6th Grade Science Review part 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
energy
the ability to do work
kinetic energy
the energy an object has due to its motion
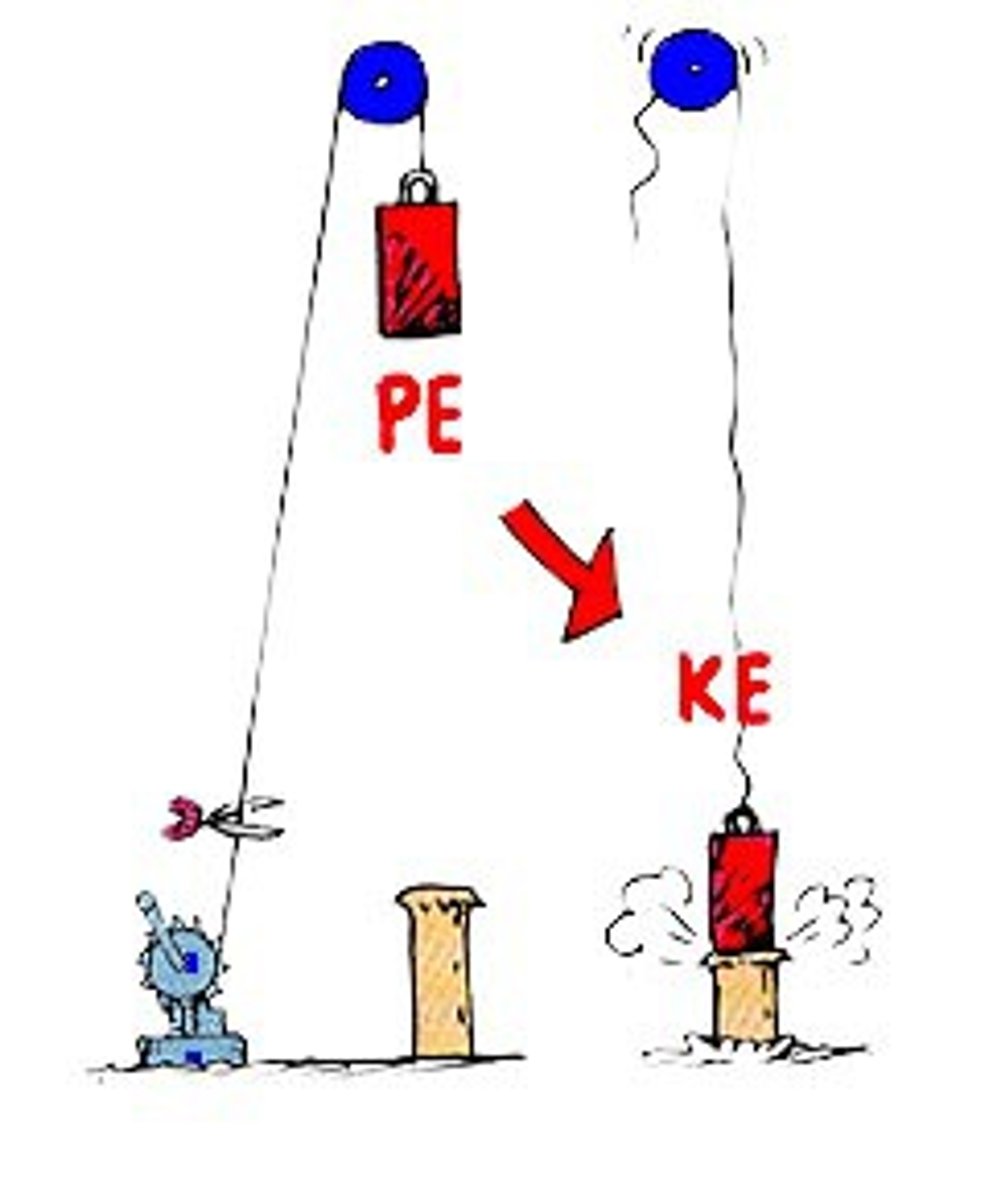
potential energy
stored energy
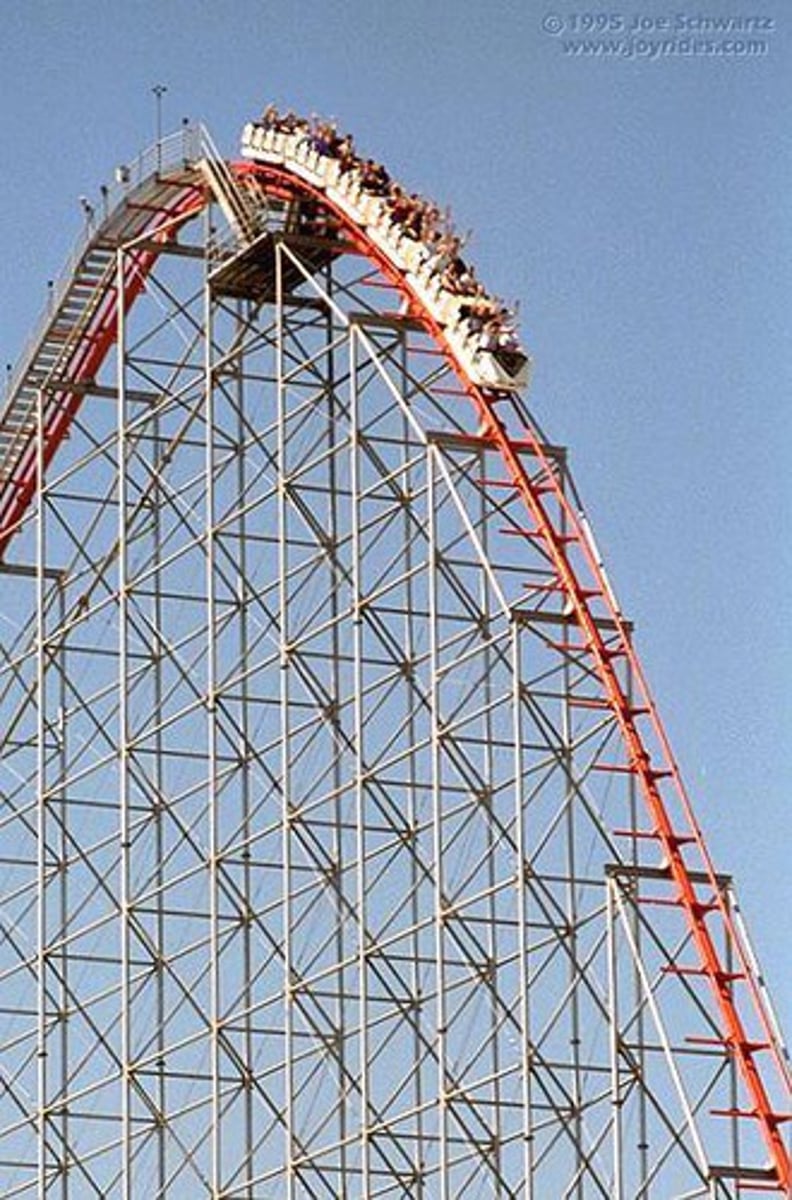
gravitational potential energy
potential energy that depends on the height of an object

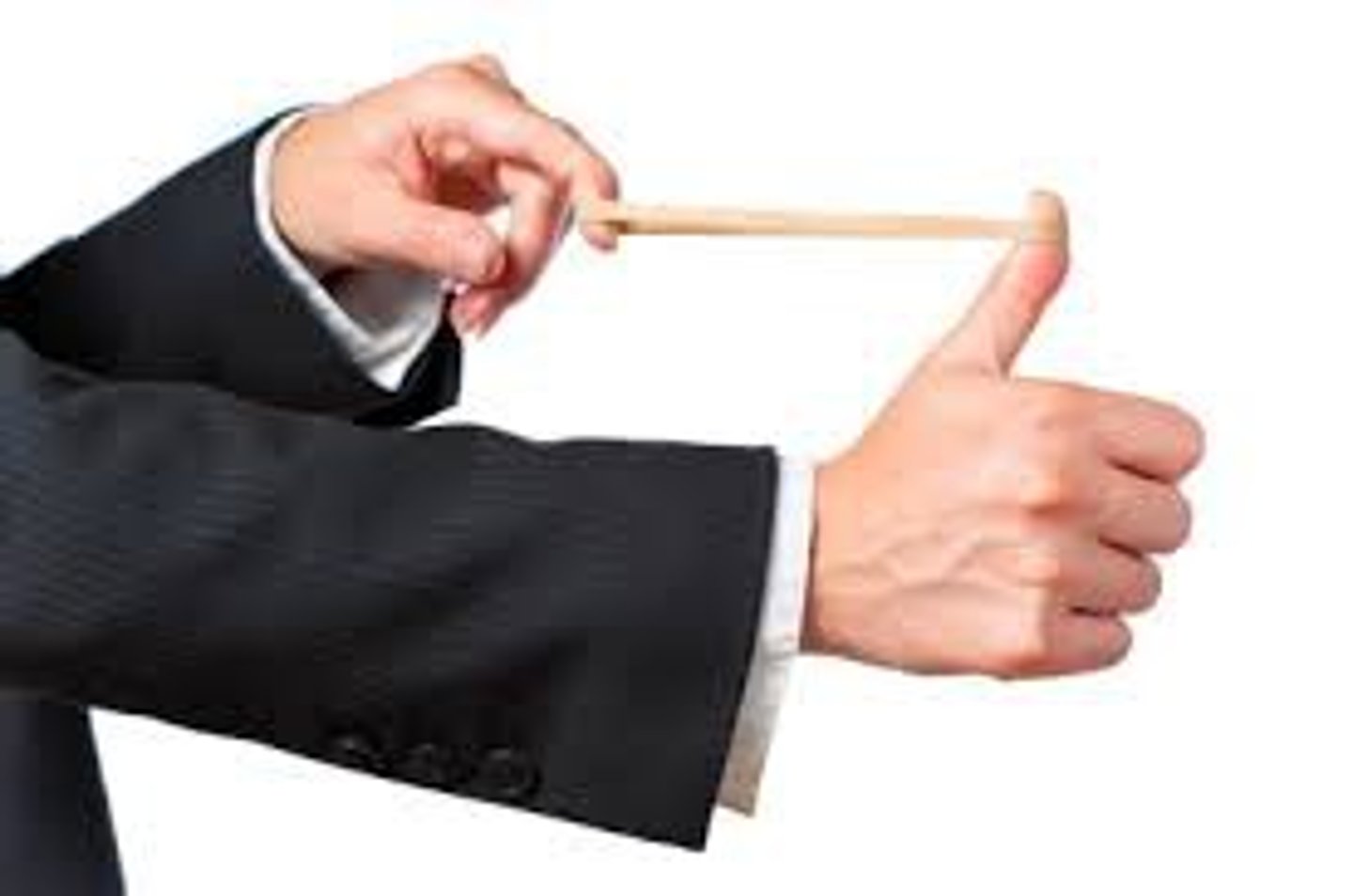
elastic potential energy
the energy of stretched or compressed objects

chemical potential energy
potential energy stored in chemical bonds

mechanical energy
the energy associated with the motion and position of everyday objects

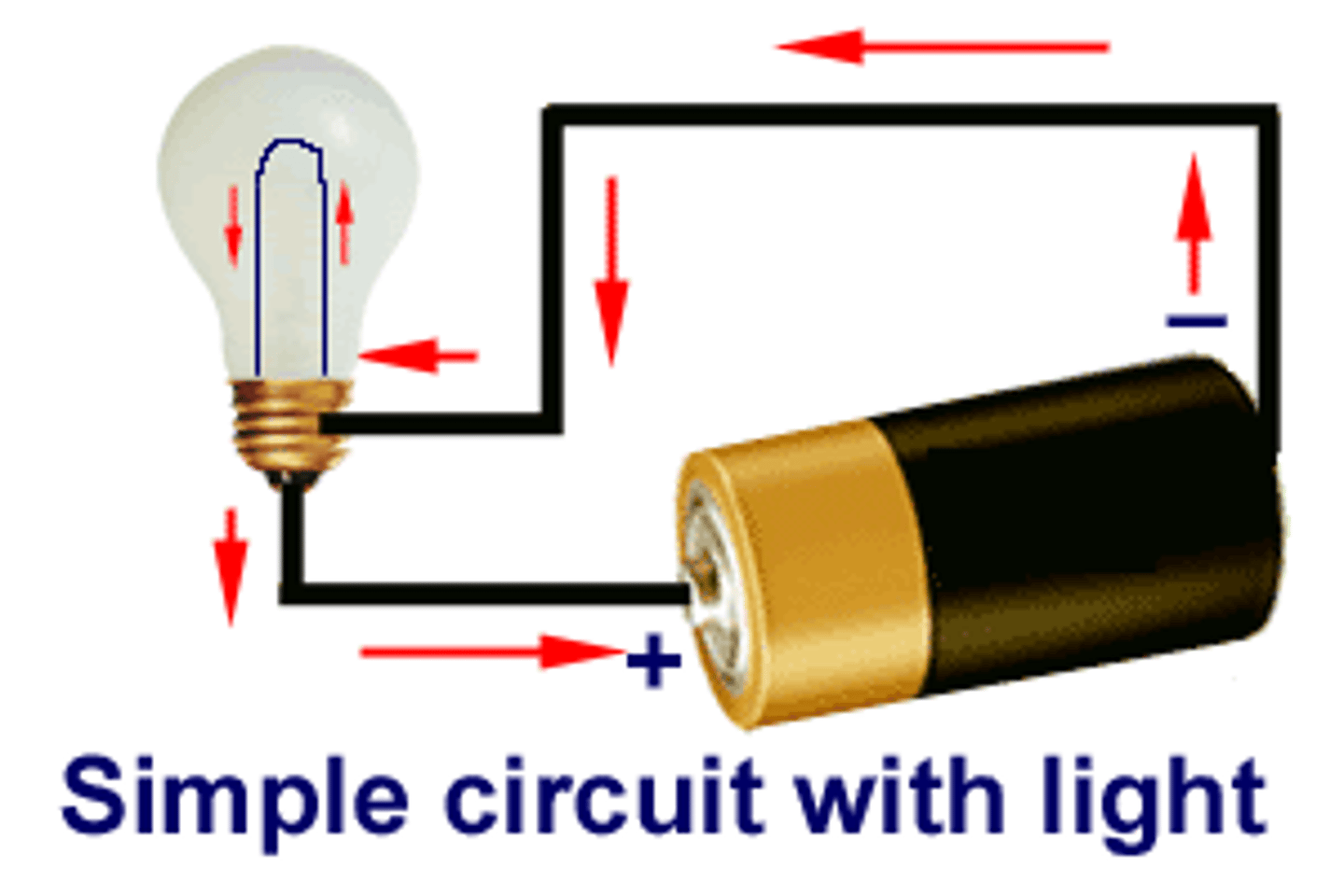
electrical energy
energy of electric charges
chemical energy
energy stored in chemical bonds

