2 tissues
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
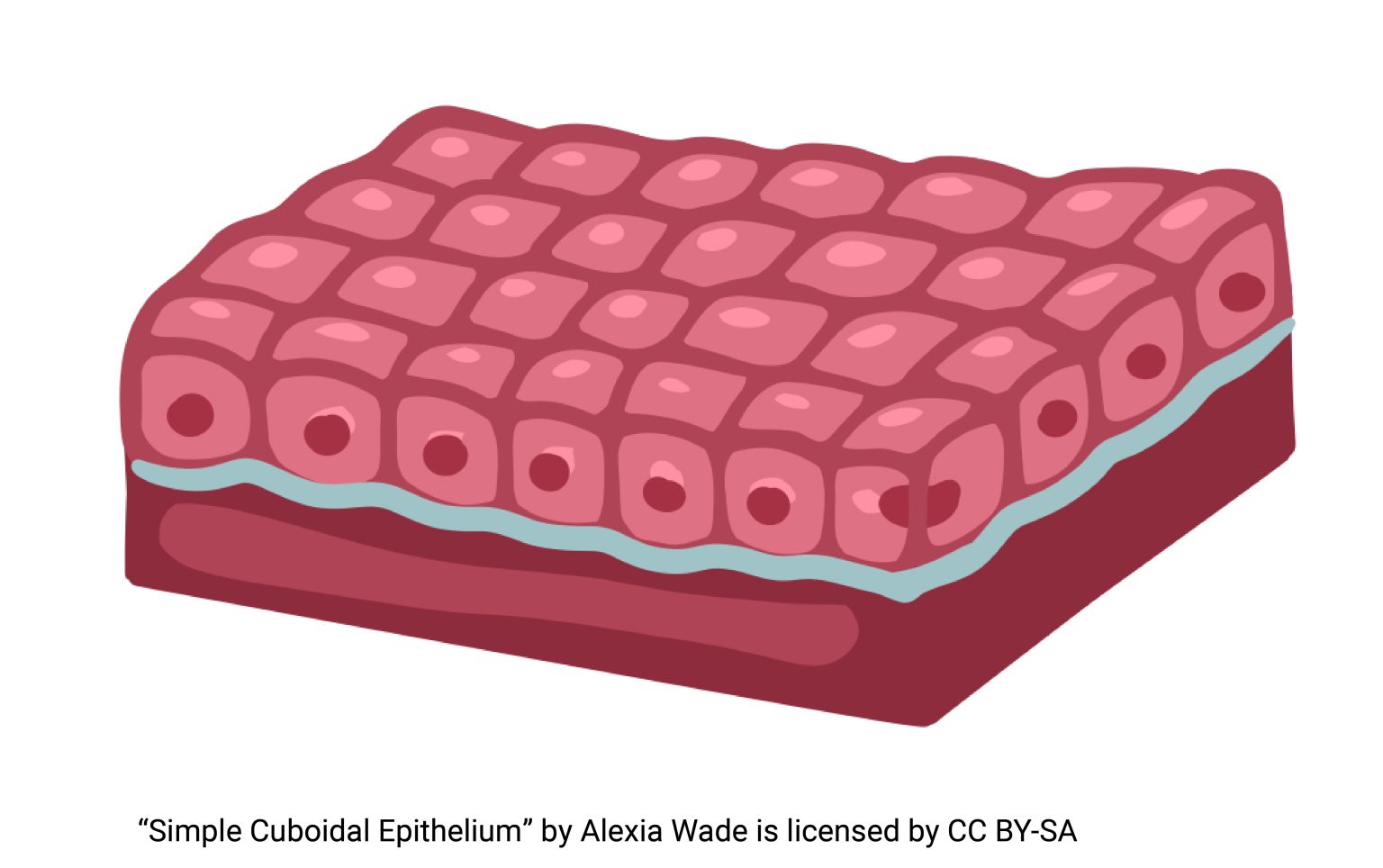
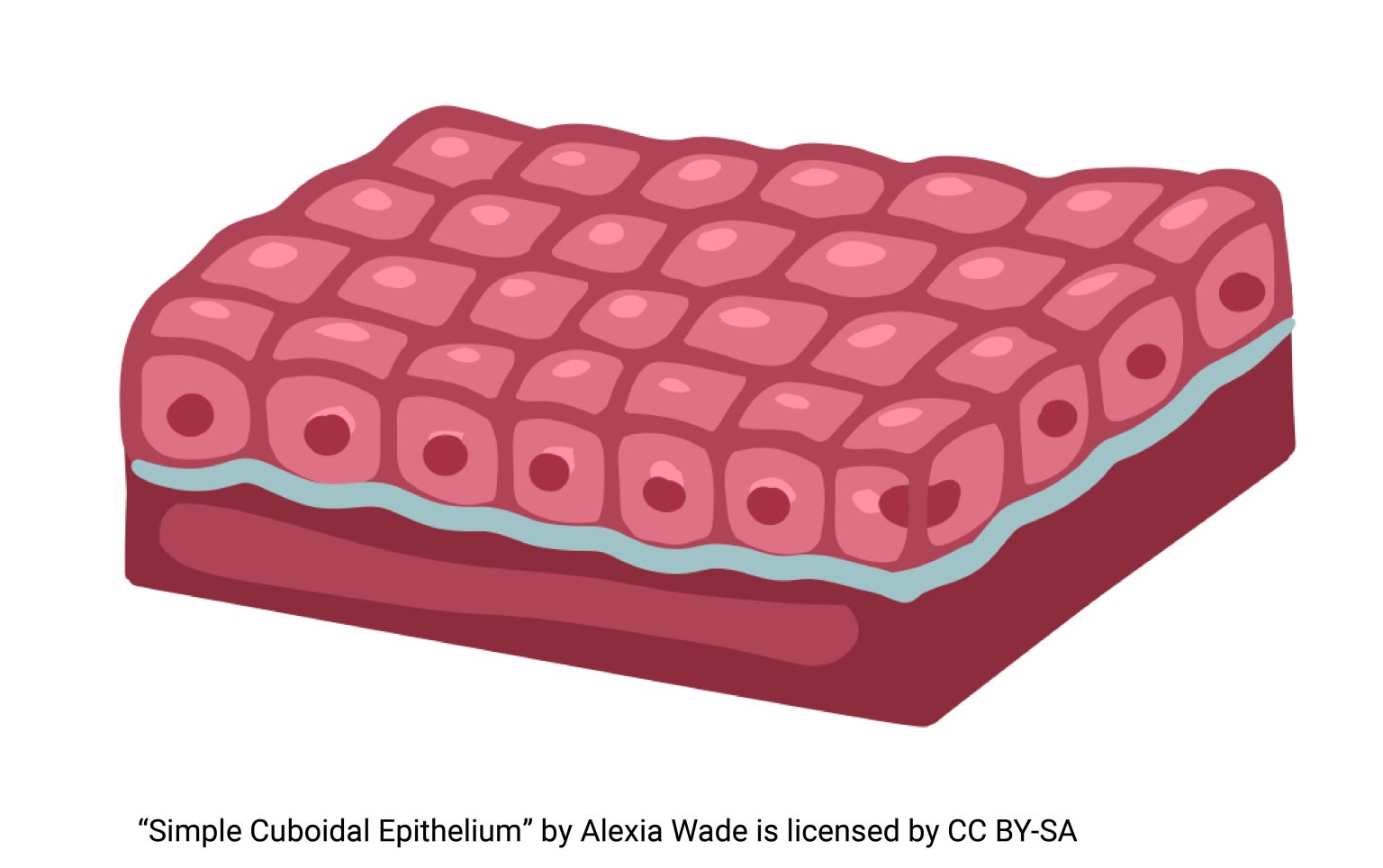
cuboidal epithelium
secretion and absorption
nucleus, microvilli, cells (combined), basement membrane
located in: kidney tubules and small gland
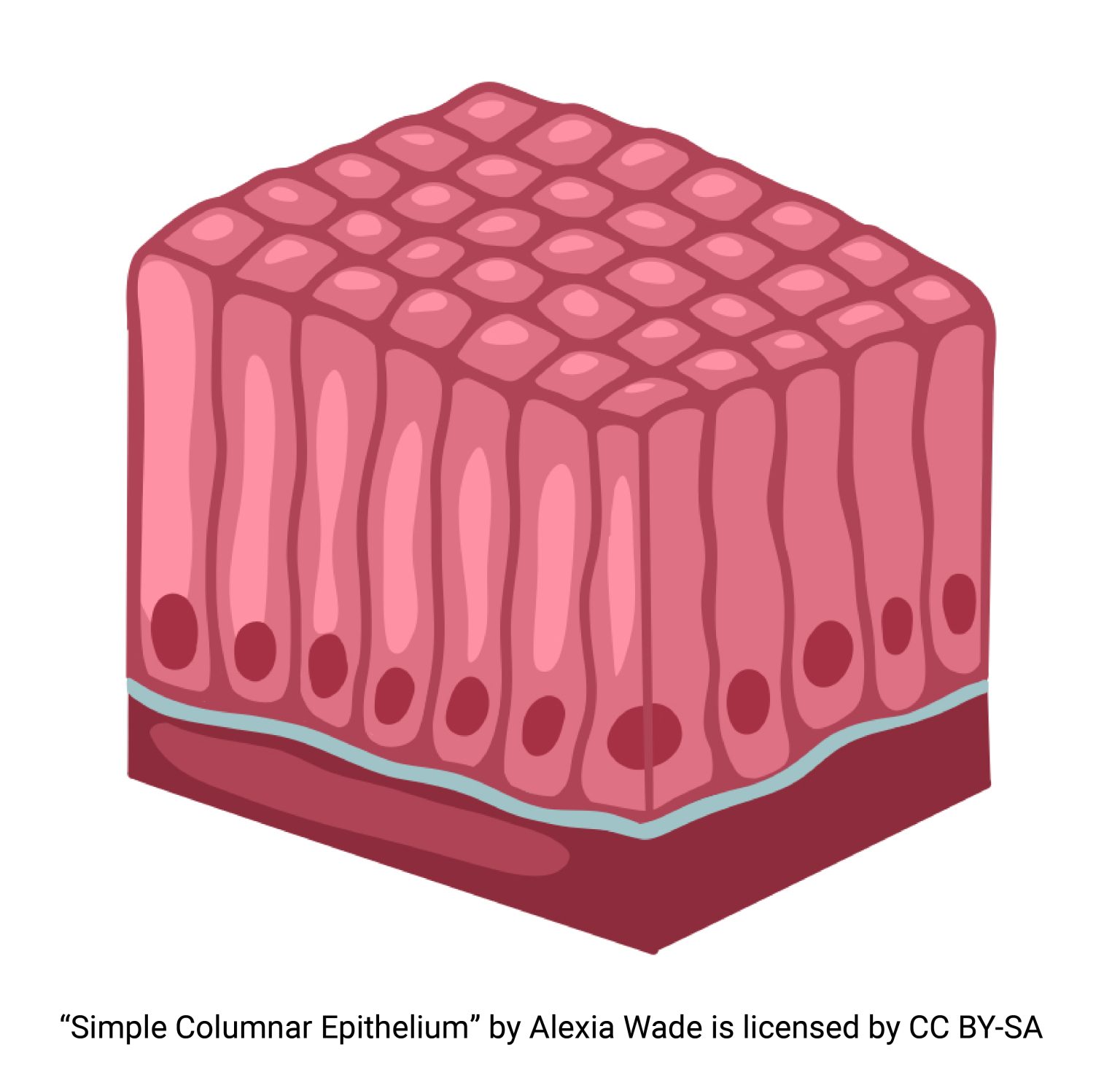

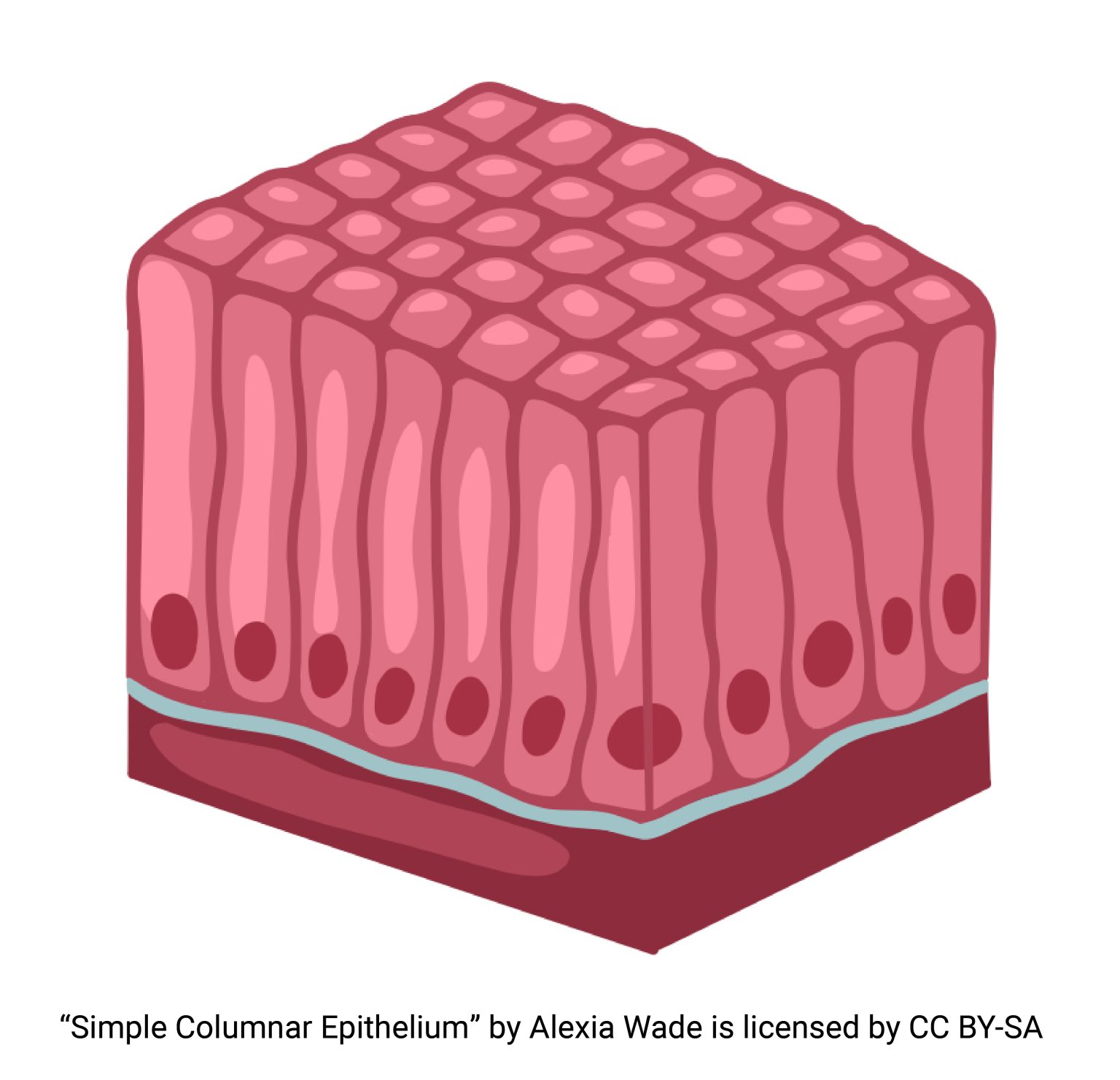
ciliated columnar epithelium
