Chemistry chapter R2.2 Collision theory and Kinetics
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Collision theory, boltzman graphs, rates of change, instantenours rates of change
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Colision theory
1)Particles must collide
2)Particles must have enugh kintetic energy to overcome electron cloud repulsion to react. This is called activation energy Ea and is directly proprotional to the temperature in kelvin
3) Particles must collide in the correct geometrical allignment (steric factor)
What does and activation energy graph contain?
y axis - potential energy
x axis - reactants products
Based on enthalpy change
What factors affect collision rate?
1) Concentration/Pressure
2) Surface area
3) Temperature
How to lower activation energ?
1) Catalyst
2) Temperature
How does concentration impact the rate?
Increasing concentration raises the number of reactant particles, leading to more frequent collisions and increase in reaction rate.
This increases the chance that the particles will have
1) More collision
2) Enough energy
3) Right 3D orientation
How does surface are impact the rate?
Increasing surface area increases the area for particles to contact therefore increases the chance for collisions.
Thus, there is more area, more collisions, so more likelyhood for particles having enough energy and colliding with the right 3D orientation.
How does temperature affect the reaction rate?
Increasing temperature provides particles with more kinetic energy. so more particles have sufficient activation energy to react.
(Also temperature means that particles move faster, so they collide more frequently)