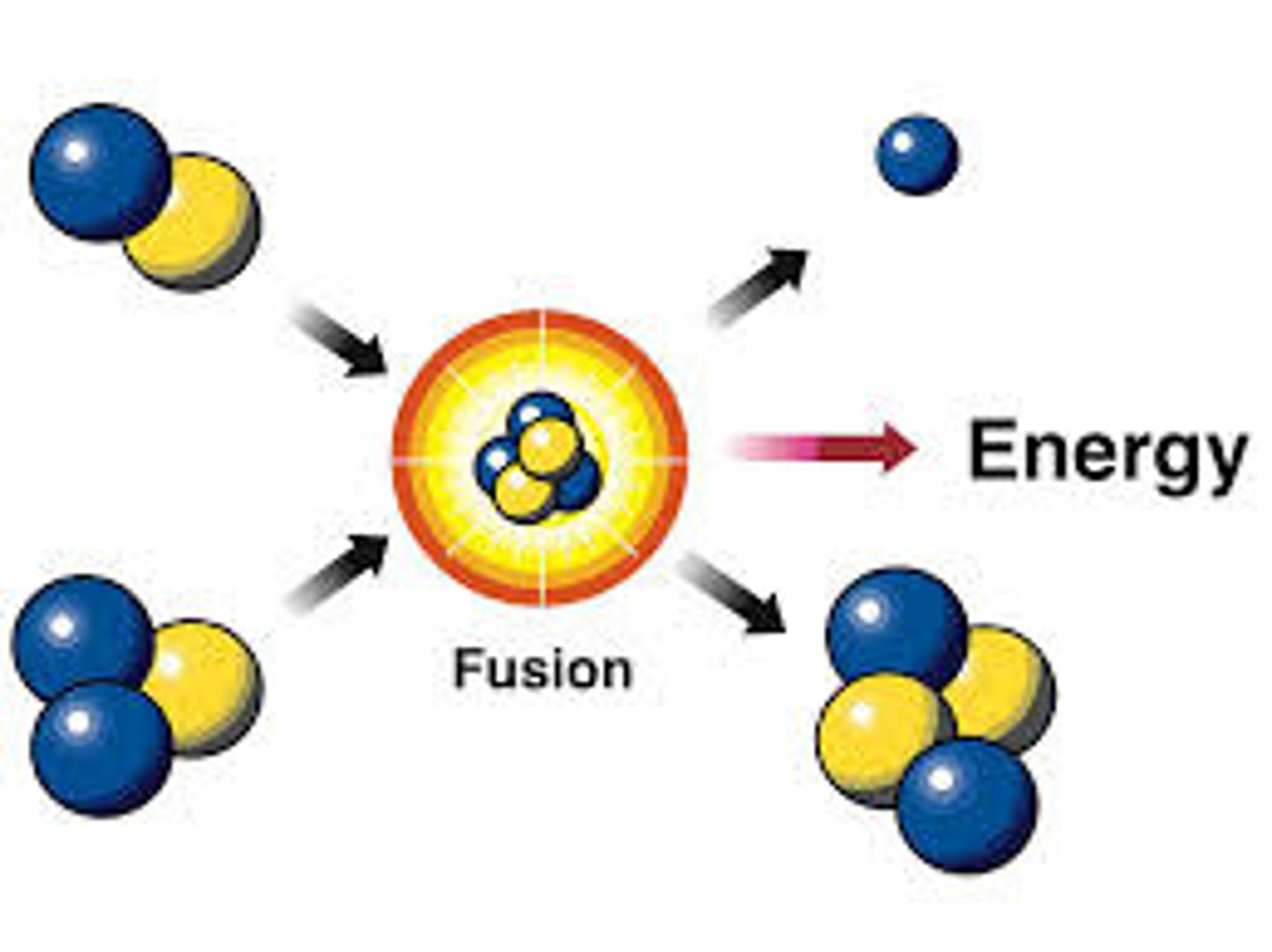
nuclear energy
energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
electromagnetic energy
a form of energy that travels through space as waves
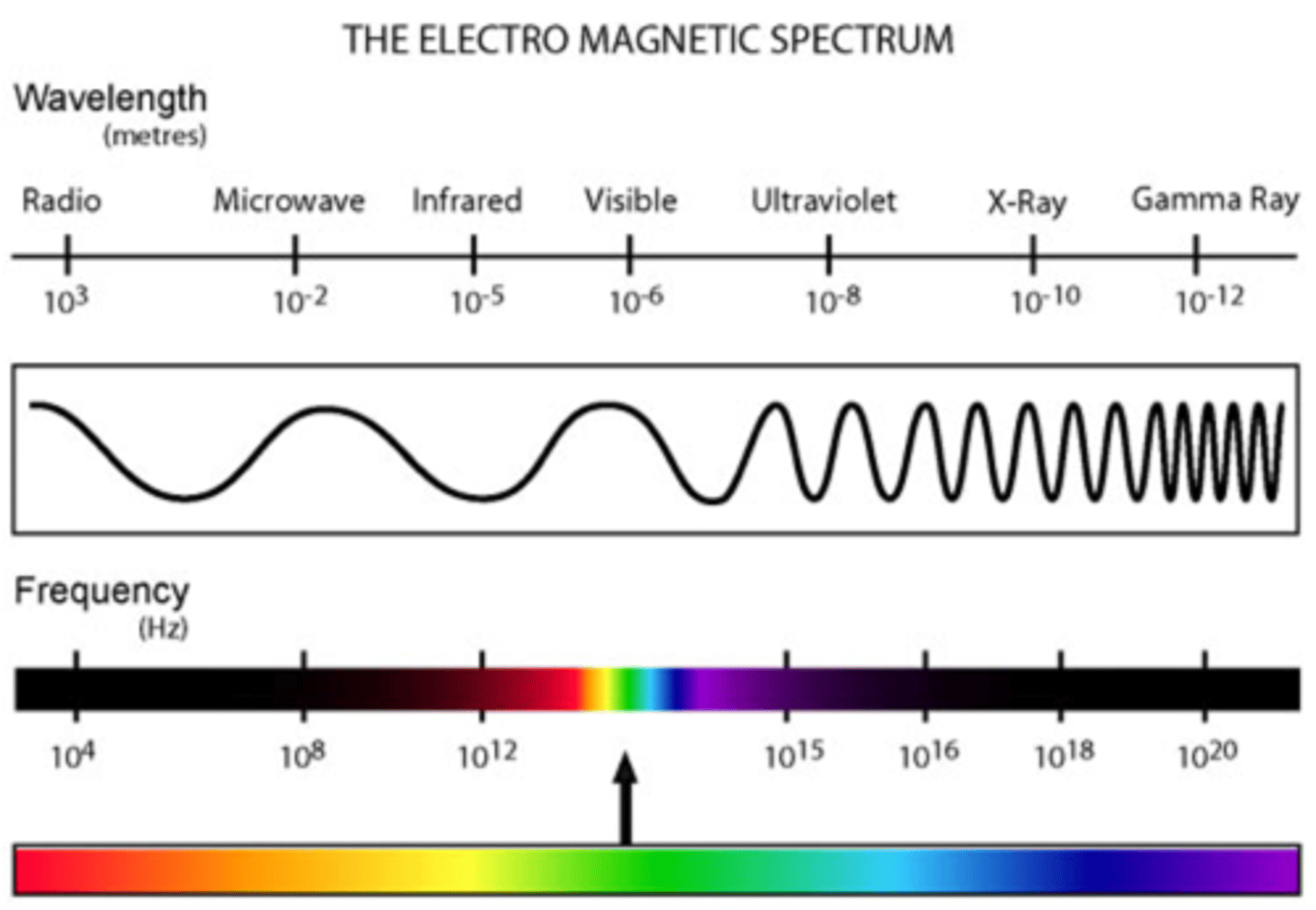
thermal energy
heat energy
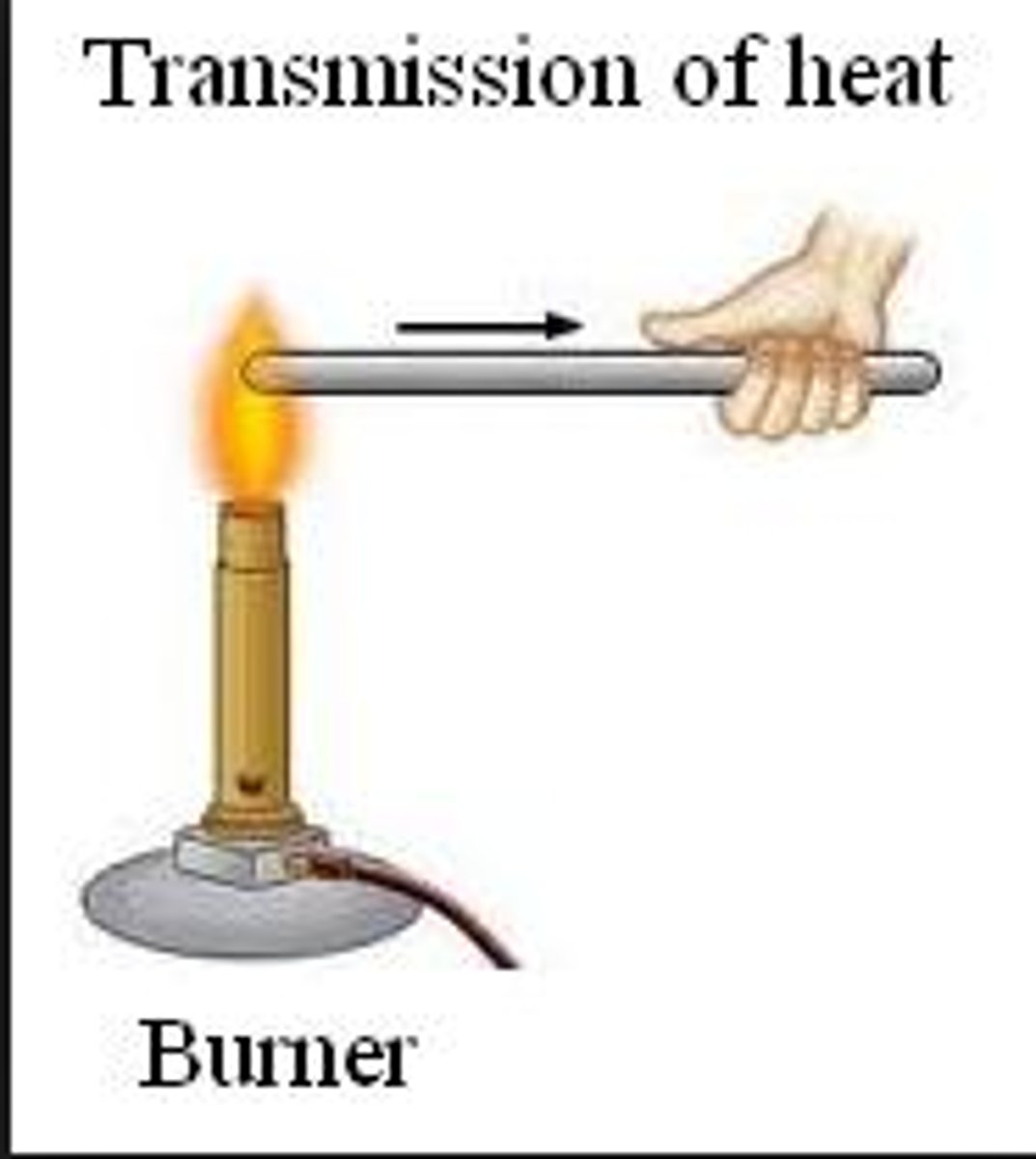
conduction
direct transfer of heat from one substance to another substance that it is touching.
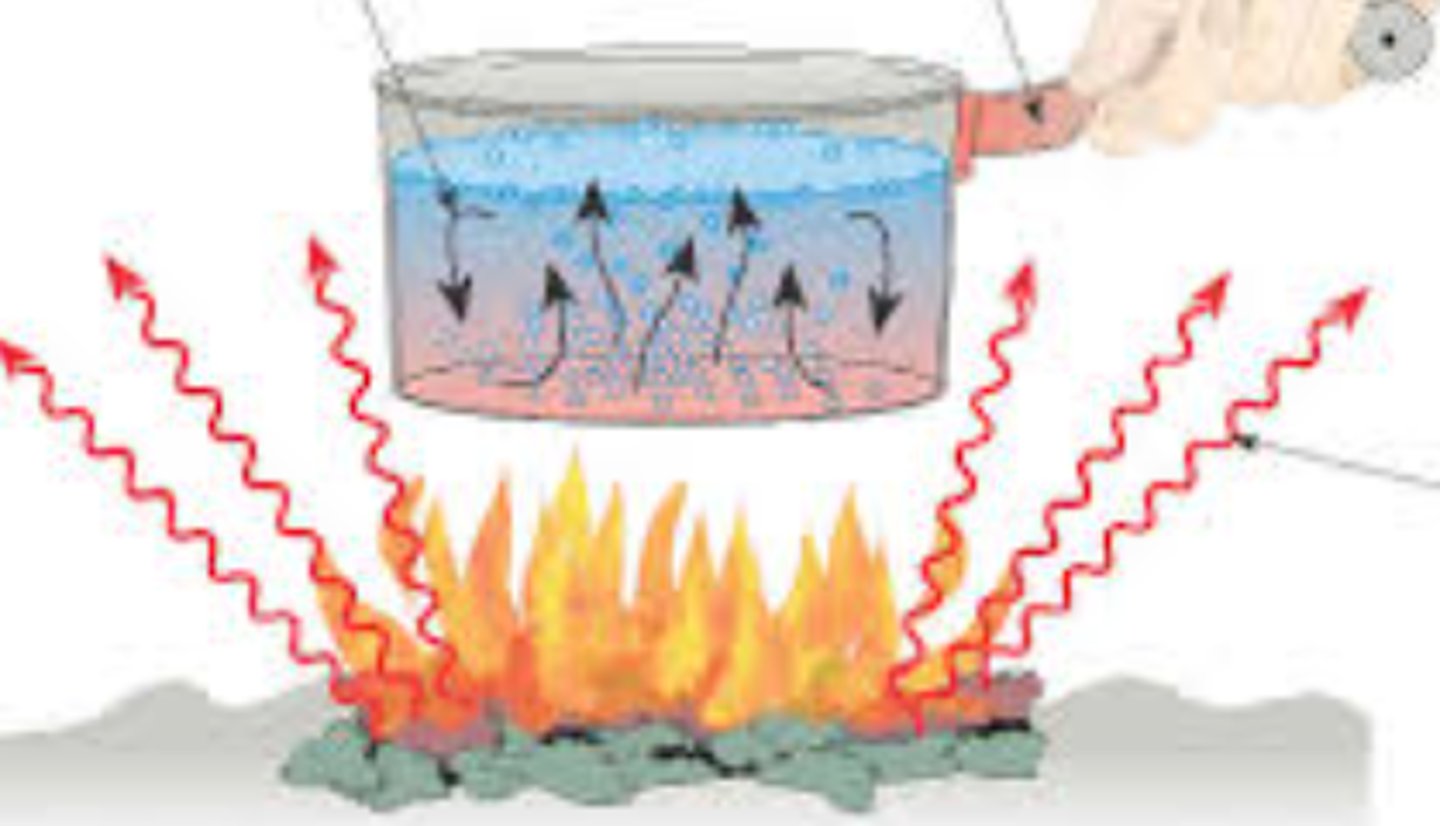
convection
transfer of thermal energy by the circulation or movement of a liquid or gas
radiation
transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves

law of conservation of energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed

temperature
measure of how hot or cold something is
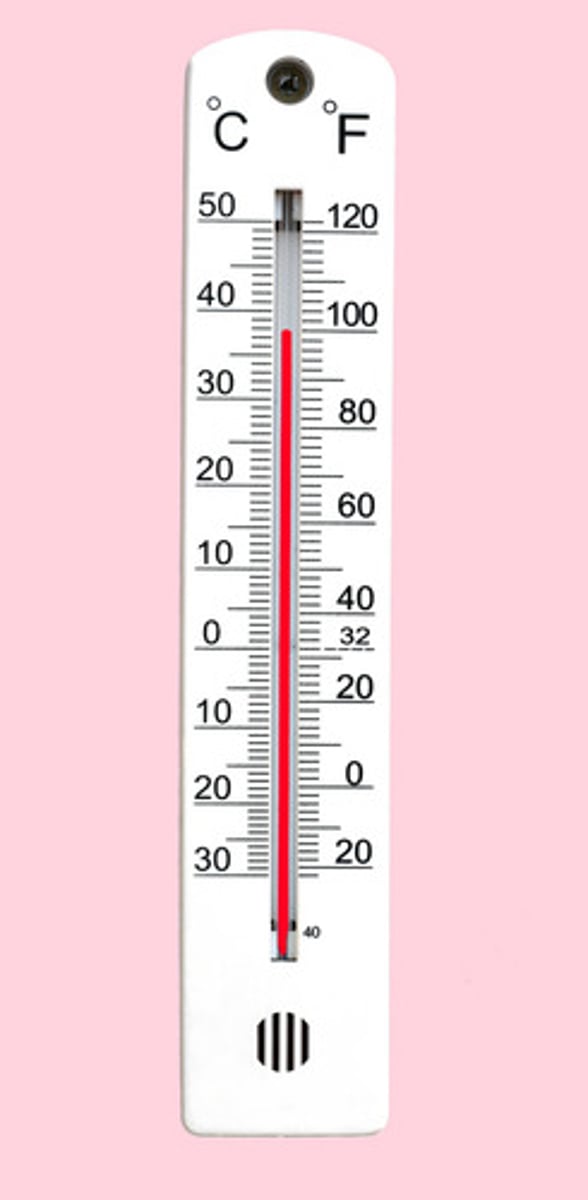
Celsius scale
temperature scale on which water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees
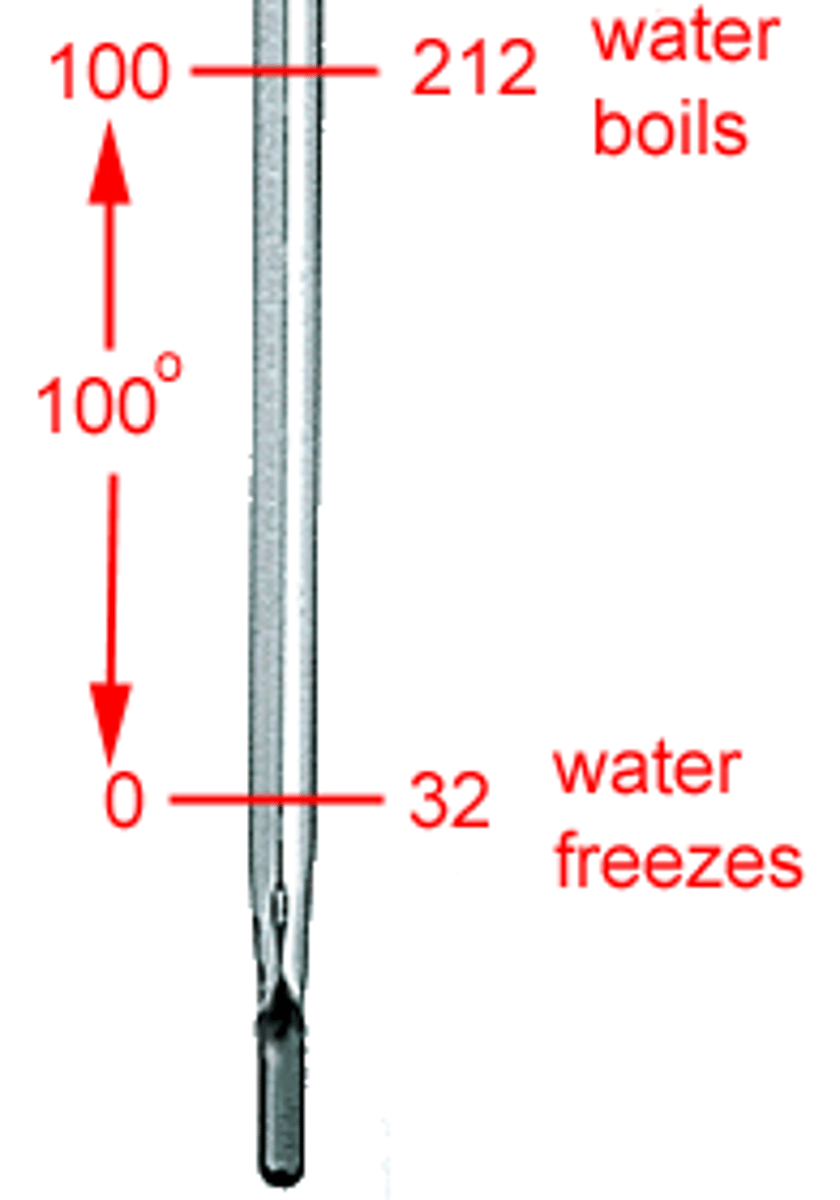
Fahrenheit scale
temperature scale on which water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees
conductor
material that conducts heat well

insulator
material that does not conduct heat well

organism
a living thing

climate
average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
evaporation
liquid to gas
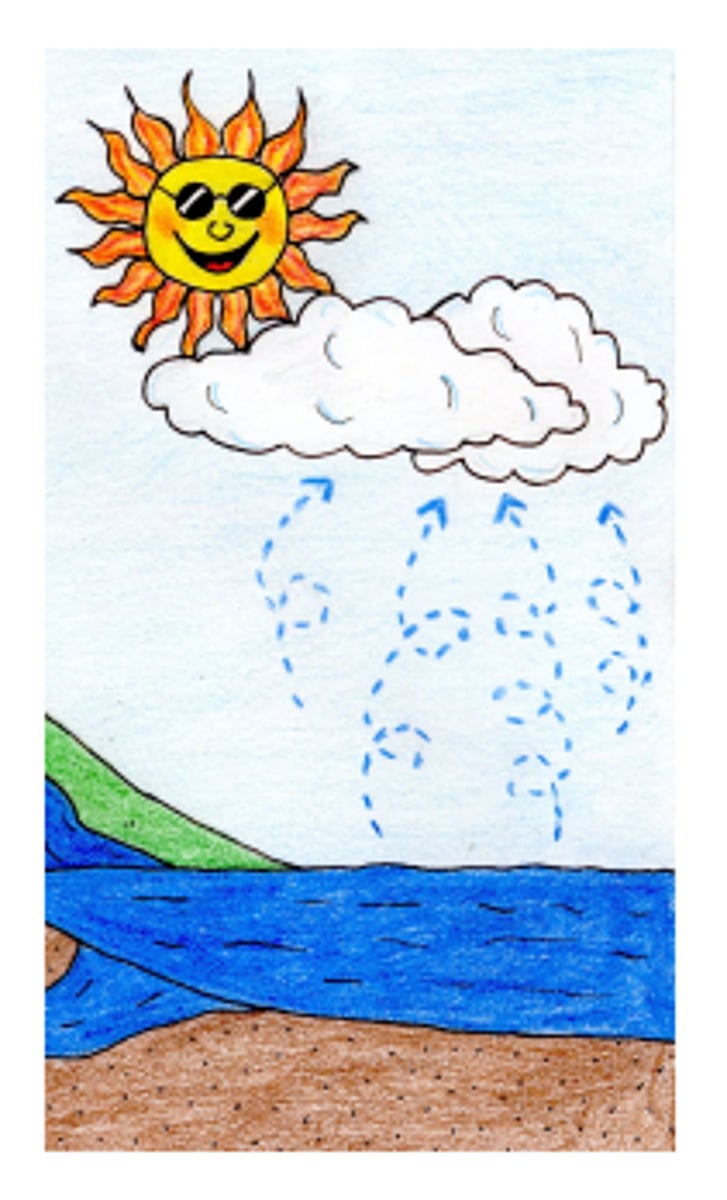

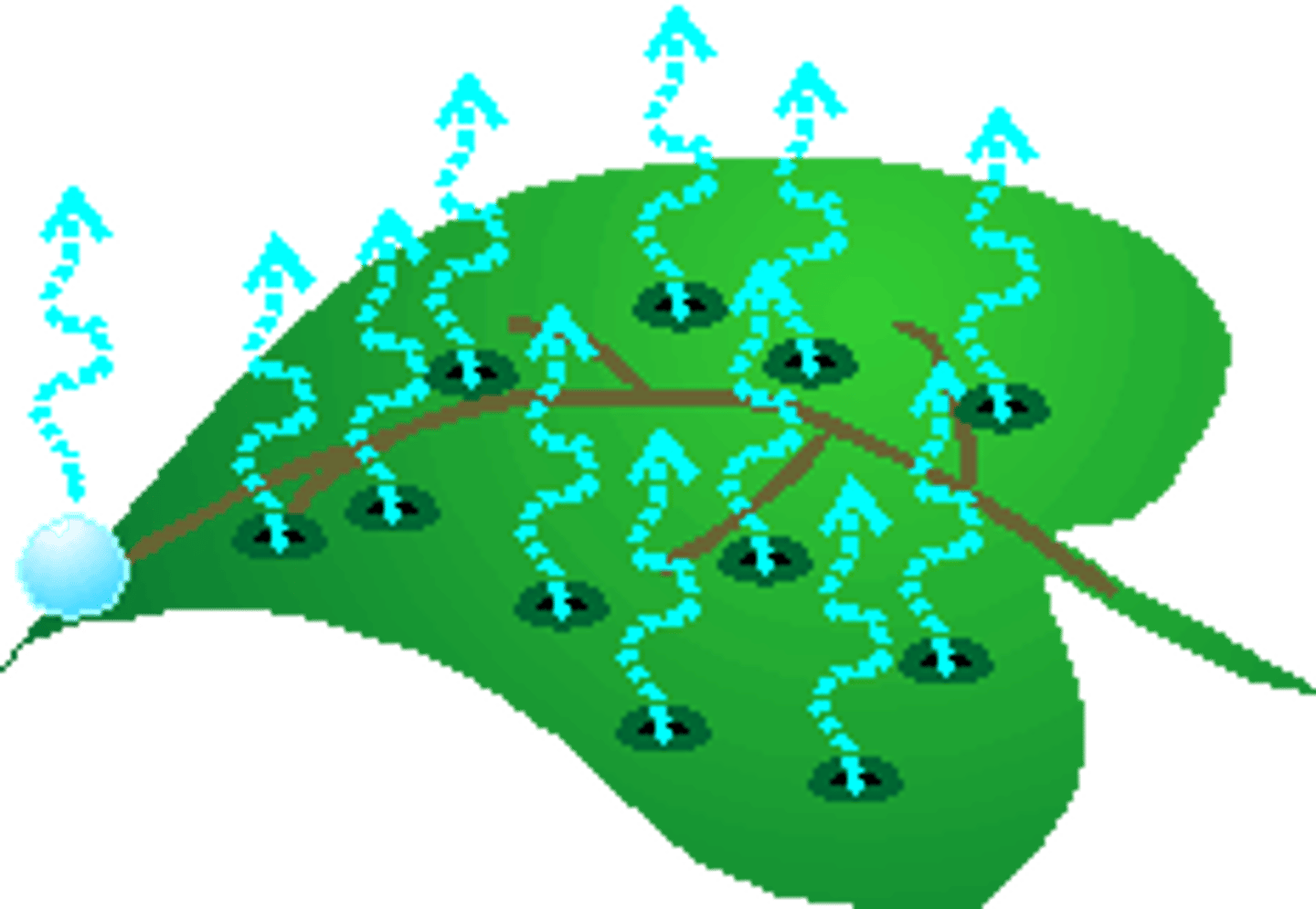
transpiration
loss of water from a plant through its leaves
condensation
gas to liquid

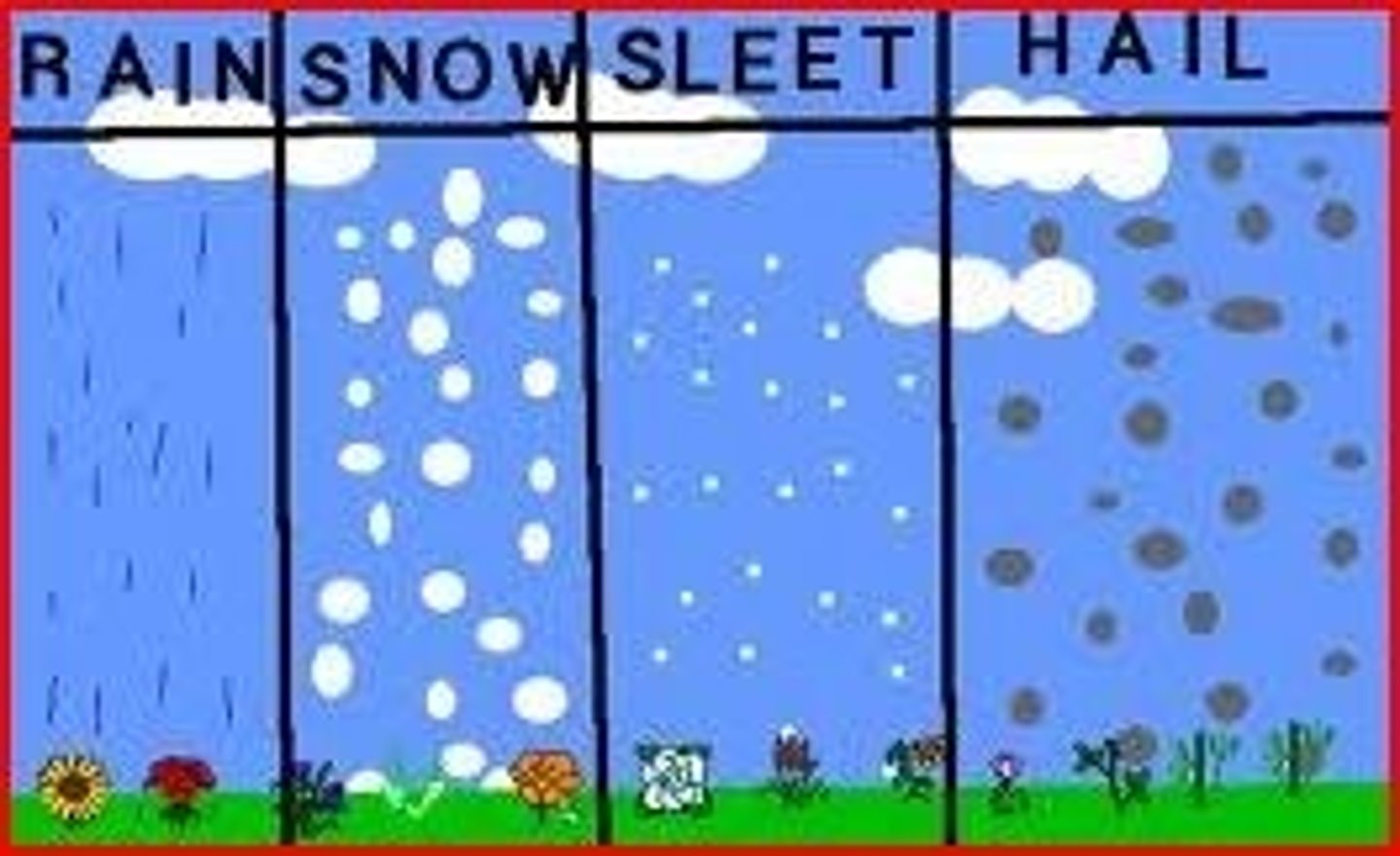
precipitation
rain, snow, sleet, or hail that falls to the ground
surface runoff
water that flows over land until it reaches lakes, rivers, or other areas