trachea: cilia moved mucus which prevents infections
oviducts: cilia moves eggs towards uterus
cells (combined), nucleus, cilium, basement membrane

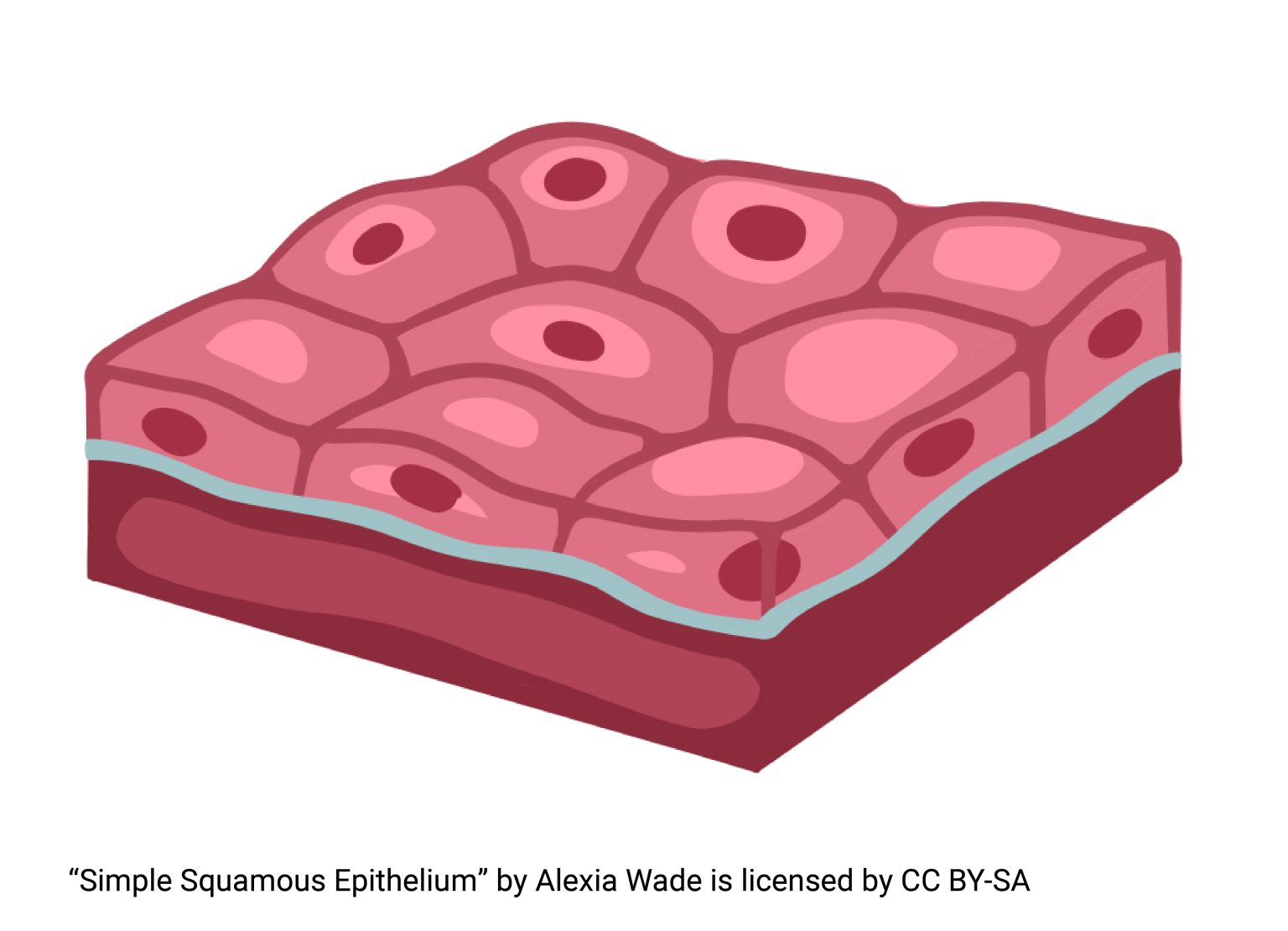
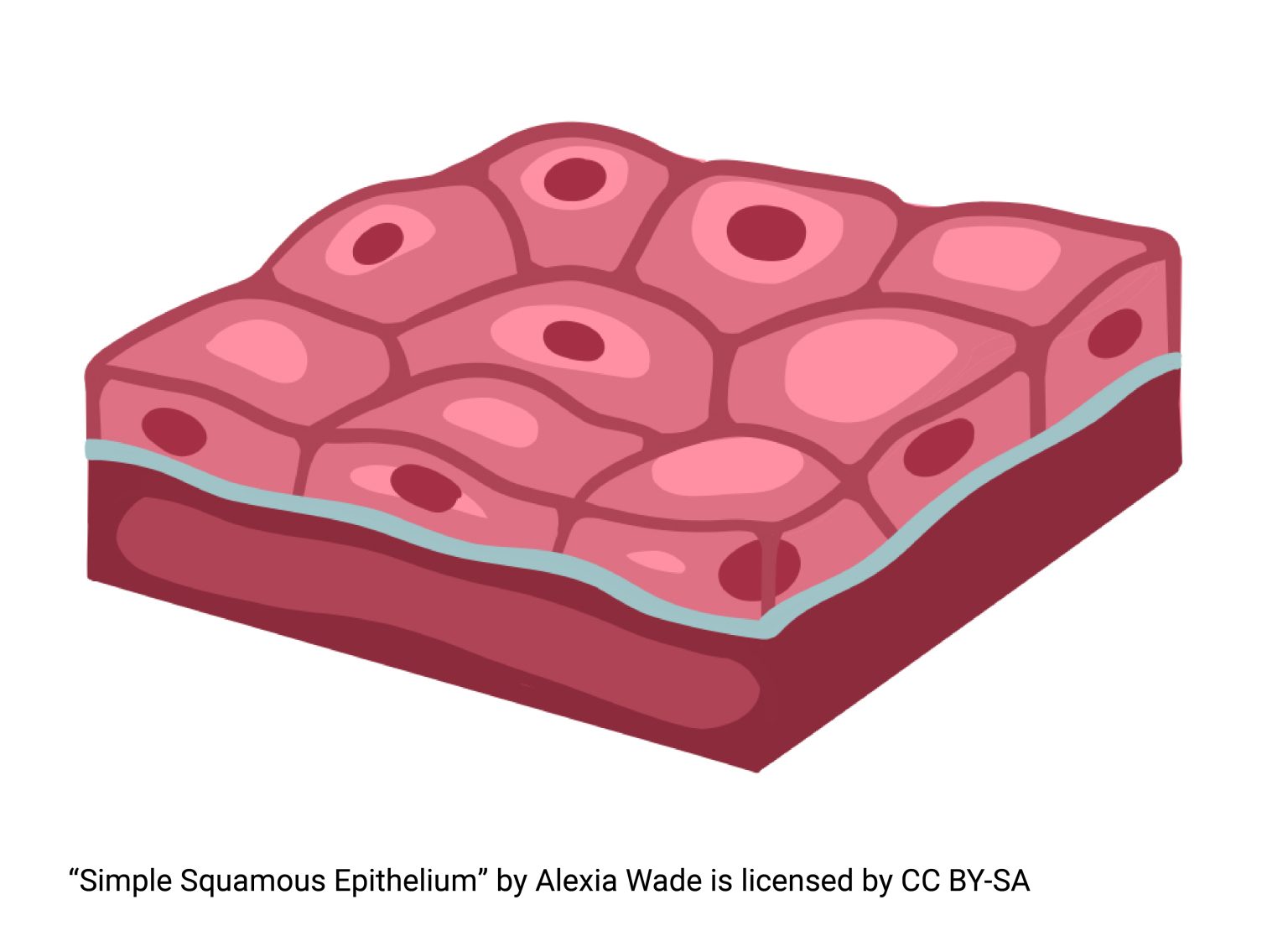
squamous epithilium
provides short diffusion distance
has nucleus and cells combined
located in alveoli in lungs and walls of capillaries
name epithelial tissue and muscle tissue types
epithelial: squamous, ciliated, columnar tissues
