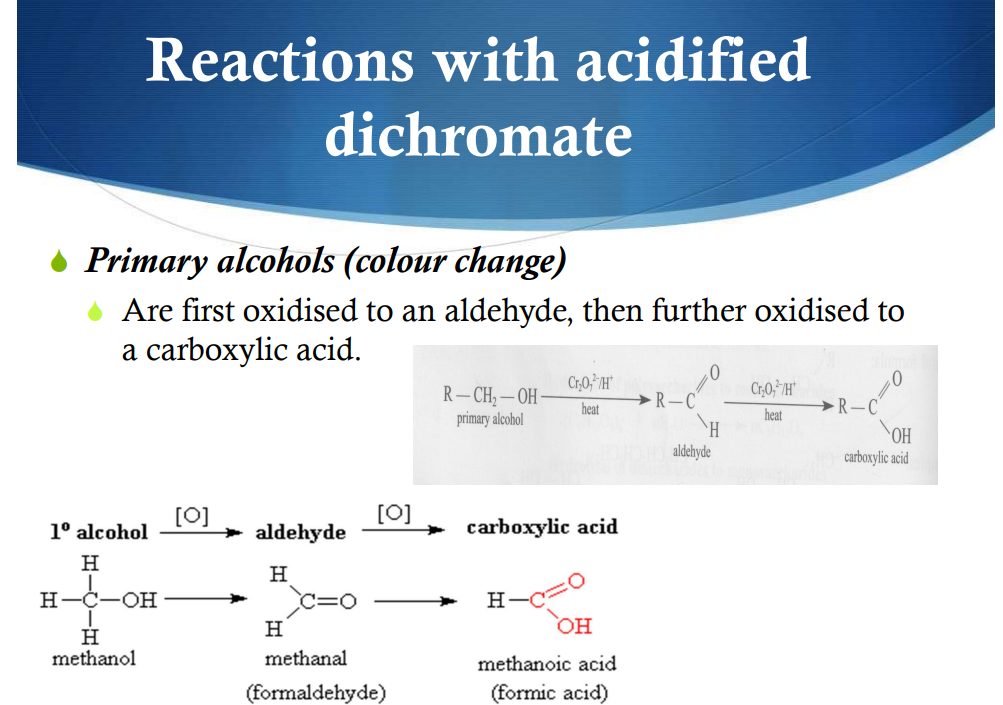
Reactions with acidific dichromate—Secondary
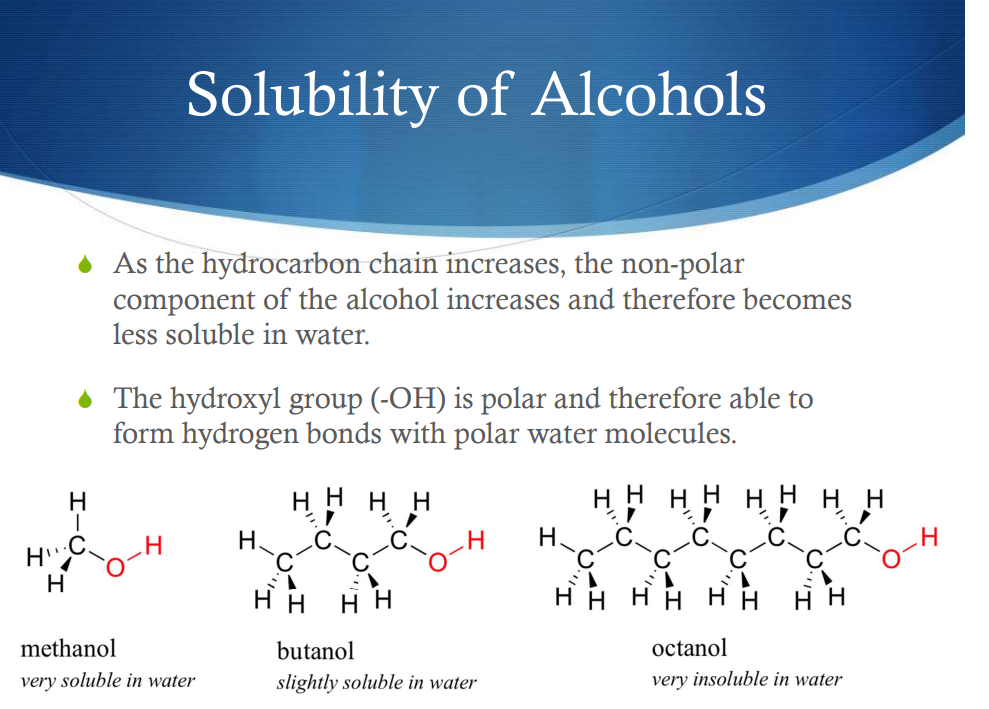
Solubility of Alcohols
-The hydroxyl (-OH) component is hydrophillic (polar: soluble in water)
-The rest of the carbon chain is Hydrophobic ( not polar: not soluble in water, basically homophobic of water type shi)
Longer carbon chain=more insoluble, because the ratio of not polar to polar components is higher (higher percentage of the compound is insoluble)
What is a homologous series?
Group of molecules with the same functional group but different number of -CH2 groups.
Functional Group
An atom or group of atoms responsible for the typical chemical reactions of a molecule
Alkanes vs Alkenes vs Alkynes
Alkanes: carbon single bonds
Alkenes: carbon double bonds
Alkynes: carbon triple bonds
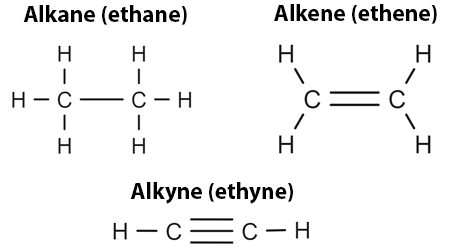
Saturated vs unsaturated hydrocarbons
Saturated: no carbon double or triple bonds
Unsatured: has one or more carbon double or triple covalent bonds