I : Introduction to Immunology & The Immune System
1/185
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
Immunology
- Study of the reactions of a host when foreign substances (i.e bacteria) are introduced into the body.
Immunology
- The study of the body’s mechanism (i.e anaphylactic response):
• That discriminated between non-self & self
• Eliminates non-self components such as infectious agents
• Medically related consequences that arise when these mechanisms either fail or respond in an exaggerated form.
Antigens
- Foreign substances that induce a host response.
Antigens
- Antibody generator
T
Antigens is all around us (t/f)
Antibody
- A glycoprotein produced by the body to neutralize & eliminate the antigens
Immunity
- Condition of being resistant to infection.
Attenuation / Change
- Making a pathogen less virulent
Attenuation / Change
- Purpose: takes a part of the weakened virus to process through heat, aging, or chemical means for the development of vaccines
Attenuation / Change
- remains the basis for many of the immunizations that are used today
heat, aging, or chemical means.
Attenuation / Change takes place through
Innate Immunity (IN)
- The ability the body to resist infection by means of normally present, nonspecific body functions.
Innate Immunity (IN)
- Considered non adaptive/nonspecific
T
Innate Immunity (IN) (t/f)
- Responses are the same for all pathogens/foreign substances to which one is exposed.
Adaptive Immunity (AI)
- Type of resistance characterized by specificity for each individual & the ability to remember a prior exposure.
lymphocytes
Adaptive Immunity (AI)
- Requires the activation of - in response to an infectious agent.
Serology
- The study of antigen-antibody reaction in vitro (outside)
Serology
- The technological application of immunologic principles in the detection & monitoring of dx states.
1798
· Edward Jenner discovered the relationship between the exposure to cowpox & immunity to smallpox.
He injected material from cowpox to px, to develop immunity against smallpox which was called vaccination from “vacca” which means cow.
Edward Jenner
who discovered the relationship between the exposure to cowpox & immunity to smallpox.
He injected material from cowpox to px, to develop immunity against smallpox which was called vaccination from “vacca” which means cow.
vacca
cow
Edward Jenner injected material from cowpox to px, to develop immunity against smallpox which was called vaccination from “-” which means -.
1879
· Louis Pasteur introduced the germ theory of the dx.
Louis Pasteur
1879
when & who accidentally discovered the use of attenuated vaccine while working with bacteria causing chicken cholera. (considered as the birth of immunology)
Louis Pasteur
who also developed that the body makes antibodies in response to infection in 1900.
1900
Louis Pasteur developed that the body makes antibodies in response to infection in -.
1920
Vacciners for diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whopping cough) & tuberculosis (BCG) were all available.
1930
· Karl Landsteiner won the Nobel prize for the discovery of ABO antigens & antibodies.
· He also coined the term “hapten”.
Karl Landsteiner
1930
who won the Nobel prize for the discovery of ABO antigens & antibodies.
· He also coined the term “hapten”.
Karl Landsteiner
1930
who coined the term “hapten”.
1930
The search for the cells that produce the antibodies encouraged the study of cellular immunity.
429 BC
Thucydides noticed that smallpox survivors did not get re-infected
900 AD
Chinese inhaled smallpox scabs to produce protection from the then deadly dx, this was called variolation.
Chinese
900 AD
who inhaled smallpox scabs to produce protection from the then deadly dx, this was called variolation.
1717
Variolation reaches Turkey & the rest of Europe through the work of Lady Mary Wortley Montagu, poet & wife of the British ambassador to Turkey.
Lady Mary Wortley Montagu
1717
Variolation reaches Turkey & the rest of Europe through the work of -, poet & wife of the British ambassador to Turkey.
1876
· Robert Koch isolated the anthrax virus & showed that it caused the dx.
1882
Robert Koch Isolated the causative agent of tuberculosis (-)
1891
when did Robert Koch explored delayed type hypersensitivity.
1883
Ellie Metchnikoff observed that foreign objects introduced into transparent starfish larvae became surrounded by motile cells that attempted to destroy these invaders. He called this phagocytosis, meaning “cells that eat cells”. He hypothesized that immunity was based on this function which was called cellular immunity.
