COMM 1500: Interpersonal Communication Unit 3 (Huggins)
1/204
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
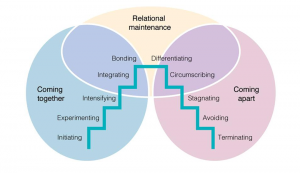
Knapp’s Stages of Romantic Relational Development
Coming Together
Initiating
Experimenting
Intensifying
Integrating
Bonding
Coming Apart
Differentiating
Circumscribing
Stagnating
Avoiding
Terminating
Initiating
(Coming Together)
Stage where people meet and interact for the first time
Am I attracted to this person?
Should I initiate conversation?
Uncomfortable/problems lead to exit
Experimenting
(Coming Together)
The stage of relationship development when individuals have conversations to learn more about each other.
Search for commonality
Question asking stage
Small talk
VERY judgmental
Do I want to continue?
Intensifying
(Coming Together)
The stage of relationship development when individuals move from being acquaintances to being friends.
Increase in self-disclosure
Use of “we” begins (unit)
Verbal Shortcuts (pet names, nicknames, inside jokes, personal idioms)
Direct Expressions of Commitment (“you’re really important to me”)
Integrating
(Coming Together-Relational Maintenance)
The stage of relationship development when a deep commitment has formed, and there is a strong sense that the relationship has its own identity.
Identify as a pair
Adopt each other’s mannerisms and speech patterns
May exchange symbols of relationship
Difficulty managing dialectical tensions of connectedness vs. autonomy
Bonding
(Coming Together-Relational Maintenance)
The stage of relationship development when people publicly announce their commitment to each other.
Public Commitment
Ritual (Marriage)
Institutionalized (joint credit card, changing last name)
Differentiating
(Coming Apart-Relational Maintenance)
The stage of relationship dissolution when partners begin to see their differences as undesirable or annoying.
Highlight Differences
Seek Individual Identity
Conflict & Argument Development
Bond-Differentiate-Recommit
Circumscribing
(Relational Maintenance-Coming Apart)
The stage of relationship dissolution characterized by decreased quality and quantity of communication between partners.
Conversation focuses on safe topics
Appears “normal” to outsiders
Limitation is Key
Quantity
Quality
Stagnating
(Coming Apart)
The stage of relationship dissolution when the relationship stops growing and the partners are barely communicating with each other.
Individuals appear to be strangers
Limit interaction to “need-to-know” basis
No need to talk - partners know what the other will say
Mentally rehearse negative interactions with partner
Avoiding
(Coming Apart)
The stage of relationship dissolution when partners create physical and emotional distance between each other.
Individuals avoid face-to-face interaction
Create physical and emotional distance
May be direct or indirect
Terminating
(Coming Apart)
The stage of relationship dissolution when the relationship is deemed to be officially over.
Formal ending of the relationship
Sever all ties
Negotiation of the new terms of the relationship
Lenses for Defining Family
Biogenetic Lens
Sociological Lens
Role Lens
Biogenetic Lens
Genetic ties
Share a genetic/reproductive link
Sociological Lens
Legal Obligations
Recognized by laws and regulations
Step-parents, adoptive parents, foster parents
Role Lens
Emotional attachments
Relationships can be either voluntary or involuntary
Parent’s friend as “uncle”/”aunt”
Family
Network of people who share their lives over longer periods of time and bound by marriage, blood, or commitment; who consider themselves as family, and who share significant history and anticipated future functioning in a family relationship
Types of Family
Origin
Procreation
Family of Origin
Family one grows up in
Typically parents and/or stepparents, siblings
Family of Procreation
Family one starts as an adult
Typically consists of spouse and children
Forms of Families
Nuclear
Blended
Single-parent
Extended
Attachment Theory
Our interpersonal relationships and their dependability are created through our relationship with our caregivers as children
Attachment Anxiety
Degree of fear of rejection
High vs Low
Attachment Avoidance
Degree of desire for close interpersonal ties
High vs Low
Secure Attachment
Low Anxiety and Low Avoidance
Not worried about rejection, let people get close to you
Secure Attachment Relationship Outcomes
Warm, Supportive
High Self-Esteem
Confident Communicator
Conflict
Work toward resolution of difficulties
Talk about it
Preoccupied Attachment
High Anxiety, Low Avoidance
Preoccupied Attachment Relationship Outcomes
Constant Worry
Demand Attention/Reassurance
Difficult for partners over long-term
Conflict:
Extreme Responses
Dismissive Attachment
Low Anxiety and High Avoidance
Dismissive Attachment Relationship Outcomes
Self-reliant
Relationships as unimportant
Casual rather than serious
Conflict:
Exit
Fearful Attachment
High Anxiety and High Avoidance
Fearful Attachment Relationship Outcomes
Stay Away from relationships
Chronic distrust
Prefer dependent partners
Conflict
Exit
Friendship
Plays a central role in our lives
Influences emotional security and self-esteem
Friendship is a voluntary interpersonal relationship characterized by intimacy and liking
Characteristics of Friendships
Permeated with ambiguities
Voluntary
Platonic
Peers
Shared Interests
Governed by rules
Differ by sex
Have a lifespan
Volatile
6 Stages of Friendship
Role-limited interaction
Friendly Relations
Moves toward friendship (could we hang out… socially??)