muscle: skeletal, smooth, cardiac tissues
cardiac muscle
contracts rhythmically and continuously without fatigue
found in heart
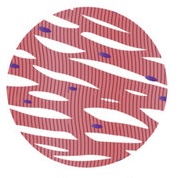
striated (skeletal) muscle
contracts quickly but fatigues fast
responsible for voluntary movment (writing, eating, talking)

smooth (involuntary) muscle
involuntary control → move substances
in the walls of blood vessels
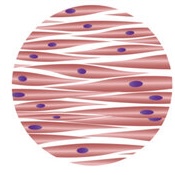
link the properties of skeletal muscle to its function
skeletal muscle allows bones to move, therefore are voluntary muscles. due to the long bands of cells it has high power.
due to the high power, skeletal muscle tires easily
explain how you would identify a smooth muscle tissue
the cells has no uniform shape, and are unstriated, they are found throughout the body
explain how you would identify a skeletal muscle tissue
made of long parallel cells arranged to form a fibre, the cells are striated (stripes), found attached to the bones
name 3 categories of tissues found in animals
epithelial, muscle and connective
explain how you would identify cardiac muscle tissue
the cells are found only in the heart, they are striated but do not form long fibres
describe the structure of connective tissue
contains fibres of collagen and elastic
link the properties of cardiac muscle to its function
cardiac muscle allow the heart to contract, therefore they do not tire and are involuntary.
they are striated so have a medium power
link the properties of skeletal muscle to its function
skeletal muscle allow bones to move, therefore they are voluntary muscles
due to long bands of cells it has high power. due to the high power, skeletal muscle tires easily