Ellie Metchnikoff
phagocytosis
cellular immunity.
In 1883, who observed that foreign objects introduced into transparent starfish larvae became surrounded by motile cells that attempted to destroy these invaders. He called this - , meaning “cells that eat cells”. He hypothesized that immunity was based on this function which was called -
1890s
Emil von Behring demonstrated that diphtheria (with Wernicke) & tetanus toxin (with Kitasato) produced by microorganisms as they grow can be neutralized by the noncellular portion of blood of those previously infected. This was called humoral immunity.
Wernicke
Kitasato
humoral immunity.
Emil von Behring demonstrated that diphtheria (with -) & tetanus toxin (with -) produced by microorganisms as they grow can be neutralized by the noncellular portion of blood of those previously infected. This was called -
1896
· Methods to detect the presence of antigens using serum (noncellular portion of the blood) were discovered.
· Gruber & Durrham described bacterial agglutination.
· Widal developed an agglutination test for typhoid fever shortly after.
· Kraus later described precipitation.
Most serologic tests are based on agglutination & precipitation as end results of the tests.
Gruber & Durrham
In 1896, who described bacterial agglutination.
Widal
In 1896, who developed an agglutination test for typhoid fever shortly after.
Kraus
In 1896, who later described precipitation.
T
Most serologic tests are based on agglutination & precipitation as end results of the tests. (t/f)
1903
· English physician Almroth Wright linked the 2 theories. He observed that certain humoral factors called “opsonins” acted to coat bacteria so that it would be more susceptible for phagocytosis.
Around this time, it was acknowledged that the serum factor was formed when an antigen is introduced. The serum factors were called “antibodies” which is also known as immunoglobulins.
Almroth Wright
In 1903, who linked the 2 theories. He observed that certain humoral factors called “opsonins” acted to coat bacteria so that it would be more susceptible for phagocytosis.
antibodies
immunoglobulins
In 1903, it was acknowledged that the serum factor was formed when an antigen is introduced. The serum factors were called “-” which is also known as -.
Leukocytes
N - Neutrophils / Polymorphonuclear Neutrophilic (PMN) Leukocyte
E - Eosinophils
B - Basophils
M - Monocytes / Macrophages
L - Lymphocytes
Cells of the Immune System
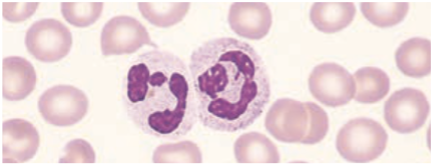
Neutrophils / Polymorphonuclear Neutrophilic (PMN) Leukocyte
Approximately 50 – 70% of total peripheral WBC
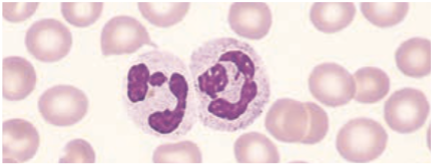
Neutrophils / Polymorphonuclear Neutrophilic (PMN) Leukocyte
Has a nucleus with 2 – 5 segments & cytoplasm filled with primary & secondary granules that contain enzymes & chemicals.
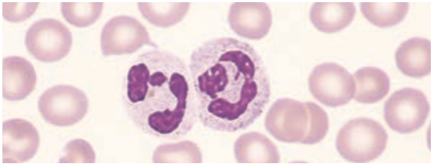
Neutrophils / Polymorphonuclear Neutrophilic (PMN) Leukocyte
Function
· 1st responder to infection, phagocytosis
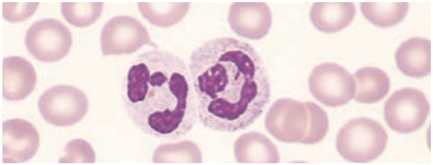
Neutrophils / Polymorphonuclear Neutrophilic (PMN) Leukocyte
Function
In the tissues they may wander randomly or be attracted to a specific area by chemotactic factors or chemotaxins.
Neutrophils / Polymorphonuclear Neutrophilic (PMN) Leukocyte
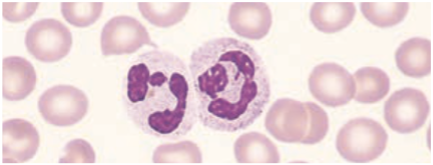
Eosinophils
- Characterized by the presence of large granules within their cytoplasm that can be stained with a dye called eosin, which gives them their name.