Nascent Friendship
Stabilized Friendship
Waning Friendship
Functions of Friendship
Companionship
Achievement of practical goals
Communal Friendship
Companionship, spending time together, having fun, let’s hang out, time revolves around leisure, emotional support, BOTH have to fulfill expectations
Agentic Friendship
Goal is to help others succeed in professional/practical way, can enjoy presence, no emotional dependence
Friendship Rules
Show support
Defend your friends
Offer Resources
(time, energy)
Be enjoyable
Provide help without being asked
Share interests and viewpoints
Be the friend that you would like to have
Challenges of Friendship
Betrayal
Geographic Separation
Attraction
Romance
FWB Relationships
Importance of Relationships
Social relationships are essential to our sense of belonging
Essential for well-being
Most Disclosive/Highly Communicative
Require Maintenance
Max of SEVEN
Social bonds need to be:
Interactive
Emotionally close
Nature of Personal Relationships
Commitment
Interdependence
Investment
Dialectical Tensions
3 Dialectical Tensions
Autonomy vs Connection
Openness vs Closedness
Predictability vs Novelty
Components of Liking
Affection
Respect
Components of Loving
Intimacy
Caring
Attachment
Theories for Forming and Maintaining Social Relationships
Attraction Theory
Uncertainty Reduction Theory
Social Exchange Theory
Relational Maintenance Theory
Attraction Theory Components
Proximity
Appearance
Similarity
Reciprocal Liking
Complementarity
Proximity
How closely together people live/work ang how often they interact
More likely to form relationships with people we see often
Mere Exposure Effect
Appearance
Is someone attractive?
What-is-beautiful-is-good effect
Matching
Similarity
When we find people with similar interests, beliefs, backgrounds, etc. we find them more comfortable and familiar
Birds-of-a-feather effect
Reciprocal Liking
Tendency of people to like others who have expressed liking for them
Complementarity
Someone is attractive (platonically, romantically, whatever) because they provide a quality we lack
Attracted to people because the differences between them and us is complementary, positive
Uncertainty Reduction Theory
We feel uncertain when we don’t know people well
Theory that we want to form relations to reduce that uncertainty by using communication behaviors
The more certain you are about someone, the more you like them
We don’t like uncertainty.
More we know, the better.
Social Exchange Theory (SET)
We seek relationships where the benefits outweigh the costs.
Social Exchange Theory Components (SET)
Rewards
Costs
Outcome (O)
Comparison Level (CL)
Comparison Level of Alternatives (CLALT)
Satisfaction
Stability
Rewards (SET)
Positives derived from relationship
Costs (SET)
Loss of privacy
Time, resources, energy
Outcome (O) (SET)
Rewards minus Costs
Comparison Level (CL) (SET)
A person’s realistic expectation of what the person wants and thinks they deserve from a relationship.
Based on past experiences and cultural norms for that relationship
Will affect how satisfied people are in a relationship
Comparison Level of Alternatives (CLALT) (SET)
A person’s assessment of how good or bad their current relationship is, compared with other options.