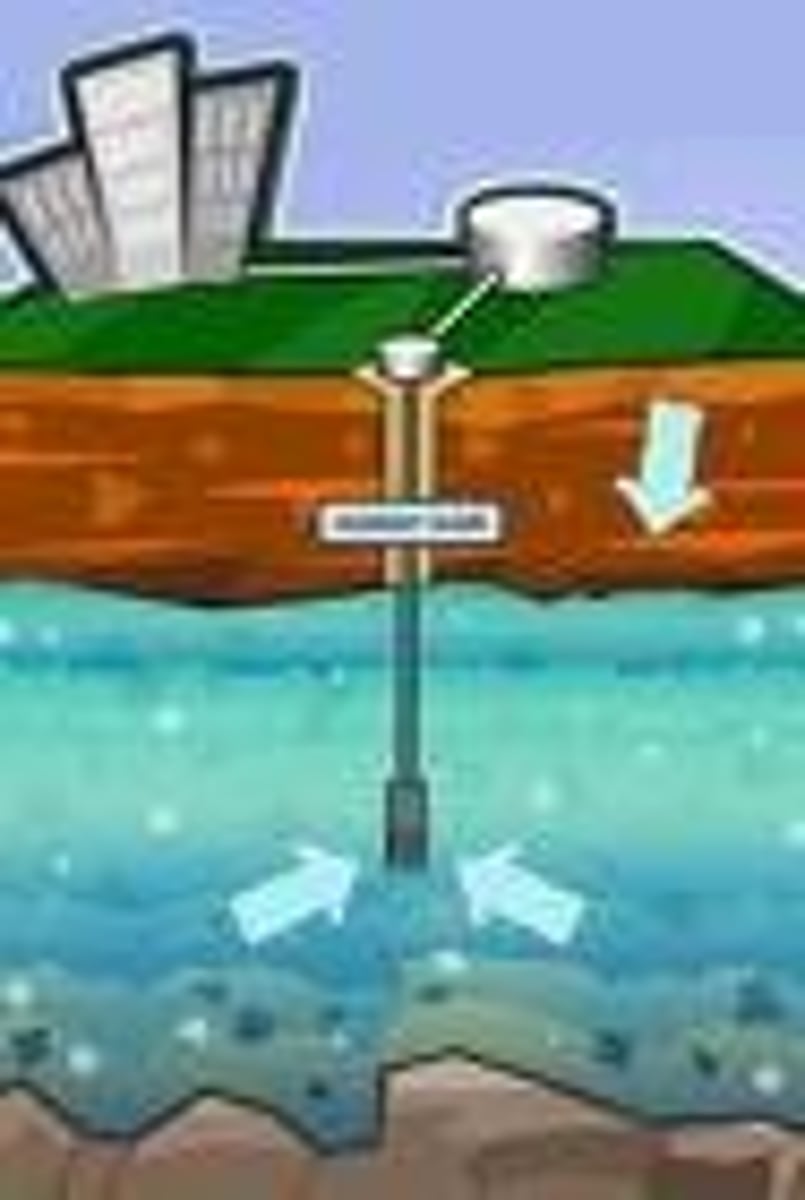
groundwater
water held underground in the soil or in pores and crevices in rock

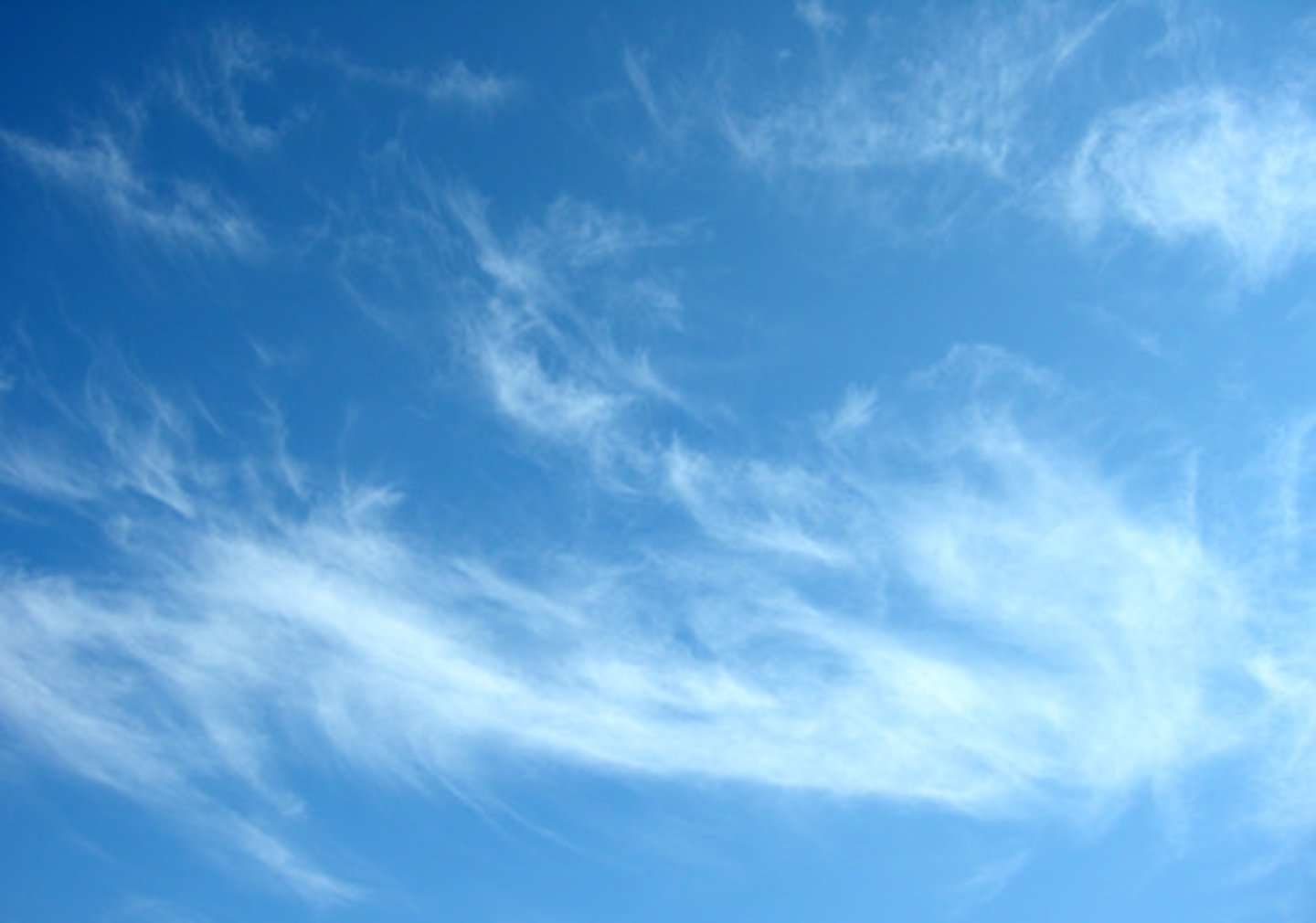
cirrus
wispy, feathery clouds

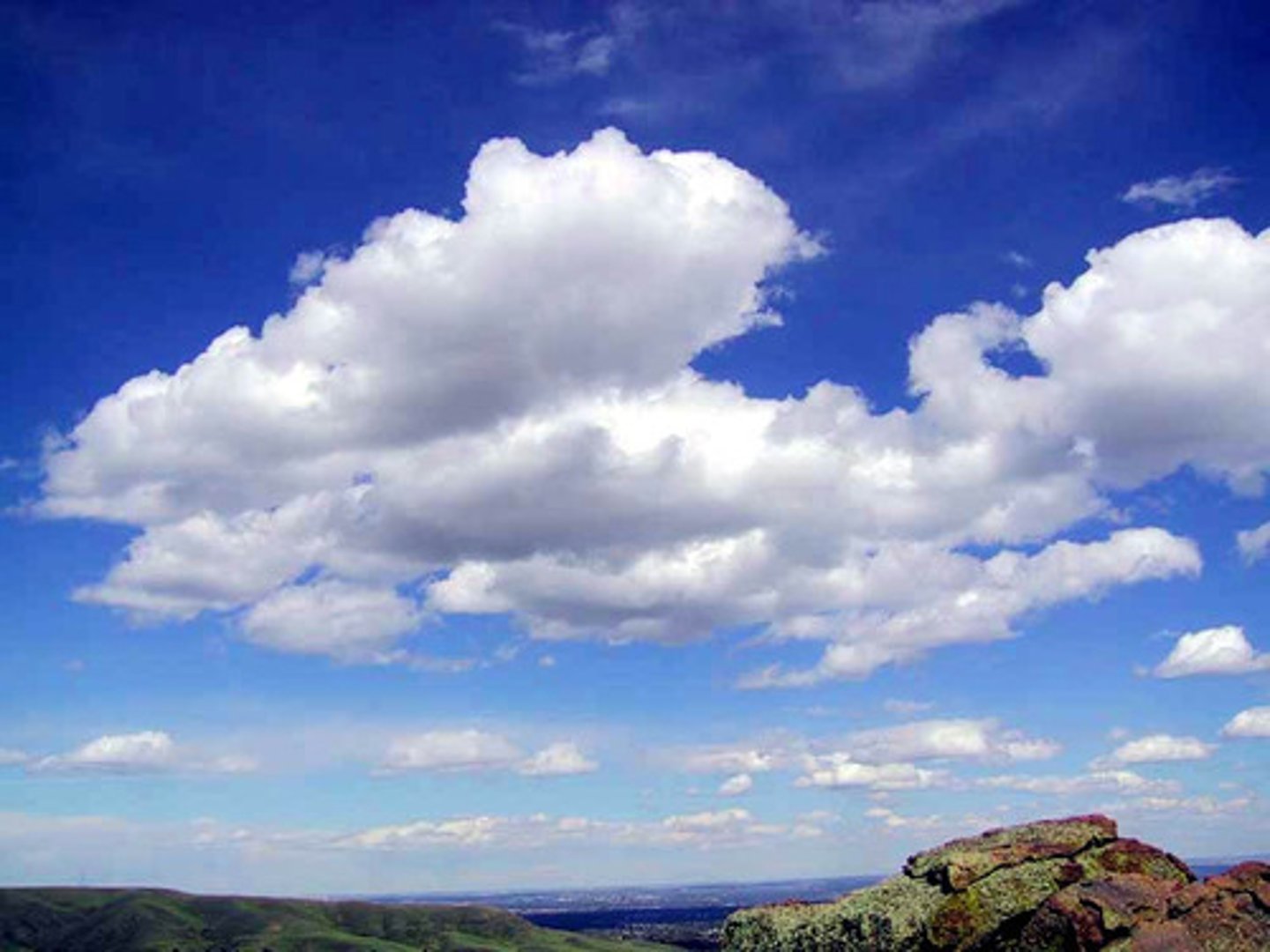
cumulus
clouds that look like fluffy, rounded piles of cotton