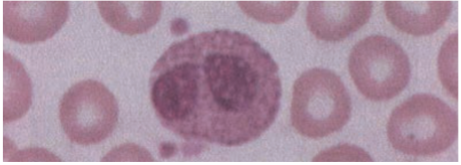
Eosinophils
1 – 3% of circulating WBCs.
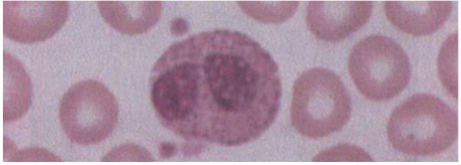
Eosinophils
· Has bilobed nucleus & cytoplasm filled with orange-red granules that also contain certain enzymes.
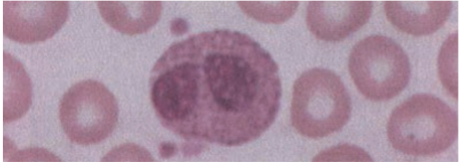
Eosinophils
Less efficient phagocytes than PMNs (bc they are present in smaller numbers & they lack digestive enzymes)
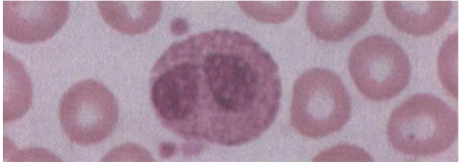
Eosinophils
Function
· Have an important role in neutralizing basophil & mast cell products.
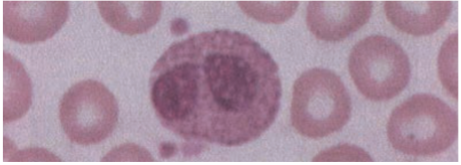
Fc epsilon receptor (FcεR)
Function of Eosinophil
· Helminths coated with IgE are recognized by eosinophils via - & release major basic protein & eosinophil cationic protein.
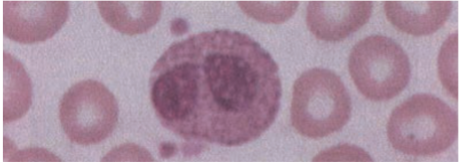
Fc epsilon receptor (FcεR
Function of EosinophilsF
· Helminths coated with IgE are recognized by eosinophils via - & release major basic protein & eosinophil cationic protein.
Kill parasites, neutralize basophil & mast cell products, regulate mast cells
Eosinophils
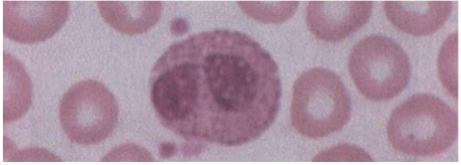
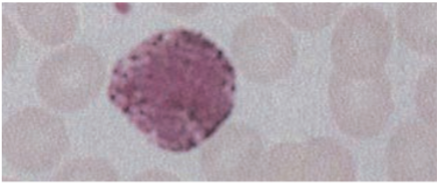
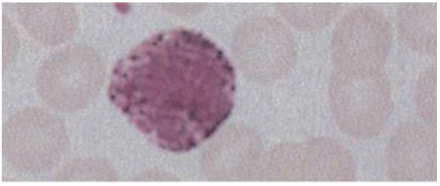
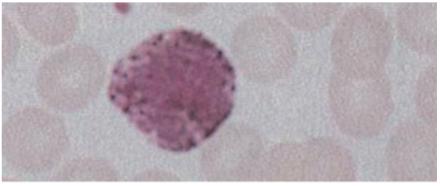
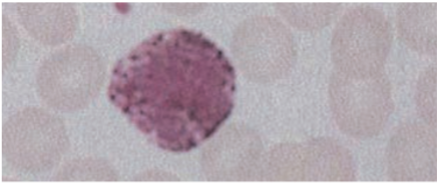
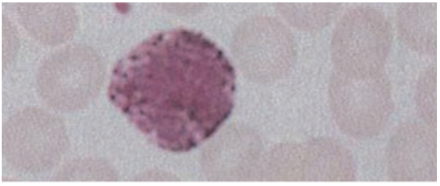
Basophils
<1% of circulating WBCs.