(More chances of right 3D orientation because there are more collisions)
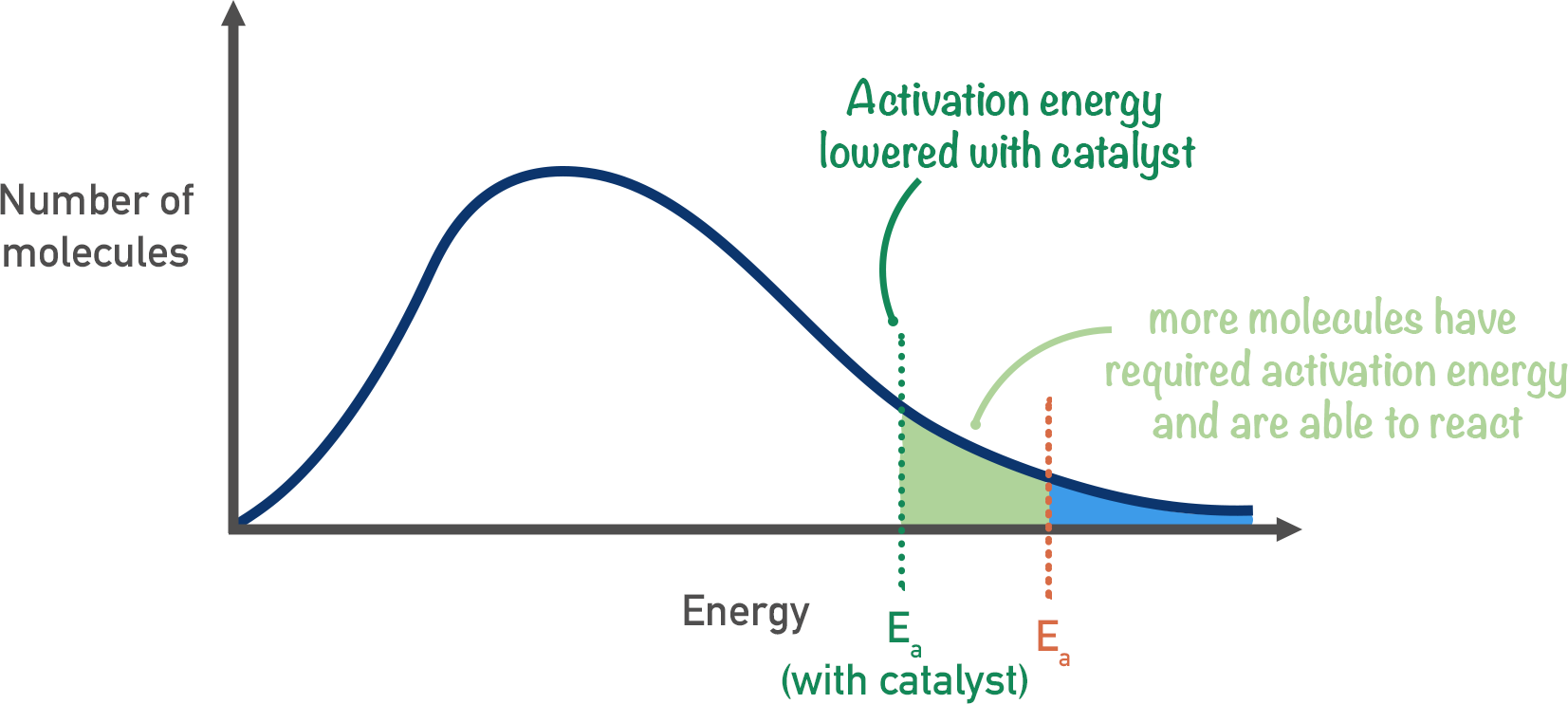
Maxwell-Boltzmann curve
Y - number of particles
X - kinetic energy
As the temperature increases so the probability of molecules having higher energy increases
What do you calculate in Maxwell-Botlzman curve? Draw one
Change in Area
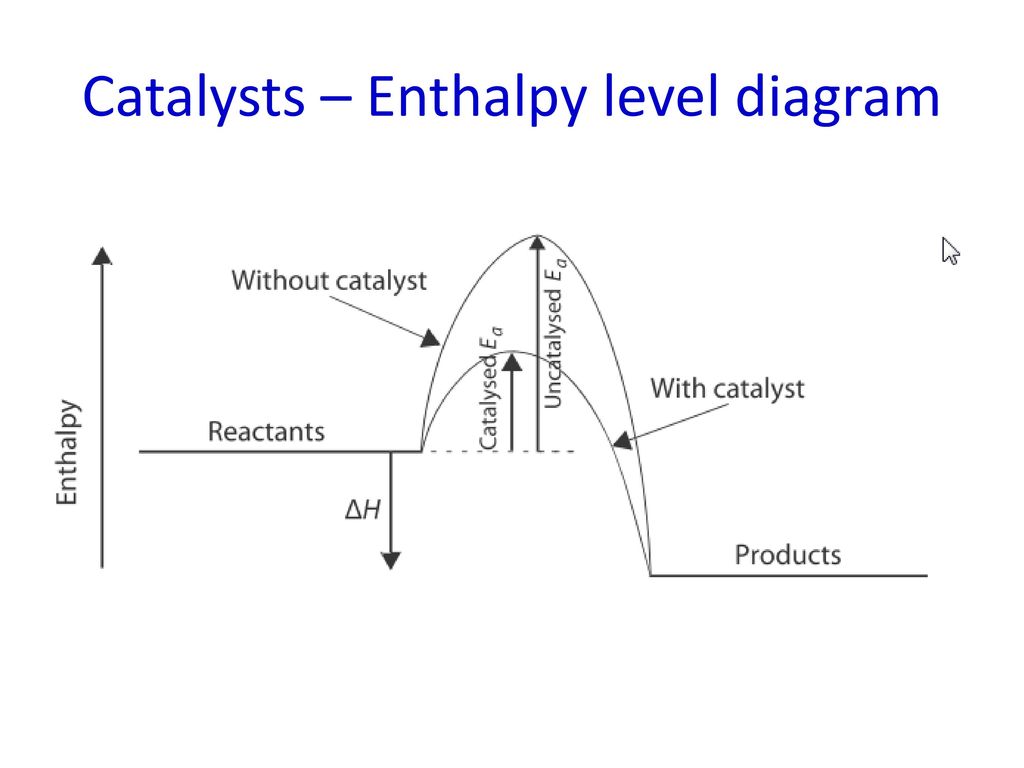
What do Catalysts do for rate of the reaction? Draw Boltzman curve
Dont change the rate but change the activation energy. Line up the molecules. Decrease the activation energy therefore increases the number of particles that have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy
Draw catalyst enthalpy diagram
Rate of reaction
The change of concentration of reactants or products with time (mol dm^*3 s^-1)
What factors will determine rate?
Surface area
Concentration or pressure
temperature
catalyst
How is the rate of the reaction found?
Through experimentatioj
Rate of decreasing reactants (-change in contnetration / change in time
Rate of increasing products (Change in concentration/ change in time)
What are the 6 ways to measure rate of a reaction?
Changes in:
1) Gas or pressure
2) Mass
3) Colour
4) pH
5) Conductivity
Gas collection syringe
What is gas collection over water not goof for?
Not goof for water soluble chemicals
Warmer water will decrease solubility
What is change in mass not good for?
Not good for light gases such as hydrogen
What is the technique for measuring change in color? What is it based on? What does it measure?
Colormitery/Spectrosphotometry
Based on absorbance and trasnmittance spectrums
Measures concentration