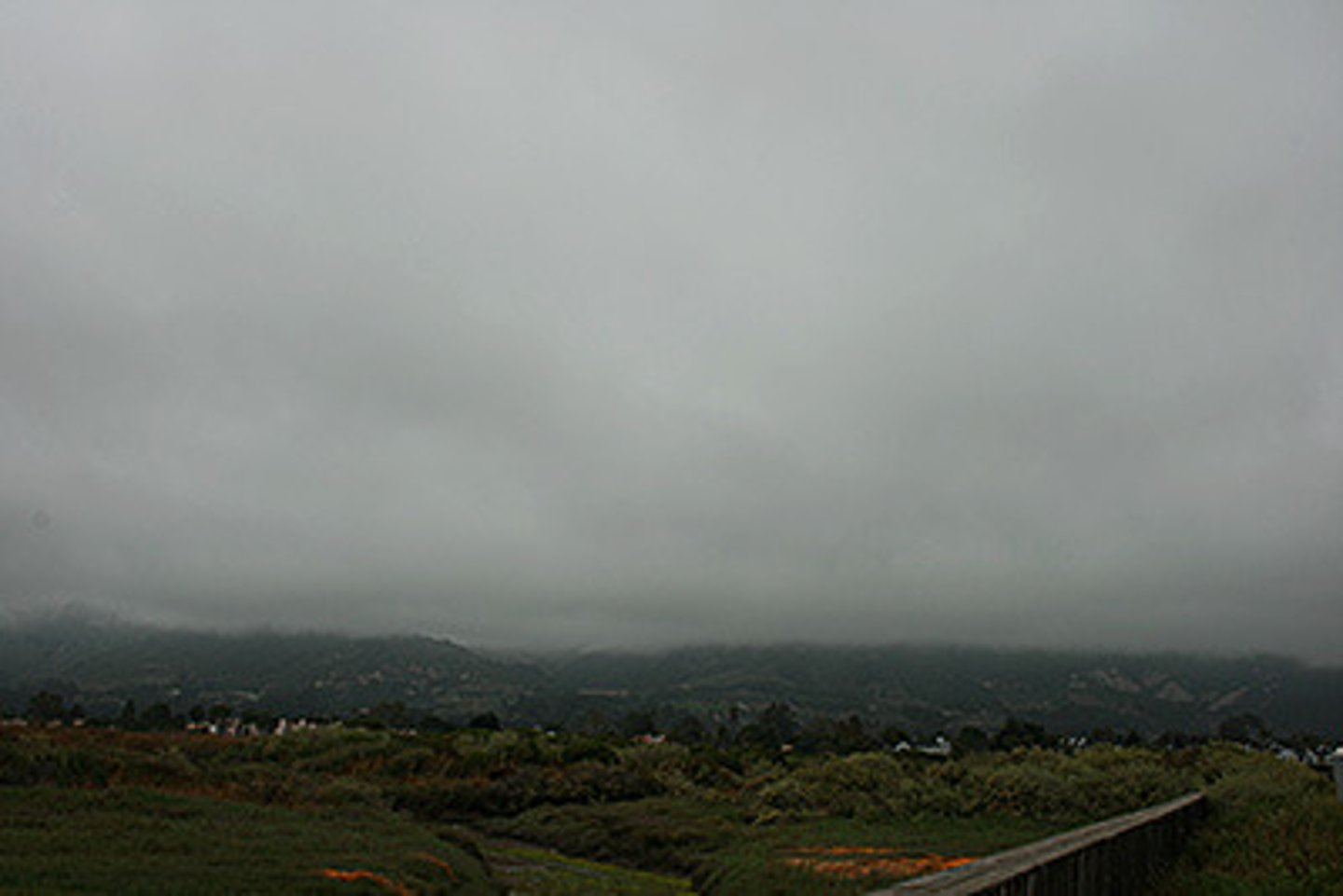
stratus
clouds that form in flat layers

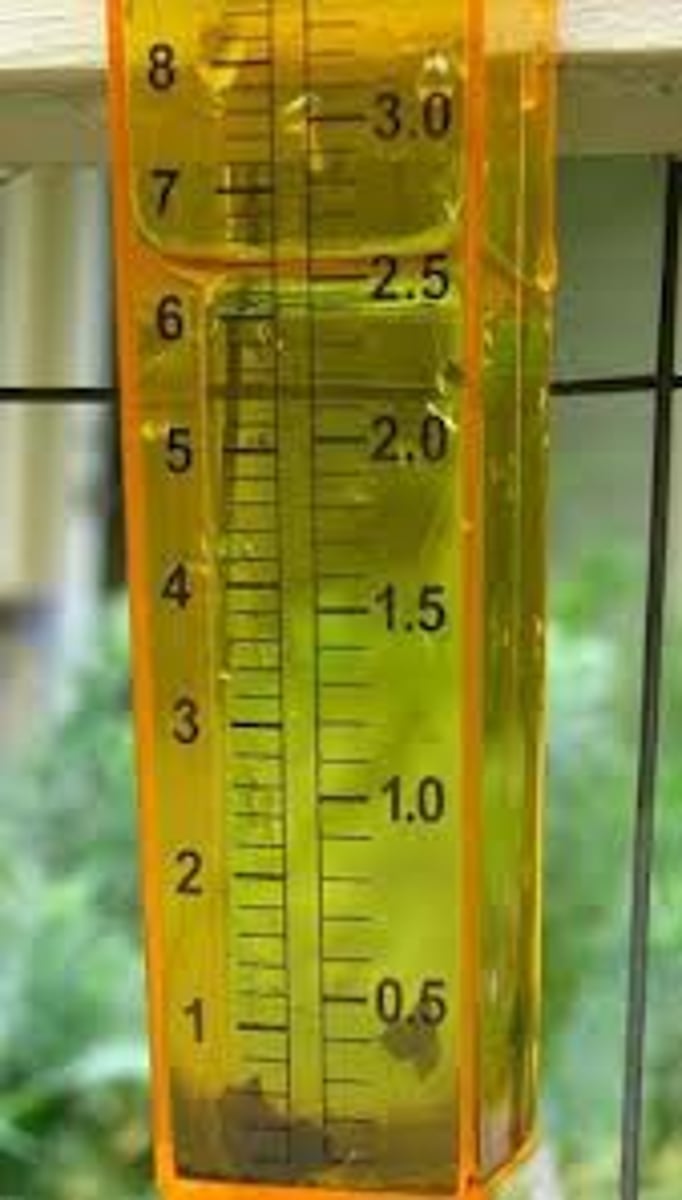
rain gauge
measures the amount of rain fall