Basophils
· Contain coarse densely staining deep bluish-purple granules that often obscure the nucleus.
Basophils
Granules contain histamine (contracts smooth muscle), eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis, & heparin (anticoagulant).
Basophils
Function
Induce & maintain allergic reactions, stimulates production of IgE.
Basophils
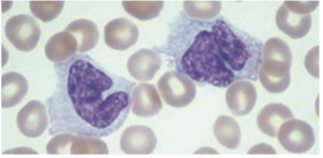
Monocytes / Macrophages
- 4 – 10% of circulating WBCs
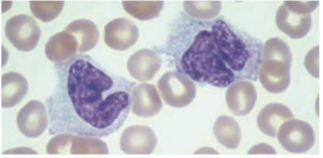
Monocytes / Macrophages
- Roam around lungs, liver & connected tx.
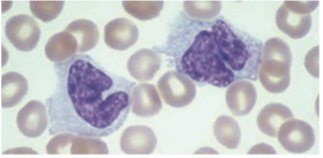
30 hrs
Monocytes stay in the peripheral blood for up to - hrs then migrates to the tx & become known as macrophages.
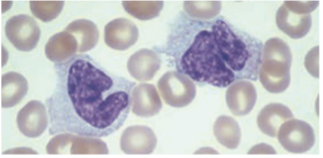
macrophages
Monocytes stay in the peripheral blood for up to 30 hrs then migrates to the tx & become known as -.
Monocytes / Macrophages
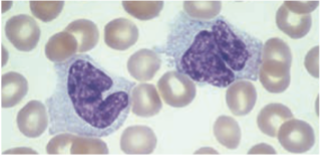
· Largest cells in peripheral blood, 12 – 22 µm in diameter

12 – 22 µm
Monocytes is the largest cells in peripheral blood, - in diameter
Monocytes / Macrophages
· Has an irregularly folded or horseshoe-shaped nucleus that occupies almost ½ of the entire cell’s volume.
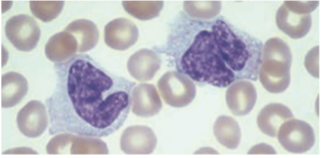
irregularly folded or horseshoe-shaped nucleus
Monocytes has - nucleus that occupies almost ½ of the entire cell’s volume.
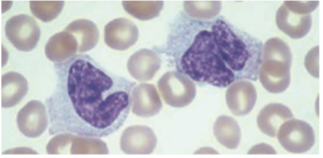
Monocytes / Macrophages
Cytoplasm stain dull-grayish blue & has a ground-glass appearance (fine dustlike granules)
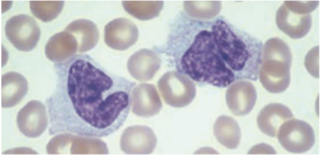
dull-grayish blue
ground-glass appearance (fine dustlike granules)
Monocytes’ cytoplasm stain - & has a -
Alveolar cell
Monocytes / Macrophages location & names:
· Lungs:
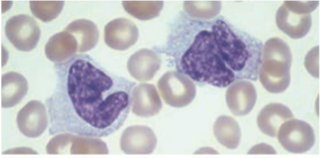
Microglial cell
Monocytes / Macrophages location & names:
· Brain:
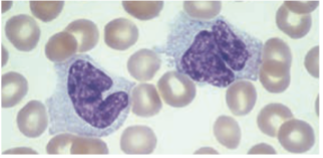
Mesangial cell
Monocytes / Macrophages location & names:
· Kidney:
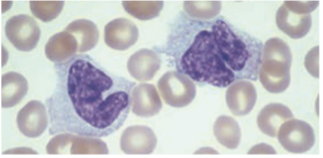
Kupffer cell
Monocytes / Macrophages location & names:
· Liver:
Osteoclasts
Monocytes / Macrophages location & names:
· Bone:
Histocyte
Monocytes / Macrophages location & names:
Connective Tx:
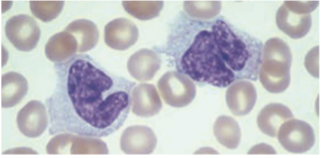
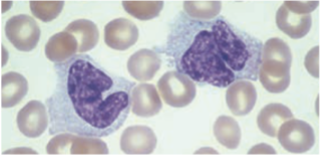
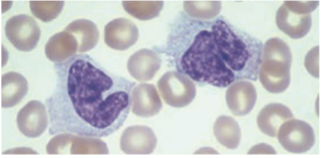
Lymphocytes
- 20 – 40% of circulating WBCs.
