Lecture 9: Amniotes: Cutting ties with Water
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Amniota
Reptilomorphs that lay amniotic eggs, with thick keratinous skin, and costal lung ventilation
Characteristics of Amniota
Amniotic Egg
An egg with elaborate extraembyronic membranes, surrounded by a shell
Relatively Impermeable Skin
Amniotes have a much thicker epidermis with elaborate keratinous structures (scales, feathers and hair) made of the protein keratin
Costal ventilation of Lungs
Have an advanced method of lung ventilation that involves the rib cage
Temporal Fenestration
Skulls are characterized by openings (temporal fenestrae) posterior to the orbit - which vary between and within groups of amniotes; may have evolved independently within Amniota
The Amniotic Egg differs from the egg of non-amniotic vertebrates by the presence of
Three additional extraembyronic membranes develop from the embryo
Amnion
Allantois
Chorion
Shell
Provides mechanical protection but is porous enough to allow movement of respiratory gases and water vapor
Amnion
Extraembryonic membrane that only surrounds the embryo
Cavity formed between the embryo and the amnion is referred to as the amniotic cavity - filled with amniotic fluid
Allantois
An extraembryonic membrane that develops as an extension of the hind gut
Acts as storage area for nitrogenous waste produced by the metabolism of the embryo - base of allantois contributes to the formation of the urinary bladder in adult stage
Highly vascularized and serves as a respiratory organ during later development
Left behind upon hatching
Chorion
An extraembryonic membrane that surrounds the other extraembryonic membranes (the chorion is the outermost membrane)
Amniotic egg shell
Shell gland in female reproductive system tract - produces outer shell
Offers mechanical protection
Have different properties, some are hard, some are soft
All are porous
Whats the advantage of the amniotic egg?
Allows amniotes to (1) dispense with the larval stage entirely, and (2) have larger offspring upon hatching
Stratum Corneum
Outermost layer of the epidermis, which is composed of dead keratin-rich cells
Stratum Corneum
Outermost layer of the epidermis, which is composed of dead keratin-rich cells
Costal Ventilation
Mode of lung ventilation that utilizes the rib cage to expand and contract lungs.
Expansion of rib cage creates negative pressure which draws air into the lungs - relaxation of rib cage forces air back out (referred to as tidal flow)
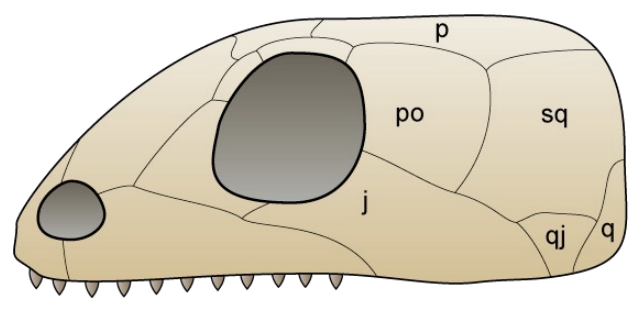
Temporal Fenestration
openings in the skull that allow lower jaw musculature to expand onto the skull roof
three different conditions
Anapsid Condition
Synapsid Condition
Diapsid Condition
Anapsid Condition
No fenestra
Early amniotes (primary) and turtles (secondary condition)
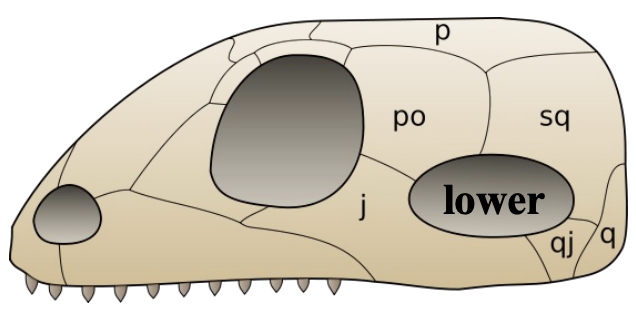
Synapsid Condition
Single fenestra (lower) behind orbit
Synapsids (mammals and mammal-like reptiles)
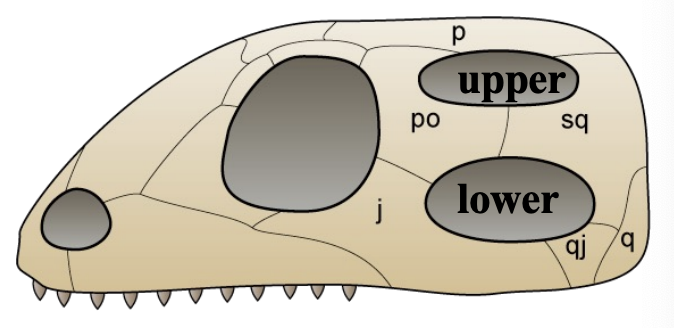
Diapsid Condition
Two fenestrae (upper and lower) behind orbit
Lepidosaurs (tuataras, lizards and snakes) and archosaurs (crocodiles, dinosaurs and birds)
Synapsida
Synapsid condition animals
Have an alveolar lung - air flows over alveoli twice
Sauropsida
Anapsid and Diapsid Condition animals.
Have a faveolar flow-through system lung where oxygenated air flows across the respiratory surface (faveoli)