anemometer
measures wind speed
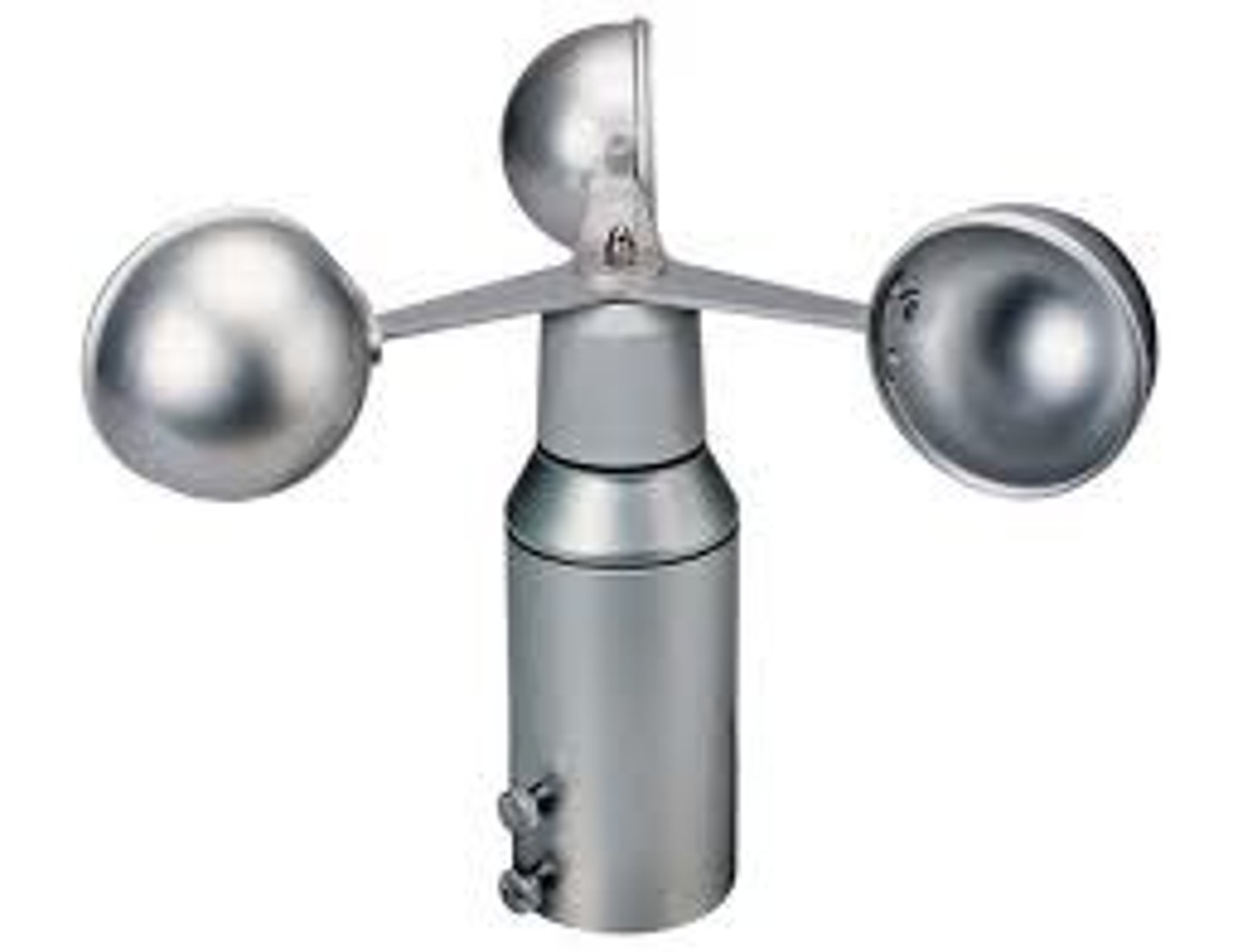

barometer
measures air pressure

wind vane
measures wind direction

hygrometer
measures humidity

psychrometer
measures relative humidity
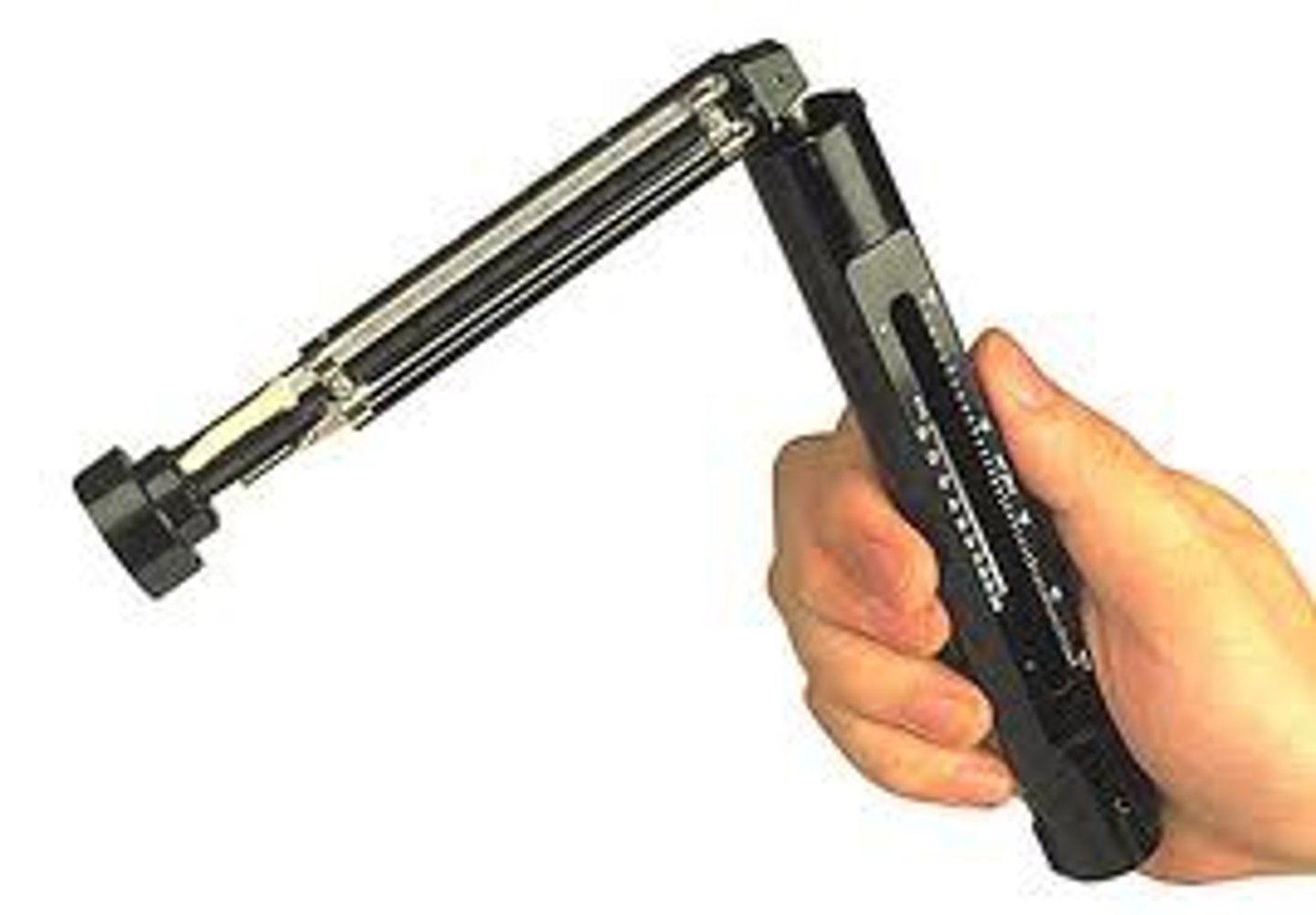

thermometer
measures temperature
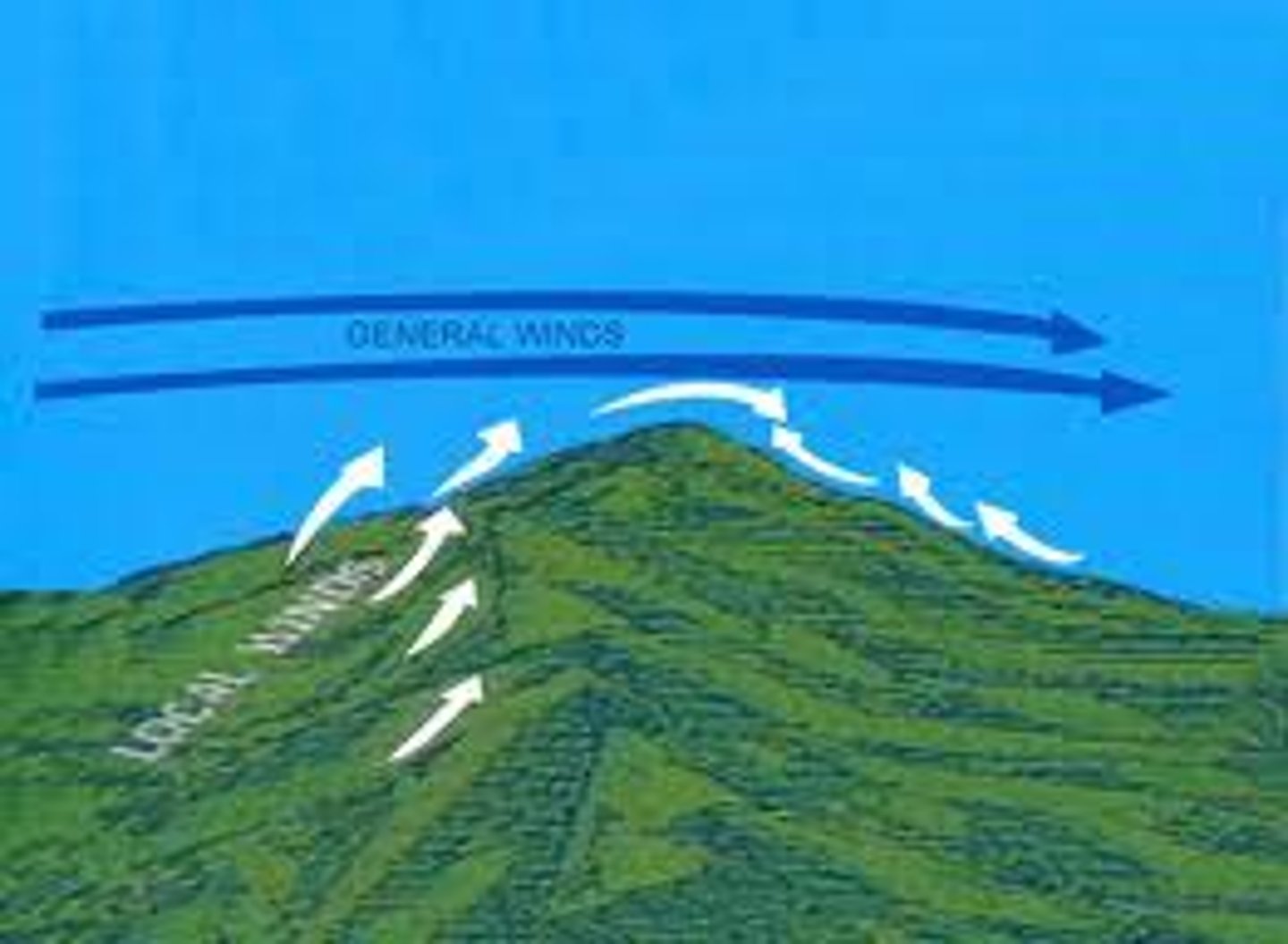
local winds
winds that blow over short distances
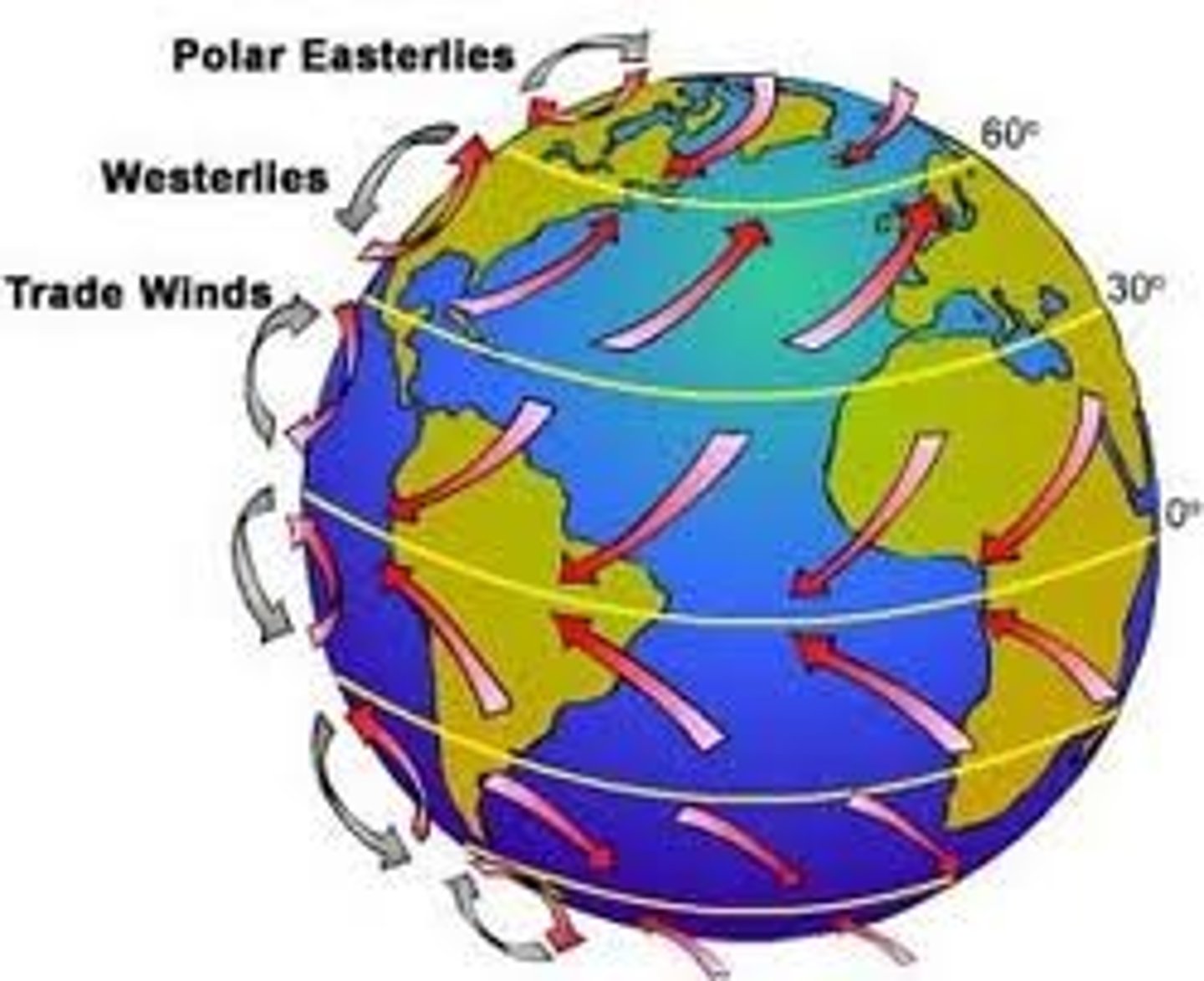
global winds
winds that blow over long distances
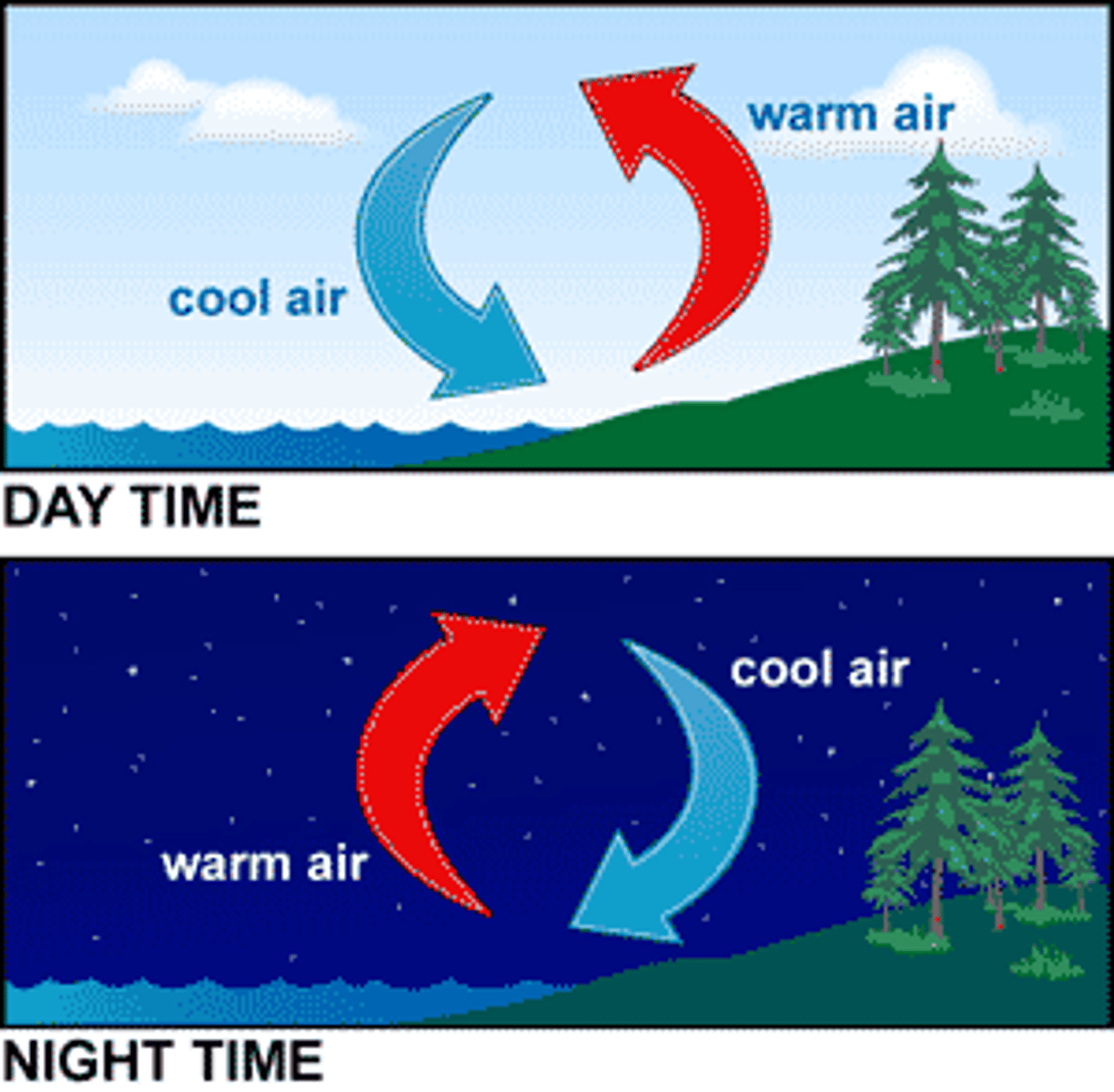
sea breeze
movement of air from sea to land during the day
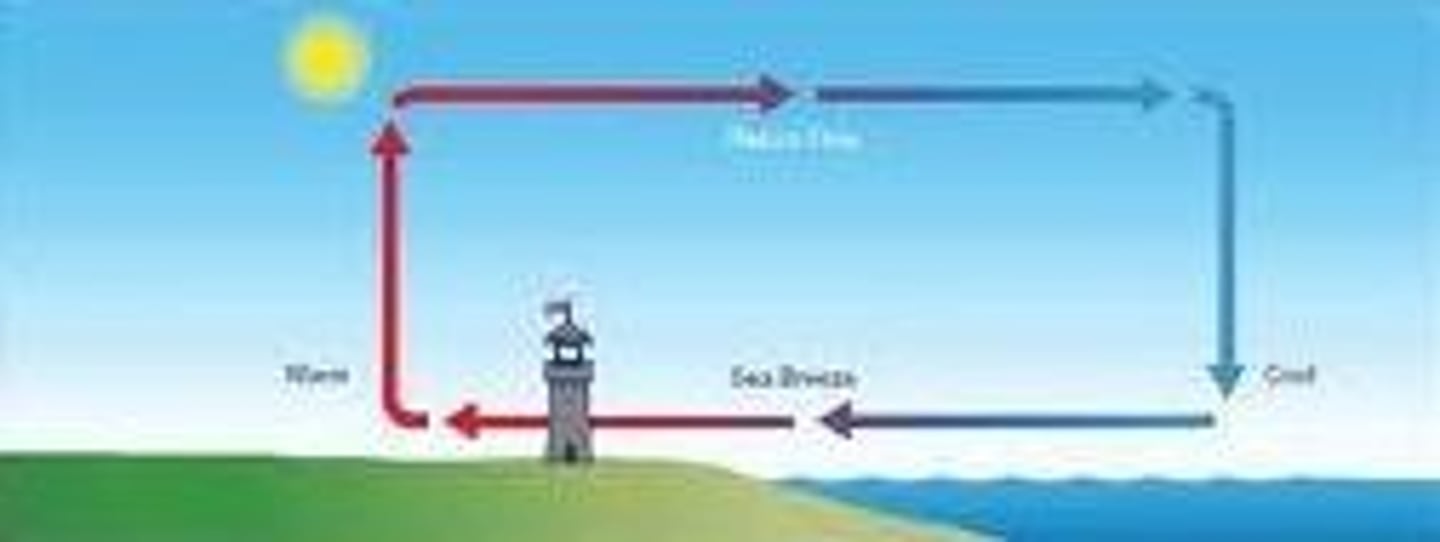
land breeze
movement of air from land to sea at night