Do you think you’d be better off with new friends, neighbors, partners
Influences how long a relationship will last
Satisfaction (SET)
Outcome greater than Comparison Level
Stability (SET)
Outcome greater than Comparison Level of ALT
4 Types of Relationships Under Social Exchange Theory
Positive
Dependent
Terminating
Uncertain
Positive Relationship (SET)
O greater than CL and CLALT
O > CL
O > CLALT
Happy, Stable
Dependent Relationship (SET)
CL greater than O greater than CLALT
CL > O > CLALT
Unhappy, Stable
Terminating Relationship (SET)
CLALT greater than CL greater than O
CLALT > CL > O
Unhappy, Unstable
Uncertain Relationship (SET)
CLALT greater than O greater than CL
CLALT > O > CL
Happy, Unstable
Relational Maintenance Behaviors (SOAPS)
Social Networks
Openness
Assurances
Positivity
Sharing Tasks
Social Networks
All the relationships one has
Typical to share social networks with closed ones
People in close relationships know the others’ families, friends, etc.
Openness
A person’s willingness to talk about their relationship with a friend/relational partner about their relationship
Disclose thoughts and feelings
Confide
Assurances
Verbal and nonverbal behaviors that people use to illustrate faithfulness and commitment to others
“Of course I’ll help you, you’re my best friend”
Positivity
Acting friendly and cheerful, being courteous, and refraining from criticizing others
Smile frequently, don’t complain, express affection and appreciation for others
Make others comfortable around us, pleasant and fun to be around
Sharing Tasks
Performing one’s fair share of the work in a relationship
Family Communications Patterns Theory- Dimensions
Conversation
Conformity
Conversation
How often families talk to each other
Openness of conversation
Conformity
How much a child is expected to conform with parent’s values, beliefs, attitudes
4 Types of Family Communication Patterns
Protective
Consensual
Laissez-Faire
Pluralistic
Consensual Families
HIGH Conversation
HIGH Conformity
High levels of disclosure
Express caring and concern
Common viewpoints
Parents are authority figures
Consensual Family Conflict Patterns
Threatened by conflict
Threatened by unresolved conflict
Engage
Constructive Approach
Pluralistic Families
HIGH Conversation
LOW Conformity
Open, unconstrained communication
Enjoy debate
Lack control over viewpoints
Children contribute
Pluralistic Family Conflict Patterns
Not threatened
Low avoidance
Engage
Collaborate
Highest rates of resolution
Protective Families
LOW Conversation
HIGH Conformity
Communication enforces obedience
Low disclosure
Power differential
Lack communication skills
Protective Family Conflict Patterns
Unlikely to have open disagreements
Threatens conformity
Avoid
Lack skills for productive management
Laissez-Faire Families
LOW Conversation
LOW Conformity
Infrequent interaction
Uninvolving communication
Few emotional bonds
Children independent thinkers
Laissez-Faire Family Conflict Patterns
Rare occurrence
Avoid
Compete
How to Maintain Balance in Relationships (SOAPS)
Social Networks
Openness
Assurances
Positivity
Sharing tasks
Conflict
The process that occurs when people perceive that they have incompatible goals or that someone is interfering in their ability to achieve their objectives
Components of Conflict
Perception
Process
Dynamic
4 “I”s of Conflict
Interdependence
Incompatible Goals
Insufficient Resources
Interference
2 Fundamental Orientations to Conflict
Engage
Avoid
Nature of Conflict Styles
Patterned responses or clusters if behavior
General response
Determined according to two dimensions
5 Conflict Styles
Competition
Compromise
Collaboration
Avoidance
Accommodation
Conflict Tactics
Individual behaviors to carry out a general approach
Specific pieces of communication
Can be conscious or unconscious
Competition
Aggressive and uncooperative behavior, engage others
High concern for self and low concern for other party
Goal is to win
Competitive Tactics
Personal Criticism
Rejection
Hostile Communication
Hostile imperatives
Hostile jokes
Hostile questions
Presumptive Remarks
Denial of Responsibility
Contempt/Disgust
Advantages of Competition
Emergency
External Goal more important than the individual
Shows commitment
Disadvantages of Competition
Can be harmful to relationships
Creates a win/lose mentality
Can be “self-encapsulating”
Compromise
Both parties give up something to gain something
Moderate concern for self and others
Intermediate Style
Dependent on shared power
Can be interpreted in different ways
Compromising Tactics
Analytic Remarks
Negotiating Remarks
Interdependence
A state in which each person’s behaviors affect everyone else in the relationship
Example: When one partner in a romantic relationship gets a job offer requiring them to relocate, that affects the other partner as well
Incompatible Goals
Goals are incompatible when it’s impossible to satisfy them both
Parties in a conflict perceive their goals to be incompatible