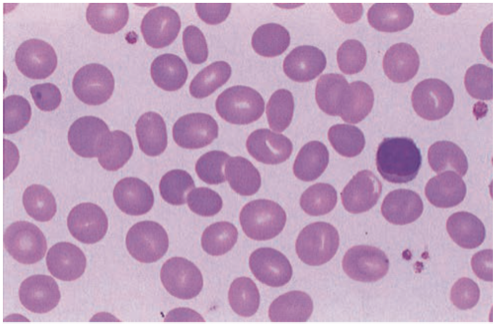
found in lymph nodes, spleen, other secondary lymphoid organs
Location of lymphocytes
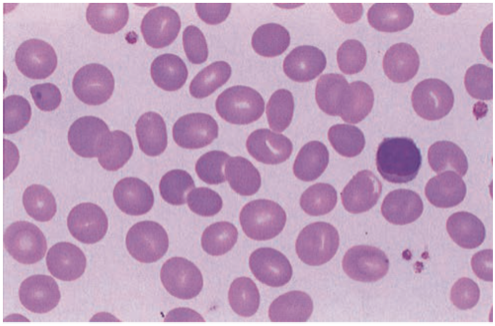
Lymphocytes
· Key mediators of adaptive immunity
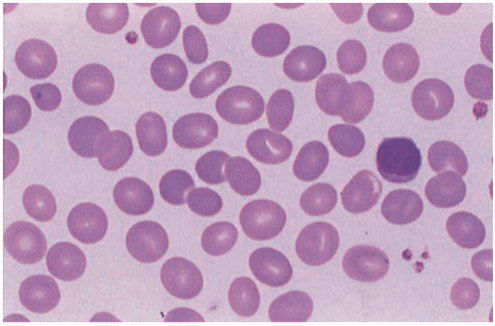
Lymphocytes
· Heterogenous in lineage, function, & phenotype & are capable of complex biologic responses & activities
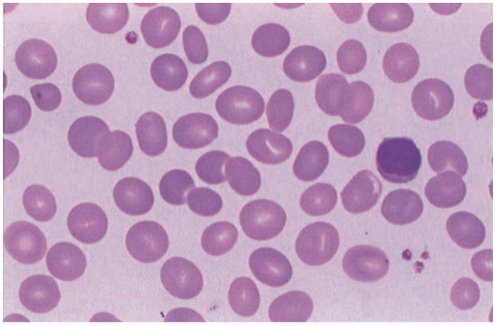
F
· Heterogenous in lineage, function, & phenotype & are capable of complex biologic responses & activities
Lymphocytes is homogenous in lineage, function, & phenotype & are capable of complex biologic responses & activities (t/f)
CD markers (clusters of differentiation).
All lymphocytes look the same but be identified by panels of monoclonal antibodies by the proteins they possess. These proteins are called -

T Cell
B Cell
NK Cell
Subtypes of Lymphocytes
T Cell
Subtypes of Lymphocytes
- – produce cytokines (cell mediated immunity) (differentiates in the thymus)
thymus
T cells differentiates in the -
B Cells
Subtypes of Lymphocytes
– produce antibody in adaptive immune response (humoral immunity)
Bone marrow
B cells is found in
NK Cells
Subtypes of Lymphocytes
– involved in innate immunity(found mainly in the liver, spleen & peripheral blood)
Macrophages
Mast Cells
Dendritic Cells
Tissue Cells
· Lungs
· Liver
· Brain
· Bone
· CT
Other tx
Locations of Macrophages