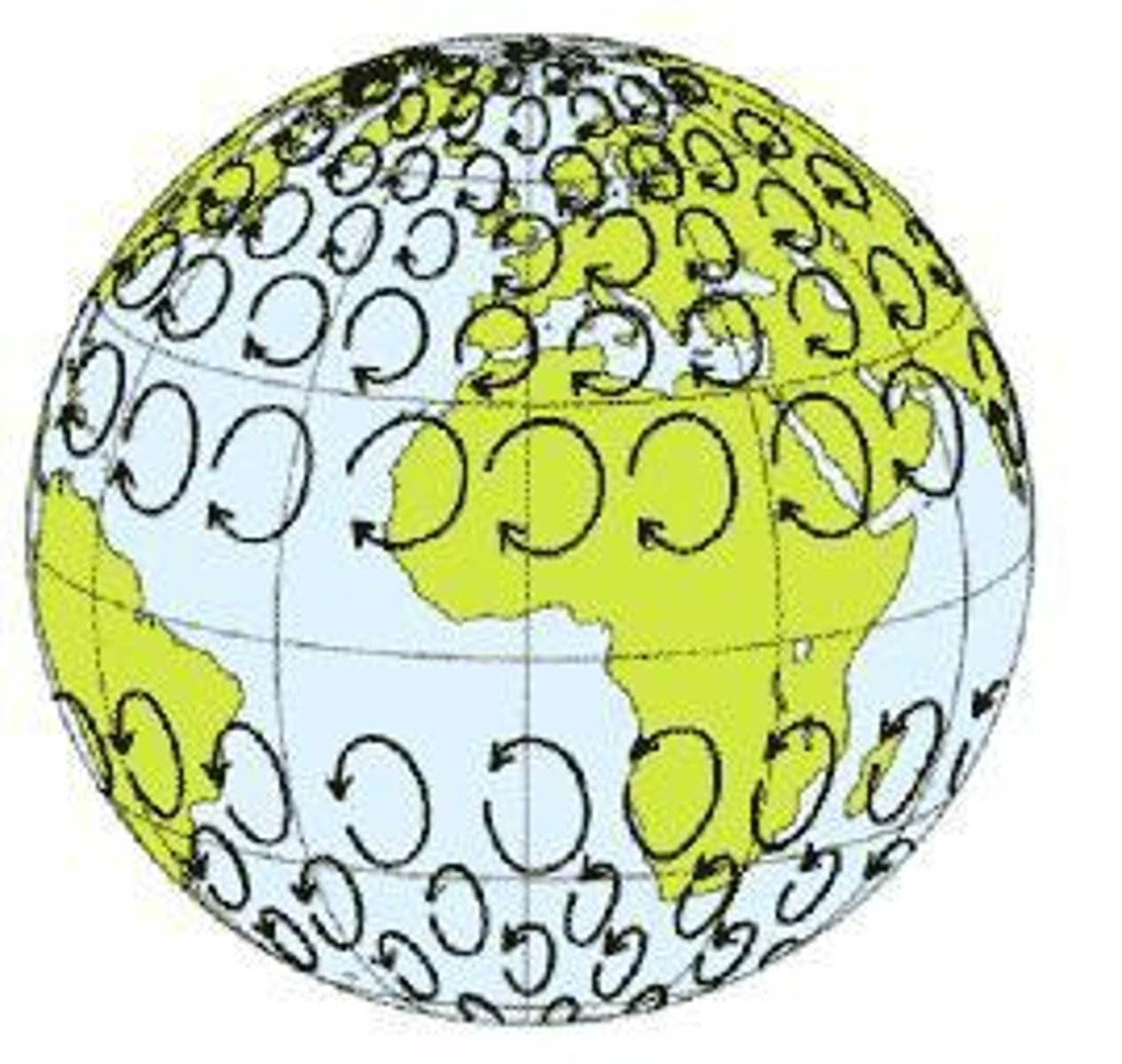
Coriolis effect
the effect of Earth's rotation on the direction of winds and currents.
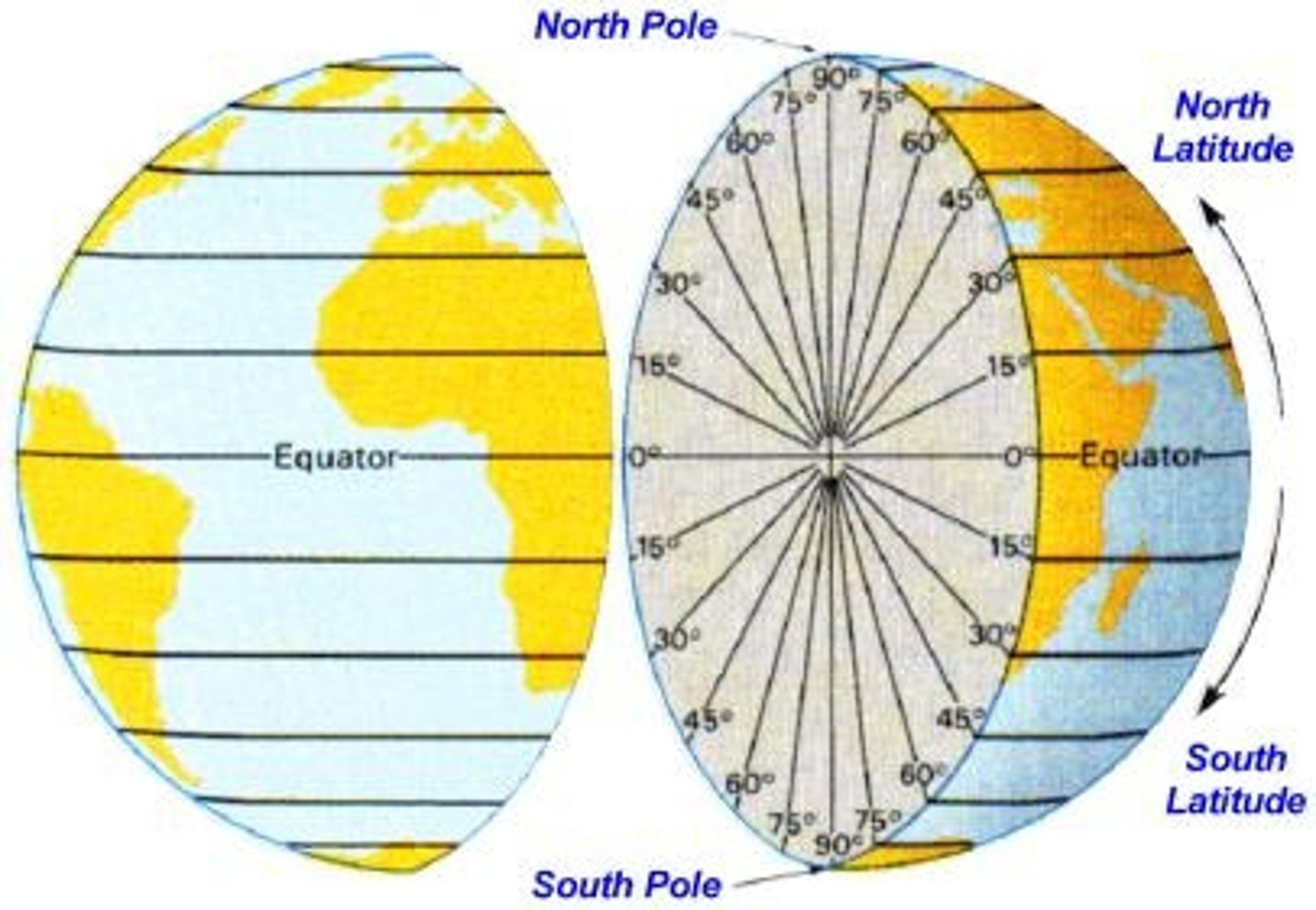
latitude
distance north or south of the equator
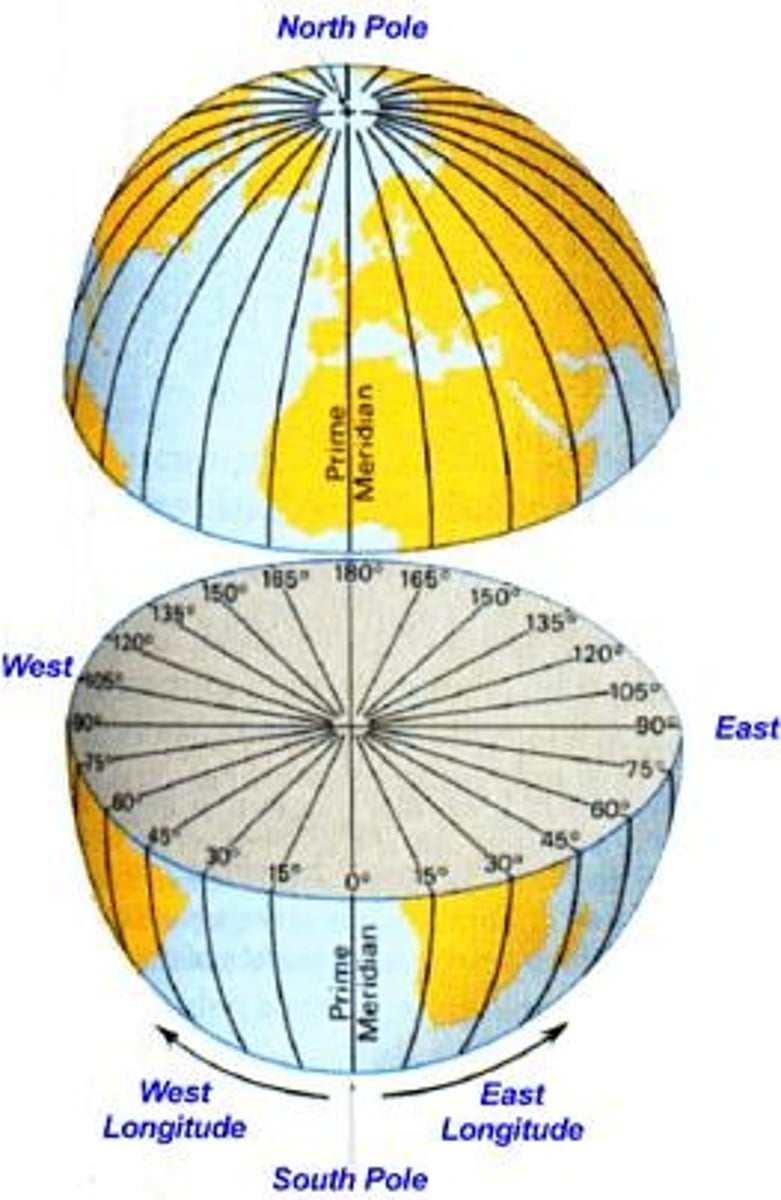
longitude
distance east or west of the prime meridian
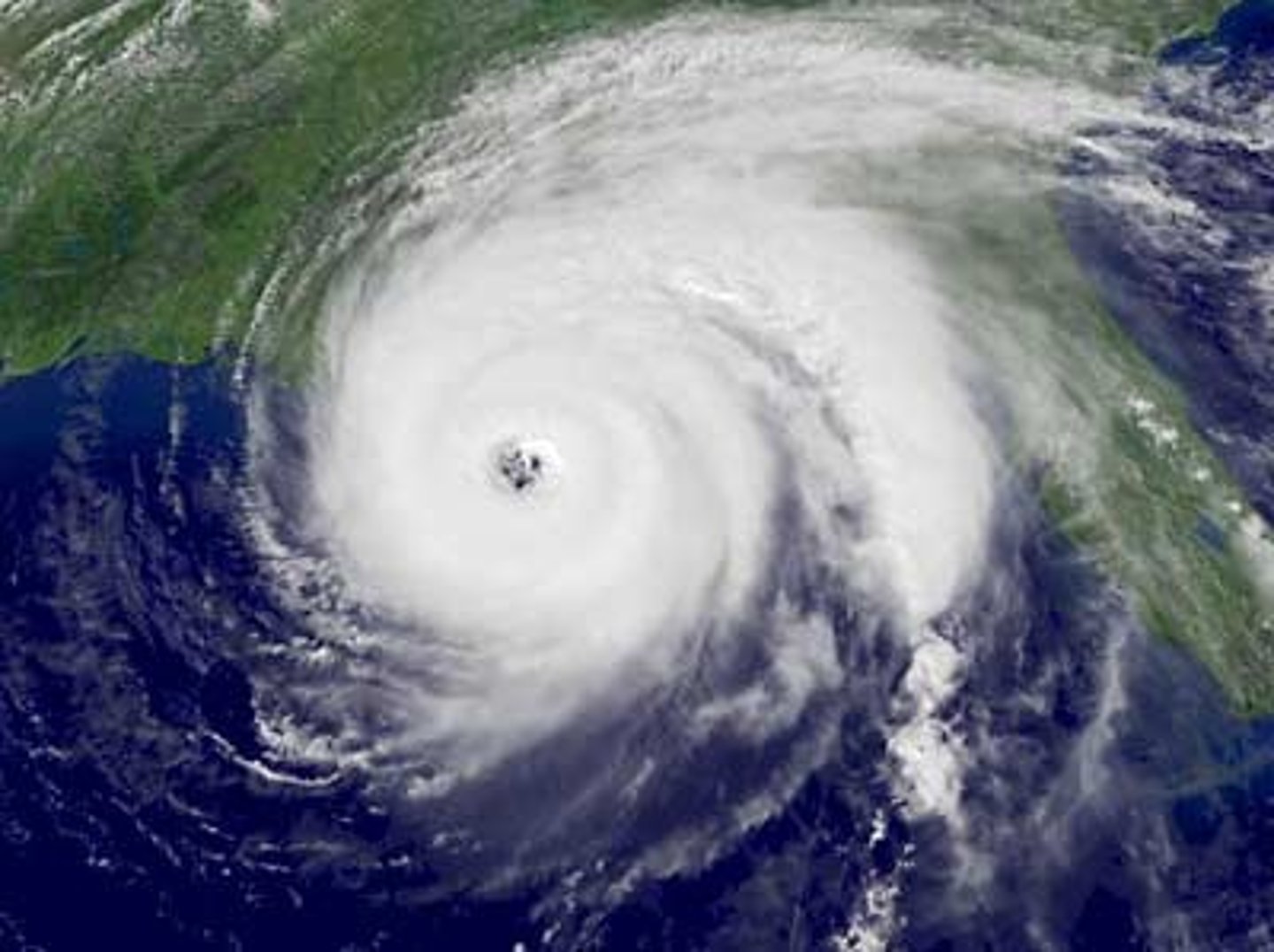
hurricane
severe storm that forms over tropical oceans

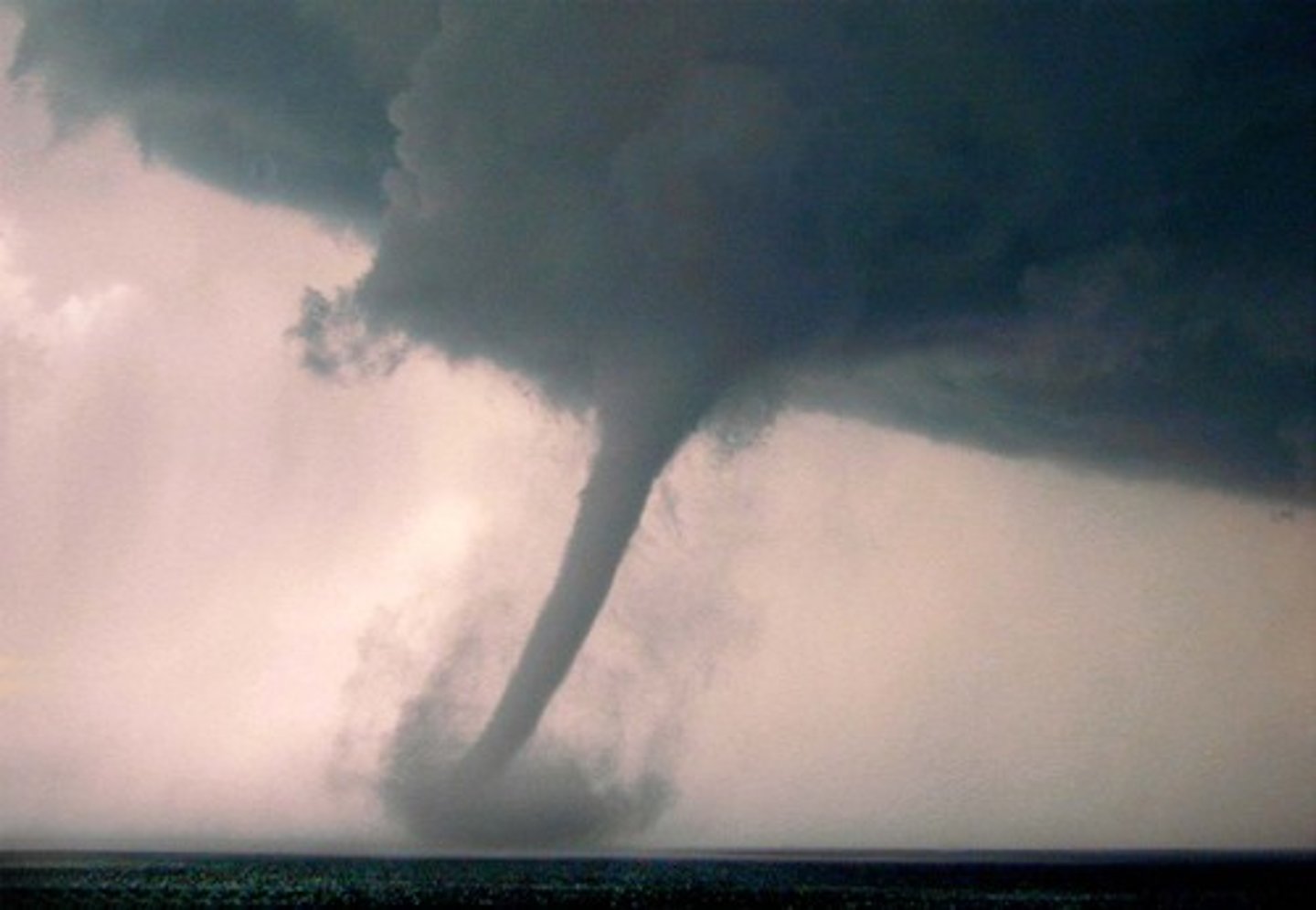
tornado
a rapidly whirling, funnel-shaped cloud that reaches down to touch Earth's surface

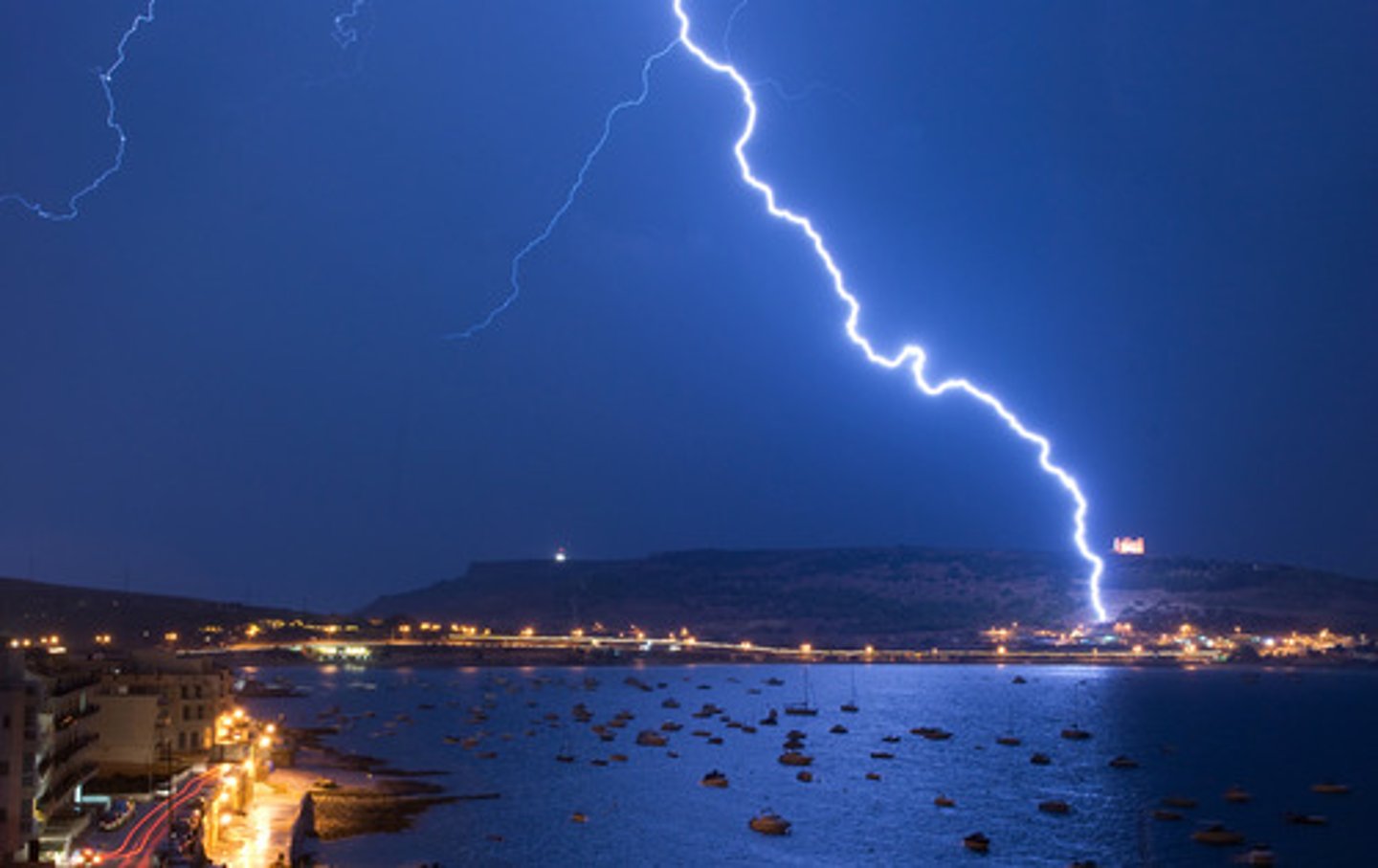
lightning
electric discharge from cloud to cloud or from cloud to earth

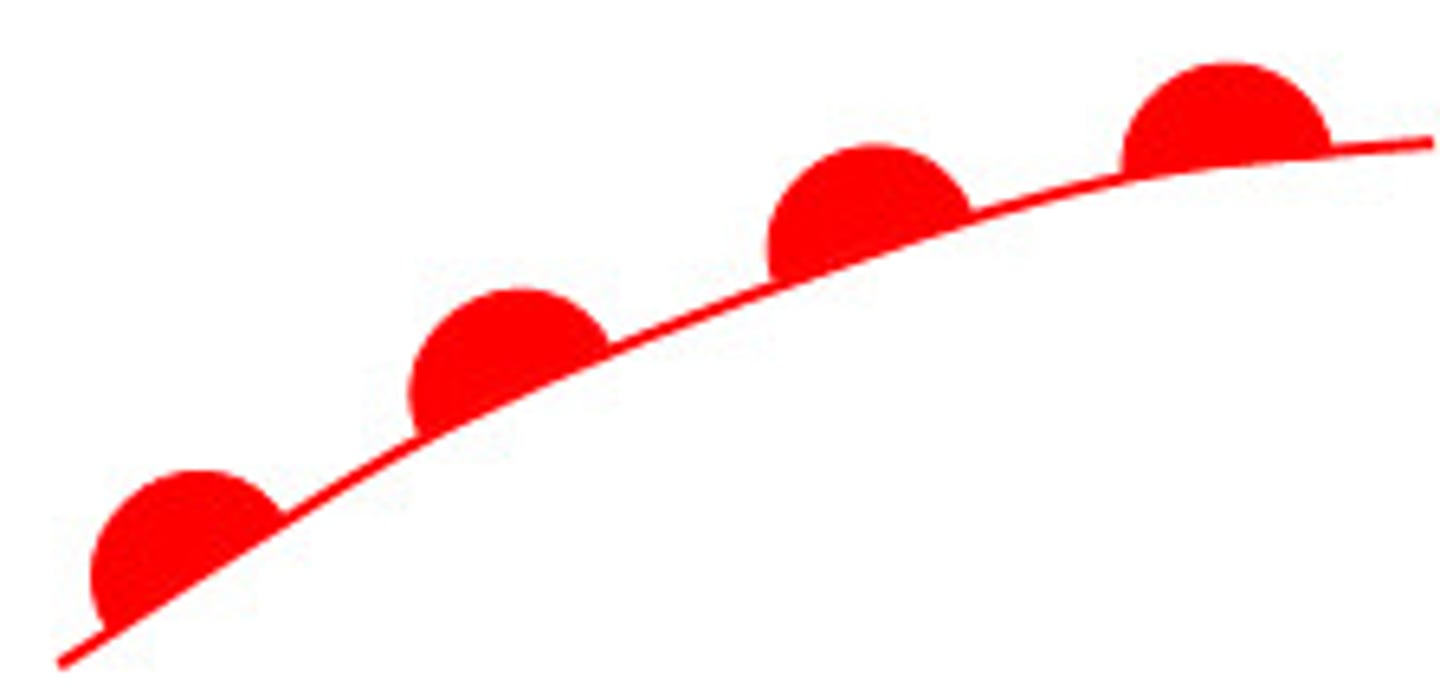
warm front
the front of an advancing mass of warmer air

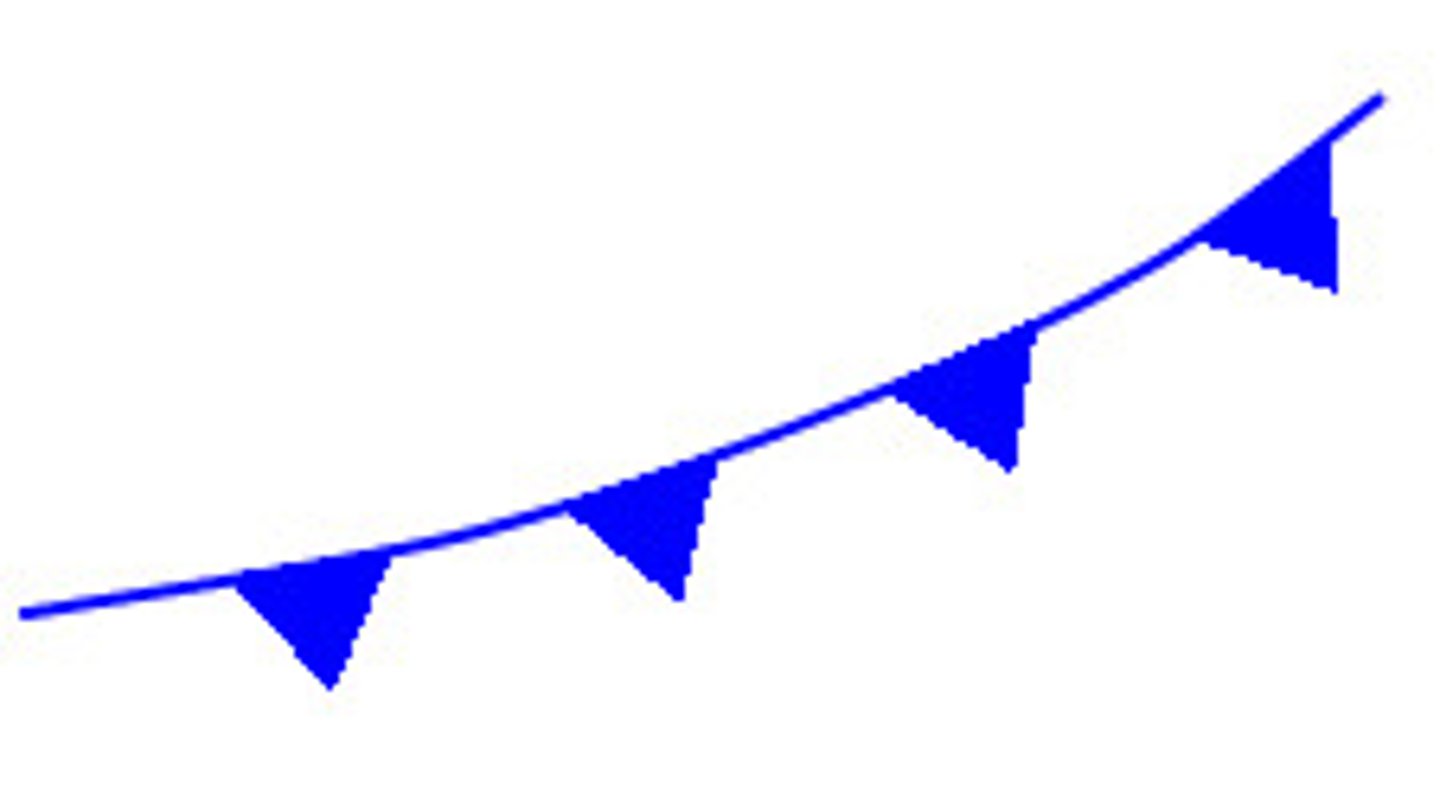
cold front
a front where cold air moves in under a warm air mass

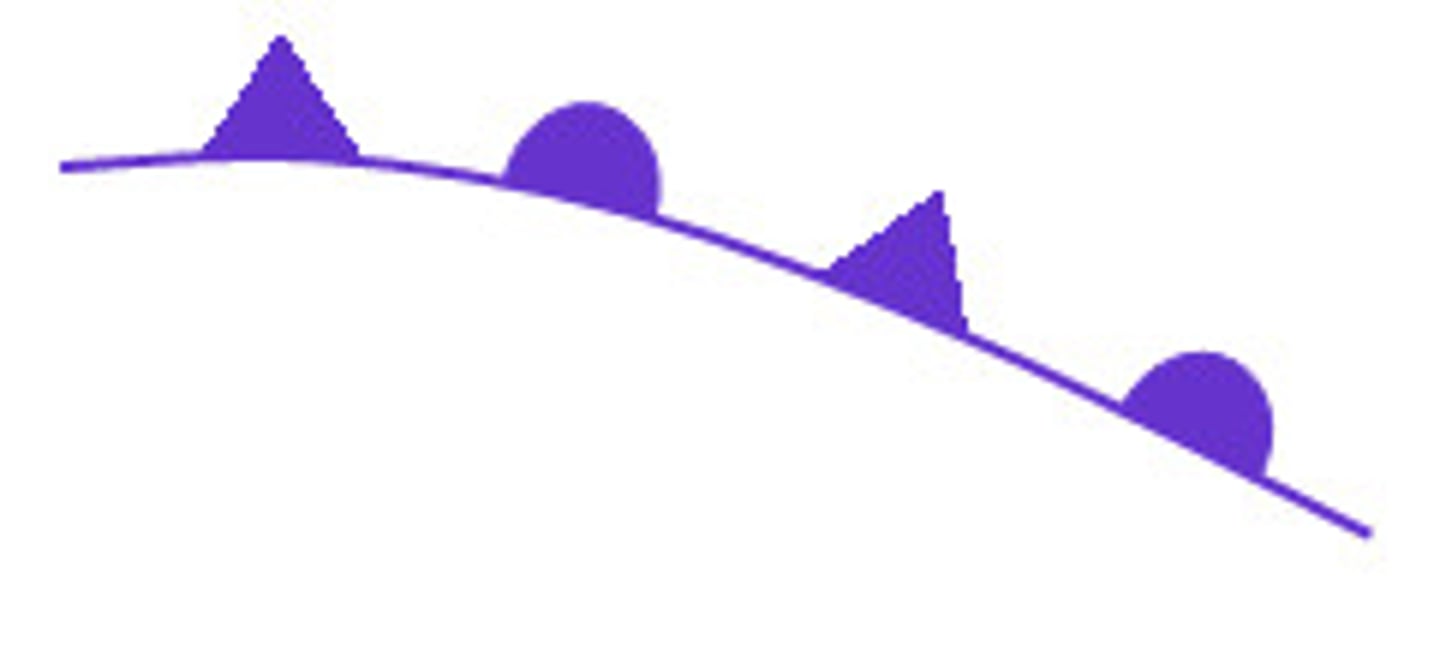
stationary front
when a warm air mass and a cold air mass meet and no movement occurs

occluded front
a front where a warm air mass is caught between two colder air masses and brings cool temperatures and large amounts of rain and snow

high pressure
a mass of sinking cool air that usually bring fair weather.
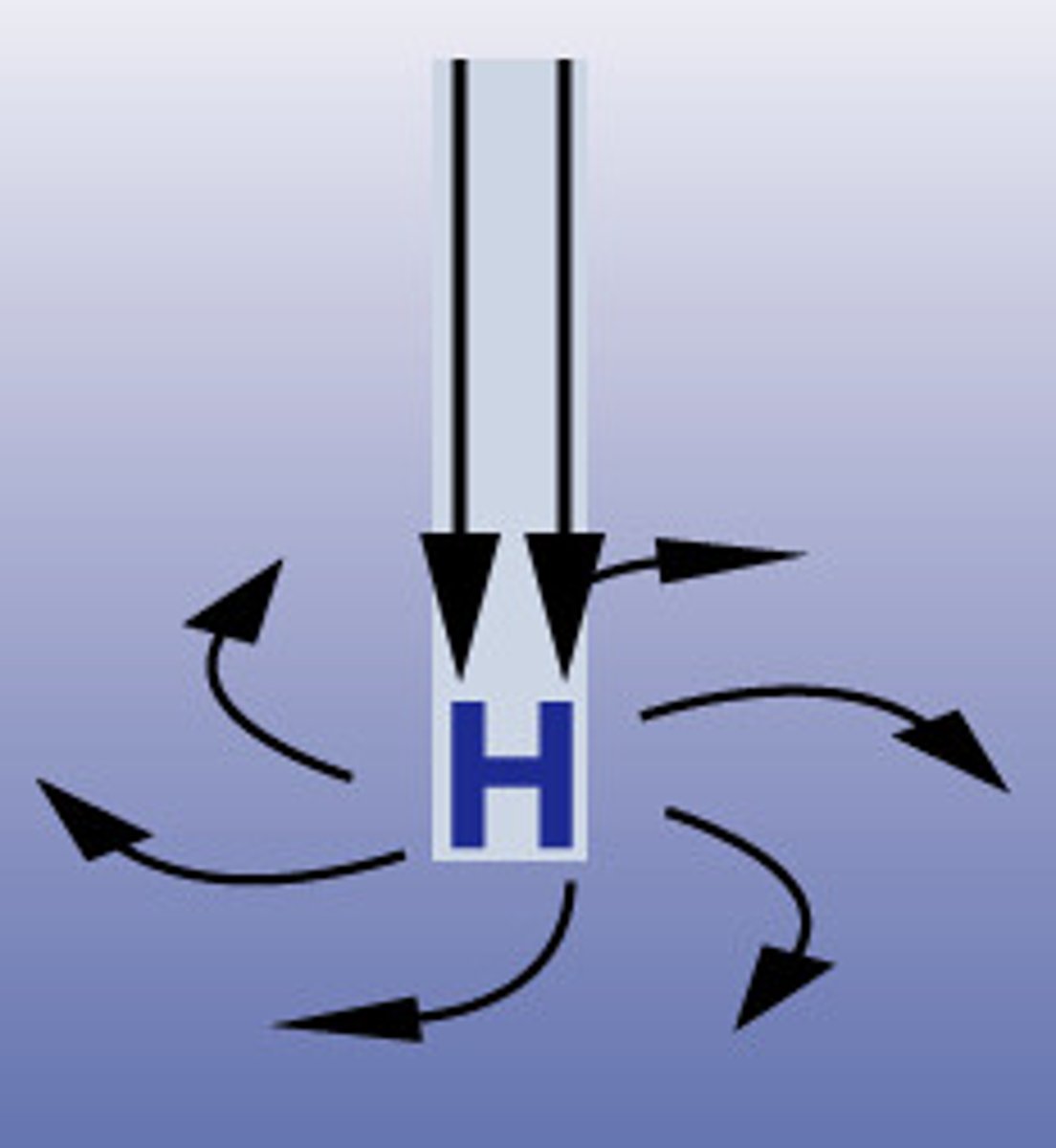
low pressure
a mass of rising warm air that usually bring wet, stormy weather